Peach vs Passion Fruit – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing peach to passion fruit, we picked the passion fruit.
Why?
It wasn’t close!
In terms of macros, passion fruit has more than 2x the protein, 2x the carbs, and 7x the fiber. That’s a big difference!
In the category of vitamins, peach has more of vitamins B1, B5, E, and K, while passion fruit has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B6, B7, B9, C, and choline. Again, not close.
When it comes to minerals, peach has more manganese and zinc, while passion fruit has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium—and most of those margins are “by multiples”, not just a fraction more. Again, a clear winner here.
Adding up these three overwhelming wins for passion fruit makes for an obvious total win for passion fruit.
As ever, enjoy both, but if you’re going to pick one, then one of these fruits is extra passionate about bringing you nutrients.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← peaches are on this list!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sensitive – by Jenn Granneman and Andre Sólo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is written for what is called the “Highly Sensitive Person”, which makes it sound like a very rare snowflake condition, when in fact the diagnostic criteria (discussed early in the book) yield a population bell curve of 30:40:30, whereupon 30% are in the band of “high sensitivity”, 40% “normal sensitivity” and the remainder “low sensitivity”. You may note that “high” and “low” together outnumber “normal”, but statistics is like that.
So, if you’re one of the approximately one in three people who fall into the higher category, and/or you have a loved one who is in that category, then this book looks at the many advantages to a commonly stigmatized and (by cruel irony) criticized personality trait.
Those advantages range from personal life to work and even public life (yes, really), and can be grown, positively highlighted, used, and enjoyed.
In the category of criticism, the book does not usefully cover the benefit of psychological resilience. Resilience does not mean losing sensitivity, just, being able to also dry one’s tears and weather life’s slings and arrows when the world is harsher than one might like. But for the authors, they have stacked all their chips on “we must make the world a better place”. Which is a noble goal, if not always an immediately attainable one.
Bottom line: if you are more sensitive than average and would like to use that to benefit yourself and those around you, then this is the book for you!
Click here to check out Sensitive, and make the most of your strengths!
Share This Post
-
Science of Stretch – by Dr. Leada Malek
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is part of a “Science of…” series, of which we’ve reviewed some others before (Yoga | HIIT | Pilates), and needless to say, we like them.
You may be wondering: is this just that thing where a brand releases the same content under multiple names to get more sales, and no, it’s not (long-time 10almonds readers will know: if it were, we’d say so!).
While flexibility and mobility are indeed key benefits in yoga and Pilates, they looked into the science of what was going on in yoga asanas and Pilates exercises, stretchy or otherwise, so the stretching element was not nearly so deep as in this book.
In this one, Dr. Malek takes us on a wonderful tour of (relevant) human anatomy and physiology, far deeper than most pop-science books go into when it comes to stretching, so that the reader can really understand every aspect of what’s going on in there.
This is important, because it means busting a lot of myths (instead of busting tendons and ligaments and things), understanding why certain things work and (critically!) why certain things don’t, how certain stretching practices will sabotage our progress, things like that.
It’s also beautifully clearly illustrated! The cover art is a fair representation of the illustrations inside.
Bottom line: if you want to get serious about stretching, this is a top-tier book and you won’t regret it.
Click here to check out Science of Stretching, and learn what you can do and how!
Share This Post
-
Taurine: An Anti-Aging Powerhouse? Exploring Its Unexpected Benefits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Mark Rosenberg explains:
Not a stimulant, but…
- Its presence in energy drinks often causes people to assume it’s a stimulant, but it’s not. In fact, it’s a GABA-agonist, thus having a calming effect.
- The real reason it’s in energy drinks is because it helps increase mitochondrial ATP production (ATP = adenosine triphosphate = how cells store energy that’s ready to use; mitochondria take glucose and make ATP)
- Taurine is also anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer.
- In the category of aging, human studies are slow to give results for obvious reasons, but mouse studies show that supplementing taurine in middle-aged mice increased their lifespan by 10–12%, as well as improving various physiological markers of aging.
- Taking a closer look at aging—literally; looking at cellular aging—taurine reduces cellular senescence and protects telomeres, thus decreasing DNA mutations.
For more on the science of these, plus Dr. Rosenberg’s personal experience, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Taurine’s Benefits For Heart Health And More
- Dr. Greger’s Anti-Aging Eight
- Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Beetroot vs Tomato – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing beetroot to tomato, we picked the beetroot.
Why?
Both are great! But we say beetroot comes out on top:
In terms of macros, beetroot has more protein, carbs, and fiber, making it the more nutritionally dense option. It has a slightly higher glycemic index, but also has specific phytochemicals that lower blood sugars and increase insulin sensitivity, more than cancelling that out. So, a clear win for beetroot in this regard.
In the category of vitamins, beetroot has more of vitamins B2, B5, B7, and B9, while tomato has more of vitamins A, C, E, and K. We’d call that a 4:4 tie, but tomato’s margins of difference are greater, so we say tomato wins this round.
When it comes to minerals, beetroot has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while tomatoes are not higher in any mineral. An easy win for beetroot here.
Looking at polyphenols and other remaining phytochemicals, beetroot has most, and especially its betalain content goes a long way. Tomatoes, meanwhile, have a famously high lycopene content (a highly beneficial carotenoid). All in all, it could swing either way based on subjective factors, so we’re saying it’s a tie this time.
Adding up the sections makes for an overall win for beetroot, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
- Beetroot For More Than Just Your Blood Pressure
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Wildfires ignite infection risks, by weakening the body’s immune defences and spreading bugs in smoke
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Over the past several days, the world has watched on in shock as wildfires have devastated large parts of Los Angeles.
Beyond the obvious destruction – to landscapes, homes, businesses and more – fires at this scale have far-reaching effects on communities. A number of these concern human health.
We know fire can harm directly, causing injuries and death. Tragically, the death toll in LA is now at least 24.
But wildfires, or bushfires, can also have indirect consequences for human health. In particular, they can promote the incidence and spread of a range of infections.
Effects on the immune system
Most people appreciate that fires can cause burns and smoke inhalation, both of which can be life-threatening in their own right.
What’s perhaps less well known is that both burns and smoke inhalation can cause acute and chronic changes in the immune system. This can leave those affected vulnerable to infections at the time of the injury, and for years to come.
Burns induce profound changes in the immune system. Some parts go into overdrive, becoming too reactive and leading to hyper-inflammation. In the immediate aftermath of serious burns, this can contribute to sepsis and organ failure.
Other parts of the immune system appear to be suppressed. Our ability to recognise and fight off bugs can be compromised after sustaining burns. Research shows people who have experienced serious burns have an increased risk of influenza, pneumonia and other types of respiratory infections for at least the first five years after injury compared to people who haven’t experienced burns.
Wildfire smoke is a complex mixture containing particulate matter, volatile organic compounds, ozone, toxic gases, and microbes. When people inhale smoke during wildfires, each of these elements can play a role in increasing inflammation in the airways, which can lead to increased susceptibility to respiratory infections and asthma.
Research published after Australia’s Black Summer of 2019–20 found a higher risk of COVID infections in areas of New South Wales where bushfires had occurred weeks earlier.
We need more research to understand the magnitude of these increased risks, how long they persist after exposure, and the mechanisms. But these effects are thought to be due to sustained changes to the immune response.
Microbes travel in smoky air
Another opportunity for infection arises from the fire-induced movement of microbes from niches they usually occupy in soils and plants in natural areas, into densely populated urban areas.
Recent evidence from forest fires in Utah shows microbes, such as bacteria and fungal spores, can be transported in smoke. These microbes are associated with particles from the source, such as burned vegetation and soil.
There are thousands of different species of microbes in smoke, many of which are not common in background, non-smoky air.
Only a small number of studies on this have been published so far, but researchers have shown the majority of microbes in smoke are still alive and remain alive in smoke long enough to colonise the places where they eventually land.
How far specific microbes can be transported remains an open question, but fungi associated with smoke particles have been detected hundreds of miles downwind from wildfires, even weeks after the fire.
So does this cause human infections?
A subset of these airborne microbes are known to cause infections in humans.
Scientists are probing records of human fungal infections in relation to wildfire smoke exposure. In particular, they’re looking at soil-borne infectious agents such as the fungi Coccidioides immitis and Coccidioides posadasii which thrive in dry soils that can be picked up in dust and smoke plumes.
These fungi cause valley fever, a lung infection with symptoms that can resemble the flu, across arid western parts of the United States.
A study of wildland firefighters in California showed high rates of valley fever infections, which spurred occupational health warnings including recommended use of respirators when in endemic regions.
A California-based study of the wider population showed a 20% increase in hospital admissions for valley fever following any amount of exposure to wildfire smoke.
However, another found only limited evidence of excess cases after smoke exposure in wildfire-adjacent populations in California’s San Joaquin Valley.
These contrasting results show more research is needed to evaluate the infectious potential of wildfire smoke from this and other fungal and bacterial causes.
Staying safe
Much remains to be learned about the links between wildfires and infections, and the multiple pathways by which wildfires can increase the risk of certain infections.
There’s also a risk people gathering together after a disaster like this, such as in potentially overcrowded shelters, can increase the transmission of infections. We’ve seen this happen after previous natural disasters.
Despite the gaps in our knowledge, public health responses to wildfires should encompass infection prevention (such as through the provision of effective masks) and surveillance to enable early detection and effective management of any outbreaks.
Christine Carson, Senior Research Fellow, School of Medicine, The University of Western Australia and Leda Kobziar, Professor of Wildland Fire Science, University of Idaho
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I’ve recovered from a cold but I still have a hoarse voice. What should I do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cold, flu, COVID and RSV have been circulating across Australia this winter. Many of us have caught and recovered from one of these common upper respiratory tract infections.
But for some people their impact is ongoing. Even if your throat isn’t sore anymore, your voice may still be hoarse or croaky.
So what happens to the voice when we get a virus? And what happens after?
Here’s what you should know if your voice is still hoarse for days – or even weeks – after your other symptoms have resolved.
Why does my voice get croaky during a cold?
A healthy voice is normally clear and strong. It’s powered by the lungs, which push air past the vocal cords to make them vibrate. These vibrations are amplified in the throat and mouth, creating the voice we hear.
The vocal cords are two elastic muscles situated in your throat, around the level of your laryngeal prominence, or Adam’s apple. (Although everyone has one, it tends to be more pronounced in males.) The vocal cords are small and delicate – around the size of your fingernail. Any small change in their structure will affect how the voice sounds.
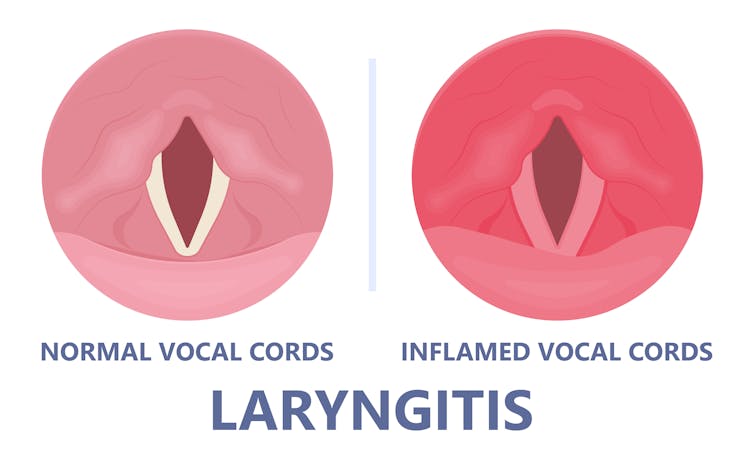
When the vocal cords become inflamed – known as laryngitis – your voice will sound different. Laryngitis is a common part of upper respiratory tract infections, but can also be caused through misuse.
Viruses such as the common cold can inflame the vocal cords. Pepermpron/Shutterstock Catching a virus triggers the body’s defence mechanisms. White blood cells are recruited to kill the virus and heal the tissues in the vocal cords. They become inflamed, but also stiffer. It’s harder for them to vibrate, so the voice comes out hoarse and croaky.
In some instances, you may find it hard to speak in a loud voice or have a reduced pitch range, meaning you can’t go as high or loud as normal. You may even “lose” your voice altogether.
Coughing can also make things worse. It is the body’s way of trying to clear the airways of irritation, including your own mucus dripping onto your throat (post-nasal drip). But coughing slams the vocal cords together with force.
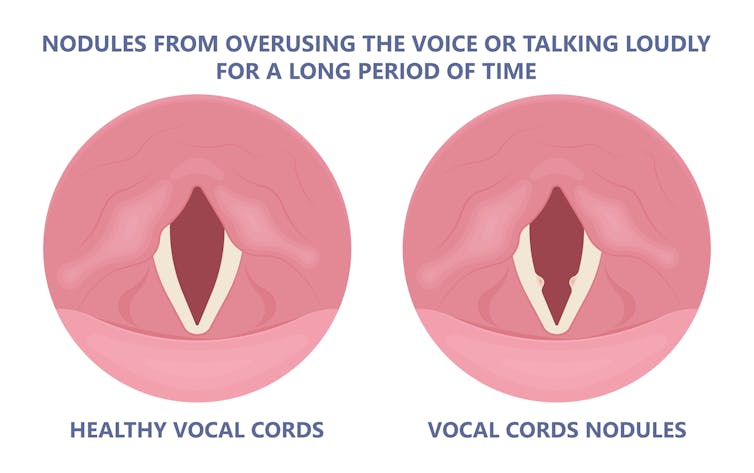
Chronic coughing can lead to persistent inflammation and even thicken the vocal cords. This thickening is the body trying to protect itself, similar to developing a callus when a pair of new shoes rubs.
Thickening on your vocal cords can lead to physical changes in the vocal cords – such as developing a growth or “nodule” – and further deterioration of your voice quality.
Coughing and exertion can cause inflamed vocal cords to thicken and develop nodules. Pepermpron/Shutterstock How can you care for your voice during infection?
People who use their voices a lot professionally – such as teachers, call centre workers and singers – are often desperate to resume their vocal activities. They are more at risk of forcing their voice before it’s ready.
The good news is most viral infections resolve themselves. Your voice is usually restored within five to ten days of recovering from a cold.
Occasionally, your pharmacist or doctor may prescribe cough suppressants to limit additional damage to the vocal cords (among other reasons) or mucolytics, which break down mucus. But the most effective treatments for viral upper respiratory tract infections are hydration and rest.
Drink plenty of water, avoid alcohol and exposure to cigarette smoke. Inhaling steam by making yourself a cup of hot water will also help clear blocked noses and hydrate your vocal cords.
Rest your voice by talking as little as possible. If you do need to talk, don’t whisper – this strains the muscles.
Instead, consider using “confidential voice”. This is a soft voice – not a whisper – that gently vibrates your vocal cords but puts less strain on your voice than normal speech. Think of the voice you use when communicating with someone close by.
During the first five to ten days of your infection, it is important not to push through. Exerting the voice by talking a lot or loudly will only exacerbate the situation. Once you’ve recovered from your cold, you can speak as you would normally.
What should you do if your voice is still hoarse after recovery?
If your voice hasn’t returned to normal after two to three weeks, you should seek medical attention from your doctor, who may refer you to an ear nose and throat specialist.
If you’ve developed a nodule, the specialist would likely refer you to a speech pathologist who will show you how to take care of your voice. Many nodules can be treated with voice therapy and don’t require surgery.
You may have also developed a habit of straining your vocal cords, if you forced yourself to speak or sing while they were inflamed. This can be a reason why some people continue to have a hoarse voice even when they’ve recovered from the cold.
In those cases, a speech pathologist may play a valuable role. They may teach you to exercises that make voicing more efficient. For example, lip trills (blowing raspberries) are a fun and easy way you can learn to relax the voice. This can help break the habit of straining your voice you may have developed during infection.
Yeptain Leung, Postdoctoral Research and Lecturer of Speech Pathology, School of Health Sciences, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: