What’s Lurking In Your Household Air?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As individuals, we can’t do much about the outside air. We can try to spend more time in green spaces* and away from traffic, and we can wear face-masks—as was popular in Tokyo and other such large cities long before the pandemic struck.
*The well-known mental health benefits aside (and contrary to British politician Amber Rudd’s famous assertion in a televised political debate that “clean air doesn’t grow on trees”), clean air comes mostly from trees—their natural process of respiration scrubs not only carbon dioxide, but also pollutants, from the air before releasing oxygen without the pollutants. Neat!
See also this study: Site new care homes near trees and away from busy roads to protect residents’ lungs
We are fortunate to be living in a world where most of us in industrialized countries can exercise a great degree of control over our home’s climate. But, what to do with all that power?
Temperature
Let’s start with the basics. Outside temperature may vary, but you probably have heating and air conditioning. There’s a simple answer here; the optimal temperature for human comfort and wellbeing is 20℃ / 68℉:
Scientists Identify a Universal Optimal Temperature For Life on Earth
Note: this does not mean that that is the ideal global average temperature, because that would mean the polar caps are completely gone, the methane stored there released, many large cities underwater, currently hot places will be too hot for human life (e.g. outside temperatures above human body temperature), there will be mass extinctions of many kinds of animals and plants, including those we humans require for survival, and a great proliferation of many bugs that will kill us. Basically we need diversity for the planet to survive, arctic through to tropical and yes, even deserts (deserts are important carbon sinks!). The ideal global average temperature is about 14℃ (we currently have about 15℃ and rising).
But, for setting the thermostat in your home, 20℃ / 68℉ is perfect for most people, though down as far as 17℃ / 61℉ is fine too, provided other things such as humidity are in order. In fact, for sleeping, 18℃ / 62℉ is ideal. This is because the cooler temperature is one of the several things that tell our brain it is nighttime now, and thus trigger secretion of melatonin.
If you’re wondering about temperatures and respiratory viruses, by the way, check out:
The Cold Truth About Respiratory Infections: The Pathogens That Came In From The Cold
Humidity
Most people pay more attention to the temperature in their home than the humidity, and the latter is just as important:
❝Conditions that fall outside of the optimal range of 40–60% can have significant impacts on health, including facilitating infectious transmission and exacerbating respiratory diseases.
When humidity is too low, it can cause dryness and irritation of the respiratory tract and skin, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
When humidity is too high, it can create a damp environment that encourages the growth of harmful microorganisms like mould, bacteria, and viruses.❞
~ Dr. Gabriella Guarnieri et al.
So, if your average indoor humidity falls outside of that range, consider getting a humidifier or dehumidifier, to correct it. Example items on Amazon, for your convenience:
Humidity monitor | Humidifier | Dehumidifier
See also, about a seriously underestimated killer:
Pneumonia: Prevention Is Better Than Cure
Now, one last component to deal with, for perfect indoor air:
Pollution
We tend to think of pollution as an outdoors thing, and indeed, the pollution in your home will (hopefully!) be lower than that of a busy traffic intersection. However…
- The air you have inside comes from outside, and that matters if you’re in an urban area
- Even in suburban and rural areas, general atmospheric pollutants will reach you, and if you’ve ever been subject to wildfire smoke, you’ll know that’s no fun either.
- Gas appliances in the home cause indoor pollution, even when carbon monoxide is within levels considered acceptable. This polluting effect is much stronger for open gas flames (such as on gas cookers/stoves, or gas fires), than for closed gas heating systems (such as a gas-powered boiler for central heating).
- Wood stoves/fireplaces are not an improvement, in fact they are worse, and don’t get us started on coal. You should not be breathing these things, and definitely should not be burning them in an enclosed space.
- That air conditioning, humidifier, dehumidifier? They may be great for temperature and humidity, but please clean/change the filter more often than you think is necessary, or things will grow there and then your device will be adding pathogens to the air as it goes.
- Plug-in air-freshening devices? They may smell clean, but they are effectively spraying cleaning fluids into your lungs. So please don’t.
So, what of air purifiers? They can definitely be of benefit. for example:
But watch out! Because if you don’t clean/change the filter regularly, guess what happens! That’s right, it’ll be colonized with bacteria/fungus and then be blowing those at you.
And no, not all of them will be visible to the naked eye:
Is Unnoticed Environmental Mold Harming Your Health?
Taking a holistic approach
The air is a very important factor for the health of your lungs (and thus, for the health of everything that’s fed oxygen by your lungs), but there are more things we can do as well:
Seven Things To Do For Good Lung Health!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Instant Quiz Results, No Email Needed
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
❓ Q&A With 10almonds Subscribers!
Q: I like that the quizzes (I’ve done two so far) give immediate results , with no “give us your email to get your results”. Thanks!
A: You’re welcome! That’s one of the factors that influences what things we include here! Our mission statement is “to make health and productivity crazy simple”, and the unwritten part of that is making sure to save your time and energy wherever we reasonably can!
Share This Post
-
Make Change That Lasts – by Dr. Rangan Chatterjee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed Dr. Chatterjee’s other books before, and now it’s time to review his latest.
First, what this isn’t: another rehash of James Clear’s “Atomic Habits” ← which is excellent, but one version of it was enough already
What this actually is: a very insightful and thought-provoking book about what causes us to create our bad habits in the first place, and how to (as per Dr. Chatterjee’s usual methodology) address the cause itself, rather than just the symptom.
This is important, because oftentimes we get into habits unconsciously without realising, so it may take some unpacking later.
He talks about the various things that we need to let go of if we want to also drop habits that aren’t serving us, and devotes a chapter to each of these (they are the 9 items mentioned in the subtitle).
The style is personal and human (this soft-hearted reviewer cried when reading about the habits that he created while his father was dying, and what happened after that death), and yet at the same time practical and instructional; this really does give the reader the understanding and the tools to not just “break” habits, but to actually deconstruct them in such a fashion that we won’t accidentally pick them up again.
A note on pictures: the US edition of this book has black and white pictures, and some reviewers have complained about them being unclear and confusing. Please take it from this European reviewer (it’s me, hi) who read the European edition with color pictures, that you’re not missing out on anything. The pictures are unclear and confusing in color, too. They appear to be mostly random stock images that serve no obvious purpose. They don’t detract from the great value offered by the book, though!
Bottom line: if you sometimes find yourself stuck in a state of not improving, this book can absolutely help you to get out of that rut and moving in the direction you want to go.
Click here to check out Make Change That Lasts, and make change that lasts!
Share This Post
-
7 things you can do if you think you sweat too much
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sweating is our body’s way of cooling down, a bit like an internal air conditioner.
When our core temperature rises (because it’s hot outside, or you’re exercising), sweat glands all over our skin release a watery fluid. As that fluid evaporates, it takes heat with it, keeping us from overheating.
But sweating can vary from person to person. Some people might just get a little dewy under the arms, others feel like they could fill a swimming pool (maybe not that dramatic, but you get the idea).
So what’s a normal amount of sweat? And what’s too much?
ERIK Miheyeu/Shutterstock Why do some people sweat more than others?
How much you sweat depends on a number of factors including:
- your age (young kids generally sweat less than adults)
- your sex (men tend to sweat more than women)
- how active you are.
The average person sweats at the rate of 300 millilitres per hour (at 30°C and about 40% humidity). But as you can’t go around measuring the volume of your own sweat (or weighing it), doctors use another measure to gauge the impact of sweating.
They ask whether sweating interferes with your daily life. Maybe you stop wearing certain clothes because of the sweat stains, or feel embarrassed so don’t go to social events or work.
If so, this is a medical condition called hyperhidrosis, which affects millions of people worldwide.
People with this condition most commonly report problematic armpit sweating, as you’d expect. But sweaty hands, feet, scalp and groin can also be an issue.
Hyperhidrosis can be a symptom of another medical condition, such as an overactive thyroid, fever or menopause.
But hyperhidrosis can have no obvious cause, and the reasons behind this so-called primary hyperhidrosis are a bit of a mystery. People have normal numbers of sweat glands but researchers think they simply over-produce sweat after triggers such as stress, heat, exercise, tobacco, alcohol and hot spices. There may also be a genetic link.
OK, I sweat a lot. What can I do?
1. Antiperspirants
Antiperspirants, particularly ones with aluminium, are your first line of defence and are formulated to reduce sweating. Deodorants only stop body odour.
Aluminum chloride hexahydrate, aluminium chloride or the weaker aluminum zirconium tetrachlorohydrex glycinate react with proteins in the sweat glands, forming a plug. This plug temporarily blocks the sweat ducts, reducing the amount of sweat reaching the skin’s surface.
These products can contain up to 25% aluminium. The higher the percentage the better these products work, but the more they irritate the skin.
Make sure you’re buying antiperspirant and not deodorant. Okrasiuk/Shutterstock 2. Beat the heat
This might seem obvious, but staying cool can make a big difference. That’s because you have less heat to lose, so the body makes less sweat.
Avoid super-hot, long showers (you will have more heat to loose), wear loose-fitting clothes made from breathable fabrics such as cotton (this allows any sweat you do produce to evaporate more readily), and carry a little hand fan to help your sweat evaporate.
When exercising try ice bandanas (ice wrapped in a scarf or cloth, then applied to the body) or wet towels. You can wear these around the neck, head, or wrists to reduce your body temperature.
Try also to modify the time or place you exercise; try to find cool shade or air-conditioned areas when possible.
If you have tried these first two steps and your sweating is still affecting your life, talk to your doctor. They can help you figure out the best way to manage it.
3. Medication
Some medications can help regulate your sweating. Unfortunately some can also give you side effects such as a dry mouth, blurred vision, stomach pain or constipation. So talk to your doctor about what’s best for you.
Your GP may also refer you to a dermatologist – a doctor like myself who specialises in skin conditions – who might recommend different treatments, including some of the following.
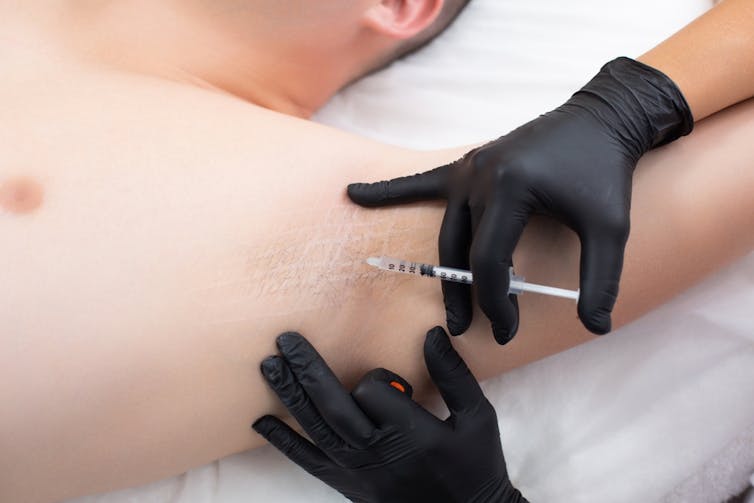
4. Botulinum toxin injections
Botulinum toxin injections are not just used for cosmetic reasons. They have many applications in medicine, including blocking the nerves that control the sweat glands. They do this for many months.
A dermatologist usually gives the injections. But they’re only subsidised by Medicare in Australia for the armpits and if you have primary hyperhidrosis that hasn’t been controlled by the strongest antiperspirants. These injections are given up to three times a year. It is not subsidised for other conditions, such as an overactive thyroid or for other areas such as the face or hands.
If you don’t qualify, you can have these injections privately, but it will cost you hundreds of dollars per treatment, which can last up to six months.
Injections are available on Medicare in some cases. Satyrenko/Shutterstock 5. Iontophoresis
This involves using a device that passes a weak electrical current through water to the skin to reducing sweating in the hands, feet or armpits. Scientists aren’t sure exactly how it works.
But this is the only way to control sweating of the hands and feet that does not require drugs, surgery or botulinum toxin injections.
This treatment is not subsidised by Medicare and not all dermatologists provide it. However, you can buy and use your own device, which tends to be cheaper than accessing it privately. You can ask your dermatologist if this is the right option for you.
6. Surgery
There is a procedure to cut certain nerves to the hands that stop them sweating. This is highly effective but can cause sweating to occur elsewhere.
There are also other surgical options, which you can discuss with your doctor.
7. Microwave therapy
This is a newer treatment that zaps your sweat glands to destroy them so they can’t work any more. It’s not super common yet, and it is quite painful. It’s available privately in a few centres.
Michael Freeman, Associate Professor of Dermatology, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What’s the difference between autism and Asperger’s disorder?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Swedish climate activist Greta Thunberg describes herself as having Asperger’s while others on the autism spectrum, such as Australian comedian Hannah Gatsby, describe themselves as “autistic”. But what’s the difference?
Today, the previous diagnoses of “Asperger’s disorder” and “autistic disorder” both fall within the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder, or ASD.
Autism describes a “neurotype” – a person’s thinking and information-processing style. Autism is one of the forms of diversity in human thinking, which comes with strengths and challenges.
When these challenges become overwhelming and impact how a person learns, plays, works or socialises, a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder is made.
Where do the definitions come from?
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) outlines the criteria clinicians use to diagnose mental illnesses and behavioural disorders.
Between 1994 and 2013, autistic disorder and Asperger’s disorder were the two primary diagnoses related to autism in the fourth edition of the manual, the DSM-4.
In 2013, the DSM-5 collapsed both diagnoses into one autism spectrum disorder.
How did we used to think about autism?
The two thinkers behind the DSM-4 diagnostic categories were Baltimore psychiatrist Leo Kanner and Viennese paediatrician Hans Asperger. They described the challenges faced by people who were later diagnosed with autistic disorder and Asperger’s disorder.
Kanner and Asperger observed patterns of behaviour that differed to typical thinkers in the domains of communication, social interaction and flexibility of behaviour and thinking. The variance was associated with challenges in adaptation and distress.
Kanner and Asperger described different thinking patterns in children with autism.
Roman Nerud/ShutterstockBetween the 1940s and 1994, the majority of those diagnosed with autism also had an intellectual disability. Clinicians became focused on the accompanying intellectual disability as a necessary part of autism.
The introduction of Asperger’s disorder shifted this focus and acknowledged the diversity in autism. In the DSM-4 it superficially looked like autistic disorder and Asperger’s disorder were different things, with the Asperger’s criteria stating there could be no intellectual disability or delay in the development of speech.
Today, as a legacy of the recognition of the autism itself, the majority of people diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder – the new term from the DSM-5 – don’t a have an accompanying intellectual disability.
What changed with ‘autism spectrum disorder’?
The move to autism spectrum disorder brought the previously diagnosed autistic disorder and Asperger’s disorder under the one new diagnostic umbrella term.
It made clear that other diagnostic groups – such as intellectual disability – can co-exist with autism, but are separate things.
The other major change was acknowledging communication and social skills are intimately linked and not separable. Rather than separating “impaired communication” and “impaired social skills”, the diagnostic criteria changed to “impaired social communication”.
The introduction of the spectrum in the diagnostic term further clarified that people have varied capabilities in the flexibility of their thinking, behaviour and social communication – and this can change in response to the context the person is in.
Why do some people prefer the old terminology?
Some people feel the clinical label of Asperger’s allowed a much more refined understanding of autism. This included recognising the achievements and great societal contributions of people with known or presumed autism.
The contraction “Aspie” played an enormous part in the shift to positive identity formation. In the time up to the release of the DSM-5, Tony Attwood and Carol Gray, two well known thinkers in the area of autism, highlighted the strengths associated with “being Aspie” as something to be proud of. But they also raised awareness of the challenges.
What about identity-based language?
A more recent shift in language has been the reclamation of what was once viewed as a slur – “autistic”. This was a shift from person-first language to identity-based language, from “person with autism spectrum disorder” to “autistic”.
The neurodiversity rights movement describes its aim to push back against a breach of human rights resulting from the wish to cure, or fundamentally change, people with autism.
Autism is one of the forms of diversity in human thinking, which comes with strengths and challenges.
Alex and Maria photo/ShutterstockThe movement uses a “social model of disability”. This views disability as arising from societies’ response to individuals and the failure to adjust to enable full participation. The inherent challenges in autism are seen as only a problem if not accommodated through reasonable adjustments.
However the social model contrasts itself against a very outdated medical or clinical model.
Current clinical thinking and practice focuses on targeted supports to reduce distress, promote thriving and enable optimum individual participation in school, work, community and social activities. It doesn’t aim to cure or fundamentally change people with autism.
A diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder signals there are challenges beyond what will be solved by adjustments alone; individual supports are also needed. So it’s important to combine the best of the social model and contemporary clinical model.
Andrew Cashin, Professor of Nursing, School of Health and Human Sciences, Southern Cross University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Covering obesity: 6 tips for dispelling myths and avoiding stigmatizing news coverage
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When researchers looked at news coverage of obesity in the United States and the United Kingdom a few years ago, they found that images in news articles often portrayed people with larger bodies “in a stigmatizing manner” — they emphasized people’s abdomens, for example, or showed them eating junk food, wearing tight clothes or lounging in front of a TV.
When people with larger bodies were featured in photos and videos, nearly half were shown only from their necks down or with part of their heads missing, according to the analysis, published in November 2023. The researchers examined a total of 445 images posted to the websites of four U.S. news outlets and four U.K. news outlets between August 2018 and August 2019.
The findings underscore the need for dramatic changes in the way journalists report on obesity and people who weigh more than what medical authorities generally consider healthy, Rebecca Puhl, one of the paper’s authors, told The Journalist’s Resource in an email interview.
“Using images of ‘headless stomachs’ is dehumanizing and stigmatizing, as are images that depict people with larger bodies in stereotypical ways (e.g., eating junk food or being sedentary),” wrote Puhl, deputy director of the Rudd Center for Food Policy and Health at the University of Connecticut and a leading scholar on weight stigma.
She noted that news images influence how the public views and interacts with people with obesity, a complicated and often misunderstood condition that the American Medical Association considers a disease.
In the U.S., an estimated 42% of adults aged 20 years and older have obesity, a number researchers predict will rise to 50% over the next six years. While the disease isn’t as common in other parts of the planet, the World Obesity Federation projects that by 2035, more than half the global population will have obesity or overweight.
Several other studies Puhl has conducted demonstrate that biased new images can have damaging consequences for individuals affected by obesity.
“Our research has found that seeing the stigmatizing image worsens people’s attitudes and weight bias, leading them to attribute obesity to laziness, increasing their dislike of people with higher weight, and increasing desire for social distance from them,” Puhl explained.
Dozens of studies spotlight problems in news coverage of obesity in the U.S. and abroad. In addition to stigmatizing images, journalists use stigmatizing language, according to a 2022 research review in eClinicalMedicine, a journal published by The Lancet.
The research also suggests people with higher weights feel excluded and ridiculed by news outlets.
“Overt or covert discourses in news media, social media, and public health campaigns included depictions of people with overweight or obesity as being lazy, greedy, undisciplined, unhappy, unattractive, and stupid,” write the authors of the review, which examines 113 academic studies completed before Dec. 2, 2021.
To help journalists reflect on and improve their work, The Journalist’s Resource asked for advice from experts in obesity, weight stigma, health communication and sociolinguistics. They shared their thoughts and opinions, which we distilled into the six tips that appear below.
In addition to Puhl, we interviewed these six experts:
Jamy Ard, a professor of epidemiology and prevention at Wake Forest University School of Medicine and co-director of the Wake Forest Baptist Health Weight Management Center. He’s also president of The Obesity Society, a professional organization of researchers, health care providers and other obesity specialists.
Leslie Cofie, an assistant professor of health education and promotion at East Carolina University’s College of Health and Human Performance. He has studied obesity among immigrants and military veterans.
Leslie Heinberg, director of Enterprise Weight Management at the Cleveland Clinic, an academic medical center. She’s also vice chair for psychology in the Cleveland Clinic’s Center for Behavioral Health Department of Psychiatry and Psychology.
Monu Khanna, a physician in Missouri who is board certified in obesity medicine.
Jenn Lonzer, manager of the Cleveland Clinic Health Library and the co-author of several academic papers on health communication.
Cindi SturtzSreetharan, an anthropologist and professor at the Arizona State University School of Human Evolution and Social Change. She studies the language people of different cultures use to describe human bodies.
1. Familiarize yourself with recent research on what causes obesity and how obesity can affect a person’s health. Many long-held beliefs about the disease are wrong.
Journalists often report incorrect or misleading information about obesity, possibly because they’re unaware that research published in recent decades dispels many long-held beliefs about the disease, the experts say. Obesity isn’t simply the result of eating too many calories and doing too little exercise. A wide range of factors drive weight gain and prevent weight loss, many of which have nothing to do with willpower or personal choices.
Scholars have learned that stress, gut health, sleep duration and quality, genetics, medication, personal income, access to healthy foods and even climate can affect weight regulation. Prenatal and early life experiences also play a role. For example, childhood trauma such as child abuse can become “biologically embedded,” altering children’s brain structures and influencing their long-term physical and mental health, according to a 2020 research review published in the journal Physiology & Behavior.
“The causes of obesity are numerous and each individual with obesity will have a unique set of contributors to their excess weight gain,” Jamy Ard, president of The Obesity Society, wrote to The Journalist’s Resource.
The experts urge journalists to help dispel myths, correct misinformation and share new research findings. News outlets should examine their own work, which often “ignores the science and sets up situation blaming,” says Leslie Heinberg, director of Enterprise Weight Management at the Cleveland Clinic.
“So much of the media portrayal is simply ‘This is a person who eats too much and the cure is simply to eat less or cut out that food’ or something overly, overly simplistic,” Heinberg says.
Journalists need to build their knowledge of the problem before they can explain it to their audiences. Experts point out that educating policymakers, health care providers and the public about obesity is key to eliminating the stigma associated with having a larger body.
Weight stigma alone is so physically and emotionally damaging that 36 international experts issued a consensus statement in 2020 to raise awareness about it. The document, endorsed by dozens of medical and academic organizations, outlines 13 recommendations for eliminating weight bias and stigma.
Recommendation No. 5: “We call on the media to produce fair, accurate, and non-stigmatizing portrayals of obesity. A commitment from the media is needed to shift the narrative around obesity.”
2. Use person-first language — the standard among health and medical professionals for communicating about people with chronic diseases.
The experts we interviewed encourage journalists to ditch the adjectives “obese” and “overweight” because they are dehumanizing. Use person-first language, which avoids labeling people as their disease by putting the person before the disease.
Instead of saying “an obese teenager,” say “a teenager who has obesity” or “a teenager affected by obesity.” Instead of writing “overweight men,” write “men who have overweight.”
Jenn Lonzer, manager of the Cleveland Clinic Health Library, says using “overweight” as a noun might look and sound awkward at first. But it makes sense considering other diseases are treated as nouns, she notes. Journalists would not typically refer to someone in a news story as “a cancerous person,” for example. They would report that the individual has cancer.
It’s appropriate to refer to people with overweight or obesity using neutral weight terminology. Puhl wrote that she uses “people with higher body weight” or “people with high weight” and, sometimes, “people with larger bodies” in her own writing.
While the Associated Press stylebook offers no specific guidance on the use of terms such as “obese” or “overweight,” it advises against “general and often dehumanizing ‘the’ labels such as the poor, the mentally ill, the disabled, the college-educated.”
The Association of Health Care Journalists recommends person-first language when reporting on obesity. But it also advises journalists to ask sources how they would like to be characterized, provided their weight or body size is relevant to the news story.
Anthropologist Cindi SturtzSreetharan, who studies language and culture, says sources’ responses to that question should be part of the story. Some individuals might prefer to be called “fat,” “thick” or “plus-sized.”
“I would include that as a sentence in the article — to signal you’ve asked and that’s how they want to be referred to,” SturtzSreetharan says.
She encourages journalists to read how authors describe themselves in their own writing. Two books she recommends: Thick by Tressie McMillan Cottom and Heavy: An American Memoir by Kiese Laymon.
3. Carefully plan and choose the images that will accompany news stories about obesity.
Journalists need to educate themselves about stigma and screen for it when selecting images, Puhl noted. She shared these four questions that journalists should ask themselves when deciding how to show people with higher weights in photos and video.
- Does the image imply or reinforce negative stereotypes?
- Does it provide a respectful portrayal of the person?
- Who might be offended, and why?
- Can an alternative image convey the same message and eliminate possible bias?
“Even if your written piece is balanced, accurate, and respectful, a stigmatizing image can undermine your message and promote negative societal attitudes,” Puhl wrote via email.
Lonzer says newsrooms also need to do a better job incorporating images of people who have different careers, interests, education levels and lifestyles into their coverage of overweight and obesity.
“We are diverse,” says Lonzer, who has overweight. “We also have diversity in body shape and size. It’s good to have images that reflect what Americans look like.”
If you’re looking for images and b-roll videos that portray people with obesity in non-stigmatizing ways, check out the Rudd Center Media Gallery. It’s a collection of original images of people from various demographic groups that journalists can use for free in their coverage.
The Obesity Action Coalition, a nonprofit advocacy organization, also provides images. But journalists must sign up to use the OAC Bias-Free Image Gallery.
Other places to find free images: The World Obesity Image Bank, a project of the World Obesity Federation, and the Flickr account of Obesity Canada.
4. Make sure your story does not reinforce stereotypes or insinuate that overcoming obesity is simply a matter of cutting calories and doing more exercise.
“Think about the kinds of language used in the context of eating habits or physical activity, as some can reinforce shame or stereotypes,” Puhl wrote.
She suggested journalists avoid phrases such as “resisting temptations,” “cheating on a diet,” “making excuses,” “increasing self-discipline” and “lacking self-control” because they perpetuate the myth that individuals can control their weight and that the key to losing weight is eating less and moving more.
Lonzer offers this advice: As you work on stories about obesity or weight-related issues, ask yourself if you would use the same language and framing if you were reporting on someone you love.
Here are other questions for journalists to contemplate:
“Am I treating this as a complex medical condition or am I treating it as ‘Hey, lay off the French fries?’” Lonzer adds. “Am I treating someone with obesity differently than someone with another disease?”
It’s important to also keep in mind that having excess body fat does not, by itself, mean a person is unhealthy. And don’t assume everyone who has a higher weight is unhappy about it.
“Remember, not everyone with obesity is suffering,” physician Monu Khanna wrote to The Journalist’s Resource.
5. To help audiences understand how difficult it is to prevent and reduce obesity, explain that even the places people live can affect their waistlines.
When news outlets report on obesity, they often focus on weight-loss programs, surgical procedures and anti-obesity medications. But there are other important issues to cover. Experts stress the need to help the public understand how factors not ordinarily associated with weight gain or loss can influence body size.
For example, a paper published in 2018 in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine indicates adults who are regularly exposed to loud noise have a higher waist circumference than adults who are not. Research also finds that people who live in neighborhoods with sidewalks and parks are more active.
“One important suggestion I would offer to journalists is that they need to critically explore environmental factors (e.g., built environment, food deserts, neighborhood safety, etc.) that lead to disproportionately high rates of obesity among certain groups, such as low-income individuals and racial/ethnic minorities,” Leslie Cofie, an assistant professor at East Carolina University, wrote to The Journalist’s Resource.
Cofie added that moving to a new area can prompt weight changes.
“We know that immigrants generally have lower rates of obesity when they first migrate to the U.S.,” he wrote. “However, over time, their obesity rates resemble that of their U.S.-born counterparts. Hence, it is critical for journalists to learn about how the sociocultural experiences of immigrants change as they adapt to life in the U.S. For example, cultural perspectives about food, physical activities, gender roles, etc. may provide unique insights into how the pre- and post-migration experiences of immigrants ultimately contribute to the unfavorable trends in their excessive weight gain.”
Other community characteristics have been linked to larger body sizes for adults or children: air pollution, lower altitudes, higher temperatures, lower neighborhood socioeconomic status, perceived neighborhood safety, an absence of local parks and closer proximity to fast-food restaurants.
6. Forge relationships with organizations that study obesity and advocate on behalf of people living with the disease.
Several organizations are working to educate journalists about obesity and help them improve their coverage. Five of the most prominent ones collaborated on a 10-page guide book, “Guidelines for Media Portrayals of Individuals Affected by Obesity.”
- The Rudd Center for Food Policy and Health, based at the University of Connecticut, “promotes solutions to food insecurity, poor diet quality, and weight bias through research and policy,” according to its website. Research topics include food and beverage marketing, weight-related bullying and taxes on sugary drinks.
- The Obesity Society helps journalists arrange interviews with obesity specialists. It also offers journalists free access to its academic journal, Obesity, and free registration to ObesityWeek, an international conference of researchers and health care professionals held every fall. This year’s conference is Nov. 2-6 in San Antonio, Texas.
- The Obesity Medicine Association represents health care providers who specialize in obesity treatment and care. It also helps journalists connect with obesity experts and offers, on an individual basis, free access to its events, including conferences and Obesity Medicine Fundamentals courses.
- The Obesity Action Coalition offers free access to its magazine, Weight Matters, and guides on weight bias at work and in health care.
- The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery represents surgeons and other health care professionals who work in the field of metabolic and bariatric surgery. It provides the public with resources such as fact sheets and brief explanations of procedures such as the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass.
For further reading
Weight Stigma in Online News Images: A Visual Content Analysis of Stigma Communication in the Depictions of Individuals with Obesity in U.S. and U.K. News
Aditi Rao, Rebecca Puhl and Kirstie Farrar. Journal of Health Communication, November 2023.Influence and Effects of Weight Stigmatization in Media: A Systematic Review
James Kite; et al. eClinicalMedicine, June 2022.Has the Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity and Central Obesity Leveled Off in the United States? Trends, Patterns, Disparities, and Future Projections for the Obesity Epidemic
Youfa Wang; et al. International Journal of Epidemiology, June 2020.This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Unleashing My Superpowers – by Dr. Patience Mpofu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Patience Mpofu is on a mission to provide women and girls with the inside-information, knowledge, resources, and strategies to break through the glass ceiling. She writes from her experience in STEM, but her lessons are applicable in any field.
Her advices range from the internal (how to deal with imposter syndrome) to the external (how to overcome cultural biases); she also explains and illustrates the importance of both role models and mentors.
While a lot of the book is half instruction manual, half memoir of her incredible life and career (to illustrate her points), and is well-worth reading—and/or perhaps worth gifting to a girl you know with ambitions in STEM?
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: