Heart-Healthy Gochujang Noodles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Soba noodles are a good source of rutin, which is great for the heart and blood. Additionally, buckwheat (as soba noodles are made from) is healthier in various ways than rice, and certainly a lot healthier than wheat (remember that despite the name, buckwheat is about as related to wheat as a lionfish is to a lion). This dish is filled with more than just fiber though; there are a lot of powerful phytochemicals at play here, in the various kinds of cabbage, plus of course things like gingerol, capsaicin, allicin, and piperine.
You will need
- 14 oz “straight to wok” style soba noodles
- 3 bok choi (about 7 oz)
- 3½ oz red cabbage, thinly sliced
- 10 oz raw and peeled large shrimp (if you are vegan, vegetarian, allergic to shellfish/crustaceans, or observant of a religion that does not eat such, substitute with small cubes of firm tofu)
- 1 can (8 oz) sliced water chestnuts, drained (drained weight about 5 oz)
- 2 tbsp gochujang paste
- 2 tbsp low-sodium soy sauce
- 1 tbsp sesame oil
- 2 tsp garlic paste
- 2 tsp ginger paste
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- Avocado oil for frying (or another oil suitable for high temperatures—so, not olive oil)
Note: ideally you will have a good quality gochujang paste always in your cupboard, as it’s a great and versatile condiment. However, you can make your own approximation, by blending 5 pitted Medjool dates, 1 tbsp rice wine vinegar, 2 tbsp tomato purée, 2 tsp red chili flakes, 1 tsp garlic granules, and ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt. This is not exactly gochujang, but unless you want to go shopping for ingredients more obscure in Western stores than gochujang, it’s close enough.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Mix together the gochujang paste with the sesame oil, soy sauce, garlic paste, and ginger paste, in a small bowl. Whisk in ¼ cup hot water, or a little more if it seems necessary, but go easy with it. This will be your stir-fry sauce.
2) Slice the base of the bok choi into thin disks; keep the leaves aside.
3) Heat the wok to the highest temperature you can safely muster, and add a little avocado oil followed by the shrimp. When they turn from gray to pink (this will take seconds, so be ready) add the sliced base of the bok choi, and also the sliced cabbage and water chestnuts, stirring frequently. Cook for about 2 minutes; do not reduce the heat.
4) Add the sauce you made, followed 1 minute later by the noodles, stirring them in, and finally the leafy tops of the bok choi.
5) Garnish with the chia seeds (or sesame seeds, but chia pack more of a nutritional punch), and serve:
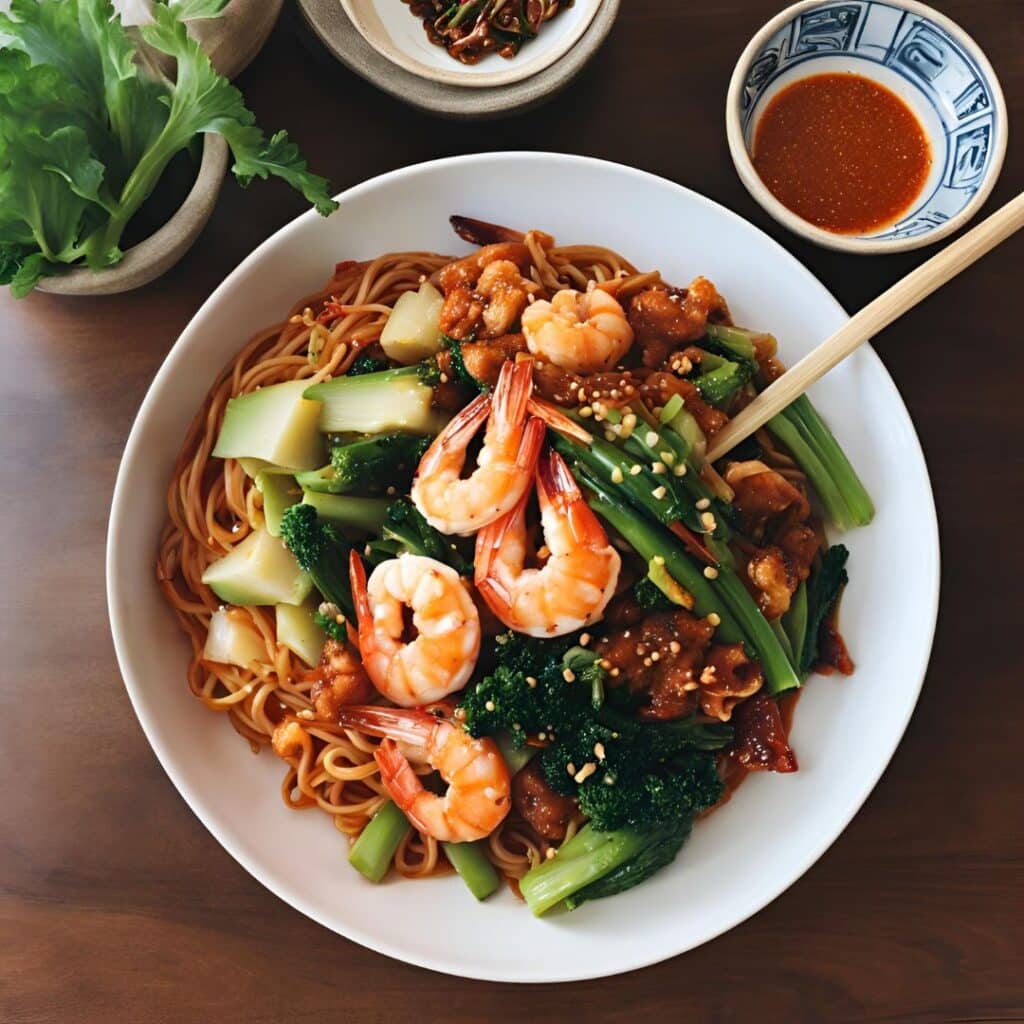

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- What Matters Most For Your Heart?
- Red Cabbage vs White Cabbage – Which is Healthier?
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
HRT Side Effects & Troubleshooting
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Heather Hirsch. She’s a board-certified internist, and her clinical expertise focuses on women’s health, particularly in midlife and menopause, and its intersection with chronic diseases (ranging from things associated with sexual health, to things like osteoporosis and heart disease).
So, what does she want us to know?
HRT can be life-changingly positive, but it can be a shaky start
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT), and in this context she’s talking specifically about the most common kind, Menopausal Hormone Therapy (MHT), involves taking hormones that our body isn’t producing enough of.
If these are “bioidentical hormones” as used in most of the industrialized world and increasingly also in N. America, then this is by definition a supplement rather than a drug, for what it’s worth, whereas some non-bioidentical hormones (or hormone analogs, which by definition function similarly to hormones but aren’t the same thing) can function more like drugs.
We wrote a little about his previously:
Hormone Replacement Therapy: A Tale Of Two Approaches
For most people most of the time, bioidentical hormones are very much the best way to go, as they are not only more effective, but also have fewer side effects.
That said, even bioidentical hormones can have some undesired effects, so, how to deal with those?
Don’t worry; bleed happy
A reprise of (usually quite light) menstrual bleeding is the most common side effect of menopausal HRT.
This happens because estrogen affects* the uterus, leading to a build-up and shedding of the uterine lining.
*if you do not have a uterus, estrogen can effect uterine tissue. That’s not a typo—here we mean the verb “effect”, as in “cause to be”. It will not grow a new uterus, but it can cause some clumps of uterine tissue to appear; this means that it becomes possible to get endometriosis without having a uterus. This information should not be too shocking, as endometriosis is a matter of uterine tissue growing inconveniently, often in places where it shouldn’t, and sometimes quite far from the uterus (if present, or its usual location, if absent). However, the risk of this happening is far lower than if you actually have a uterus:
What you need to know about endometriosis
Back to “you have a uterus and it’s making you wish you didn’t”:
This bleeding should, however, be light. It’ll probably be oriented around a 28-day cycle even if you are taking your hormones at the same dose every day of the month, and the bleeding will probably taper off after about 6 months of this.
If the bleeding is heavier, all the time, or persists longer than 6 months, then speak to your gynecologist about it. Any of those three; it doesn’t have to be all three!
Bleeding outside of one’s normal cycle can be caused by anything from fibroids to cancer; statistically speaking it’s probably nothing too dire,but when your safety is in question, don’t bet on “probably”, and do get it checked out:
When A Period Is Very Late (i.e., Post-Menopause)
Dr. Hirsch recommends, as possible remedies to try (preferably under your gynecologist’s supervision):
- lowering your estrogen dose
- increasing your progesterone dose
- taking progesterone continuously instead of cyclically
And if you’re not taking progesterone, here’s why you might want to consider taking this important hormone that works with estrogen to do good things, and against estrogen to rein in some of estrogen’s less convenient things:
Progesterone Menopausal HRT: When, Why, And How To Benefit
(the above link contains, as well as textual information, an explanatory video from Dr. Hirsch herself)
Get the best of the breast
Calm your tits. Soothe your boobs. Destress your breasts. Hakuna your tatas. Undo the calamity beleaguering your mammaries.
Ok, more seriously…
Breast tenderness is another very common symptom when starting to take estrogen. It can worry a lot of people (à la “aagh, what is this and is it cancer!?”), but is usually nothing to worry about. But just to be sure, do also check out:
Keeping Abreast Of Your Cancer Risk: How To Triple Your Breast Cancer Survival Chances
Estrogen can cause feelings of breast fullness, soreness, nipple irritation, and sometimes lactation, but this later will be minimal—we’re talking a drop or two now and again, not anything that would feed a baby.
Basically, it happens when your body hasn’t been so accustomed to normal estrogen levels in a while, and suddenly wakes up with a jolt, saying to itself “Wait what are we doing puberty again now? I thought we did menopause? Are we pregnant? What’s going on? Ok, checking all systems!” and then may calm down not too long afterwards when it notes that everything is more or less as it should be already.
If this persists or is more than a minor inconvenience though, Dr. Hirsch recommends looking at the likely remedies of:
- Adjust estrogen (usually the cause)
- Adjust progesterone (less common)
- If it’s progesterone, changing the route of administration can ameliorate things
What if it’s not working? Is it just me?
Dr. Hirsch advises the most common reasons are simply:
- wrong formulation (e.g. animal-derived estrogen or hormone analog, instead of bioidentical)
- wrong dose (e.g. too low)
- wrong route of administration (e.g. oral vs transdermal; usually transdermal estradiol is most effective but many people do fine on oral; progesterone meanwhile is usually best as a pessary/suppository, but many people do fine on oral)
Writer’s example: in 2022 there was an estrogen shortage in my country, and while I had been on transdermal estradiol hemihydrate gel, I had to go onto oral estradiol valerate tablets for a few months, because that’s what was available. And the tablets simply did not work for me at all. I felt terrible and I have a good enough intuitive sense of my hormones to know when “something wrong is not right”, and a good enough knowledge of the pharmacology & physiology to know what’s probably happening (or not happening). And sure enough, when I got my blood test results, it was as though I’d been taking nothing. It was such a relief to get back on the gel once it became available again!
So, if something doesn’t seem to be working for you, speak up and get it fixed if at all possible.
See also: What You Should Have Been Told About Menopause Beforehand
Want to know more from Dr. Hirsch?
You might like this book of hers, which we haven’t reviewed yet, but present here for your interest:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Nutrivore – by Dr. Sarah Ballantyne
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The core idea of this book is that foods can be assigned a numerical value according to their total nutritional value, and that this number can be used to guide a person’s diet such that we will eat, in aggregate, a diet that is more nutritious. So far, so simple.
What Dr. Ballantyne also does, besides explaining and illustrating this system (there are chapters explaining the calculation system, and appendices with values), is also going over what to consider important and what we can let slide, and what things we might need more of to address a wide assortment of potential health concerns. And yes, this is definitely a “positive diet” approach, i.e. it focuses on what to add in, not what to cut out.
The premise of the “positive diet” approach is simple, by the way: if we get a full set of good nutrients, we will be satisfied and not crave unhealthy food.
She also offers a lot of helpful “rules of thumb”, and provides a variety of cheat-sheets and suchlike to make things as easy as possible.
There’s also a recipes section! Though, it’s not huge and it’s probably not necessary, but it’s just one more “she’s thinking of everything” element.
Bottom line: if you’d like a single-volume “Bible of” nutrition-made-easy, this is a very usable tome.
Click here to check out Nutrivore, and start filling up your diet!
Share This Post
-
No, you don’t need the ‘Barbie drug’ to tan, whatever TikTok says. Here’s why melanotan-II is so risky
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
TikTok and Instagram influencers have been peddling the “Barbie drug” to help you tan.
But melanotan-II, as it’s called officially, is a solution that’s too good to be true. Just like tanning, this unapproved drug has a dark side.
Doctors, researchers and Australia’s drug regulator have been warning about its side effects – from nausea and vomiting to brain swelling and erection problems.
There are also safer ways of getting the tanned look, if that’s what you’re after.
AtlasStudio/Shutterstock What is melanotan-II?
No, it’s not a typo. Melanotan-II is very different from melatonin, which is a hormonal supplement used for insomnia and jet lag.
Melanotan-II is a synthetic version of the naturally ocurring hormone α-melanocyte stimulating hormone. This means the drug mimics the body’s hormone that stimulates production of the pigment melanin. This is what promotes skin darkening or tanning, even in people with little melanin.
Although the drug is promoted as a way of getting a “sunless tan”, it is usually promoted for use with UV exposure, to enhance the effect of UV and kickstart the tanning process.
Melanotan-II is related to, but different from, melanotan-I (afamelanotide), an approved drug used to treat the skin condition erythropoietic protoporphyria.
Melanotan-II is not registered for use with Australia’s Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). It is illegal to advertise it to the public or to provide it without a prescription.
However, social media has been driving unlicensed melanotan-II sales, a study published last year confirms.
There are many black market suppliers of melanotan-II injections, tablets and creams. More recently, nasal sprays have become more popular.
What are the risks?
Just like any drug, melanotan-II comes with the risk of side effects, many of which we’ve known about for more than a decade. These include changes in the size and pigmentation of moles, rapid appearance of new moles, flushing to the face, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, chest pain and brain swelling.
It can also cause rhabdomyolysis, a dangerous syndrome where muscle breaks down and releases proteins into the bloodstream that damage the kidneys.
For men, the drug can cause priapism – a painful erection that does not go away and can damage the penis, requiring emergency treatment.
Its use has been linked with melanoma developing from existing moles either during or shortly after using the drug. This is thought to be due to stimulating pigment cells and causing the proliferation of abnormal cells.
Despite reports of melanoma, according to a study of social media posts the drug is often marketed as protecting against skin cancer. In fact, there’s no evidence to show it does this.
Social media posts about melanotan-II rarely mention health risks.
There are no studies on long-term safety of melanotan-II use.
Then there’s the issue of the drug not held to the high safety standards as TGA-approved products. This could result in variability in dose, undeclared ingredients and potential microbial contamination.
Thinking about melanotan-II? The drug can cause a long-lasting painful erection needing urgent medical care. Eugenio Marongiu/Shutterstock The TGA has previously warned consumers to steer clear of the drug due to its “serious side effects that can be very damaging to your health”.
According to an ABC article published earlier this week, the TGA is cracking down on the illegal promotion of the drug on various websites. However, we know banned sellers can pop back up under a different name.
TikTok has banned the hashtags #tanningnasalspray, #melanotan and #melanotan2, but these products continue to be promoted with more generic hashtags, such as #tanning.
Part of a wider trend
Australia has some of the highest rates of skin cancer in the world. The “slip, slop, slap” campaign is a public health success story, with increased awareness of sun safety, a cultural shift and a decline in melanoma in young people.
However, the image of a bronzed beach body remains a beauty standard, especially among some young people.
Disturbingly, tan lines are trending on TikTok as a sought after summer accessory and the hashtag #sunburnttanlines has millions of views. We’ve also seen a backlash against sunscreen among some young people, again promoted on TikTok.
The Cancer Council is so concerned about the trend towards normalising tanning it has launched the campaign End the Trend.
You have other options
There are options beyond spraying an illegal, unregulated product up your nose, or risking unprotected sun exposure: fake tan.
Fake tan tends to be much safer than melanotan-II and there’s more long-term safety data. It also comes with potential side effects, albeit rare ones, including breathing issues (with spray products) and skin inflammation in some people.
Better still, you can embrace your natural skin tone.
Rose Cairns, Senior Lecturer in Pharmacy, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
International Day of Women and Girls in Science
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Today is the International Day of Women and Girls in Science, so we’ve got a bunch of content for the ladies out there. Let’s start with the statement Sima Bahous (the Executive Director of UN Women) made:
❝This year, the sixty-seventh session of the Commission on the Status of Women (CSW67) will consider as its priority theme “Innovation and technological change, and education in the digital age for achieving gender equality and the empowerment of all women and girls”.
This is an unprecedented opportunity for the Commission to develop a definitive agenda for progress towards women’s full and equal participation and representation in STEM. Its implementation will require bold, coordinated, multi-stakeholder action.❞
Here at 10almonds, we are just one newsletter, and maybe we can’t change the world (…yet), but we’re all for this!
We’re certainly all in favour of education in the digital age, and more of our subscribers are women and girls than not (highest of fives from your writer today, also a woman—and I do bring most of the sciency content).
Medical News Today asks “Why Are Women Less Likely To Survive Cardiac Arrest Than Men?”
You can read the full article here, but the short version is:
- People (bystanders and EMS professionals alike!) are less likely to intervene to give CPR when the patient is a woman (we appreciate that “your hands on an unknown woman’s chest” is a social taboo, but there’s a time and a place!)
- People trained to give CPR (volunteers or professionals!) are often less confident about how to do so with female anatomy—training is almost entirely on “male” dummies.
A quick take-away from this is: to give effective CPR, you need to be giving two-inch compressions!
On a side note, do you want to learn how to correctly do chest compressions on female anatomy? This short (1:55) video could save a woman’s life!
As a science-based health and productivity newsletter, we make no apologies if occasional issues sometimes have a slant to women’s health! Heaven help us, the bias in science at large is certainly the opposite:
The list of examples is far too long for us to include here, but two that spring immediately to mind are:
- PCOS (Polycystic ovary syndrome), which affects nearly 1 in 5 women, can lead to infertility, never mind the inconvenience of irregular bleeding, chronic pain, and diabetes (amongst other things), and… nobody knows what causes it, or what to do about it.
- Endometriosis (the lining of the womb starts growing in other places), meanwhile, affects around 1 in 10 women. It causes chronic pain and fatigue, and again, nobody knows what causes it or how to cure it.
Maybe if women in STEM weren’t on the receiving end of rampant systemic misogyny, we’d have more women in science, and some answers by now!
❗️NOT-SO-FUN FACT:
Women make up only 28% of the workforce in science, technology, engineering and math (STEM), and men vastly outnumber women majoring in most STEM fields in college. The gender gaps are particularly high in some of the fastest-growing and highest-paid jobs of the future, like computer science and engineering.
Source: AAUW
The US census suggests change is happening, but is a very long way from equality!
WHAT OUR SUBSCRIBERS SAY:
❝Women are slowly gaining more of a place in academia, and slowly making more of a difference when they get there, and start doing research that reflects ourselves. But I still think that it’s a struggle to get there, and it’s a struggle to be heard and be respected.
It’s a matter of pride, it’s a matter of proving yourself, being in STEM, and [women in STEM] still report being extremely disrespected, not taken seriously all, despite being very very good.
It’s worth noting as well, that we’ve had women in STEM for a while and there are so many things we appreciate nowadays that they were a part of, but they were never given credit for—it’s still a problem today and something we need to more actively fight.❞
Isabella F. Lima, Occupational Psychologist
Are you a woman in STEM, and have a story to tell? We’d love to hear it! Just reply to this email 🙂
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
With all this bird flu around, how safe are eggs, chicken or milk?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Enzo Palombo, Swinburne University of Technology
Recent outbreaks of bird flu – in US dairy herds, poultry farms in Australia and elsewhere, and isolated cases in humans – have raised the issue of food safety.
So can the virus transfer from infected farm animals to contaminate milk, meat or eggs? How likely is this?
And what do we need to think about to minimise our risk when shopping for or preparing food?
AS Foodstudio/Shutterstock How safe is milk?
Bird flu (or avian influenza) is a bird disease caused by specific types of influenza virus. But the virus can also infect cows. In the US, for instance, to date more than 80 dairy herds in at least nine states have been infected with the H5N1 version of the virus.
Investigations are under way to confirm how this happened. But we do know infected birds can shed the virus in their saliva, nasal secretions and faeces. So bird flu can potentially contaminate animal-derived food products during processing and manufacturing.
Indeed, fragments of bird flu genetic material (RNA) were found in cow’s milk from the dairy herds associated with infected US farmers.
However, the spread of bird flu among cattle, and possibly to humans, is likely to have been caused through contact with contaminated milking equipment, not the milk itself.
The test used to detect the virus in milk – which uses similar PCR technology to lab-based COVID tests – is also highly sensitive. This means it can detect very low levels of the bird flu RNA. But the test does not distinguish between live or inactivated virus, just that the RNA is present. So from this test alone, we cannot tell if the virus found in milk is infectious (and capable of infecting humans).
It’s best to stick with pasteurised milk. Amnixia/Shutterstock Does that mean milk is safe to drink and won’t transmit bird flu? Yes and no.
In Australia, where bird flu has not been reported in dairy cattle, the answer is yes. It is safe to drink milk and milk products made from Australian milk.
In the US, the answer depends on whether the milk is pasteurised. We know pasteurisation is a common and reliable method of destroying concerning microbes, including influenza virus. Like most viruses, influenza virus (including bird flu virus) is inactivated by heat.
Although there is little direct research on whether pasteurisation inactivates H5N1 in milk, we can extrapolate from what we know about heat inactivation of H5N1 in chicken and eggs.
So we can be confident there is no risk of bird flu transmission via pasteurised milk or milk products.
However, it’s another matter for unpasteurised or “raw” US milk or milk products. A recent study showed mice fed raw milk contaminated with bird flu developed signs of illness. So to be on the safe side, it would be advisable to avoid raw milk products.
How about chicken?
Bird flu has caused sporadic outbreaks in wild birds and domestic poultry worldwide, including in Australia. In recent weeks, there have been three reported outbreaks in Victorian poultry farms (two with H7N3 bird flu, one with H7N9). There has been one reported outbreak in Western Australia (H9N2).
The strains of bird flu identified in the Victorian and Western Australia outbreaks can cause human infection, although these are rare and typically result from close contact with infected live birds or contaminated environments.
Therefore, the chance of bird flu transmission in chicken meat is remote.
Nonetheless, it is timely to remind people to handle chicken meat with caution as many dangerous pathogens, such as Salmonella and Campylobacter, can be found on chicken carcasses.
Always handle chicken meat carefully when shopping, transporting it home and storing it in the kitchen. For instance, make sure no meat juices cross-contaminate other items, consider using a cool bag when transporting meat, and refrigerate or freeze the meat within two hours.
Avoid washing your chicken before cooking to prevent the spread of disease-causing microbes around the kitchen.
Finally, cook chicken thoroughly as viruses (including bird flu) cannot survive cooking temperatures.
Are eggs safe?
The recent Australian outbreaks have occurred in egg-laying or mixed poultry flocks, so concerns have been raised about bird flu transmission via contaminated chicken eggs.
Can flu viruses contaminate chicken eggs and potentially spread bird flu? It appears so. A report from 2007 said it was feasible for influenza viruses to enter through the eggshell. This is because influenza virus particles are smaller (100 nanometres) than the pores in eggshells (at least 200 nm).
So viruses could enter eggs and be protected from cleaning procedures designed to remove microbes from the egg surface.
Therefore, like the advice about milk and meat, cooking eggs is best.
The US Food and Drug Administration recommends cooking poultry, eggs and other animal products to the proper temperature and preventing cross-contamination between raw and cooked food.
In a nutshell
If you consume pasteurised milk products and thoroughly cook your chicken and eggs, there is nothing to worry about as bird flu is inactivated by heat.
The real fear is that the virus will evolve into highly pathogenic versions that can be transmitted from human to human.
That scenario is much more frightening than any potential spread though food.
Enzo Palombo, Professor of Microbiology, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Bone on Bone – by Dr. Meredith Warner
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What this is not: a book about one specific condition, injury, or surgery.
What this is: a guide to dealing with the common factors of many musculoskeletal conditions, inflammatory diseases, and their consequences.
Dr. Warner takes the opportunity to address the whole patient—presumably: the reader, though it could equally be a reader’s loved one, or even a reader’s patient, insofar as this book will probably be read by doctors also.
She takes an “inside-out and outside-in” approach; that is to say, addressing the problem from as many vectors as reasonably possible—including supplements, diet, dietary habits (things like intermittent fasting etc), exercise, and even sleep. And yes, she knows how difficult those latter items can be, and addresses them not merely with a “but it’s important” but also with practical advice.
As an orthopedic surgeon, she’s not a fan of surgery, and counsels the reader to avoid that if reasonably possible. She also talks about how many people in the US are encouraged to have MRI scans for financial reasons (as in, they can be profitable for the doctor/institution), and then any abnormality is used as justification for surgery, to backwards-justify the use of the MRI, even if the abnormality is not actually the cause of the pain.
Noteworthily, humans in general are a typically a pile of abnormalities in a trenchcoat. Our propensity to mutation has made us one of the most adaptable species on the planet, yet many would have us pretend that the insides of people look like they do in textbooks, or else are wrong. The reality is not so, and Dr. Warner rightly shows this for what it is.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one are suffering from, or at risk of, musculoskeletal and/or inflammatory conditions, this is a top-tier book for having a much easier time of it.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: