Mediterranean Diet… In A Pill?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does It Come In A Pill?
For any as yet unfamiliar with the Mediterranean diet, you may be wondering what it involves, beyond a general expectation that it’s a diet popularly enjoyed in the Mediterranean. What image comes to mind?
We’re willing to bet that tomatoes feature (great source of lycopene, by the way, and if you’re not getting lycopene, you’re missing out), but what else?
- Salads, perhaps? Vegetables, olives? Olive oil, yea or nay?
- Bread? Pasta? Prosciutto, salami? Cheese?
- Pizza but only if it’s Romana style, not Chicago?
- Pan-seared liver, with some fava beans and a nice Chianti?
In fact, the Mediterranean diet is quite clear on all these questions, so to read about these and more (including a “this yes, that no” list), see:
What Is The Mediterranean Diet, And What Is It Good For?
So, how do we get that in a pill?
A plucky band of researchers, Dr. Chiara de Lucia et al. (quite a lot of “et al.”; nine listed authors on the study), wondered to what extent the benefits of the Mediterranean diet come from the fact that the Mediterranean diet is very rich in polyphenols, and set about testing that, by putting the same polyphenols in capsule form, and running a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover clinical intervention trial.
Now, polyphenols are not the only reason the Mediterranean diet is great; there are also other considerations, such as:
- a great macronutrient balance with lots of fiber, healthy fats, moderate carbs, and protein from select sources
- the absence or at least very low presence of a lot of harmful substances such as refined seed oils, added sugars, refined carbohydrates, and the like (“but pasta” yes pasta; in moderation and wholegrain and served with extra sources of fiber and healthy fats, all of which slow down the absorption of the carbs)
…but polyphenols are admittedly very important too; we wrote about some common aspects of them here:
Tasty Polyphenols: Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
As for what Dr. de Lucia et al. put into the capsule, behold…
The ingredients:
- Apple Extract 10.0%
- Pomegranate Extract 10.0%
- Tomato Powder 2.5%
- Beet, Spray Dried 2.5%
- Olive Extract 7.5%
- Rosemary Extract 7.5%
- Green Coffee Bean Extract (CA) 7.5%
- Kale, Freeze Dried 2.5%
- Onion Extract 10.0%
- Ginger Extract 10.0%
- Grapefruit Extract 2.5%
- Carrot, Air Dried 2.5%
- Grape Skin Extract 17.5%
- Blueberry Extract 2.5%
- Currant, Freeze Dried 2.5%
- Elderberry, Freeze Dried 2.5%
And the relevant phytochemicals they contain:
- Quercetin
- Luteolin
- Catechins
- Punicalagins
- Phloretin
- Ellagic Acid
- Naringin
- Apigenin
- Isorhamnetin
- Chlorogenic Acids
- Rosmarinic Acid
- Anthocyanins
- Kaempferol
- Proanthocyanidins
- Myricetin
- Betanin
And what, you may wonder, did they find? Well, first let’s briefly summarise the setup of the study:
They took volunteers (n=30), average age 67, BMI >25, without serious health complaints, not taking other supplements, not vegetarian or vegan, not consuming >5 cups of coffee per day, and various other stipulations like that, to create a fairly homogenous study group who were expected to respond well to the intervention. In contrast, someone who takes antioxidant supplements, already eats many different color plants per day, and drinks 10 cups of coffee, probably already has a lot of antioxidant activity going on, and someone with a lower BMI will generally have lower resting levels of inflammatory markers, so it’s harder to see a change, proportionally.
About those inflammatory markers: that’s what they were testing, to see whether the intervention “worked”; essentially, did the levels of inflammatory markers go up or down (up is bad; down is good).
For more on inflammation, by the way, see:
How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
…which also explains what it actually is, and some important nuances about it.
Back to the study…
They gave half the participants the supplement for a week and the other half placebo; had a week’s gap as a “washout”, then repeated it, switching the groups, taking blood samples before and after each stage.
What they found:
The group taking the supplement had lower inflammatory markers after a week of taking it, while the group taking the placebo had relatively higher inflammatory markers after a week of taking it; this trend was preserved across both groups (i.e., when they switched roles for the second half).
The results were very significant (p=0.01 or thereabouts), and yet at the same time, quite modest (i.e. the supplement made a very reliable, very small difference), probably because of the small dose (150mg) and small intervention period (1 week).
What the researchers concluded from this
The researchers concluded that this was a success; the study had been primarily to provide proof of principle, not to rock the world. Now they want the experiment to be repeated with larger sample sizes, greater heterogeneity, larger doses, and longer intervention periods.
This is all very reasonable and good science.
What we conclude from this
That ingredients list makes for a good shopping list!
Well, not the extracts they listed, necessarily, but rather those actual fruits, vegetables, etc.
If nine top scientists (anti-aging specialists, neurobiologists, pharmacologists, and at least one professor of applied statistics) came to the conclusion that to get the absolute most bang-for-buck possible, those are the plants to get the phytochemicals from, then we’re not going to ignore that.
So, take another list above and ask yourself: how many of those 16 foods do you eat regularly, and could you work the others in?
Want to make your Mediterranean diet even better?
While the Mediterranean diet is a top-tier catch-all, it can be tweaked for specific areas of health, for example giving it an extra focus on heart health, or brain health, or being anti-inflammatory, or being especially gut healthy:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
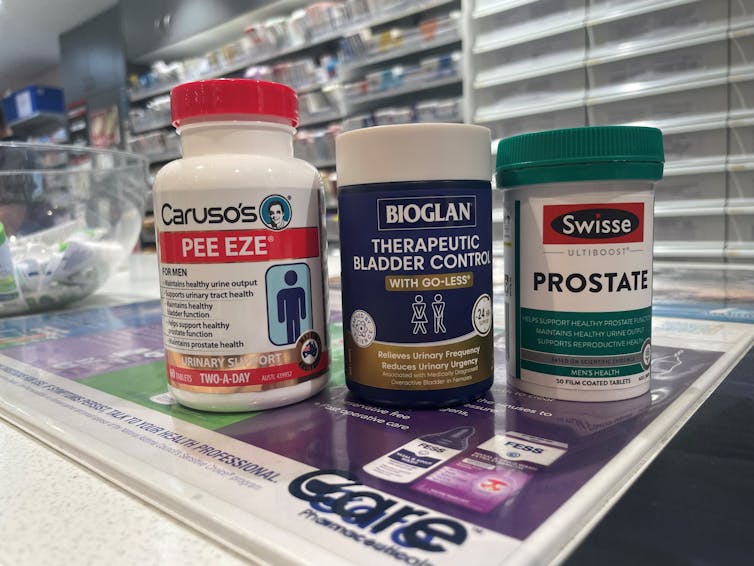
What’s in the supplements that claim to help you cut down on bathroom breaks? And do they work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
With one in four Australian adults experiencing problems with incontinence, some people look to supplements for relief.
With ingredients such as pumpkin seed oil and soybean extract, a range of products promise relief from frequent bathroom trips.
But do they really work? Let’s sift through the claims and see what the science says about their efficacy.
Christian Moro/Shutterstock What is incontinence?
Incontinence is the involuntary loss of bladder or bowel control, leading to the unintentional leakage of urine or faeces. It can range from occasional minor leaks to a complete inability to control urination and defecation.
This condition can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life, and affects women more often than it affects men.
Some people don’t experience bladder leakage but can sometimes feel an urgent need to go to the bathroom. This is known as overactive bladder syndrome, and occurs when the muscles around the bladder tighten on their own, which greatly reduces its capacity. The result is the person feels the need to go to the bathroom much more frequently.
There are many potential causes of incontinence and overactive bladders, including menopause, pregnancy and child birth, urinary tract infections, pelvic floor disorders, and an enlarged prostate. Conditions such as diabetes, neurological disorders and certain medications (such as diuretics, sleeping pills, antidepressants and blood-pressure drugs) can also contribute.
While pelvic muscle rehabilitation and behavioural techniques for bladder retraining can be helpful, some people are interested in pharmaceutical solutions.
What’s in these products?
A number of supplements are available in Australia that include ingredients used in traditional medicine for urinary incontinence and overactive bladders. The three most common ingredients are:
- Cucurbita pepo (pumpkin seed extract)
- glycine max (soybean extract)
- an extract from the bark of the Crateva magna or nurvala (Varuna) tree.
The supplements have common ingredients. Author How are they supposed to work?
Pumpkin seeds are rich in plant sterols that are thought to reduce the testosterone-related enlargement of the prostate, as well as having broader anti-inflammatory effects. The seed extracts can also contain oleic acid, which may help increase bladder capacity by relaxing the muscles around the organ.
Soybean extracts are rich in isoflavones, especially daidzen and genistein. Like olieic acid, these are thought to act on the muscles around the bladder. Because isoflavones are similar in structure to the female hormone oestrogen, soy extracts may be most beneficial for postmenopausal women who have overactive bladders.
Crateva extract is rich in lupeol- and sterol-based chemicals which have strong anti-inflammatory effects. This has benefits not just for enlarged prostates but possibly also for reducing urinary tract infections.
Do they actually work?
It’s important to note that the government has only approved these types of supplements as “listed medicines”. This means the ingredients have only been assessed for safety. The companies behind the products have not had to provide evidence they actually work.
A 2014 clinical trial examined a combined pumpkin seed and soybean extract called cucurflavone on people with overactive bladders. The 120 participants received either a placebo or a daily 1,000mg dose of the herbal mixture over a period of 12 weeks.
By the end of study, those in the cucurflavone group went to the bathroom around three fewer times per day, compared with people in the control group, who only went to the bathroom on average one fewer time each day.
In a different trial, researchers examined a combination of Crateva bark extract with herbal extracts of horsetail and Japanese evergreen spicebush, called Urox.
For the 150 participants, the Urox formulation helped participants go to the bathroom less frequently when compared with placebo treatment.
After eight weeks of treatment, participants in the placebo group were going to the bathroom to urinate 11 times per day. Those in the Urox group were only going around to 7.5 times per day. And those who took Urox also needed to go to the bathroom one fewer time during the night.
Finally, another study also examined a Creteva, horsetail and Japanese spicebush combination, but this time in children. They were given either a 420mg dose of the supplement or a placebo, and then monitored for how many times they wet the bed.
After two months of taking the supplement, slightly more than 40% of the 24 kids in the supplement group wet the bed less often.
While these results may look promising, there are considerable limitations to the studies which means the data may not be reliable. For example, the trials didn’t include enough participants to have reliable data. To conclusively provide efficacy, final-stage clinical trials require data for between 300 and 3,000 patients.
From the studies, it is also not clear whether some participants were also taking other medicines as well as the supplement. This is important, as medications can interfere with how the supplements work, potentially making them less or more effective.
What if you want to take them?
If you have incontinence or an overactive bladder, you should always discuss this with your doctor, as it may due to a serious or treatable underlying condition.
Otherwise, your GP may give you strategies or exercises to improve your bladder control, prescribe medications or devices, or refer you to a specialist.
If you do decide to take a supplement, discuss this with your doctor and local pharmacist so they can check that any product you choose will not interfere with any other medications you may be taking.
Nial Wheate, Professor of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Macquarie University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How do I handle it if my parent is refusing aged care? 4 things to consider
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s a shock when we realise our parents aren’t managing well at home.
Perhaps the house and garden are looking more chaotic, and Mum or Dad are relying more on snacks than nutritious meals. Maybe their grooming or hygiene has declined markedly, they are socially isolated or not doing the things they used to enjoy. They may be losing weight, have had a fall, aren’t managing their medications correctly, and are at risk of getting scammed.
You’re worried and you want them to be safe and healthy. You’ve tried to talk to them about aged care but been met with swift refusal and an indignant declaration “I don’t need help – everything is fine!” Now what?
Here are four things to consider.
1. Start with more help at home
Getting help and support at home can help keep Mum or Dad well and comfortable without them needing to move.
Consider drawing up a roster of family and friends visiting to help with shopping, cleaning and outings. You can also use home aged care services – or a combination of both.
Government subsidised home care services provide from one to 13 hours of care a week. You can get more help if you are a veteran or are able to pay privately. You can take advantage of things like rehabilitation, fall risk-reduction programs, personal alarms, stove automatic switch-offs and other technology aimed at increasing safety.
Call My Aged Care to discuss your options.
Is Mum or Dad OK at home?
Nadino/Shutterstock2. Be prepared for multiple conversations
Getting Mum or Dad to accept paid help can be tricky. Many families often have multiple conversations around aged care before a decision is made.
Ideally, the older person feels supported rather than attacked during these conversations.
Some families have a meeting, so everyone is coming together to help. In other families, certain family members or friends might be better placed to have these conversations – perhaps the daughter with the health background, or the auntie or GP who Mum trusts more to provide good advice.
Mum or Dad’s main emotional support person should try to maintain their relationship. It’s OK to get someone else (like the GP, the hospital or an adult child) to play “bad cop”, while a different person (such as the older person’s spouse, or a different adult child) plays “good cop”.
3. Understand the options when help at home isn’t enough
If you have maximised home support and it’s not enough, or if the hospital won’t discharge Mum or Dad without extensive supports, then you may be considering a nursing home (also known as residential aged care in Australia).
Every person has a legal right to choose where we live (unless they have lost capacity to make that decision).
This means families can’t put Mum or Dad into residential aged care against their will. Every person also has the right to choose to take risks. People can choose to continue to live at home, even if it means they might not get help immediately if they fall, or eat poorly. We should respect Mum or Dad’s decisions, even if we disagree with them. Researchers call this “dignity of risk”.
It’s important to understand Mum or Dad’s point of view. Listen to them. Try to figure out what they are feeling, and what they are worried might happen (which might not be rational).
Try to understand what’s really important to their quality of life. Is it the dog, having privacy in their safe space, seeing grandchildren and friends, or something else?
Older people are often understandably concerned about losing independence, losing control, and having strangers in their personal space.
Sometimes families prioritise physical health over psychological wellbeing. But we need to consider both when considering nursing home admission.
Research suggests going into a nursing home temporarily increases loneliness, risk of depression and anxiety, and sense of losing control.
Mum and Dad should be involved in the decision-making process about where they live, and when they might move.
Some families start looking “just in case” as it often takes some time to find the right nursing home and there can be a wait.
After you have your top two or three choices, take Mum or Dad to visit them. If this is not possible, take pictures of the rooms, the public areas in the nursing home, the menu and the activities schedule.
We should give Mum or Dad information about their options and risks so they can make informed (and hopefully better) decisions.
For instance, if they visit a nursing home and the manager says they can go on outings whenever they want, this might dispel a belief they are “locked up”.
Having one or two weeks “respite” in a home may let them try it out before making the big decision about staying permanently. And if they find the place unacceptable, they can try another nursing home instead.
You might need to have multiple conversations about aged care.
CGN089/Shutterstock4. Understand the options if a parent has lost capacity to make decisions
If Mum or Dad have lost capacity to choose where they live, family may be able to make that decision in their best interests.
If it’s not clear whether a person has capacity to make a particular decision, a medical practitioner can assess for that capacity.
Mum or Dad may have appointed an enduring guardian to make decisions about their health and lifestyle decisions when they are not able to.
An enduring guardian can make the decision that the person should live in residential aged care, if the person no longer has the capacity to make that decision themselves.
If Mum or Dad didn’t appoint an enduring guardian, and have lost capacity, then a court or tribunal can appoint that person a private guardian (usually a family member, close friend or unpaid carer).
If no such person is available to act as private guardian, a public official may be appointed as public guardian.
Deal with your own feelings
Families often feel guilt and grief during the decision-making and transition process.
Families need to act in the best interest of Mum or Dad, but also balance other caring responsibilities, financial priorities and their own wellbeing.
Lee-Fay Low, Professor in Ageing and Health, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
What Happened to You? – by Dr. Bruce Perry and Oprah Winfrey
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The very title “What Happened To You?” starts with an assumption that the reader has suffered trauma. This is not just a sample bias of “a person who picks up a book about healing from trauma has probably suffered trauma”, but is also a statistically safe assumption. Around 60% of adults report having suffered some kind of serious trauma.
The authors examine, as the subtitle suggests, these matters in three parts:
- Trauma
- Resilience
- Healing
Trauma can take many forms; sometimes it is a very obvious dramatic traumatic event; sometimes less so. Sometimes it can be a mountain of small things that eroded our strength leaving us broken. But what then, of resilience?
Resilience (in psychology, anyway) is not imperviousness; it is the ability to suffer and recover from things.
Healing is the tail-end part of that. When we have undergone trauma, displayed whatever amount of resilience we could at the time, and now have outgrown our coping strategies and looking to genuinely heal.
The authors present many personal stories and case studies to illustrate different kinds of trauma and resilience, and then go on to outline what we can do to grow from there.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one has suffered trauma, this book may help a lot in understanding and processing that, and finding a way forwards from it.
Click here to check out “What Happened To You?” and give yourself what you deserve.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
4 Ways Vaccine Skeptics Mislead You on Measles and More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Measles is on the rise in the United States. In the first quarter of this year, the number of cases was about 17 times what it was, on average, during the same period in each of the four years before, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Half of the people infected — mainly children — have been hospitalized.
It’s going to get worse, largely because a growing number of parents are deciding not to get their children vaccinated against measles as well as diseases like polio and pertussis. Unvaccinated people, or those whose immunization status is unknown, account for 80% of the measles cases this year. Many parents have been influenced by a flood of misinformation spouted by politicians, podcast hosts, and influential figures on television and social media. These personalities repeat decades-old notions that erode confidence in the established science backing routine childhood vaccines. KFF Health News examined the rhetoric and explains why it’s misguided:
The No-Big-Deal Trope
A common distortion is that vaccines aren’t necessary because the diseases they prevent are not very dangerous, or too rare to be of concern. Cynics accuse public health officials and the media of fear-mongering about measles even as 19 states report cases.
For example, an article posted on the website of the National Vaccine Information Center — a regular source of vaccine misinformation — argued that a resurgence in concern about the disease “is ‘sky is falling’ hype.” It went on to call measles, mumps, chicken pox, and influenza “politically incorrect to get.”
Measles kills roughly 2 of every 1,000 children infected, according to the CDC. If that seems like a bearable risk, it’s worth pointing out that a far larger portion of children with measles will require hospitalization for pneumonia and other serious complications. For every 10 measles cases, one child with the disease develops an ear infection that can lead to permanent hearing loss. Another strange effect is that the measles virus can destroy a person’s existing immunity, meaning they’ll have a harder time recovering from influenza and other common ailments.
Measles vaccines have averted the deaths of about 94 million people, mainly children, over the past 50 years, according to an April analysis led by the World Health Organization. Together with immunizations against polio and other diseases, vaccines have saved an estimated 154 million lives globally.
Some skeptics argue that vaccine-preventable diseases are no longer a threat because they’ve become relatively rare in the U.S. (True — due to vaccination.) This reasoning led Florida’s surgeon general, Joseph Ladapo, to tell parents that they could send their unvaccinated children to school amid a measles outbreak in February. “You look at the headlines and you’d think the sky was falling,” Ladapo said on a News Nation newscast. “There’s a lot of immunity.”
As this lax attitude persuades parents to decline vaccination, the protective group immunity will drop, and outbreaks will grow larger and faster. A rapid measles outbreak hit an undervaccinated population in Samoa in 2019, killing 83 people within four months. A chronic lack of measles vaccination in the Democratic Republic of the Congo led to more than 5,600 people dying from the disease in massive outbreaks last year.
The ‘You Never Know’ Trope
Since the earliest days of vaccines, a contingent of the public has considered them bad because they’re unnatural, as compared with nature’s bounty of infections and plagues. “Bad” has been redefined over the decades. In the 1800s, vaccine skeptics claimed that smallpox vaccines caused people to sprout horns and behave like beasts. More recently, they blame vaccines for ailments ranging from attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder to autism to immune system disruption. Studies don’t back the assertions. However, skeptics argue that their claims remain valid because vaccines haven’t been adequately tested.
In fact, vaccines are among the most studied medical interventions. Over the past century, massive studies and clinical trials have tested vaccines during their development and after their widespread use. More than 12,000 people took part in clinical trials of the most recent vaccine approved to prevent measles, mumps, and rubella. Such large numbers allow researchers to detect rare risks, which are a major concern because vaccines are given to millions of healthy people.
To assess long-term risks, researchers sift through reams of data for signals of harm. For example, a Danish group analyzed a database of more than 657,000 children and found that those who had been vaccinated against measles as babies were no more likely to later be diagnosed with autism than those who were not vaccinated. In another study, researchers analyzed records from 805,000 children born from 1990 through 2001 and found no evidence to back a concern that multiple vaccinations might impair children’s immune systems.
Nonetheless, people who push vaccine misinformation, like candidate Robert F. Kennedy Jr., dismiss massive, scientifically vetted studies. For example, Kennedy argues that clinical trials of new vaccines are unreliable because vaccinated kids aren’t compared with a placebo group that gets saline solution or another substance with no effect. Instead, many modern trials compare updated vaccines with older ones. That’s because it’s unethical to endanger children by giving them a sham vaccine when the protective effect of immunization is known. In a 1950s clinical trial of polio vaccines, 16 children in the placebo group died of polio and 34 were paralyzed, said Paul Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and author of a book on the first polio vaccine.
The Too-Much-Too-Soon Trope
Several bestselling vaccine books on Amazon promote the risky idea that parents should skip or delay their children’s vaccines. “All vaccines on the CDC’s schedule may not be right for all children at all times,” writes Paul Thomas in his bestselling book “The Vaccine-Friendly Plan.” He backs up this conviction by saying that children who have followed “my protocol are among the healthiest in the world.”
Since the book was published, Thomas’ medical license was temporarily suspended in Oregon and Washington. The Oregon Medical Board documented how Thomas persuaded parents to skip vaccines recommended by the CDC, and reported that he “reduced to tears” a mother who disagreed. Several children in his care came down with pertussis and rotavirus, diseases easily prevented by vaccines, wrote the board. Thomas recommended fish oil supplements and homeopathy to an unvaccinated child with a deep scalp laceration, rather than an emergency tetanus vaccine. The boy developed severe tetanus, landing in the hospital for nearly two months, where he required intubation, a tracheotomy, and a feeding tube to survive.
The vaccination schedule recommended by the CDC has been tailored to protect children at their most vulnerable points in life and minimize side effects. The combination measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine isn’t given for the first year of a baby’s life because antibodies temporarily passed on from their mother can interfere with the immune response. And because some babies don’t generate a strong response to that first dose, the CDC recommends a second one around the time a child enters kindergarten because measles and other viruses spread rapidly in group settings.
Delaying MMR doses much longer may be unwise because data suggests that children vaccinated at 10 or older have a higher chance of adverse reactions, such as a seizure or fatigue.
Around a dozen other vaccines have discrete timelines, with overlapping windows for the best response. Studies have shown that MMR vaccines may be given safely and effectively in combination with other vaccines.
’They Don’t Want You to Know’ Trope
Kennedy compares the Florida surgeon general to Galileo in the introduction to Ladapo’s new book on transcending fear in public health. Just as the Roman Catholic inquisition punished the renowned astronomer for promoting theories about the universe, Kennedy suggests that scientific institutions oppress dissenting voices on vaccines for nefarious reasons.
“The persecution of scientists and doctors who dare to challenge contemporary orthodoxies is not a new phenomenon,” Kennedy writes. His running mate, lawyer Nicole Shanahan, has campaigned on the idea that conversations about vaccine harms are censored and the CDC and other federal agencies hide data due to corporate influence.
Claims like “they don’t want you to know” aren’t new among the anti-vaccine set, even though the movement has long had an outsize voice. The most listened-to podcast in the U.S., “The Joe Rogan Experience,” regularly features guests who cast doubt on scientific consensus. Last year on the show, Kennedy repeated the debunked claim that vaccines cause autism.
Far from ignoring that concern, epidemiologists have taken it seriously. They have conducted more than a dozen studies searching for a link between vaccines and autism, and repeatedly found none. “We have conclusively disproven the theory that vaccines are connected to autism,” said Gideon Meyerowitz-Katz, an epidemiologist at the University of Wollongong in Australia. “So, the public health establishment tends to shut those conversations down quickly.”
Federal agencies are transparent about seizures, arm pain, and other reactions that vaccines can cause. And the government has a program to compensate individuals whose injuries are scientifically determined to result from them. Around 1 to 3.5 out of every million doses of the measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine can cause a life-threatening allergic reaction; a person’s lifetime risk of death by lightning is estimated to be as much as four times as high.
“The most convincing thing I can say is that my daughter has all her vaccines and that every pediatrician and public health person I know has vaccinated their kids,” Meyerowitz-Katz said. “No one would do that if they thought there were serious risks.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Lymphatic System Against Cancer & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ask Not What Your Lymphatic System Can Do For You…
Just kidding; we’ll cover that first, as it’s definitely not talked about enough.
The lymphatic system is the system in the body that moves lymph around. It’s made of glands, nodes, and vessels:
- The glands (such as the tonsils and the adenoids) and nodes filter out bacteria and produce white blood cells. Specific functions may be, well, specialized—beyond the scope of today’s article—but that’s the broad function.
- The vessels are the tubes that allow those things to be moved around, suspended in lymph.
What’s lymph? It’s a colorless water-like liquid that transports immune cells, nutrients (and waste) around the body (through the lymphatic system).
Yes, it works alongside your vasculature; when white blood cells aren’t being deployed en masse into your bloodstream to deal with some threat, they’re waiting in the wings in the lymphatic system.
While your blood is pumped around by your heart, lymph moves based on a variety of factors, including contractions of small specialized lymphatic muscles, the pressure gradient created by the combination of those and gravity, and the movements of your body itself.
Here’s a larger article than we have room for, with diagrams we also don’t have room for:
Modelling the lymphatic system
To oversimplify it in few words for the sake of moving on: you can most of the time: think of it as an ancillary network supporting your circulatory system that unlike blood, doesn’t deal with oxygen or sugars, but does deal with a lot of other things, including:
- water and salt balance
- immune cells and other aspects of immune function
- transports fats (and any fat-soluble vitamins in them) into circulation
- cleans up stuff that gets stuck between cells
- general detoxification
There’s a lot that can go wrong if lymph isn’t flowing as it should
Too much to list here, but to give an idea:
- Arthritis and many autoimmune diseases
- Cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome
- Obesity, diabetes, and organ failure
- Alzheimer’s and other dementias
- Lymphadenitis, lymphangitis, and lymphedenopathy
- Lymphomas and Hodgkin’s disease (both are types of lymphatic cancer)
- Cancers of other kinds, because of things not being cleaned up where and when they should be
Yikes! That’s a lot of important things for a mostly-forgotten system to be taking care of protecting us from!
What you can do for your lymphatic system, to avoid those things!
Happily, there are easy things we can do to give our lymph some love, such as:
Massage therapy (and foam rolling)
This is the go-to that many people/publications recommend. It’s good! It’s certainly not the most important thing to do, but it’s good.
You can even use a simple gadget like this one to help move the lymph around, without needing to learn arcane massage techniques.
Exercise (move your body!)
This is a lot more important. The more we move our body, the more lymph moves around. The more lymph moves around today, the more easily it will move around tomorrow. A healthy constant movement of lymph throughout the lymphatic system is key to keeping everything running smoothly.
If you pick only one kind of exercise, make it High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT):
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
If for some reason you really can’t do that, just spend as much of your waking time as reasonably possible, moving, per:
For ideas on how to do that, check out…
Get thee to a kitchen
This is about getting healthy food that gives your body’s clean-up crew (the lymphatic system) an easier time of it.
Rather than trying to “eat clean” which can be a very nebulous term and it’s often not at all clear (and/or hotly debated) what counts as “clean”, instead, stick to foods that constitute an anti-inflammatory diet:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Five Flavors & Five Benefits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Five Flavors Of Good Health
Schisandra chinensis, henceforth Schisandra, is also called the “five flavor fruit”, for covering the culinary bases of sweet, salt, bitter, sour, and pungent.
It can be eaten as a fruit (small red berries), juiced from the fruit, or otherwise extracted into supplements (dried powder of the fruit being a common one).
It has long enjoyed usage in various traditional medicines, especially in China and Siberia.
So, what are its health claims, and how does the science stack up?
Menopause
Most of the studies are mouse studies, and we prefer studies on humans, so here’s a small (n=36) randomized clinical trial that concluded…
❝Schisandra chinensis can be a safe and effective complementary medicine for menopausal symptoms, especially for hot flushes, sweating, and heart palpitations❞
~ Dr. Joon Young Park & Dr. Kye Hyun Kim
Read more: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of Schisandra chinensis for menopausal symptoms
Antioxidant (and perhaps more)
Like many berries, it’s a good source of lignans offering antioxidant effects:
Antioxidant Effects of Schisandra chinensis Fruits and Their Active Constituents
Lignans usually have anticancer effects too (which is reasonably, given what is antioxidant is usually anticancer and anti-inflammatory as well, by the same mechanism) but those have not yet been studied in schisandra specifically.
Antihepatotoxicity
In other words, it’s good for your liver. At least, so animal studies tell us, because human studies haven’t been done yet for this one. The effect is largely due to its antioxidant properties, but it seems especially effective for the liver—which is not surprising, giving the liver’s regeneration mechanism.
Anyway, here’s a fascinating study that didn’t even need to use the fruit itself, just the pollen from the plant, it was that potent:
Athletics enhancer
While it’s not yet filling the shelves of sports nutrition stores, we found a small (n=45) study with healthy post-menopausal women who took either 1g of schisandra (experimental group) or 1g of starch (placebo group), measured quadriceps muscle strength and resting lactate levels over the course of a 12 week intervention period, and found:
❝Supplementation of Schisandra chinensis extract can help to improve quadriceps muscle strength as well as decrease lactate level at rest in adult women ❞
Anti-Alzheimers & Anti-Parkinsons
The studies for this are all in vitro, but that’s because it’s hard to find volunteers willing to have their brains sliced and looked at under a microscope while they’re still alive.
Nevertheless, the results are compelling, and it seems uncontroversial to say that schisandra, or specifically Schisandrin B, a compound it contains, has not only anti-inflammatory properties, but also neuroprotective properties, and specifically blocks the formation of excess amyloid-β peptides in the brain (which are critical for the formation of amyloid plaque, as found in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients):
Is it safe?
For most people, yes! Some caveats:
- As it can stimulate the uterus, it’s not recommended if you’re pregant.
- Taking more than the recommended amount can worsen symptoms of heartburn, GERD, ulcers, or other illnesses like that.
And as ever, do speak with our own doctor/pharmacist if unsure, as your circumstances may vary and we cannot cover all possibilities here.
Where can I get some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: