Antihistamines for Runny Nose?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Do you have any articles about using Anti-Histamines? My nose seems to be running a lot. I don’t have a cold or any allergies that I know of. I tried a Nasal spray Astepro, but it doesn’t do much.?❞
Just for you, we wrote such an article yesterday in response to this question!
The Astepro that you tried, by the way, is a brand name of the azelastine we mentioned near the end, before we got to talking about systemic corticosteroids such as beclometasone dipropionate—this latter might help you if antihistamines haven’t, and if your doctor advises there’s no contraindication (for most people it is safe for there are exceptions, such as if you are immunocompromised and/or currently fighting some infection).
You can find more details on all this in yesterday’s article, which in case you missed it, can be found at:
Antihistamines’ Generation Gap: Are You Ready For Allergy Season?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Doctors Feel – by Dr. Danielle Ofri
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book discusses how feelings such as shame, fear, anger, empathy, and even love influence patient care. Dr. Ofri notes early on:
❝One might reasonably say, I don’t give a damn how my doctor feels as long as she gets me better. In straightforward medical cases, this line of thinking is probably valid. Doctors who are angry, nervous, jealous, burned out, terrified, or ashamed can usually still treat bronchitis or ankle sprains competently.
The problems arise when clinical situations are convoluted, unyielding, or overlaid with unexpected complications, medical errors, or psychological components. This is where factors other than clinical competency come into play.❞
~ Dr. Danielle Ofri
What then follows is very much a no-holds-barred account of the emotional side of medicine.
Not portraying doctors as heroes or martyrs, just as people. Indeed, she even talks about an early, abject failure of hers as a medical student, literally hiding from a patient who badly needed attention and to whom she had been assigned.
We learn not just about the mistakes of doctors, but also the mistakes of patients that lead to mistakes by doctors. For example, emphasizing the severity of your symptom(s) can sometimes be useful to ensure they get attention, but if your regular doctor has heard you rating every symptom always as a 10 every appointment for the past many years, then the end result is that they don’t have information to work from, and will—at best—become frustrated, which will not work out well for you.
Mostly, though, it’s about what goes on behind that calm collected professional exterior that most doctors show most of the time.
The style is a fascinating blend of well-researched science (there’s an extensive bibliography) and very human tales of suffering, compassion, hope, loss, isolation, connection, and more.
Bottom line: if you want to understand your doctor(s), then you want to read this book.
Click here to check out What Doctors Feel, and learn how emotions affect the practice of medicine!
Share This Post
-
Cherries vs Grapes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cherries to grapes, we picked the cherries.
Why?
First, let’s mention: we are looking at sour cherries and Californian grapes. Even those will of course vary in quality, but the nutritional values here are quite reliable averages.
In terms of macros you might have guessed this one: cherries have nearly 2x the fiber and grapes have about 50% more carbs. So, while neither fruit is bad and they are both low glycemic index foods, cherry is the winner in this category.
When it comes to vitamins, cherries have more of vitamins A, B3, B5, B9, C, and choline, while grapes have more of vitamins B1, B2, B6, E, and K. That’s a 6:5 win for cherries, and the respective margins of difference bear that out too.
In the category of minerals, cherries have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc, while grapes have more manganese and potassium. An easy 6:2 win for cherries.
You might be wondering about polyphenols: both are very abundant in very many polyphenols; so much and so many, in fact, that we couldn’t possibly try to adjudicate between them without doing some complex statistical modeling (especially given how much this can vary from one sample to another, much more so than the micro-and macronutrient values discussed above), so we’ll call it a tie on these.
Adding up the section makes for a clear win for cherries, but of course, enjoy either or both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Cherries’ Very Healthy Wealth Of Benefits!
Resveratrol & Healthy AgingTake care!
Share This Post
-
Bird flu has been detected in a pig in the US. Why does that matter?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The United States Department of Agriculture last week reported that a pig on a backyard farm in Oregon was infected with bird flu.
As the bird flu situation has evolved, we’ve heard about the A/H5N1 strain of the virus infecting a range of animals, including a variety of birds, wild animals and dairy cattle.
Fortunately, we haven’t seen any sustained spread between humans at this stage. But the detection of the virus in a pig marks a worrying development in the trajectory of this virus.
David MG/Shutterstock How did we get here?
The most concerning type of bird flu currently circulating is clade 2.3.4.4b of A/H5N1, a strain of influenza A.
Since 2020, A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b has spread to a vast range of birds, wild animals and farm animals that have never been infected with bird flu before.
While Europe is a hotspot for A/H5N1, attention is currently focused on the US. Dairy cattle were infected for the first time in 2024, with more than 400 herds affected across at least 14 US states.
Bird flu has enormous impacts on farming and commercial food production, because infected poultry flocks have to be culled, and infected cows can result in contaminated diary products. That said, pasteurisation should make milk safe to drink.
While farmers have suffered major losses due to H5N1 bird flu, it also has the potential to mutate to cause a human pandemic.
Birds and humans have different types of receptors in their respiratory tract that flu viruses attach to, like a lock (receptors) and key (virus). The attachment of the virus allows it to invade a cell and the body and cause illness. Avian flu viruses are adapted to birds, and spread easily among birds, but not in humans.
So far, human cases have mainly occurred in people who have been in close contact with infected farm animals or birds. In the US, most have been farm workers.
The concern is that the virus will mutate and adapt to humans. One of the key steps for this to happen would be a shift in the virus’ affinity from the bird receptors to those found in the human respiratory tract. In other words, if the virus’ “key” mutated to better fit with the human “lock”.
A recent study of a sample of A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b from an infected human had worrying findings, identifying mutations in the virus with the potential to increase transmission between human hosts.
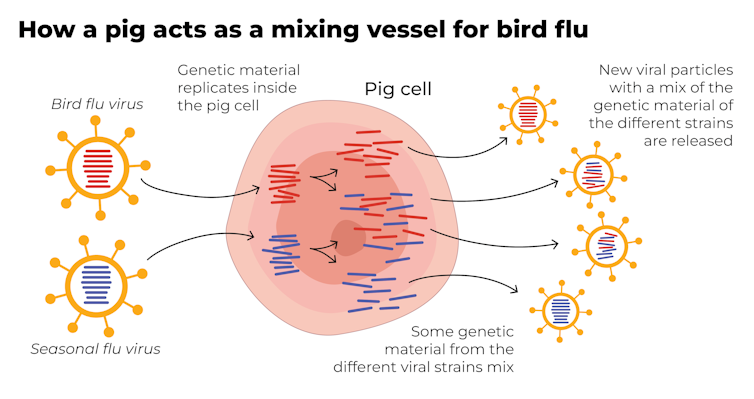
Why are pigs a problem?
A human pandemic strain of influenza can arise in several ways. One involves close contact between humans and animals infected with their own specific flu viruses, creating opportunities for genetic mixing between avian and human viruses.
Pigs are the ideal genetic mixing vessel to generate a human pandemic influenza strain, because they have receptors in their respiratory tracts which both avian and human flu viruses can bind to.
This means pigs can be infected with a bird flu virus and a human flu virus at the same time. These viruses can exchange genetic material to mutate and become easily transmissible in humans.
The Conversation, CC BY-SA Interestingly, in the past pigs were less susceptible to A/H5N1 viruses. However, the virus has recently mutated to infect pigs more readily.
In the recent case in Oregon, A/H5N1 was detected in a pig on a non-commercial farm after an outbreak occurred among the poultry housed on the same farm. This strain of A/H5N1 was from wild birds, not the one that is widespread in US dairy cows.
The infection of a pig is a warning. If the virus enters commercial piggeries, it would create a far greater level of risk of a pandemic, especially as the US goes into winter, when human seasonal flu starts to rise.
How can we mitigate the risk?
Surveillance is key to early detection of a possible pandemic. This includes comprehensive testing and reporting of infections in birds and animals, alongside financial compensation and support measures for farmers to encourage timely reporting.
Strengthening global influenza surveillance is crucial, as unusual spikes in pneumonia and severe respiratory illnesses could signal a human pandemic. Our EPIWATCH system looks for early warnings of such activity, which can speed up vaccine development.
If a cluster of human cases occurs, and influenza A is detected, further testing (called subtyping) is essential to ascertain whether it’s a seasonal strain, an avian strain from a spillover event, or a novel pandemic strain.
Early identification can prevent a pandemic. Any delay in identifying an emerging pandemic strain enables the virus to spread widely across international borders.
Australia’s first human case of A/H5N1 occurred in a child who acquired the infection while travelling in India, and was hospitalised with illness in March 2024. At the time, testing revealed Influenza A (which could be seasonal flu or avian flu), but subtyping to identify A/H5N1 was delayed.
This kind of delay can be costly if a human-transmissible A/H5N1 arises and is assumed to be seasonal flu because the test is positive for influenza A. Only about 5% of tests positive for influenza A are subtyped further in Australia and most countries.
In light of the current situation, there should be a low threshold for subtyping influenza A strains in humans. Rapid tests which can distinguish between seasonal and H5 influenza A are emerging, and should form part of governments’ pandemic preparedness.
A higher risk than ever before
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the current risk posed by H5N1 to the general public remains low.
But with H5N1 now able to infect pigs, and showing worrying mutations for human adaptation, the level of risk has increased. Given the virus is so widespread in animals and birds, the statistical probability of a pandemic arising is higher than ever before.
The good news is, we are better prepared for an influenza pandemic than other pandemics, because vaccines can be made in the same way as seasonal flu vaccines. As soon as the genome of a pandemic influenza virus is known, the vaccines can be updated to match it.
Partially matched vaccines are already available, and some countries such as Finland are vaccinating high-risk farm workers.
C Raina MacIntyre, Professor of Global Biosecurity, NHMRC L3 Research Fellow, Head, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW Sydney and Haley Stone, Research Associate, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute & CRUISE lab, Computer Science and Engineering, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Elderberries vs Cranberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing elderberries to cranberries, we picked the elderberries.
Why?
In terms of macros, elderberry has slightly more carbs and 2x the fiber, the ratio of which gives elderberries the lower glycemic index also. A win for elderberries, then.
Looking at the vitamins, elderberries have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, and C, while cranberries have more vitamin B5. An easy win for elderberries in this category.
In the category of minerals, we see a similar story: elderberries have more calcium, copper, iron, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while cranberries have (barely) more magnesium. Another clear win for elderberries.
Both of these fruits have additional “special” properties, and it’s worth noting that:
- elderberries’ bonus properties include that they significantly hasten recovery from upper respiratory tract viral infections.
- cranberries’ bonus properties (including: famously very good at reducing UTI risk) come with some warnings, including that they may increase the risk of kidney stones if you are prone to such, and also that cranberries have anti-clotting effects, which are great for heart health but can be a risk of you’re on blood thinners or have a bleeding disorder.
You can read about both of these fruits’ special properties in more detail below:
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Herbs for Evidence-Based Health & Healing ← elderberry is in the list. We haven’t, at time of writing, done a main feature just on elderberry. Maybe soon!
- Health Benefits Of Cranberries (But: You’d Better Watch Out)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Zucchini vs Okra – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing zucchini to okra, we picked the okra.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, okra has nearly 2x the protein and more than 3x the fiber (for about 2x the carbs).
In terms of vitamins, things are also quite one-sided; zucchini has a little more vitamin B2, while okra has a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline.
Nor does the mineral situation make any compelling counterargument; zucchini is higher only in sodium, while okra has a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium*, selenium, and zinc.
*Actually it’s only a little more potassium. But the rest are with big margins of difference.
Both of these on-the-cusp-of-being-pungent vegetables have beneficial antioxidant polyphenols (especially various forms of quercetin), but okra has more.
In short: enjoy both, of course, but there’s a clear winner here and it’s okra.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy Bitter/Astringent/Pungent Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Knitting helps Tom Daley switch off. Its mental health benefits are not just for Olympians
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Olympian Tom Daley is the most decorated diver in Britain’s history. He is also an avid knitter. At the Paris 2024 Olympics Daley added a fifth medal to his collection – and caught the world’s attention knitting a bright blue “Paris 24” jumper while travelling to the games and in the stands.
At the Tokyo Olympics, where Daley was first spotted knitting, he explained its positive impact on his mental health.
It just turned into my mindfulness, my meditation, my calm and my way to escape the stresses of everyday life and, in particular, going to an Olympics.
The mental health benefits of knitting are well established. So why is someone famous like Daley knitting in public still so surprising?
Africa Voice/Shutterstock Knitting is gendered
Knitting is usually associated with women – especially older women – as a hobby done at home. In a large international survey of knitting, 99% of respondents identified as female.
But the history of yarn crafts and gender is more tangled. In Europe in the middle ages, knitting guilds were exclusive and reserved for men. They were part of a respected Europe-wide trade addressing a demand for knitted products that could not be satisfied by domestic workers alone.
The industrial revolution made the production of clothed goods cheaper and faster than hand-knitting. Knitting and other needle crafts became a leisure activity for women, done in the private sphere of the home.
World Wars I and II turned the spotlight back on knitting as a “patriotic duty”, but it was still largely taken up by women.
During COVID lockdowns, knitting saw another resurgence. But knitting still most often makes headlines when men – especially famous men like Daley or actor Ryan Gosling – do it.
Men who knit are often seen as subverting the stereotype it’s an activity for older women.
Knitting the stress away
Knitting can produce a sense of pride and accomplishment. But for an elite sportsperson like Daley – whose accomplishments already include four gold medals and one silver – its benefits lie elsewhere.
Olympics-level sport relies on perfect scores and world records. When it comes to knitting, many of the mental health benefits are associated with the process, rather than the end result.
Daley says knitting is the “one thing” that allows him to switch off completely, describing it as “my therapy”. https://www.youtube.com/embed/6wwXGOki–c?wmode=transparent&start=0
The Olympian says he could
knit for hours on end, honestly. There’s something that’s so satisfying to me about just having that rhythm and that little “click-clack” of the knitting needles. There is not a day that goes by where I don’t knit.
Knitting can create a “flow” state through rhythmic, repetitive movements of the yarn and needle. Flow offers us a balance between challenge, accessibility and a sense of control.
It’s been shown to have benefits relieving stress in high-pressure jobs beyond elite sport. Among surgeons, knitting has been found to improve wellbeing as well as manual dexterity, crucial to their role.
For other health professionals – including oncology nurses and mental health workers – knitting has helped to reduce “compassion fatigue” and burnout. Participants described the soothing noise of their knitting needles. They developed and strengthened team bonds through collective knitting practices. https://www.youtube.com/embed/dTTJjD_q2Ik?wmode=transparent&start=0 A Swiss psychiatrist says for those with trauma, knitting yarn can be like “knitting the two halves” of the brain “back together”.
Another study showed knitting in primary school may boost children’s executive function. That includes the ability to pay attention, remember relevant details and block out distractions.
As a regular creative practice, it has also been used in the treatment of grief, depression and subduing intrusive thoughts, as well countering chronic pain and cognitive decline.
Knitting is a community
The evidence for the benefits of knitting is often based on self-reporting. These studies tend to produce consistent results and involve large population samples.
This may point to another benefit of knitting: its social aspect.
Knitting and other yarn crafts can be done alone, and usually require simple materials. But they also provide a chance to socialise by bringing people together around a common interest, which can help reduce loneliness.
The free needle craft database and social network Ravelry contains more than one million patterns, contributed by users. “Yarn bombing” projects aim to engage the community and beautify public places by covering objects such as benches and stop signs with wool.
The interest in Daley’s knitting online videos have formed a community of their own.
In them he shows the process of making the jumper, not just the finished product. That includes where he “went wrong” and had to unwind his work.
His pride in the finished product – a little bit wonky, but “made with love” – can be a refreshing antidote to the flawless achievements often on display at the Olympics.
Michelle O’Shea, Senior Lecturer, School of Business, Western Sydney University and Gabrielle Weidemann, Associate Professor in Psychological Science, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: