What Too Much Exercise Does To Your Body And Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Get more exercise” is a common rallying-cry for good health, but it is possible to overdo it. And, this is not just a matter of extreme cases of “exercise addiction”, but even going much above certain limits can already result in sabotaging one’s healthy gains. But how, and where does the line get drawn?
Too Much Of A Good Thing
The famous 150 minutes per week of moderate exercise (or 75 minutes of intense exercise) is an oft-touted figure. This video, on the other hand, springs for 5 hours of moderate exercise or 2.5 hours intense exercise as a good guideline.
We’re advised that going over those guidelines doesn’t necessarily increase health benefits, and on the contrary, may reduce or even reverse them. For example, we are told…
- Light to moderate running reduces the risk of death, but running intensely more than 3 times a week can negate these benefits.
- Extreme endurance exercises, like ultra-marathons, may cause heart damage, heart rhythm disorders, and artery enlargement.
- Women who exercise strenuously every day have a higher risk of heart attacks and strokes compared to those who exercise moderately.
- Excessive exercise in women can lead to the “female athlete triad” (loss of menstruation, osteoporosis, and eating disorders).
- In men, intense exercise can lower libido due to fatigue and reduced testosterone levels.
- Both men and women are at increased risk of overuse injuries (e.g., tendinitis, stress fractures) and impaired immunity from excessive exercise.
- There is a 72-hour window of impaired immunity after intense exercise, increasing the risk of infections.
Exercise addiction is rare, though, with this video citing “around 1 million people in the US suffer from exercise addiction”.
For more on finding the right balance, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

The Link Between Introversion & Sensory Processing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve talked before about how to beat loneliness and isolation, and how that’s important for all of us, including those of us on the less social end of the scale.
However, while we all need at least the option of social contact in order to be at our best, there’s a large portion of the population who also need to be able to retreat to somewhere quiet to recover from too much social goings-on.
Clinically speaking, this sometimes gets called introversion, or at least a negative score for extroversion on the “Big Five Inventory”, the only personality-typing system that actually gets used in science. Today we’re going to be focusing on a term that typically gets applied to those generally considered introverts:
The “highly sensitive person”
This makes it sound like a very rare snowflake condition, when in fact the diagnostic criteria yield a population bell curve of 30:40:30, whereupon 30% are in the band of “high sensitivity”, 40% “normal sensitivity” and the remaining 30% “low sensitivity”.
You may note that “high” and “low” together outnumber “normal”, but statistics is like that. It is interesting to note, though, that this statistical spread renders it not a disorder, so much as simply a description.
You can read more about it here:
Sensory-processing sensitivity and its relation to introversion and emotionality
What it means in practical terms
Such a person will generally seek solitude more frequently during the day than others will, and it’s not because of misanthropy (at least, statistically speaking it’s not; can’t speak for individuals!), but rather, it’s about needing downtime after what has felt like too much sensory processing resulting:
If this need for solitude is not met (sometimes it’s simply not practicable), then it can lead to overwhelm.
Sidenote about overwhelm: pick your battles! No, pick fewer than that. Put some back. That’s still too many 😜
Back to seriousness: if you’re the sort of person to walk into a room and immediately do the Sherlock Holmes thing of noticing everything about everyone, who is doing what, what has changed about the room since last time you were there, etc… Then that’s great; it’s a sign of a sharp mind, but it’s also a lot of information to process and you’re probably going to need a little decompression afterwards:
This is the biological equivalent of needing to let an overworked computer or phone cool down after excessive high-intensity use of its CPU.
The same goes if you’re the sort of person who goes into “performance mode” when in company, is “the life and soul of the party” etc, and/or perhaps “the elegant hostess”, but needs to then collapse afterwards because it’s more of a role you play than your natural inclination.
Take care of your battery
To continue the technological metaphor from earlier, if you repeatedly overuse a device without allowing it cooldown periods, it will break down (and if it’s a certain generation of iPhone, it might explode).
Similarly, if you repeatedly overuse your own highly sensitive senses (such as being often in social environment where there’s a lot going on) without allowing yourself adequate cooldown periods, you will break down (or indeed, explode: not literally, but some people are prone to emotional outbursts after bottling things up).
None of this is good for the health, not in the short term and not in the long term, either:
With that in mind, take care to take care of yourself, meeting your actual needs instead of just those that get socially assumed.
Want to take the test?
Here’s a two-minute test (results available immediately right there on-screen; no need to give your email or anything) 😎
Want to know more?
We reviewed this book about playing to one’s strengths in the context of sensitivity, a while back, and highly recommend it:
Sensitive – by Jenn Granneman and Andre Sólo
Enjoy!
Share This Post

Kettlebell Sport & Fitness Basics – by Audrey Burgio
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Professional athlete & coach Audrey Burgio covers how to get a full-body workout that will make you stronger and more flexible (there are stretches here too, and many exercises are about strength and suppleness), as well as building stability and balance. In short, more robust and with better mobility.
Which is one of the best things about kettlebell training—unlike dumbbells and barbells, a kettlebell requires the kind of strength that one has to use when doing many routine tasks, from carrying the groceries to moving a big pan in the kitchen.
Because it is otherwise absolutely possible to look like Arnold Schwarzenegger in the gym, and then still pull a muscle moving something at home because the angle was awkward or somesuch!
However, making one’s body so robust does require training safely, and the clear instructions in this book will help the reader avoid injuries that might otherwise be incurred by just picking up some kettlebells and guessing.
Bottom line: if you’d like to get strong and supple from the comfort of your own home, this book can definitely lead the way!
Click here to check out Kettlebell Sport & Fitness Basics, and see the difference in your body!
Share This Post

Peripheral Neuropathy: How To Avoid It, Manage It, Treat It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Peripheral neuropathy (and what can be done about it)
Peripheral neuropathy is nerve damage, usually of the extremities. It can be caused by such things as:
- Diabetes
- Alcoholism
- Infection
- Injury
The manifestations can be different:
- In the case of diabetes, it’s also called diabetic neuropathy, and almost always affects the feet first.
- In the case of alcoholism, it is more generalized, but tends towards affecting the extremities first.
- In the case of infection, a lot depends on the nature of the infection and the body’s response.
- In the case of injury, it’ll naturally be the injured part, or a little “downstream” of the injured part.
- This could be the case of a single traumatic injury (e.g. hand got trapped in a slammed door)
This could be the case of a repetitive injury (carpal tunnel syndrome is a kind of peripheral neuropathy, and is usually caused by consistent misalignment of the carpal tunnel, the aperture through which a bundle of nerves make their way from the forearm to the hand)
Prevention is better than cure
If you already have peripheral neuropathy, don’t worry, we’ll get to that. But, if you can, prevention is better than cure. This means:
- Diabetes: if you can, avoid. This may seem like no-brainer advice, but it’s often something people don’t think about until hitting a pre-diabetic stage. Obviously, if you are Type 1 Diabetic, you don’t have this luxury. But in any case, whatever your current status, take care of your blood sugars as best you can, so that your blood can take care of you (and your nerves) in turn. You might want to check out our previous main feature about this:
- Alcoholism: obviously avoid, if you can. You might like this previous edition of 10almonds addressing this:
- Infection: this is so varied that one-liner advice is really just “try to look after your immune health”.
- We’ll do a main feature on this soon!
- Injury: obviously, try to be careful. But that goes for the more insidious version too! For example, if you spend a lot of time at your computer, consider an ergonomic mouse and keyboard.
- There are many kinds available, so read reviews, but here’s an example product on Amazon
Writer’s note: as you might guess, I spend a lot of time at my computer, and a lot of that time, writing. I additionally spend a lot of time reading. I also have assorted old injuries from my more exciting life long ago. Because of this, it’s been an investment in my health to have:
A standing desk
A vertical ergonomic mouse
An ergonomic split keyboard
A Kindle*
*Far lighter and more ergonomic than paper books. Don’t get me wrong, I’m writing to you from a room that also contains about a thousand paper books and I dearly love those too, but more often than not, I read on my e-reader for comfort and ease.
If you already have peripheral neuropathy
Most advice popular on the Internet is just about pain management, but what if we want to treat the cause rather than the symptom?
Let’s look at the things commonly suggested: try ice, try heat, try acupuncture, try spicy rubs (from brand names like Tiger Balm, to home-made chilli ointments), try meditation, try a warm bath, try massage.
And, all of these are good options; do you see what they have in common?
It’s about blood flow. And that’s why they can help even in the case of peripheral neuropathy that’s not painful (it can also manifest as numbness, and/or tingling sensations).
By getting the blood flowing nicely through the affected body part, the blood can nourish the nerves and help them function correctly. This is, in effect, the opposite of what the causes of peripheral neuropathy do.
But also don’t forget: rest
- Put your feet up (literally! But we’re talking horizontal here, not elevated past the height of your heart)
- Rest that weary wrist that has carpal tunnel syndrome (again, resting it flat, so your hand position is aligned with your forearm, so the nerves between are not kinked)
- Use a brace if necessary to help the affected part stay aligned correctly
- You can get made-for-purpose wrist and ankle braces—you can also get versions that are made for administering hot/cold therapy, too. That’s just an example product linked that we can recommend; by all means read reviews and choose for yourself, though. Try them and see what helps.
One more top tip
We did a feature not long back on lion’s mane mushroom, and it’s single most well-established, well-researched, well-evidenced, completely uncontested benefit is that it aids peripheral neurogenesis, that is to say, the regrowth and healing of the peripheral nervous system.
So you might want to check that out:
Share This Post
Related Posts

Water Water Everywhere, But Which Is Best To Drink?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Well Well Well…

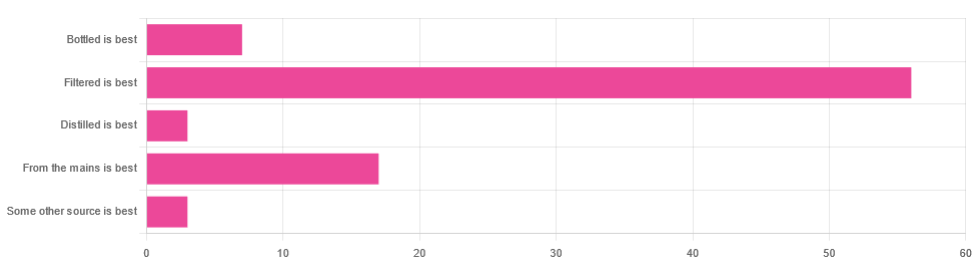
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your (health-related) opinion on drinking water—with the understanding that this may vary from place to place. We got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 65% said “Filtered is best”
- About 20% said “From the mains is best”
- About 8% said “Bottled is best”
- About 3% said “Distilled is best”
- About 3% said “Some other source is best”
Of those who said “some other source is best”, one clarified that their preferred source was well water.
So what does the science say?
Fluoridated water is bad for you: True or False?
False, assuming a normal level of consumption. Rather than take up more space today though, we’ll link to what we previously wrote on this topic:
You may be wondering: but what if my level of consumption is higher than normal?
Let’s quickly look at some stats:
- The maximum permitted safety level varies from place to place, but is (for example) 2mg/l in the US, 1.5mg/l in Canada & the UK.
- The minimum recommended amount also varies from place to place, but is (for example) 0.7mg/l in Canada and the US, and 1mg/l in the UK.
It doesn’t take grabbing a calculator to realize that if you drink twice as much water as someone else, then depending on where you are, water fluoridated to the minimum may give you more than the recommended maximum.
However… Those safety margins are set so much lower than the actual toxicity levels of fluoride, that it doesn’t make a difference.
For example: your writer here takes a medication that has the side effect of causing dryness of the mouth, and consequently she drinks at least 3l of water per day in a climate that could not be described as hot (except perhaps for about 2 weeks of the year). She weighs 72kg (that’s about 158 pounds), and the toxicity of fluoride (for ill symptoms, not death) is 0.2mg/kg. So, she’d need 14.4mg of fluoride, which even if the water fluoridation here were 2mg/l (it’s not; it’s lower here, but let’s go with the highest figure to make a point), would require drinking more than 7l of water faster than the body can process it.
For more about the numbers, check out:
Acute Fluoride Poisoning from a Public Water System
Bottled water is the best: True or False?
False, if we consider “best” to be “healthiest”, which in turn we consider to be “most nutrients, with highest safety”.
Bottled water generally does have higher levels of minerals than most local mains supply water does. That’s good!
But you know what else is generally has? Microplastics and nanoplastics. That’s bad!
We don’t like to be alarmist in tone; it’s not what we’re about here, but the stats on bottled water are simply not good; see:
We Are Such Stuff As Bottles Are Made Of
You may be wondering: “but what about bottled water that comes in glass bottles?”
Indeed, water that comes in glass bottles can be expected to have lower levels of plastic than water that comes in plastic bottles, for obvious reasons.
However, we invite you to consider how likely you believe it to be that the water wasn’t stored in plastic while being processed, shipped and stored, before being portioned into its final store-ready glass bottles for end-consumer use.
Distilled water is the best: True or False?
False, generally, with caveats:
Distilled water is surely the safest water anywhere, because you know that you’ve removed any nasties.
However, it’s also devoid of nutrients, because you also removed any minerals it contained. Indeed, if you use a still, you’ll be accustomed to the build-up of these minerals (generally simplified and referenced as “limescale”, but it’s a whole collection of minerals).
Furthermore, that loss of nutrients can be more than just a “something good is missing”, because having removed certain ions, that water could now potentially strip minerals from your teeth. In practice, however, you’d probably have to swill it excessively to cause this damage.
Nevertheless, if you have the misfortune of living somewhere like Flint, Michigan, then a water still may be a fair necessity of life. In other places, it can simply be useful to have in case of emergency, of course.
Here’s an example product on Amazon if you’d like to invest in a water still for such cases.
PS: distilled water is also tasteless, and is generally considered bad, tastewise, for making tea and coffee. So we really don’t recommend distilling your water unless you have a good reason to do so.
Filtered water is the best: True or False?
True for most people in most places.
Let’s put it this way: it can’t logically be worse than whatever source of water you put into it…
Provided you change the filter regularly, of course.
Otherwise, after overusing a filter, at best it won’t be working, and at worst it’ll be adding in bacteria that have multiplied in the filter over however long you left it there.
You may be wondering: can water filters remove microplastics, and can they remove minerals?
The answer in both cases is: sometimes.
- For microplastics it depends on the filter size and the microplastic size (see our previous article for details on that).
- For minerals, it depends on the filter type. Check out:
The H2O Chronicles | 5 Water Filters That Remove Minerals
One other thing to think about: while most water filtration jugs are made of PFAS-free BPA-free plastics for obvious reasons, for greater peace of mind, you might consider investing in a glass filtration jug, like this one ← this is just one example product on Amazon; by all means shop around and find one you like
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

The Fascinating Truth About Aspartame, Cancer, & Neurotoxicity
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is Aspartame’s Reputation Well-Deserved?

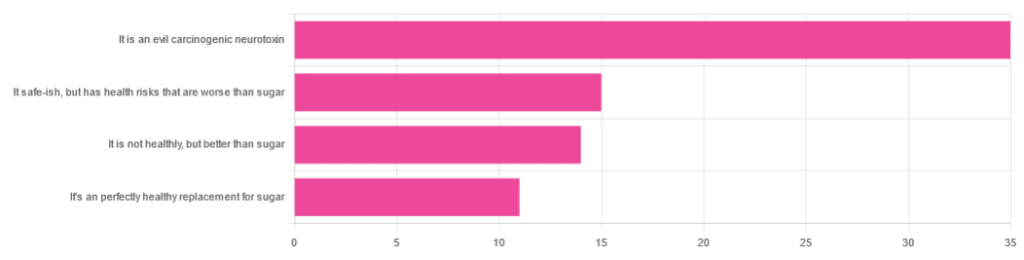
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your health-related opinions on aspartame, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 47% said “It is an evil carcinogenic neurotoxin”
- 20% said “It is safe-ish, but has health risks that are worse than sugar”
- About 19% said “It is not healthy, but better than sugar”
- About 15% said “It’s a perfectly healthy replacement for sugar”
But what does the science say?
Aspartame is carcinogenic: True or False?
False, assuming consuming it in moderation. In excess, almost anything can cause cancer (oxygen is a fine example). But for all meaningful purposes, aspartame does not appear to be carcinogenic. For example,
❝The results of these studies showed no evidence that these sweeteners cause cancer or other harms in people.❞
~ NIH | National Cancer Institute
Source: Artificial Sweeteners and Cancer
Plenty of studies and reviews have also confirmed this; here are some examples:
- Evaluation of aspartame cancer epidemiology studies based on quality appraisal criteria
- Aspartame, low-calorie sweeteners and disease: Regulatory safety and epidemiological issues
- Aspartame: A review of genotoxicity data
Why then do so many people believe it causes cancer, despite all the evidence against it?
Well, there was a small study involving giving megadoses to rats, which did increase their cancer risk. So of course, the popular press took that and ran with it.
But those results have not been achieved outside of rats, and human studies great and small have all been overwhelmingly conclusive that moderate consumption of aspartame has no effect on cancer risk.
Aspartame is a neurotoxin: True or False?
False, again assuming moderate consumption. If you’re a rat being injected with a megadose, your experience may vary. But a human enjoying a diet soda, the aspartame isn’t the part that’s doing you harm, so far as we know.
For example, the European Food Safety Agency’s scientific review panel concluded:
❝there is still no substantive evidence that aspartame can induce such effects❞
~ Dr. Atkin et al (it was a pan-European team of 21 experts in the field)
Source: Report on the Meeting on Aspartame with National Experts
See also,
❝The data from the extensive investigations into the possibility of neurotoxic effects of aspartame, in general, do not support the hypothesis that aspartame in the human diet will affect nervous system function, learning or behavior.
The weight of existing evidence is that aspartame is safe at current levels of consumption as a nonnutritive sweetener.❞
and
❝The safety testing of aspartame has gone well beyond that required to evaluate the safety of a food additive.
When all the research on aspartame, including evaluations in both the premarketing and postmarketing periods, is examined as a whole, it is clear that aspartame is safe, and there are no unresolved questions regarding its safety under conditions of intended use.❞
Source: Regulatory Toxicology & Pharmacology | Aspartame: Review of Safety
Why then do many people believe it is a neurotoxin? This one can be traced back to a chain letter hoax from about 26 years ago; you can read it here, but please be aware it is an entirely debunked hoax:
Urban Legends | Aspartame Hoax
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Breadfruit vs Custard Apple – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing breadfruit to custard apple, we picked the breadfruit.
Why?
Today in “fruits pretending to be less healthy things than they are”, both are great, but one of these fruits just edges out the other in all categories. This is quite simple today:
In terms of macros, being fruits they’re both fairly high in carbs and fiber, however the carbs are close to equal and breadfruit has nearly 2x the fiber.
This also means that breadfruit has the lower glycemic index, but they’re both medium-low GI foods with a low insulin index.
When it comes to vitamins, breadfruit has more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, and C, while custard apple has more of vitamins A, B2, and B6. So, a 4:3 win for breadfruit.
In the category of minerals, breadfruit has more copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while custard apple has more calcium and iron.
In short, enjoy both, but if you’re going just for one, breadfruit is the healthiest.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: