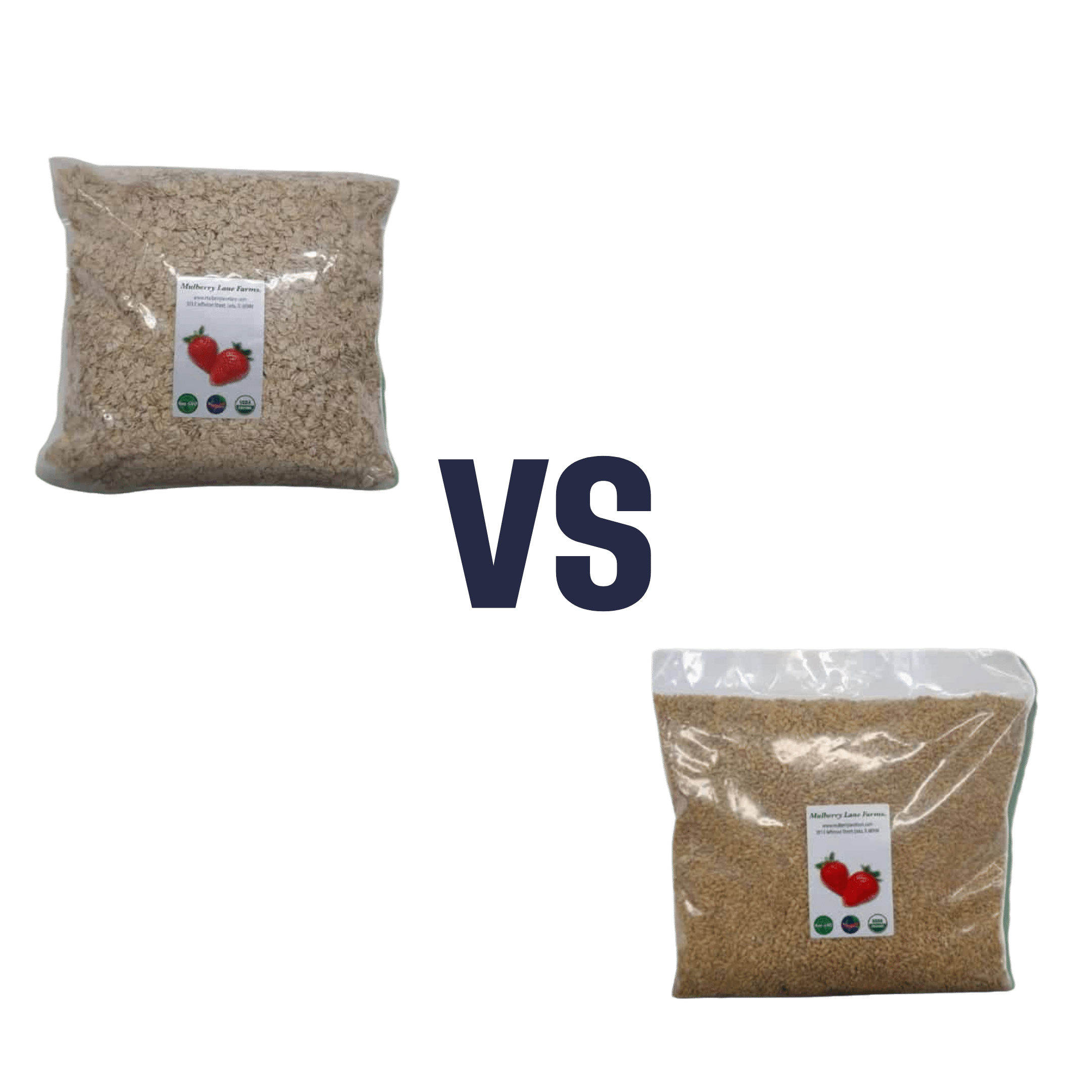
Oats vs Pearl Barley – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing oats to pearl barley, we picked the oats.
Why?
In terms of macronutrients first, pearl barley has about three times the carbs for only the same amount of protein and fiber—if it had been regular barley rather than pearl parley, it’d have about twice the fiber, but pearl barley has had the fibrous husk removed.
Vitamins really set the two part, though: oats have a lot more (60x more) vitamin A, and notably more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and B9, as well as 6x more vitamin E. In contrast, pearl barley has a little more vitamin K and choline. An easy win for oats in this section.
In the category of minerals, oats have over 6x more calcium, 3x more iron, and a little more magnesium, manganese, and phosphorus. Meanwhile, pearl barley boats a little more copper, potassium, selenium, and zinc. So, a more moderate win for oats in this category.
They are both very good for the gut, unless you have a gluten intolerance/allergy, in which case, oats are the only answer here since pearl barley, as per barley in general, has gluten as its main protein (oats, meanwhile, do not contain gluten, unless by cross-contamination).
Adding up all the sections, this one’s a clear win for oats.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Gluten: What’s The Truth?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

10 Ways To Naturally Boost Dopamine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dopamine is the “reward” hormone, and is responsible for motivation, as well as various oft-forgotten functions (such as spatial skills, motor functions, task processing, planning, and language). Sometimes, our relationship with dopamine isn’t what it could be, so here’s how to fix that:
Let’s get hormone-hacking…
Here are the 10 ways:
- The seesaw effect: reduce overstimulation by taking tolerance breaks from high-dopamine activities that aren’t particularly useful (like social media or phone games), allowing for natural enjoyment of daily activities that you’d normally find enjoyable. Think: if you died and negotiated to be sent back to life on the condition you’d appreciate it properly this time, what things would you then spend your time doing? It’s probably not Kingdom Crush Saga Farm 2, is it?
- Conscious state meditation: practise conscious state meditation, focusing inward to reduce anxiety and release dopamine. Even a few minutes a day can significantly enhance dopamine levels.
- Hack your REM cycles: optimize sleep, especially REM cycles, which produce the most dopamine. Aim to wake up after your final REM cycle to feel energized and happy.
- The runner’s high: engage in regular exercise, which boosts dopamine through physical exertion and can lead to feelings of relaxation and euphoria, often known as the “runner’s high.”
- Mood-enhancing music: listen to music that makes you feel good. Favorite songs can stimulate dopamine production, improving your mood and well-being.
- Bright light therapy: spend time in natural sunlight to stimulate dopamine production and elevate your mood, countering the negative effects of extended indoor time. If natural sunlight is not very available where you are (e.g. this writer who lives next to an ancient bog surrounded by fog and the days are getting short, at time of writing), then artificial daylight lamps are respectable supplement—but just that, a supplement, not a replacement. Despite how it looks/feels, natural sunlight (especially in the morning, to cue the circadian rhythm to do its thing) is beneficial even through cloud cover.
- Relieve stress for good: actively reduce stress, as it inhibits dopamine. Simplify daily routines and eliminate stressors to naturally boost dopamine and feel more relaxed. Of course, you cannot remove all stress from your life, so get good at managing the stress created by the stressors that do remain.
- Tap into your flow state: enter a “flow state” by focusing deeply on an engaging task, which can elevate dopamine levels and boost motivation and happiness.
- The hormesis effect: embrace mild physical challenges, like cold showers. The temporary discomfort will paradoxically increase dopamine (it’s the body’s way of saying “congratulations, you survived the hard thing, here’s a little treat, so that you’ll be motivated to survive the next hard thing, too”)
- Activate your inner artist: engage in creative activities that you find fun. The process of creating boosts dopamine and provides motivation, enhancing mood and enjoyment in life.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Rebalancing Dopamine (Without “Dopamine Fasting”)
Take care!
Share This Post

Avocado vs Olives – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing avocado to olives, we picked the avocado.
Why?
Both are certainly great! And when it comes to their respective oils, olive oil wins out as it retains many micronutrients that avocado oil loses. But, in their whole form, avocado beats olive:
In terms of macros, avocado has more protein, carbs, fiber, and (healthy) fats. Simply, it’s more nationally-dense than the already nutritionally-dense food that is olives.
When it comes to vitamins, olives are great but avocados really shine; avocado has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7 B9, C, E, K, and choline, while olives boast only more vitamin A.
In the category of minerals, things are closer to even; avocado has more magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while olives have a lot more calcium, copper, iron, and selenium. Still, a marginal victory for avocado here.
In short, this is another case of one very healthy food looking bad by standing next to an even better one, so by all means enjoy both—if you’re going to pick one though, avocado is the more nutritionally dense.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier? ← when made into oils, olive oil wins, but avocado oil is still a good option too
Take care!
Share This Post

The Things You Can See Only When You Slow Down – by Haemin Sunim
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this one’s not about: noticing raindrops on roses and whiskers on kittens.
That’s great too, though. This writer particularly loves the cute faces of baby jumping spiders. Sounds unlikely, but have you seen them?
What it’s rather about: noticing what’s between your ears, and paying closer attention to that, so that we can go about our business more mindfully.
This is, fundamentally, a book about living a happier life, whatever the potentially crazy circumstances of the hustle and bustle around us. Not because of disinterest; quite the opposite. Sunim bids us ask the question of ourselves, what are we really doing and why?
The writing style is very light and easy, while being heavy-hitting in terms of the ideas it brings. Little wonder that this one is so highly-rated on Amazon, with more than 5,000 ratings.
Bottom line: if sometimes you feel like the world is a little hectic and all that is around you is out of your control, this is a great book for you.
Share This Post
Related Posts

The Brain-Skin Doctor
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Of Brains And Breakouts
This is Dr. Claudia Aguirre. She’s a molecular neuroscientist, and today she’s going to be educating us about skin.
What? Why?
When we say “neuroscience”, we generally think of the brain. And indeed, that’s a very important part of it.
We might think about eyes, which are basically an extension of the brain.
We don’t usually think about skin, which (just like our eyes) is constantly feeding us a lot of information about our surroundings, via a little under three million nerve endings. Guess where the other ends of those nerves lead!
There’s a constant two-way communication going on between our brain and our skin.
What does she want us to know?
Psychodermatology
The brain and the skin talk to each other, and maladies of one can impact the other:
- Directly, e.g. stress prompting skin breakouts (actually this is a several-step process physiologically, but for the sake of brevity we’ll call this direct)
- Indirectly, e.g. nervous disorders that result in people scratching or picking at their skin, which prompts a whole vicious cycle of one thing making the other worse
Read more: Psychodermatology: The Brain-Skin Connection
To address both kinds of problems, clearly something beyond moisturizer is needed!
Mindfulness (meditation and beyond)
Mindfulness is a well-evidenced healthful practice for many reasons, and Dr. Aguirra argues the case for it being good for our skin too.
As she points out,
❝Cultural stress and anxiety can trigger or aggravate many skin conditions—from acne to eczema to herpes, psoriasis, and rosacea.
Conversely, a disfiguring skin condition can trigger stress, anxiety, depression, and even suicide.
Chronic, generalized anxiety can create chronic inflammation and exacerbate inflammatory skin conditions, such as those I mentioned previously.
Chronic stress can result in chronic anxiety, hypervigilance, poor sleep, and a whole cascade of effects resulting in a constant breakdown of tissues and organs, including the skin.❞
So, she recommends mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), for the above reasons, along with others!
Read more: Mind Matters
How to do it: No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
And as for “and beyond?”
Do you remember in the beginning of the pandemic, when people were briefly much more consciously trying to avoid touching their faces so much? That, too, is mindfulness. It may have been a stressed and anxious mindfulness for many*, but mindfulness nonetheless.
*which is why “mindfulness-based stress reduction” is not a redundant tautology repeated more than once unnecessarily, one time after another 😉
So: do try to keep aware of what you are doing to your skin, and so far as is reasonably practicable, only do the things that are good for it!
The skin as an endocrine organ
Nerves are not the only messengers in the body; hormones do a lot of our body’s internal communication too. And not just the ones everyone remembers are hormones (e.g. estrogen, testosterone, although yes, they do both have a big impact on skin too), but also many more, including some made in the skin itself!
Dr. Aguirra gives us a rundown of common conditions, the hormones behind them, and what we can do if we don’t want them:
Read more: Rethinking The Skin As An Endocrine Organ
Take-away advice:
For healthy skin, we need to do more than just hydrate, get good sleep, have good nutrition, and get a little sun (but not too much).
- We should also practice mindfulness-based stress reduction, and seek help for more serious mental health issues.
- We should also remember the part our hormones play in our skin, and not just the obvious ones.
Did you know that vitamin D is also a hormone, by the way? It’s not the only hormone at play in your skin by a long way, but it is an important one:
Society for Endocrinology | Vitamin D
Want to know more?
You might like this interview with Dr. Aguirre:
The Brain in Our Skin: An Interview with Dr. Claudia Aguirre
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Is white rice bad for me? Can I make it lower GI or healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Rice is a culinary staple in Australia and around the world.
It might seem like a given that brown rice is healthier than white and official public health resources often recommend brown rice instead of white as a “healthy swap”.
But Australians definitely prefer white rice over brown. So, what’s the difference, and what do we need to know when choosing rice?

Dragne Marius/Unsplash What makes rice white or brown?
Rice “grains” are technically seeds. A complete, whole rice seed is called a “paddy”, which has multiple parts:
- the “hull” is the hard outer layer which protects the seed
- the “bran”, which is a softer protective layer containing the seed coat
- the “germ” or the embryo, which is the part of the seed that would develop into a new plant if was germinated
- the “endosperm”, which makes up most of the seed and is essentially the store of nutrients that feeds the developing plant as a seed grows into a plant.
Rice needs to be processed for humans to eat it.
Along with cleaning and drying, the hard hulls are removed since we can’t digest them. This is how brown rice is made, with the other three parts of the rice remaining intact. This means brown rice is regarded as a “wholegrain”.
White rice, however, is a “refined” grain, as it is further polished to remove the bran and germ, leaving just the endosperm. This is a mechanical and not a chemical process.
What’s the difference, nutritionally?
Keeping the bran and the germ means brown rice has more magnesium, phosphorus, potassium B vitamins (niacin, folate, riboflavin and pyridoxine), iron, zinc and fibre.
The germ and the bran also contain more bioactives (compounds in foods that aren’t essential nutrients but have health benefits), like oryzanols and phenolic compounds which have antioxidant effects.

Brown rice is cleaned and dried and the hard hulls are removed. Sung Min/Shutterstock But that doesn’t mean white rice is just empty calories. It still contains vitamins, minerals and some fibre, and is low in fat and salt, and is naturally gluten-free.
White and brown rice actually have similar amounts of calories (or kilojoules) and total carbohydrates.
There are studies that show eating more white rice is linked to a higher risk of type 2 diabetes. But it is difficult to know if this is down to the rice itself, or other related factors such as socioeconomic variables or other dietary patterns.
What about the glycaemic index?
The higher fibre means brown rice has a lower glycaemic index (GI), meaning it raises blood sugar levels more slowly. But this is highly variable between different rices within the white and brown categories.
The GI system uses low (less than 55), medium (55–70) and high (above 70) categories. Brown rices fall into the low and medium categories. White rices fall in the medium and high.
There are specific low-GI types available for both white and brown types. You can also lower the GI of rice by heating and then cooling it. This process converts some of the “available carbohydrates” into “resistant starch”, which then functions like dietary fibre.
Are there any benefits to white rice?
The taste and textural qualities of white and brown rices differ. White rice tends to have a softer texture and more mild or neutral flavour. Brown rice has a chewier texture and nuttier flavour.
So, while you can technically substitute brown rice into most recipes, the experience will be different. Or other ingredients may need to be added or changed to create the desired texture.
Removing more of the outer layers may also reduce the levels of contaminants such as pesticides.
We don’t just eat rice

You’ll likely have vegetables and protein with your rice. Chay_Tee/Shutterstock Comparing white and brown rice seems like an easy way to boost nutritional value. But just because one food (brown rice) is more nutrient-dense doesn’t make the other food (white rice) “bad”.
Ultimately, it’s not often that we eat just rice, so we don’t need the rice we choose to be the perfect one. Rice is typically the staple base of a more complex dish. So, it’s probably more important to think about what we eat with rice.
Adding vegetables and lean proteins to rice-based dishes can easily add the micronutrients, bioactives and fibre that white rice is comparatively lacking, and this can likely do more to contribute to diet quality than eating brown rice instead.
Emma Beckett, Adjunct Senior Lecturer, Nutrition, Dietetics & Food Innovation – School of Health Sciences, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Bacopa Monnieri: A Well-Evidenced Cognitive Enhancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bacopa monnieri: a powerful nootropic
Bacopa monnieri is one of those “from traditional use” herbs that has made its way into science.
It’s been used for at least 1,400 years in Ayurvedic medicine, for cognitive enhancement, against anxiety, and some disease-specific treatments.
See: Pharmacological attributes of Bacopa monnieri extract: current updates and clinical manifestation
What are its claimed health benefits?
Bacopa monnieri is these days mostly sold and bought as a nootropic, and that’s what the science supports best.
Nootropic benefits claimed:
- Improves attention, learning, and memory
- Reduces depression, anxiety, and stress
- Reduces restlessness and impulsivity
Other benefits claimed:
- Antioxidant properties
- Anti-inflammatory properties
- Anticancer properties
What does the science say?
Those last three, the antioxidant / anti-inflammatory / anticancer properties, when something has one of those qualities it often has all three, because there are overlapping systems at hand when it comes to oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular damage.
Bacopa monnieri is no exception to this “rule of thumb”, and/but studies to support these benefits have mostly been animal studies and/or in vitro studies (i.e., cell cultures in a petri dish in lab conditions).
For example:
- Inhibition of lipoxygenases and cyclooxygenase-2 enzymes by extracts isolated from Bacopa monnieri
- Assessing the anti-inflammatory effects of Bacopa-derived bioactive compounds using network pharmacology and in vitro studies
- The evolving roles of Bacopa monnieri as potential anticancer agent: a review
In the category of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in the brain, sometimes results differ depending on the test population, for example:
- Neuroprotective effects of Bacopa monnieri in experimental model of dementia (it worked for rats)
- Use of Bacopa monnieri in the treatment of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review of randomized controlled trials (it didn’t work for humans)
Anything more promising than that?
Yes! The nootropic effects have been much better-studied in humans, and with much better results.
For example, in this 12-week study in healthy adults, taking 300mg/day significantly improved visual information processing, learning, and memory (tested against placebo):
The chronic effects of an extract of Bacopa monnieri on cognitive function in healthy human subjects
Another 12-week study showed older adults enjoyed the same cognitive enhancement benefits as their younger peers:
Children taking 225mg/day, meanwhile, saw a significant reduction in ADHD symptoms, such as restlessness and impulsivity:
And as for the mood benefits, 300mg/day significantly reduced anxiety and depression in elderly adults:
In summary
Bacopa monnieri, taken at 300mg/day (studies ranged from 225mg/day to 600mg/day, but 300mg is most common) has well-evidenced cognitive benefits, including:
- Improved attention, learning, and memory
- Reduced depression, anxiety, and stress
- Reduced restlessness and impulsivity
It may also have other benefits, including against oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer, but the research is thinner and/or not as conclusive for those.
Where to get it
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience, here is an example product on Amazon.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: