Walking can prevent low back pain, a new study shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
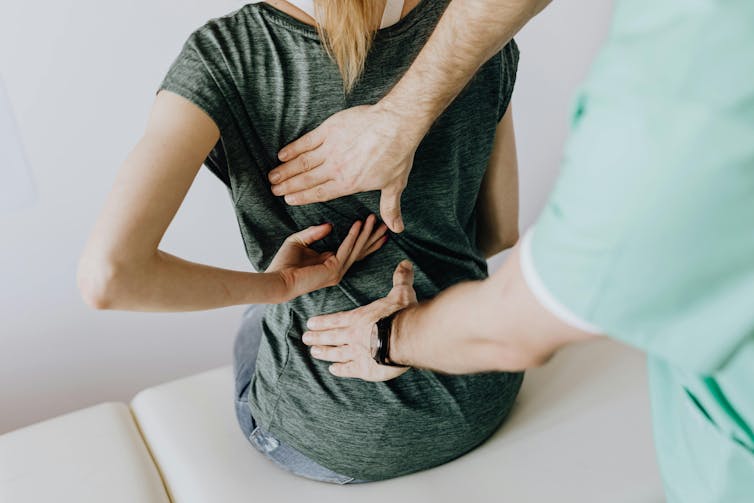
Do you suffer from low back pain that recurs regularly? If you do, you’re not alone. Roughly 70% of people who recover from an episode of low back pain will experience a new episode in the following year.
The recurrent nature of low back pain is a major contributor to the enormous burden low back pain places on individuals and the health-care system.
In our new study, published today in The Lancet, we found that a program combining walking and education can effectively reduce the recurrence of low back pain.

The WalkBack trial
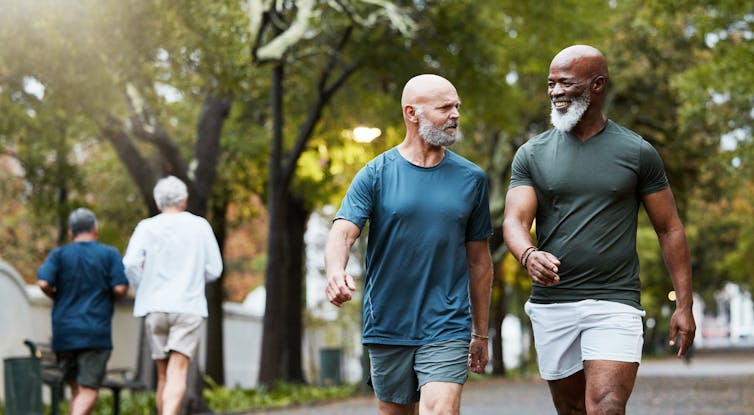
We randomly assigned 701 adults who had recently recovered from an episode of low back pain to receive an individualised walking program and education (intervention), or to a no treatment group (control).
Participants in the intervention group were guided by physiotherapists across six sessions, over a six-month period. In the first, third and fifth sessions, the physiotherapist helped each participant to develop a personalised and progressive walking program that was realistic and tailored to their specific needs and preferences.
The remaining sessions were short check-ins (typically less than 15 minutes) to monitor progress and troubleshoot any potential barriers to engagement with the walking program. Due to the COVID pandemic, most participants received the entire intervention via telehealth, using video consultations and phone calls.

The program was designed to be manageable, with a target of five walks per week of roughly 30 minutes daily by the end of the six-month program. Participants were also encouraged to continue walking independently after the program.
Importantly, the walking program was combined with education provided by the physiotherapists during the six sessions. This education aimed to give people a better understanding of pain, reduce fear associated with exercise and movement, and give people the confidence to self-manage any minor recurrences if they occurred.
People in the control group received no preventative treatment or education. This reflects what typically occurs after people recover from an episode of low back pain and are discharged from care.
What the results showed
We monitored the participants monthly from the time they were enrolled in the study, for up to three years, to collect information about any new recurrences of low back pain they may have experienced. We also asked participants to report on any costs related to their back pain, including time off work and the use of health-care services.
The intervention reduced the risk of a recurrence of low back pain that limited daily activity by 28%, while the recurrence of low back pain leading participants to seek care from a health professional decreased by 43%.
Participants who received the intervention had a longer average period before they had a recurrence, with a median of 208 days pain-free, compared to 112 days in the control group.

Overall, we also found this intervention to be cost-effective. The biggest savings came from less work absenteeism and less health service use (such as physiotherapy and massage) among the intervention group.
This trial, like all studies, had some limitations to consider. Although we tried to recruit a wide sample, we found that most participants were female, aged between 43 and 66, and were generally well educated. This may limit the extent to which we can generalise our findings.
Also, in this trial, we used physiotherapists who were up-skilled in health coaching. So we don’t know whether the intervention would achieve the same impact if it were to be delivered by other clinicians.
Walking has multiple benefits
We’ve all heard the saying that “prevention is better than a cure” – and it’s true. But this approach has been largely neglected when it comes to low back pain. Almost all previous studies have focused on treating episodes of pain, not preventing future back pain.
A limited number of small studies have shown that exercise and education can help prevent low back pain. However, most of these studies focused on exercises that are not accessible to everyone due to factors such as high cost, complexity, and the need for supervision from health-care or fitness professionals.
On the other hand, walking is a free, accessible way to exercise, including for people in rural and remote areas with limited access to health care.
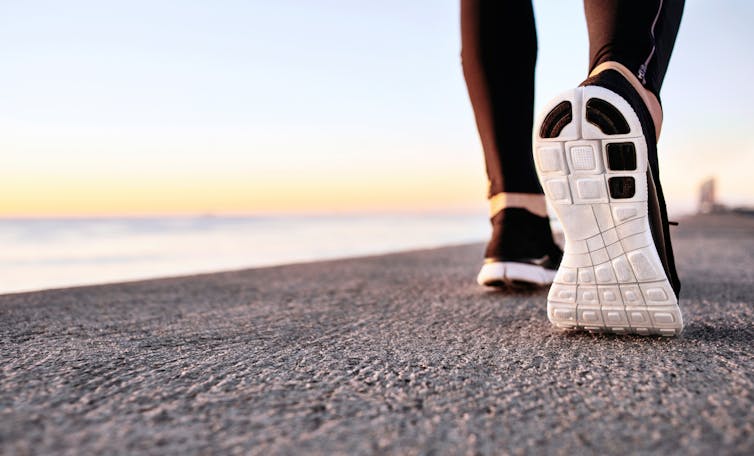

Walking also delivers many other health benefits, including better heart health, improved mood and sleep quality, and reduced risk of several chronic diseases.
While walking is not everyone’s favourite form of exercise, the intervention was well-received by most people in our study. Participants reported that the additional general health benefits contributed to their ongoing motivation to continue the walking program independently.
Why is walking helpful for low back pain?
We don’t know exactly why walking is effective for preventing back pain, but possible reasons could include the combination of gentle movements, loading and strengthening of the spinal structures and muscles. It also could be related to relaxation and stress relief, and the release of “feel-good” endorphins, which block pain signals between your body and brain – essentially turning down the dial on pain.
It’s possible that other accessible and low-cost forms of exercise, such as swimming, may also be effective in preventing back pain, but surprisingly, no studies have investigated this.
Preventing low back pain is not easy. But these findings give us hope that we are getting closer to a solution, one step at a time.
Tash Pocovi, Postdoctoral research fellow, Department of Health Sciences, Macquarie University; Christine Lin, Professor, Institute for Musculoskeletal Health, University of Sydney; Mark Hancock, Professor of Physiotherapy, Macquarie University; Petra Graham, Associate Professor, School of Mathematical and Physical Sciences, Macquarie University, and Simon French, Professor of Musculoskeletal Disorders, Macquarie University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

7-Minute Face Fitness For Lymphatic Drainage & Youthful Jawline
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Valeriia Veksler is a registered nurse with a background in cosmetic medicine. She’s been practicing for 7 years, and on the strength of that, is going to teach us how to give our face some love for 7 minutes:
The routine, step by step
Preparation: clean your face and apply your usual moisturizer. Breathe deeply: Inhale through the nose, exhale to release tension.
Neck massage: use fingertips in circular motion from the bottom of the neck to the hairline and back for 30 seconds. This helps promote blood flow to the face.
Sternocleidomastoid massage: use knuckles to massage in circles from the sternal area up to the jawline and down to the collarbone for 30 seconds. Keep posture straight, shoulders down, and relax muscles.
Collarbone pressure: apply and release pressure with fingertips above the collarbones for 30 seconds. This stimulates lymphatic flow and helps reduce puffiness.
Under-chin massage: use knuckles to massage side-to-side under the chin for 30 seconds. Relax the under-chin area and promote lymphatic drainage.
Jawline massage: with knuckles, massage from the chin towards the ears in circular motion for 30 seconds. Relax the jaw.
Nasolabial fold and nose massage: place index fingers near nostrils and move mouth in a “O” shape, then massage around the nostrils and up the nose for 30 seconds.
Smile line lift: press palms on the smile lines and slide hands up towards the temples for 30 seconds. This helps lift the face and sculpt cheekbones.
Under-eye massage: use index fingers in a hook shape, massaging under the eyes along the bone structure for 30 seconds. This promotes blood flow and lymphatic drainage.
Temple lift: use fingertips to lift the area near the left temple for 30 seconds, then assist with the opposite hand to lift further. Repeat on the other side. This reduces crow’s feet and lifts the corners of the eyes.
Forehead lift: place hands on the forehead, lock fingers, and gently elevate the skin upwards. Glide fingers towards the hairline for 30 seconds. This promotes blood flow and smooths the forehead.
Relax 11 Lines: place fingers at the center of the forehead, gently press into the tissue, and let them glide away from each other towards the eyebrows for 30 seconds.
Bonus:
- Ensure good posture throughout.
- Relax, stay mindful, and breathe deeply during the exercises.
- Feel the warmth and energy from improved circulation, after the routine.
For more on all of this plus a visual demonstration of everything, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Top 10 Foods That Promote Lymphatic Drainage and Lymph Flow
Take care!
Share This Post

The Food For Life Cookbook – by Dr. Tim Spector
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Dr. Spector’s “Food For Life”, and while that was more of an “explanatory science” book, this one takes that science (reiterating it more briefly this time, by way of introduction) and makes a cookbook of it.
The nutritional emphasis in these recipes is on two things: maximizing fiber, and maximizing plant diversity. The recipes are not all vegan or even vegetarian, but they are plant-centric, and if the reader is vegetarian/vegan, then substitutions are easy to make.
The recipes themselves are simple without being boring, and are easy to follow, with full-page photos to accompany them. The science parts are very clear, accessible, and pop-science in style.
Bottom line: if you’d like to incorporate more fiber and more plants into your diet without it being a burden, this book is great for that.
Click here to check out the Food For Life Cookbook, and get cooking for life!
Share This Post

Inheritance – by Dr. Sharon Moalem
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We know genes make a big difference to a lot about us, but how much? And, the genes we have, we’re stuck with, right?
Dr. Sharon Moalem shines a bright light into some of the often-shadowier nooks and crannies of our genetics, covering such topics as:
- How much can (and can’t) be predicted from our parents’ genes—even when it comes to genetic traits that both parents have, and Gregor Mendel himself would (incorrectly) think obvious
- How even something so seemingly simple and clear as genetic sex, very definitely isn’t
- How traumatic life events can cause epigenetic changes that will scar us for generations to come
- How we can use our genetic information to look after our health much better
- How our life choices can work with, or overcome, the hand we got dealt in terms of genes
The style of the book is conversational, down to how there’s a lot of “I” and “you” in here, and the casual style belies the heavy, sharp, up-to-date science contained within.
Bottom line: if you’d like insight into the weird and wonderful nuances of genetics as found in this real, messy, perfectly chaotic world, this book is an excellent choice.
Click here to check out Inheritance, and learn more about yours!
Share This Post
Related Posts

How often should you wash your sheets and towels?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Everyone seems to have a different opinion when it comes to how often towels and bed sheets should be washed. While many people might wonder whether days or weeks is best, in one survey from the United Kingdom, almost half of single men reported not washing their sheets for up to four months at a time.
It’s fairly clear that four months is too long to leave it, but what is the ideal frequency?
Bed linen and towels are quite different and so should be washed at different intervals. While every week or two will generally suffice for sheets, towels are best washed every few days.
Anyway, who doesn’t love the feeling of a fresh set of sheets or the smell of a newly laundered towel?
Why you should wash towels more often
When you dry yourself, you deposit thousands of skin cells and millions of microbes onto the towel. And because you use your towel to dry yourself after a shower or bath, your towel is regularly damp.
You also deposit a hefty amount of dead skin, microbes, sweat and oils onto your sheets every night. But unless you’re a prolific night sweater, your bedding doesn’t get wet after a night’s sleep.
Towels are also made of a thicker material than sheets and therefore tend to stay damp for longer.
So what is it about the dampness that causes a problem? Wet towels are a breeding ground for bacteria and moulds. Moulds especially love damp environments. Although mould won’t necessarily be visible (you would need significant growth to be able to see it) this can lead to an unpleasant smell.
As well as odours, exposure to these microbes in your towels and sheets can cause asthma, allergic skin irritations, or other skin infections.

People don’t always agree on how often to change the sheets.
http://rawpixel.com/ShutterstockSo what’s the ideal frequency?
For bedding, it really depends on factors such as whether you have a bath or shower just before going to bed, or if you fall into bed after a long, sweaty day and have your shower in the morning. You will need to wash your sheets more regularly in the latter case. As a rule of thumb, once a week or every two weeks should be fine.
Towels should ideally be washed more regularly – perhaps every few days – while your facecloth should be cleaned after every use. Because it gets completely wet, it will be wet for a longer time, and retain more skin cells and microbes.
Wash your towels at a high temperature (for example, 65°C) as that will kill many microbes. If you are conscious of saving energy, you can use a lower temperature and add a cup of vinegar to the wash. The vinegar will kill microbes and prevent bad smells from developing.
Clean your washing machine regularly and dry the fold in the rubber after every wash, as this is another place microbes like to grow.
Smelly towels
What if you regularly wash your towels, but they still smell bad? One of the reasons for this pong could be that you’ve left them in the washing machine too long after the wash. Especially if it was a warm wash cycle, the time they’re warm and damp will allow microbes to happily grow. Under lab conditions the number of these bacteria can double every 30 minutes.
It’s important to hang your towel out to dry after use and not to leave towels in the washing machine after the cycle has finished. If possible, hang your towels and bedding out in the sun. That will dry them quickly and thoroughly and will foster that lovely fresh, clean cotton smell. Using a dryer is a good alternative if the weather is bad, but outdoors in the sun is always better if possible.
Also, even if your towel is going to be washed, don’t throw a wet towel into the laundry basket, as the damp, dirty towel will be an ideal place for microbes to breed. By the time you get to doing your washing, the towel and the other laundry around it may have acquired a bad smell. And it can be difficult to get your towels smelling fresh again.

Towels should be washed more often than sheets.
New Africa/ShutterstockWhat about ‘self-cleaning’ sheets and towels?
Some companies sell “quick-dry” towels or “self-cleaning” towels and bedding. Quick-dry towels are made from synthetic materials that are weaved in a way to allow them to dry quickly. This would help prevent the growth of microbes and the bad smells that develop when towels are damp for long periods of time.
But the notion of self-cleaning products is more complicated. Most of these products contain nanosilver or copper, antibacterial metals that kill micro-organisms. The antibacterial compounds will stop the growth of bacteria and can be useful to limit smells and reduce the frequency with which you need to clean your sheets and towels.
However, they’re not going to remove dirt like oils, skin flakes and sweat. So as much as I would love the idea of sheets and towels that clean themselves, that’s not exactly what happens.
Also, excessive use of antimicrobials such as nanosilver can lead to microbes becoming resistant to them.

Rietie Venter, Associate professor, Clinical and Health Sciences, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

How a Friend’s Death Turned Colorado Teens Into Anti-Overdose Activists
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Gavinn McKinney loved Nike shoes, fireworks, and sushi. He was studying Potawatomi, one of the languages of his Native American heritage. He loved holding his niece and smelling her baby smell. On his 15th birthday, the Durango, Colorado, teen spent a cold December afternoon chopping wood to help neighbors who couldn’t afford to heat their homes.
McKinney almost made it to his 16th birthday. He died of fentanyl poisoning at a friend’s house in December 2021. His friends say it was the first time he tried hard drugs. The memorial service was so packed people had to stand outside the funeral home.
Now, his peers are trying to cement their friend’s legacy in state law. They recently testified to state lawmakers in support of a bill they helped write to ensure students can carry naloxone with them at all times without fear of discipline or confiscation. School districts tend to have strict medication policies. Without special permission, Colorado students can’t even carry their own emergency medications, such as an inhaler, and they are not allowed to share them with others.
“We realized we could actually make a change if we put our hearts to it,” said Niko Peterson, a senior at Animas High School in Durango and one of McKinney’s friends who helped write the bill. “Being proactive versus being reactive is going to be the best possible solution.”
Individual school districts or counties in California, Maryland, and elsewhere have rules expressly allowing high school students to carry naloxone. But Jon Woodruff, managing attorney at the Legislative Analysis and Public Policy Association, said he wasn’t aware of any statewide law such as the one Colorado is considering. Woodruff’s Washington, D.C.-based organization researches and drafts legislation on substance use.
Naloxone is an opioid antagonist that can halt an overdose. Available over the counter as a nasal spray, it is considered the fire extinguisher of the opioid epidemic, for use in an emergency, but just one tool in a prevention strategy. (People often refer to it as “Narcan,” one of the more recognizable brand names, similar to how tissues, regardless of brand, are often called “Kleenex.”)
The Biden administration last year backed an ad campaign encouraging young people to carry the emergency medication.
Most states’ naloxone access laws protect do-gooders, including youth, from liability if they accidentally harm someone while administering naloxone. But without school policies explicitly allowing it, the students’ ability to bring naloxone to class falls into a gray area.
Ryan Christoff said that in September 2022 fellow staff at Centaurus High School in Lafayette, Colorado, where he worked and which one of his daughters attended at the time, confiscated naloxone from one of her classmates.
“She didn’t have anything on her other than the Narcan, and they took it away from her,” said Christoff, who had provided the confiscated Narcan to that student and many others after his daughter nearly died from fentanyl poisoning. “We should want every student to carry it.”
Boulder Valley School District spokesperson Randy Barber said the incident “was a one-off and we’ve done some work since to make sure nurses are aware.” The district now encourages everyone to consider carrying naloxone, he said.
Community’s Devastation Turns to Action
In Durango, McKinney’s death hit the community hard. McKinney’s friends and family said he didn’t do hard drugs. The substance he was hooked on was Tapatío hot sauce — he even brought some in his pocket to a Rockies game.
After McKinney died, people started getting tattoos of the phrase he was known for, which was emblazoned on his favorite sweatshirt: “Love is the cure.” Even a few of his teachers got them. But it was classmates, along with their friends at another high school in town, who turned his loss into a political movement.
“We’re making things happen on behalf of him,” Peterson said.
The mortality rate has spiked in recent years, with more than 1,500 other children and teens in the U.S. dying of fentanyl poisoning the same year as McKinney. Most youth who die of overdoses have no known history of taking opioids, and many of them likely thought they were taking prescription opioids like OxyContin or Percocet — not the fake prescription pills that increasingly carry a lethal dose of fentanyl.
“Most likely the largest group of teens that are dying are really teens that are experimenting, as opposed to teens that have a long-standing opioid use disorder,” said Joseph Friedman, a substance use researcher at UCLA who would like to see schools provide accurate drug education about counterfeit pills, such as with Stanford’s Safety First curriculum.
Allowing students to carry a low-risk, lifesaving drug with them is in many ways the minimum schools can do, he said.
“I would argue that what the schools should be doing is identifying high-risk teens and giving them the Narcan to take home with them and teaching them why it matters,” Friedman said.
Writing in The New England Journal of Medicine, Friedman identified Colorado as a hot spot for high school-aged adolescent overdose deaths, with a mortality rate more than double that of the nation from 2020 to 2022.
“Increasingly, fentanyl is being sold in pill form, and it’s happening to the largest degree in the West,” said Friedman. “I think that the teen overdose crisis is a direct result of that.”
If Colorado lawmakers approve the bill, “I think that’s a really important step,” said Ju Nyeong Park, an assistant professor of medicine at Brown University, who leads a research group focused on how to prevent overdoses. “I hope that the Colorado Legislature does and that other states follow as well.”
Park said comprehensive programs to test drugs for dangerous contaminants, better access to evidence-based treatment for adolescents who develop a substance use disorder, and promotion of harm reduction tools are also important. “For example, there is a national hotline called Never Use Alone that anyone can call anonymously to be supervised remotely in case of an emergency,” she said.
Taking Matters Into Their Own Hands
Many Colorado school districts are training staff how to administer naloxone and are stocking it on school grounds through a program that allows them to acquire it from the state at little to no cost. But it was clear to Peterson and other area high schoolers that having naloxone at school isn’t enough, especially in rural places.
“The teachers who are trained to use Narcan will not be at the parties where the students will be using the drugs,” he said.
And it isn’t enough to expect teens to keep it at home.
“It’s not going to be helpful if it’s in somebody’s house 20 minutes outside of town. It’s going to be helpful if it’s in their backpack always,” said Zoe Ramsey, another of McKinney’s friends and a senior at Animas High School.
“We were informed it was against the rules to carry naloxone, and especially to distribute it,” said Ilias “Leo” Stritikus, who graduated from Durango High School last year.
But students in the area, and their school administrators, were uncertain: Could students get in trouble for carrying the opioid antagonist in their backpacks, or if they distributed it to friends? And could a school or district be held liable if something went wrong?
He, along with Ramsey and Peterson, helped form the group Students Against Overdose. Together, they convinced Animas, which is a charter school, and the surrounding school district, to change policies. Now, with parental permission, and after going through training on how to administer it, students may carry naloxone on school grounds.
Durango School District 9-R spokesperson Karla Sluis said at least 45 students have completed the training.
School districts in other parts of the nation have also determined it’s important to clarify students’ ability to carry naloxone.
“We want to be a part of saving lives,” said Smita Malhotra, chief medical director for Los Angeles Unified School District in California.
Los Angeles County had one of the nation’s highest adolescent overdose death tallies of any U.S. county: From 2020 to 2022, 111 teens ages 14 to 18 died. One of them was a 15-year-old who died in a school bathroom of fentanyl poisoning. Malhotra’s district has since updated its policy on naloxone to permit students to carry and administer it.
“All students can carry naloxone in our school campuses without facing any discipline,” Malhotra said. She said the district is also doubling down on peer support and hosting educational sessions for families and students.
Montgomery County Public Schools in Maryland took a similar approach. School staff had to administer naloxone 18 times over the course of a school year, and five students died over the course of about one semester.
When the district held community forums on the issue, Patricia Kapunan, the district’s medical officer, said, “Students were very vocal about wanting access to naloxone. A student is very unlikely to carry something in their backpack which they think they might get in trouble for.”
So it, too, clarified its policy. While that was underway, local news reported that high school students found a teen passed out, with purple lips, in the bathroom of a McDonald’s down the street from their school, and used Narcan to revive them. It was during lunch on a school day.
“We can’t Narcan our way out of the opioid use crisis,” said Kapunan. “But it was critical to do it first. Just like knowing 911.”
Now, with the support of the district and county health department, students are training other students how to administer naloxone. Jackson Taylor, one of the student trainers, estimated they trained about 200 students over the course of three hours on a recent Saturday.
“It felt amazing, this footstep toward fixing the issue,” Taylor said.
Each trainee left with two doses of naloxone.
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Grapefruit vs Orange – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing grapefruit to orange, we picked the orange.
Why?
It’s easy, when guessing which is the healthier out of two things, to guess that the more expensive or perhaps less universally available one is the healthier. But it’s not always so, and today is one of those cases!
In terms of macros, they are very similar fruits, with almost identical levels of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, as well as water. Looking more carefully, we find that grapefruit’s sugars contain a slightly high proportion of fructose; not enough to make it unhealthy by any means (indeed, no whole unprocessed fruit is unhealthy unless it’s literally poisonous), but it is a thing to note if we’re micro-analysing the macronutrients. Also, oranges have slightly more fiber, which is always a plus.
When it comes to vitamins, oranges stand out with more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, C, and E, while grapefruit boasts more vitamin A (hence its color). Still, we’re calling this category another win for oranges.
In the category of minerals, oranges again sweep with more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, and selenium, while grapefruit has just a little more phosphorus. So, another easy win for oranges.
One final consideration that’s not shown in the nutritional values, is that grapefruit contains furanocoumarin, which can inhibit cytochrome P-450 3A4 isoenzyme and P-glycoptrotein transporters in the intestine and liver—slowing down their drug metabolism capabilities, thus effectively increasing the bioavailability of many drugs manifold. It can also be found in lower quantities in Seville (sour) oranges, and it’s not present (or at least, if it is, it’s in truly tiny quantities) in most oranges.
This may sound superficially like a good thing (improving bioavailability of things we want), but in practice it means that in the case of many drugs, if you take them with (or near in time to) grapefruit or grapefruit juice, then congratulations, you just took an overdose. This happens with a lot of meds for blood pressure, cholesterol (including statins), calcium channel-blockers, anti-depressants, benzo-family drugs, beta-blockers, and more. Oh, and Viagra, too. Which latter might sound funny, but remember, Viagra’s mechanism of action is blood pressure modulation, and that is not something you want to mess around with unduly. So, do check with your pharmacist to know if you’re on any meds that would be affected by grapefruit or grapefruit juice!
All in all, today’s sections add up to an overwhelming win for oranges!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: