Are plant-based burgers really bad for your heart? Here’s what’s behind the scary headlines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re hearing a lot about ultra-processed foods and the health effects of eating too many. And we know plant-based foods are popular for health or other reasons.
So it’s not surprising new research out this week including the health effects of ultra-processed, plant-based foods is going to attract global attention.
And the headlines can be scary if that research and the publicity surrounding it suggests eating these foods increases your risk of heart disease, stroke or dying early.
Here’s how some media outlets interpreted the research. The Daily Mail ran with:
Vegan fake meats are linked to increase in heart deaths, study suggests: Experts say plant-based diets can boost health – but NOT if they are ultra-processed
The New York Post’s headline was:
Vegan fake meats linked to heart disease, early death: study
But when we look at the study itself, it seems the media coverage has focused on a tiny aspect of the research, and is misleading.
So does eating supermarket plant-based burgers and other plant-based, ultra-processed foods really put you at greater risk of heart disease, stroke and premature death?
Here’s what prompted the research and what the study actually found.

Remind me, what are ultra-processed foods?
Ultra-processed foods undergo processing and reformulation with additives to enhance flavour, shelf-life and appeal. These include everything from packet macaroni cheese and pork sausages, to supermarket pastries and plant-based mince.
There is now strong and extensive evidence showing ultra-processed foods are linked with an increased risk of many physical and mental chronic health conditions.
Although researchers question which foods should be counted as ultra-processed, or if all of them are linked to poorer health, the consensus is that, generally, we should be eating less of them.
We also know plant-based diets are popular. These are linked with a reduced risk of chronic health conditions such as heart disease and stroke, cancer and diabetes. And supermarkets are stocking more plant-based, ultra-processed food options.
How about the new study?
The study looked for any health differences between eating plant-based, ultra-processed foods compared to eating non-plant based, ultra-processed foods. The researchers focused on the risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease and stroke) and deaths from it.
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods in this study included mass-produced packaged bread, pastries, buns, cakes, biscuits, cereals and meat alternatives (fake meats). Ultra-processed foods that were not plant-based included milk-based drinks and desserts, sausages, nuggets and other reconstituted meat products.
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank. This is a large biomedical database that contains de-identified genetic, lifestyle (diet and exercise) and health information and biological samples from half a million UK participants. This databank allows researchers to determine links between this data and a wide range of diseases, including heart disease and stroke.
They used data from nearly 127,000 people who provided details of their diet between 2009 and 2012. The researchers linked this to their hospital records and death records. On average, the researchers followed each participant’s diet and health for nine years.

What did the study find?
With every 10% increase of total energy from plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods there was an associated 5% increased risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease or stroke) and a 12% higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
But for every 10% increase in plant-sourced, non-ultra-processed foods consumed there was an associated 7% lower risk of cardiovascular disease and a 13% lower risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
The researchers found no evidence for an association between all plant-sourced foods (whether or not they were ultra-processed) and either an increased or decreased risk of cardiovascular disease or dying from it.
This was an observational study, where people recalled their diet using questionnaires. When coupled with other data, this can only tell us if someone’s diet is associated with a particular risk of a health outcome. So we cannot say that, in this case, the ultra-processed foods caused the heart disease and deaths from it.
Why has media coverage focused on fake meats?
Much of the media coverage has focused on the apparent health risks associated with eating fake meats, such as sausages, burgers, nuggets and even steaks.
These are considered ultra-processed foods. They are made by deconstructing whole plant foods such as pea, soy, wheat protein, nuts and mushrooms, and extracting the protein. They are then reformulated with additives to make the products look, taste and feel like traditional red and white meats.
However this was only one type of plant-based, ultra-processed food analysed in this study. This only accounted for an average 0.2% of the dietary energy intake of all the participants.
Compare this to bread, pastries, buns, cakes and biscuits, which are other types of plant-based, ultra-processed foods. These accounted for 20.7% of total energy intake in the study.

It’s hard to say why the media focused on fake meat. But there is one clue in the media release issued to promote the research.
Although the media release did not mention the words “fake meat”, an image of plant-based burgers, sausages and meat balls or rissoles featured prominently.
The introduction of the study itself also mentions plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods, such as sausages, nuggets and burgers.
So it’s no wonder people can be confused.
Does this mean fake meats are fine?
Not necessarily. This study analysed the total intake of plant-based, ultra-processed foods, which included fake meats, albeit a very small proportion of people’s diets.
From this study alone we cannot tell if there would be a different outcome if someone ate large amounts of fake meats.
In fact, a recent review of fake meats found there was not enough evidence to determine their impact on health.
We also need more recent data to reflect current eating patterns of fake meats. This study used dietary data collected from 2009 to 2012, and fake meats have become more popular since.
What if I really like fake meat?
We have known for a while that ultra-processed foods can harm our health. This study tells us that regardless if an ultra-processed food is plant-based or not, it may still be harmful.
We know fake meat can contain large amounts of saturated fats (from coconut or palm oil), salt and sugar.
So like other ultra-processed foods, they should be eaten infrequently. The Australian Dietary Guidelines currently recommends people should only consume foods like this sometimes and in small amounts.
Are some fake meats healthier than others?
Check the labels and nutrition information panels. Look for those lowest in fat and salt. Burgers and sausages that are a “pressed cake” of minced ingredients such as nuts, beans and vegetables will be preferable to reformulated products that look identical to meat.
You can also eat whole plant-based protein foods such as legumes. These include beans, lentils, chickpeas and soy beans. As well as being high in protein and fibre, they also provide essential nutrients such as iron and zinc. Using spices and mushrooms alongside these in your recipes can replicate some of the umami taste associated with meat.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Quick Healthy Recipe Ideas
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
“It was superb !! Just loved that healthy recipe !!! I would love to see one of those every day, if possible !! Keep up the fabulous work !!! ”
We’re glad you enjoyed! We can’t promise a recipe every day, but here’s one just for you:
Share This Post
-
Healthy Tiramisu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tiramisu (literally “pick-me-up”, “tira-mi-su”) is a delightful dish that, in its traditional form, is also a trainwreck for the health, being loaded with inflammatory cream and sugar, not to mention the cholesterol content. Here we recreate the dish in healthy fashion, being loaded with protein, fiber, and healthy fats, not to mention that the optional sweetener is an essential amino acid. The coffee and cocoa, of course, are full of antioxidants too. All in all, what’s not celebrate?
You will need
- 2 cups silken tofu (no need to press it) (do not substitute with any firmer tofu or it will not work)
- 1 cup oat cream (you can buy this ready-made, or make it yourself by blending oats in water until you get the desired consistency) (you can also just use dairy cream, but that will be less healthy)
- 1 cup almond flour (also simply called “ground almonds”)
- 1 cup espresso ristretto, or otherwise the strongest black coffee you have facility to make
- ¼ cup unsweetened cocoa powder, plus more for dusting
- 1 pack savoiardi biscuits, also called “ladyfinger” biscuits (this was the only part we couldn’t make healthy—if you figure out a way to make it healthy, let us know!) (if vegan, obviously use a vegan substitute biscuit; this writer uses Lotus/Biscoff biscuits, which work well)
- 1 tsp vanilla essence
- ½ tsp almond essence
- Optional: glycine, per taste
- Garnish: roasted coffee beans
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add glycine to the coffee first if you want the overall dish to be sweeter. Glycine has approximately the same sweetness as sugar, and can be used as a 1:1 substitution. Use that information as you see fit.
2) Blend the tofu and the oat cream together in a high-speed blender until smooth. It should have a consistency like cake-batter; if it is too liquidy, add small amounts of almond flour until it is thicker. If it’s too thick, add oat cream until it isn’t. If you want it to be sweeter than it is, add glycine to taste. When happy with its taste and consistency, divide it evenly into two bowls.
3) Add the vanilla essence and almond essence to one bowl, and the cocoa powder to the other, mixing well (in a food processor, or just by using a whisk)
4) Coat the base of a glass dish (such as a Pyrex oven dish, but any dish is fine, and any glass dish will allow for viewing the pretty layers we’ll be making) with a very thin layer of almond flour (if you want sweetness there, you can mix some glycine in with the almond flour first).
4) One by one, soak the biscuits briefly in the coffee, and use them to line to base of the dish.
5) Add a thin layer of chocolate cream, ensuring the surface is as flat as possible. Dust it with cocoa powder, to increase the surface tension.
6) Add a thin layer of vanilla-and-almond cream, ensuring the surface is as flat as possible. Dust it with cocoa powder, to increase the surface tension.
7) Stop and assess: do you have enough ingredients left to repeat these layers? It will depend on the size and shape dish you used. If you do, repeat them, finishing with a vanilla-and-almond cream layer.
8) Dust the final layer with cocoa powder if you haven’t already, and add the coffee bean garnish, if using.
9) Refrigerate for at least 8 hours, and if you have time to prepare it the day before you will eat it, that is best of all.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Easily Digestible Vegetarian Protein Sources
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- The Sweet Truth About Glycine
- Tiramisu Crunch Bites ← craving tiramisu but not keen on all that effort? Enjoy these!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Podiatrists Debunk 11 Feet Myths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Podiatrists Dr. Sarah Haller and Dr. Brad Schaeffer put us on a better path:
Don’t get wrong-footed
We’ll not keep the 11 myths a mystery; they are…
- “You have warts because your feet are dirty.”
False! Warts are caused by a virus, not dirt. Viruses can be picked up from surfaces like yoga mats, pools, gyms, and showers. - “Bunions are caused by wearing heels.”
False! Bunions are genetic deformities where the bone behind the big toe shifts. Heels might worsen them but don’t cause them. - “Cutting the sides of my toenail will prevent an ingrown toenail.”
False! Toenails should be cut straight across. Cutting the sides can make ingrown toenails worse. - “Pedicures gave me toenail fungus.”
Partially true! You can get fungus from many places, but safe, sterile pedicures are generally fine. - “Only athletes get athlete’s foot.”
False! Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection caused by warm, moist environments. Anyone can get it, not just athletes. - “My feet are fine because I trained them to walk in stilettos.”
False! You can get used to stilettos, but they aren’t healthy long-term. They shorten the Achilles tendon and put pressure on the foot. - “You can’t do anything for a broken toe.”
False! Broken toes can be treated and should be checked by a doctor. They may need to be set for proper healing. - “It’s normal for your feet to hurt from standing all day.”
False! Foot pain isn’t normal and can be prevented with proper footwear, support, and compression socks. - “All inserts are the same.”
False! Everyone’s feet are different. Some may benefit from over-the-counter insoles, but others need custom orthotics. - “Sprained ankles are no big deal.”
False! Sprains can damage ligaments and lead to instability or arthritis if untreated. Proper stabilization is essential. - “If I can walk after an injury, I don’t need to see a doctor.”
False! You can still have serious injuries like fractures even if you can walk. Always get checked after an injury.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
Take care!
Share This Post
- “You have warts because your feet are dirty.”
Related Posts
-
Why do I need to take some medicines with food?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have you ever been instructed to take your medicine with food and wondered why? Perhaps you’ve wondered if you really need to?
There are varied reasons, and sometimes complex science and chemistry, behind why you may be advised to take a medicine with food.
To complicate matters, some similar medicines need to be taken differently. The antibiotic amoxicillin with clavulanic acid (sold as Amoxil Duo Forte), for example, is recommended to be taken with food, while amoxicillin alone (sold as Amoxil), can be taken with or without food.
Different brands of the same medicine may also have different recommendations when it comes to taking it with food.
Ron Lach/Pexels Food impacts drug absorption
Food can affect how fast and how much a drug is absorbed into the body in up to 40% of medicines taken orally.
When you have food in your stomach, the makeup of the digestive juices change. This includes things like the fluid volume, thickness, pH (which becomes less acidic with food), surface tension, movement and how much salt is in your bile. These changes can impair or enhance drug absorption.
Eating a meal also delays how fast the contents of the stomach move into the small intestine – this is known as gastric emptying. The small intestine has a large surface area and rich blood supply – and this is the primary site of drug absorption.
Eating a meal with medicine will delay its onset. Farhad/Pexels Eating a larger meal, or one with lots of fibre, delays gastric emptying more than a smaller meal. Sometimes, health professionals will advise you to take a medicine with food, to help your body absorb the drug more slowly.
But if a drug can be taken with or without food – such as paracetamol – and you want it to work faster, take it on an empty stomach.
Food can make medicines more tolerable
Have you ever taken a medicine on an empty stomach and felt nauseated soon after? Some medicines can cause stomach upsets.
Metformin, for example, is a drug that reduces blood glucose and treats type 2 diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome. It commonly causes gastrointestinal symptoms, with one in four users affected. To combat these side effects, it is generally recommended to be taken with food.
The same advice is given for corticosteroids (such as prednisolone/prednisone) and certain antibiotics (such as doxycycline).
Taking some medicines with food makes them more tolerable and improves the chance you’ll take it for the duration it’s prescribed.
Can food make medicines safer?
Ibuprofen is one of the most widely used over-the-counter medicines, with around one in five Australians reporting use within a two-week period.
While effective for pain and inflammation, ibuprofen can impact the stomach by inhibiting protective prostaglandins, increasing the risk of bleeding, ulceration and perforation with long-term use.
But there isn’t enough research to show taking ibuprofen with food reduces this risk.
Prolonged use may also affect kidney function, particularly in those with pre-existing conditions or dehydration.
The Australian Medicines Handbook, which guides prescribers about medicine usage and dosage, advises taking ibuprofen (sold as Nurofen and Advil) with a glass of water – or with a meal if it upsets your stomach.
If it doesn’t upset your stomach, ibuprofen can be taken with water. Tbel Abuseridze/Unsplash A systematic review published in 2015 found food delays the transit of ibuprofen to the small intestine and absorption, which delays therapeutic effect and the time before pain relief. It also found taking short courses of ibuprofen without food reduced the need for additional doses.
To reduce the risk of ibuprofen causing damage to your stomach or kidneys, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration, stay hydrated and avoid taking other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines at the same time.
For people who use ibuprofen for prolonged periods and are at higher risk of gastrointestinal side effects (such as people with a history of ulcers or older adults), your prescriber may start you on a proton pump inhibitor, a medicine that reduces stomach acid and protects the stomach lining.
How much food do you need?
When you need to take a medicine with food, how much is enough?
Sometimes a full glass of milk or a couple of crackers may be enough, for medicines such as prednisone/prednisolone.
However, most head-to-head studies that compare the effects of a medicine “with food” and without, usually use a heavy meal to define “with food”. So, a cracker may not be enough, particularly for those with a sensitive stomach. A more substantial meal that includes a mix of fat, protein and carbohydrates is generally advised.
Your health professional can advise you on which of your medicines need to be taken with food and how they interact with your digestive system.
Mary Bushell, Clinical Associate Professor in Pharmacy, University of Canberra
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
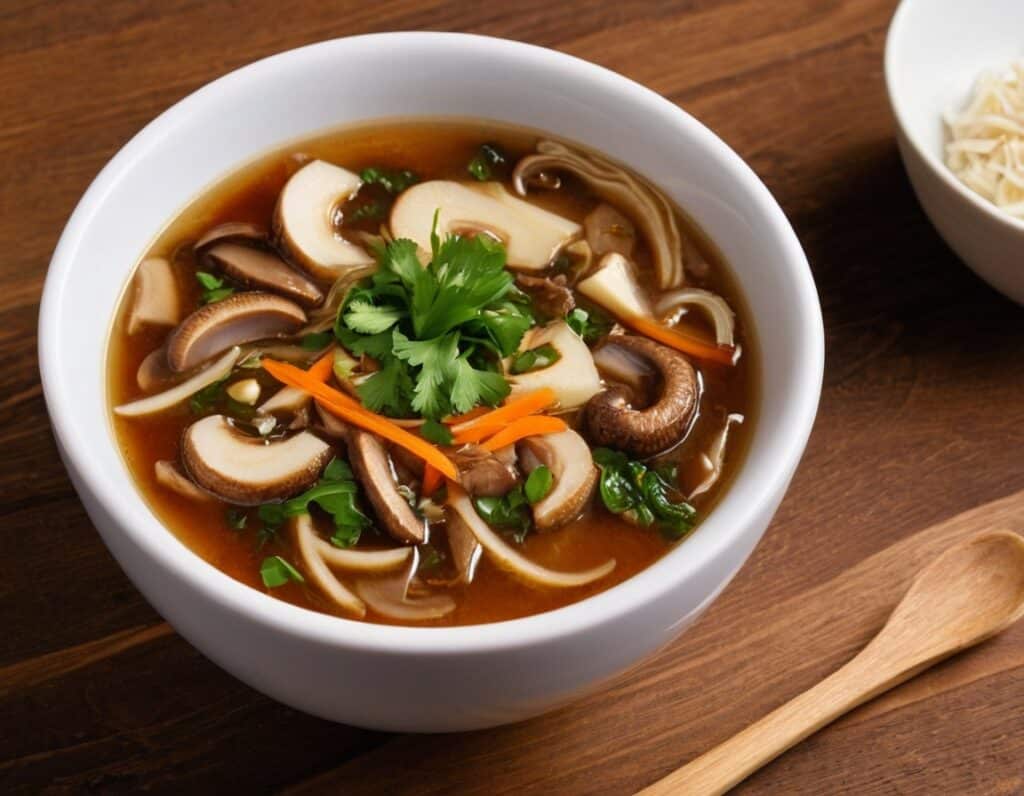
Hot And Sour Shiitake Soup
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a popular, easy, and delicious soup that nonetheless is not found in many western kitchens, despite being enjoyed in restaurants/take-out. Best of all, making it at home means that you know all the ingredients, can account for quality, and also can customize it per your preferences (i.e. how much heat/sourness you like).
You will need
- 3 cups shiitake mushrooms, sliced
- 3 cups bok choy, chopped
- 2 cups cherry tomatoes, quartered
- 1 cup carrot, grated
- 3 spring onions, chopped
- 2 shallots, sliced lengthways
- 2 serrano chilis (or similar), sliced thinly
- 2 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 tbsp fresh ginger, sliced into 1″ strips
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 6 cups low-sodium vegetable stock. Ideally you will have made it yourself from vegetable cuttings that you saved in the freezer until you had enough to make stock from, but if that’s not an option, then low-sodium vegetable stock cubes can be purchased and used.
- Garnish: ¼ cup (or 4 tbsp) cilantro, chopped, or if you have the soap gene, then this time we recommend chopped basil as the subsitution
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the ginger in a big pot with the stock; cover and simmer for about 20 minutes (otherwise the ginger flavor will remain mostly concentrated in the ginger strips).
2) Bring it to a boil and add the bok choy, mushrooms, shallots, chili peppers, and the carrot; simmer for another 5 minutes
3) Add the remaining ingredients except for the garnish, and simmer for another 5 minutes
4) Serve, adding the garnish
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The (Longevity) Magic of Mushrooms
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- Enjoy Bitter/Hot/Sour/Pungent Foods For Your Heart & Brain
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Nutritional Profiles to Recipes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I like the recipes. Most don’t seem to include nutritional profile. would lilke to see that. Macro/micro world…. Thank you❞
We’re glad you’re enjoying them! There are a couple of reasons why we don’t, but the reasons can be aggregated into one (admittedly rare) concept: honesty
To even try to give you these figures, we’d first need to use the metric system (or at least, a strictly mass-based system) which would likely not go well with our largely American readership, because “half a bulb of garlic, or more if you like”, and “1 cucumber” or “1 cup chopped carrot” could easily way half or twice as much, depending on the sizes of the vegetables or the chopping involved, and in the case of chopped vegetables measured by the cup, even the shape of the cup (because of geometry and the spaces left; it’s like Tetris in there). We can say “4 cups low-sodium broth” but we can’t say how much sodium is in your broth. And so on.
And that’s without getting into the flexibility we offer with substitutions, often at a rate of several per recipe.
We’d also need to strictly regulate your portion sizes for you, because we (with few exceptions, such as when they are a given number of burger patties, or a dessert-in-a-glass, etc) give you a recipe for a meal and leave it to you how you divide it and whether there’s leftovers.
Same goes for things like “Extra virgin olive oil for frying”; a recipe could say to use “2 tbsp” but let’s face it, you’re going to use what you need to use, and that’s going to change based on the size of your pan, how quickly it’s absorbed into the specific ingredients that you got, which will change depending on how fresh they are, and things like that.
By the time we’ve factored in your different kitchen equipment, how big your vegetables are, the many factors effecting how much oil you need, substitutions per recipe per making something dairy-free, or gluten-free, or nut-free, etc, how big your portion size is (we all know that “serves 4” is meaningless in reality)… Even an estimated average would be wildly misleading.
So, in a sea of recipes saying “500 kcal per serving” from the same authors who say you can caramelize onions in 4–5 minutes “or until caramelized” and then use the 4–5 minutes figure for calculating the overall recipe time… We prefer to stay honest.
PS: for any wondering, caramelizing onions takes closer to 45 minutes than 4–5 minutes, and again will depend on many factors, including the onions, how finely you chopped them, the size and surface of your pan, the fat you’re using, whether you add sugar, what kind, how much you stir them, the mood of your hob,
and the phase of the moon. Under very favorable circumstances, it could conceivably be rushed in 20 minutes or so, but it could also take 60. Slow-cooking them (i.e. in a crock pot) over 3–4 hours is a surprisingly viable “cheat” option, by the way. It’ll take longer, obviously, but provided you plan in advance, they’ll be ready when you need them, and perfectly done (the same claim cannot be made if you budgeted 4–5 minutes because you trusted a wicked and deceitful author who wants to poop your party).Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: