Aspirin, CVD Risk, & Potential Counter-Risks
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Aspirin Pros & Cons
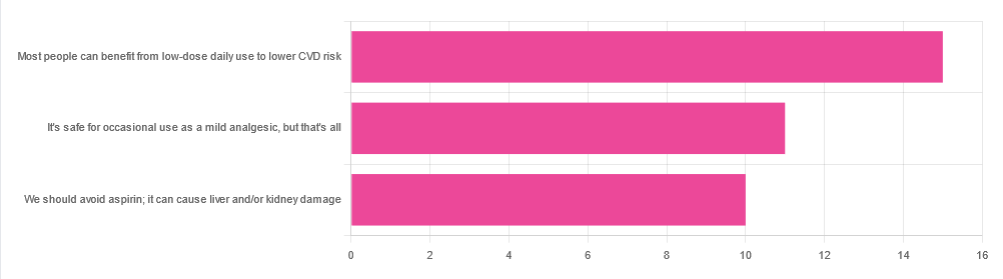
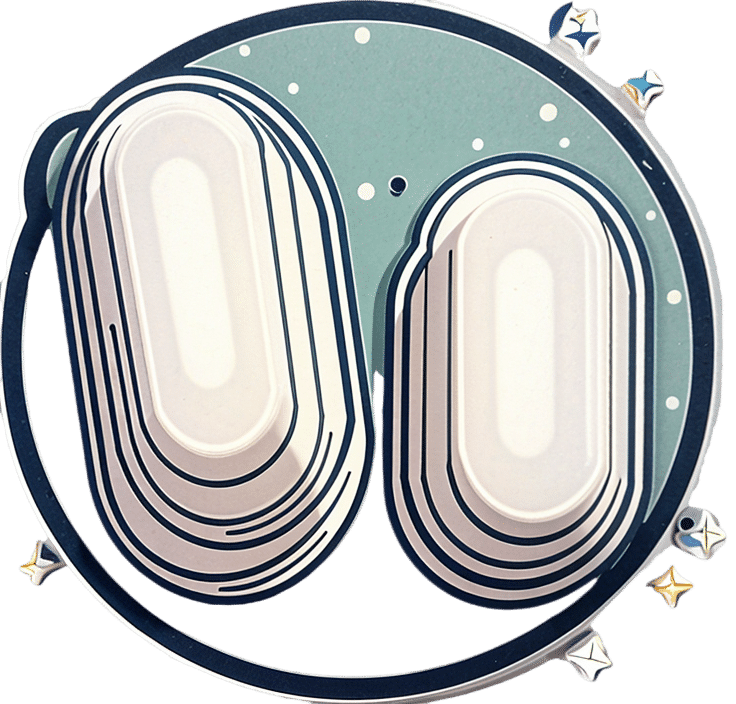
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked your health-related opinion of aspirin, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- About 42% said “Most people can benefit from low-dose daily use to lower CVD risk”
- About 31% said “It’s safe for occasional use as a mild analgesic, but that’s all”
- About 28% said “We should avoid aspirin; it can cause liver and/or kidney damage”
So, what does the science say?
Most people can benefit from low-dose daily aspirin use to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease: True or False?
True or False depending on what we mean by “benefit from”. You see, it works by inhibiting platelet function, which means it simultaneously:
- decreases the risk of atherothrombosis
- increases the risk of bleeding, especially in the gastrointestinal tract
When it comes to balancing these things and deciding whether the benefit merits the risk, you might be asking yourself: “which am I most likely to die from?” and the answer is: neither
While aspirin is associated with a significant improvement in cardiovascular disease outcomes in total, it is not significantly associated with reductions in cardiovascular disease mortality or all-cause mortality.
In other words: speaking in statistical generalizations of course, it may improve your recovery from minor cardiac events but is unlikely to help against fatal ones
The current prevailing professional (amongst cardiologists) consensus is that it may be recommended for secondary prevention of ASCVD (i.e. if you have a history of CVD), but not for primary prevention (i.e. if you have no history of CVD). Note: this means personal history, not family history.
In the words of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology:
❝Low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg orally daily) might be considered for the primary prevention of ASCVD among select adults 40 to 70 years of age who are at higher ASCVD risk but not at increased bleeding risk (S4.6-1–S4.6-8).
Low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg orally daily) should not be administered on a routine basis for the primary prevention of ASCVD among adults >70 years of age (S4.6-9).
Low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg orally daily) should not be administered for the primary prevention of ASCVD among adults of any age who are at increased risk of bleeding (S4.6-10).❞
~ Dr. Donna Arnett et al. (those section references are where you can find this information in the document)
Read in full: Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology
Or if you’d prefer a more pop-science presentation:
Many older adults still use aspirin for CVD prevention, contrary to clinical guidance
Aspirin can cause liver and/or kidney damage: True or False?
True, but that doesn’t mean we must necessarily abstain, so much as exercise caution.
Aspirin is (at recommended doses) not usually hepatotoxic (toxic to the liver), but there is a strong association between aspirin use in children and the development of Reye’s syndrome, a disease involving encephalopathy and a fatty liver. For this reason, most places have an official recommendation that aspirin not be used by children (cut-off age varies from place to place, for example 12 in the US and 16 in the UK, but the key idea is: it’s potentially dangerous for those who are not fully grown).
Aspirin is well-established as nephrotoxic (toxic to the kidneys), however, the toxicity is sufficiently low that this is not expected to be a problem to otherwise healthy adults taking it at no more than the recommended dose.
For numbers, symptoms, and treatment, see this very clear and helpful resource:
An evidence based flowchart to guide the management of acute salicylate (aspirin) overdose
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
More research shows COVID-19 vaccines are safe for young adults
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- Myocarditis, or inflammation of the heart muscle, is most commonly caused by a viral infection like COVID-19, not by vaccination.
- In line with previous research, a recent CDC study found no association between COVID-19 vaccination and sudden cardiac death in previously healthy young people.
- A COVID-19 infection is much more likely to cause inflammation of the heart muscle than a COVID-19 vaccine, and those cases are typically more severe.
Since the approval of the first COVID-19 vaccines, anti-vaccine advocates have raised concerns about heart muscle inflammation, also called myocarditis, after vaccination to suggest that vaccines are unsafe. They’ve also used concerns about myocarditis to spread false claims that vaccines cause sudden deaths, which is not true.
Research has consistently shown that cases of myocarditis after vaccination are extremely rare and usually mild, and a new study from the CDC found no association between sudden cardiac death and COVID-19 vaccination in young adults.
Read on to learn more about myocarditis and what the latest research says about COVID-19 vaccine safety.
What is myocarditis?
Myocarditis is inflammation of the myocardium, or the middle muscular layer of the heart wall. This inflammation weakens the heart’s ability to pump blood. Symptoms may include fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid or irregular heartbeat, and flu-like symptoms.
Myocarditis may resolve on its own. In rare cases, it may lead to stroke, heart failure, heart attack, or death.
What causes myocarditis?
Myocarditis is typically caused by a viral infection like COVID-19. Bacteria, parasites, fungi, chemicals, and certain medications can also cause myocarditis.
In very rare cases, some people develop myocarditis after receiving a COVID-19 vaccine, but these cases are usually mild and resolve on their own. In contrast, a COVID-19 infection is much more likely to cause myocarditis, and those cases are typically more severe.
Staying up to date on vaccines reduces your risk of developing myocarditis from a COVID-19 infection.
Are COVID-19 vaccines safe for young people?
Yes. COVID-19 vaccines have been rigorously tested and monitored over the past three years and have been determined to be safe for everyone 6 months and older. A recent CDC study found no association between COVID-19 vaccination and sudden cardiac death in previously healthy young adults.
The benefits of vaccination outweigh any potential risks. Staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines reduces your risk of severe illness, hospitalization, death, long COVID, and COVID-19-related complications, such as myocarditis.
The CDC recommends people 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring—if at least four months have passed since they received a COVID-19 vaccine.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Why You Can’t Deep Squat (And the Benefits You’re Missing)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Matt Hsu fought his own battle with chronic pain from the age of 16 in his feet, knees, hips, back, shoulders, elbows, forearms, wrists, hands, and head. Seeking answers, he’s spent a career in corrective exercise, posture alignment, structural integration, orthopedic exercise, sports medicine, and has more certifications than we care to list. In short, he knows his stuff.
Yes you can (with some work)
The deep squat, also called Asian squat, Slav squat, sitting squat, resting squat, primal squat, and various other names, is an important way of sitting that has implications for a lot of aspects of health.
Why it’s so important: it preserves the mobility of our hips, ankles, and everything in between, and maintaining especially the hip mobility makes a big difference not only to general health, but also to reducing the risk of injury. It also maintains lower body strength, making falls in older age less likely in the first place, and if falls do happen, makes injury less likely, and if injury does happen, makes the injury likely less severe.
An important misconception: there is a popular, but unfounded, belief that the ability or inability to do this is decided by genes—or if not outright decided, that at the very least Asians and Slavs have a genetic advantage. However, this is simply not true. Westerners and others can learn to do it just fine, and on the flipside, Asians and Slavs who grew up in the West may often struggle with it. The truth is, the deciding factor is lifestyle: if your culture involves sitting this way more often, you’ll be able to do it more comfortably and easily than if you’re just now trying it for the first time.
Factors that you can control: you can’t change where you grew up, but you can change how you sit down now. Achieving the squat requires repeated position practice, and the more frequently you do so (even if you just start with a few seconds and work your way up to longer periods), the better you’ll get at it. And, on the contrary, sitting in chairs weakens and shortens the muscles involved, so any time you spend sitting in chairs is working against you. There are many reasons it’s advisable to avoid sitting in chairs more than necessary, and this is one of them.
10almonds tip: a limiting factor for many people initially is ankle flexibility, which may result in one’s center of gravity being a bit far back, leading to a tendency to have to change something to avoid toppling over backwards. Rather than holding onto something immobile (e.g. furniture) in front of where you are sitting, consider simply holding an object in front of you in your hands. A book is a fine example; holding that in front of you (feel free to read the book) will shift your center of gravity forwards a bit, and will thus allow you to sit there a little longer, thus improving your strength and flexibility while you do, until you can do it without holding something in front of you. If you try with a book and you’re still prone to toppling backwards, try with something heavier, but do use the minimum weight necessary, because ultimately the counterbalance is just a crutch to get you to where you need to be.
For more visual advice on how to do it, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Retrain Your Brain – by Dr. Seth Gillihan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
15-Minute Arabic”, “Sharpen Your Chess Tactics in 24 Hours”, “Change Your Life in 7 Days”, “Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in 7 weeks”—all real books from this reviewer’s shelves.
The thing with books with these sorts of time periods in the titles is that the time period in the title often bears little relation to how long it takes to get through the book. So what’s the case here?
You’ll probably get through it in more like 7 days, but the pacing is more important than the pace. By that we mean:
Dr. Gillihan starts by assuming the reader is at best “in a rut”, and needs to first pick a direction to head in (the first “week”) and then start getting one’s life on track (the second “week”).
He then gives us, one by one, an array of tools and power-ups to do increasingly better. These tools aren’t just CBT, though of course that features prominently. There’s also mindfulness exercises, and holistic / somatic therapy too, for a real “bringing it all together” feel.
And that’s where this book excels—at no point is the reader left adrift with potential stumbling-blocks left unexamined. It’s a “whole course”.
Bottom line: whether it takes you 7 hours or 7 months, “Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in 7 Weeks” is a CBT-and-more course for people who like courses to work through. It’ll get you where you’re going… Wherever you want that to be for you!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Yoga Therapy for Arthritis – by Dr. Steffany Moonaz & Erin Byron
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Two quick notes to start with:
- One of the problems with arthritis and exercise is that arthritis can often impede exercise.
- Another of the problems with arthritis and exercise is that some kinds of exercise can exacerbate arthritis.
This book deals with both of those issues, by providing yoga specifically tailored to living with arthritis. Indeed, the first-listed author’s PhD in public health was the result of 8 years of study developing an evidence-based yoga program for people with arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
The authors take the view that arthritis is a whole-person disease (i.e. it affects all parts of you), and so addressing it requires a whole-person approach, which is what this book delivers.
As such, this is not just a book of asana (yoga postures). It does provide that, of course (as well as breathing exercises), but also its 328 pages additionally cover a lot of conscious work from the inside out, including attention to the brain, energy levels, pain, and so forth, and that the practice of yoga should not merely directly improve the joints via gentle physical exercise, but also should help to heal the whole person, including reducing stress levels, reducing physical tension, and with those two things, reducing inflammation also—and also, due to both that and the asana side of practice, better-functioning organs, which is always a bonus.
The style is interesting, as it refers to both science (8 pages of hard-science bibliography) and yogic principles (enough esoterica to put off, say, James Randi or Penn & Teller). This reviewer is very comfortable with both, and so if you, dear reader, are comfortable with both too, then you will surely enjoy this book.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one has arthritis, you’ll wish you got this book sooner.
Click here to check out Yoga Therapy For Arthritis, and live better!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Grapes vs Strawberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing strawberries to grapes, we picked the strawberries.
Why?
In terms of macros, grapes have more than 2x the carbs while strawberries have more than 2x the fiber, making this category an easy win for strawberries.
In the category of vitamins, grapes have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, and K, while strawberries have more of vitamins B3, B5, B9, C, and E, making for a 5:5 tie with comparable margins of difference.
Looking at minerals, grapes have more potassium and manganese, while strawberries have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. A clear win for strawberries here.
When it comes to polyphenols, both of these fruits are abundant in many polyphenols, but it might interest you to know that strawberries have slightly more resveratrol than red/black grapes! Still, it’s close, and there are many other polyphenols in both, and honestly we’re calling this category a tie.
Adding up the sections makes for a compelling overall win for strawberries, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Can We Drink To Good Health? ← while there are polyphenols such as resveratrol in red wine that per se would boost heart health, there’s so little per glass that you may need 100–1000 glasses per day to get the dosage that provides benefits in mouse studies.
If you’re not a mouse, you might even need more than that!
To this end, many people prefer resveratrol supplementation ← link is to an example product on Amazon, but there are plenty more so feel free to shop around 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Chia Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing chia seeds to pumpkin seeds, we picked the chia.
Why?
Both are great! But chia is best.
Note: we’re going to abbreviate them both to “chia” and “pumpkin”, respectively, but we’ll still be referring to the seeds throughout.
In terms of macros, pumpkin has a little more protein and notably higher carbs, whereas chia has nearly 2x the fiber, as well as more fat, and/but they are famously healthy fats. We’ll call this category a subjective win for chia, though you might disagree if you want to prioritize an extra 2g of protein per 100g (for pumpkin) over an extra 16g of fiber per 100g (for chia). Chia is also vastly preferable for omega-3.
When it comes to vitamins, pumpkin is marginally higher in vitamin A, while chia is a lot higher in vitamins B1, B2, B3, B9, C, and E. An easy win for chia.
In the category of minerals, for which pumpkin seeds are so famously a good source, chia has a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and selenium. On the other hand, pumpkin has more potassium and zinc. Still, that’s a 7:2 win for chia.
Adding up the categories makes for a very compelling win for the humble chia seed.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: