Green Curry Salmon Burgers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These lean and healthy burgers are as quick and easy to make as they are good for entertaining. The serving-bed has its nutritional secrets too! All in all, an especially heart-healthy and brain-healthy dish.
You will need
- 4 skinless salmon fillets, cubed (Vegetarian/Vegan? Consider this Plant-Based Salmon Recipe or, since they are getting blended, simply substitute 1½ cups cooked chickpeas instead with 1 tbsp tahini)
- 2 cloves garlic, chopped
- 2 tbsp thai green curry paste
- juice of two limes, plus wedges to serve
- 1 cup quinoa
- ½ cup edamame beans, thawed if they were frozen
- large bunch fresh cilantro (or parsley if you have the “soap “cilantro tastes like soap” gene), chopped
- extra virgin olive oil, for frying
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the salmon, garlic, curry paste, nutritional yeast, and half the lime juice into a food processor, and blend until smooth.
2) Remove, divide into four parts, and shape into burger patty shapes. Put them in the fridge where they can firm up while we do the next bit.
3) Cook the quinoa with the tablespoon of chia seeds added (which means boiling water and then letting it simmer for 10–15 minutes; when the quinoa is tender and unfurled a little, it’s done).
4) Drain the quinoa with a sieve, and stir in the edamame beans, the rest of the lime juice, the cilantro, and the black pepper. Set aside.
5) Using the olive oil, fry the salmon burgers for about 5 minutes on each side.
6) Serve; we recommend putting the burgers atop the rest, and adding a dash of lime at the table.

(it can also be served this way!)
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Farmed Fish vs Wild–Caught
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
More research shows COVID-19 vaccines are safe for young adults
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- Myocarditis, or inflammation of the heart muscle, is most commonly caused by a viral infection like COVID-19, not by vaccination.
- In line with previous research, a recent CDC study found no association between COVID-19 vaccination and sudden cardiac death in previously healthy young people.
- A COVID-19 infection is much more likely to cause inflammation of the heart muscle than a COVID-19 vaccine, and those cases are typically more severe.
Since the approval of the first COVID-19 vaccines, anti-vaccine advocates have raised concerns about heart muscle inflammation, also called myocarditis, after vaccination to suggest that vaccines are unsafe. They’ve also used concerns about myocarditis to spread false claims that vaccines cause sudden deaths, which is not true.
Research has consistently shown that cases of myocarditis after vaccination are extremely rare and usually mild, and a new study from the CDC found no association between sudden cardiac death and COVID-19 vaccination in young adults.
Read on to learn more about myocarditis and what the latest research says about COVID-19 vaccine safety.
What is myocarditis?
Myocarditis is inflammation of the myocardium, or the middle muscular layer of the heart wall. This inflammation weakens the heart’s ability to pump blood. Symptoms may include fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid or irregular heartbeat, and flu-like symptoms.
Myocarditis may resolve on its own. In rare cases, it may lead to stroke, heart failure, heart attack, or death.
What causes myocarditis?
Myocarditis is typically caused by a viral infection like COVID-19. Bacteria, parasites, fungi, chemicals, and certain medications can also cause myocarditis.
In very rare cases, some people develop myocarditis after receiving a COVID-19 vaccine, but these cases are usually mild and resolve on their own. In contrast, a COVID-19 infection is much more likely to cause myocarditis, and those cases are typically more severe.
Staying up to date on vaccines reduces your risk of developing myocarditis from a COVID-19 infection.
Are COVID-19 vaccines safe for young people?
Yes. COVID-19 vaccines have been rigorously tested and monitored over the past three years and have been determined to be safe for everyone 6 months and older. A recent CDC study found no association between COVID-19 vaccination and sudden cardiac death in previously healthy young adults.
The benefits of vaccination outweigh any potential risks. Staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines reduces your risk of severe illness, hospitalization, death, long COVID, and COVID-19-related complications, such as myocarditis.
The CDC recommends people 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring—if at least four months have passed since they received a COVID-19 vaccine.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
I’m a medical forensic examiner. Here’s what people can expect from a health response after a sexual assault
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
An estimated one in five women and one in 16 men in Australia have experienced sexual violence.
After such a traumatic experience, it’s understandable many are unsure if they want to report it to the police. In fact, less than 10% of Australian women who experience sexual assault ever make a police report.
In Australia there is no time limit on reporting sexual assault to police. However, there are tight time frames for collecting forensic evidence, which can sometimes be an important part of the police investigation, whether it’s commenced at the time or later.
This means the decision of whether or not to undergo a medical forensic examination needs to be made quite quickly after an assault.
I work as a medical forensic examiner. Here’s what you can expect if you present for a medical forensic examination after a sexual assault.
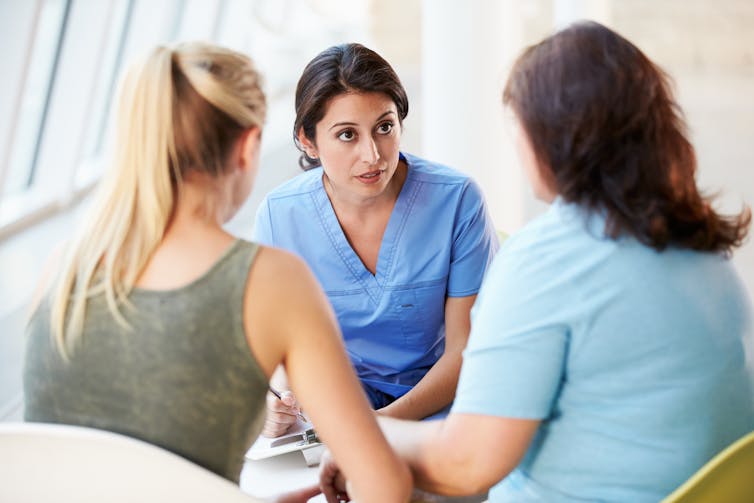
fizkes/Shutterstock A team of specialists
There are about 100 sexual assault services throughout Australia providing 24-hour care. As with other areas of health care, there are extra challenges in regional and rural areas, where there are often further distances to travel and staff shortages.
Sexual assault services in Australia are free regardless of Medicare status. To find your nearest service you can call 1800 RESPECT (1800 737 732) or Full Stop Australia (1800 385 578) who can also provide immediate telephone counselling support.
It’s important to call the local sexual assault service before turning up. They can provide the victim-survivor with information and advice to prevent delays and make the process as helpful as possible.
The consultation usually occurs in a hospital emergency department which has a designated forensic suite, or in a specialised forensic service.
The victim-survivor is seen by a doctor or nurse trained in medical and forensic care. There’s a sexual assault counsellor, crisis worker or social worker present to support the patient and offer counselling advice. This is called an “integrated response” with medical and psychosocial staff working together.
In most cases the victim-survivor can have their own support person present too.
Depending on what the victim-survivor wants, the doctor or nurse will take a history of the assault to guide any medical care which may be needed (such as emergency contraception) and to guide the examination.
Sexual assault services are always very aware of giving victim-survivors a choice about having a medical forensic examination. If a person presents to a sexual assault service, they can receive counselling and medical care without undergoing a forensic examination if they do not wish to. https://www.youtube.com/embed/CGlbTgia0Ek?wmode=transparent&start=0 Sexual assault services are inclusive of all genders.
Collecting forensic samples
Samples collected during a medical forensic examination can sometimes identify the perpetrator’s DNA or intoxicating substances (alcohol or drugs that might be relevant to the investigation). The window of opportunity to collect these samples can be as short as 12 hours, or up to 5–7 days, depending on the nature of the sexual assault.
In most of Australia, an adult who has experienced a recent sexual assault can be offered a medical forensic examination without making a report to police.
Depending on the state or territory, the forensic samples can usually be stored for 3 to 12 months (up to 100 years in Tasmania). This allows the victim-survivor time to decide if they want to release them to police for processing.
The doctor or nurse will collect the samples using a sexual assault investigation kit, or a “rape kit”.
Collecting these samples might involve taking swabs to try to detect DNA from external and internal genital areas and anywhere there may have been DNA transfer. This can be from skin cells, where the perpetrator touched the victim-survivor, or from bodily fluids including semen or saliva.
The doctor or nurse carrying out the examination do their best to minimise re-traumatisation, by providing the victim-survivor information, choices and control at every step of the process.
The victim-survivor can usually have a support person with them. Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock How about STIs and pregnancy?
During the consultation, the doctor or nurse will address any concerns about sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and pregnancy, if applicable.
In most cases the risk of STIs is small. But follow-up testing at 1–2 weeks for infections such as chlamydia and gonorrhoea, and at 6–12 weeks for infections such as syphilis and HIV, is usually recommended.
Emergency contraception (sometimes called the “morning after pill”) can be provided to prevent pregnancy. It can be taken up to five days after sexual assault (but the sooner the better) with follow-up pregnancy testing recommended at 2–3 weeks.
Things have improved over time
When I was a junior doctor in the late 90s, taking forensic swabs was usually the responsibility of the busy obstetrics and gynaecology trainee in the emergency department, who was often managing multiple patients and had little training in forensics. There was also usually no supportive counsellor.
Anecdotally, both the doctor and the patient were traumatised by this experience. Research shows that when specialised, integrated services are not provided, victim-survivors’ feelings of powerlessness are magnified.
But the way we carry out medical forensic examinations after sexual assault in Australia has improved over the years.
With patient-centred practices, and designated forensic and counselling staff, the experience for the patient is thought to be empowering rather than re-traumatising.
Our research
In new research published in the Australian Journal of General Practice, my colleagues and I explored the experience of the medical forensic examination from the victim-survivor’s perspective.
We surveyed 291 patients presenting to a sexual assault service in New South Wales (where I work) over four years.
Some 75% of patients reported the examination was reassuring and another 20% reported it was OK. Only 2% reported that it was traumatising. The majority (98%) said they would recommend a friend present to a sexual assault service if they were in a similar situation.
While patients spoke positively about the care they received, many commented that the sexual assault service was not visible enough. They didn’t know how to find it or even that it existed.
We know many victim-survivors don’t present to a sexual assault service or undergo a medical forensic examination after a sexual assault. So we need to do more to increase the visibility of these services.
The National Sexual Assault, Family and Domestic Violence Counselling Line – 1800 RESPECT (1800 737 732) – is available 24 hours a day, seven days a week for any Australian who has experienced, or is at risk of, family and domestic violence and/or sexual assault.
Mary Louise Stewart, Senior Career Medical Officer, Northern Sydney Local Health District; PhD Candidate, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
21% Stronger Bones in a Year at 62? Yes, It’s Possible (No Calcium Supplements Needed!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bone density is a concern for a lot of people past a certain age, and it can lead to an endless juggling of vitamin and mineral supplements to try to get the right balance. Sachiaki Takamiya advocates for a natural diet- and exercise-based approach instead, showing good results with his Okinawan-influenced Blue Zones diet and lifestyle.
As a caveat, he has not gone through menopause, so this video does completely overlook the implications of that. Nevertheless, even if some of us must get our hormones from a bottle these days, this diet and exercise approach is a very good foundation and the advice here is important for all—we can take all the estrogen we need and still have weak bones if our diet and exercise aren’t there as needed.
From strength to strength
Sachiaki Takamiya’s bone density wasn’t bad the previous year, but this year it is better, hitting 123.4%. This is important information, because it’s easier to achieve an n% increase (for any given value of n) if your starting point is lower. For example, a 50% increase from 1g is 1.5g (so, 0.5g difference), whereas a 50% increase from 20g is 30g (so, a 10g difference). Since his starting value was high, this makes his 21% rise particularly noteworthy—and mean that a reader with a lower starting value will most likely see even better gains, if implementing this protocol.
You may be wondering: isn’t a bone mass density of 123.4% about 23.4% more than we want it? And the answer is that the 100% value is taken from an average peak bone mass in young adults, so having it at 100% is fine, and having it a bit higher is still better—it just means he’s outclassing healthy young adults, less likely to break a bone if he falls, etc.
As for what he ate: he focused on getting calcium and magnesium, as well as vitamins D and K2, all from food sources. Key foods included small fish (sardines, niosi, jaco), nattō, mushrooms, and seaweed (nori, wakame, hijiki). In particular, he emphasizes nattō’s benefits for bones, as well as for the gut, heart, and brain.
As for his exercise: he did weight-bearing exercise and resistance training—including calisthenics and yoga, as well as sport, and simply walking and running. His weekly routine looked like this:
- Monday: heart rate zone 2 jogging (45 min)
- Tuesday: bodyweight HIIT and flexibility (20 min)
- Wednesday: heart rate zone 2 jogging (60 min)
- Thursday: bodyweight HIIT and flexibility (40 min)
- Friday: heart rate zone 2 jogging (45 min)
- Saturday: bodyweight HIIT and flexibility (20 min)
…as well as social sports (e.g. tennis, amongst others), and additional activities such as gardening, and cycling for groceries.
For more on all of the above (this is a very information-dense video), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Vit D + Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
- The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
- Which Osteoporosis Medication, If Any, Is Right For You?
- How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
- The Five Pillars Of Blue Zone Longevity
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Common Hospital Blood Pressure Mistake (Don’t Let This Happen To You Or A Loved One)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a major issue in healthcare, Dr. Suneel Dhand tells us, pertaining to the overtreatment of hypertension in hospitals. Here’s how to watch out for it and know when to question it:
Under pressure
When patients, particularly from older generations, are admitted to the hospital, their blood pressure often fluctuates due to illness, dehydration, and other factors. Despite this, they are often continued on their usual blood pressure medications, which can lead to dangerously low blood pressure.
Why does this happen? The problem arises from rigid protocols that dictate stopping blood pressure medication only if systolic pressure is below a certain threshold, often 100. However, Dr. Dhand argues that 100 is already low*, and administering medication when blood pressure is close to this can cause it to drop dangerously lower
*10almonds note: low for an adult, anyway, and especially for an older adult. To be clear: it’s not a bad thing! That is the average systolic blood pressure of a healthy teenager and it’s usually the opposite of a problem if we have that when older (indeed, this very healthy writer’s blood pressure averages 100/70, and suffice it to say, it’s been a long time since I was a teenager). But it does mean that we definitely don’t want to take medications to artificially lower it from there.
Low blood pressure from overtreatment can lead to severe consequences, requiring emergency interventions to stabilize the patient.
Dr. Dhand’s advice for patients and families is:
- Ensure medication accuracy: make sure the medical team knows the correct blood pressure medications and dosages for you or your loved one.
- Monitor vital signs: actively check blood pressure readings, especially if they are in the low 100s or even 110s, and discuss any medication concerns with the medical team.
- Watch for symptoms of low blood pressure: be alert for symptoms like dizziness or weakness, which could indicate dangerously low blood pressure.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Insider’s Guide To Making Hospital As Comfortable As Possible
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Teenage Brain – by Dr. Frances Jensen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We realize that we probably have more grandparents of teenagers than parents of teenagers here, but most of us have at least some teenage relative(s). Which makes this book interesting.
There are a lot of myths about the teenage brain, and a lot of popular assumptions that usually have some basis in fact but are often misleading.
Dr. Jensen gives us a strong foundational grounding in the neurophysiology of adolescence, from the obvious-but-often-unclear (such as the role of hormones) to less-known things like the teenage brain’s general lack of myelination. Not just “heightened neuroplasticity” but, if you imagine the brain as an electrical machine, then think of myelin as the insulation between the wires. Little wonder some wires may get crossed sometimes!
She also talks about such things as the teenage circadian rhythm’s innate differences, the impact of success and failure on the brain, and harder topics such as addiction—and the adolescent cortisol functions that can lead to teenagers needing to seek something to relax in the first place.
In criticism, we can only say that sometimes the author makes sweeping generalizations without acknowledging such, but that doesn’t detract from what she has to say on the topic of neurophysiology.
Bottom line: if there’s a teenager in your life whose behavior and/or moods are sometimes baffling to you, and whose mysteries you’d like to unravel, this is a great book.
Click here to check out the Teenage Brain, and better understand those around you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What are compound exercises and why are they good for you?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So you’ve got yourself a gym membership or bought a set of home weights. Now what? With the sheer amount of confusing exercise advice out there, it can be hard to decide what to include in a weights routine.
It can help to know there are broadly two types of movements in resistance training (lifting weights): compound exercises and isolation exercises.
So what’s the difference? And what’s all this got to do with strength, speed and healthy ageing?
What’s the difference?
Compound exercises involve multiple joints and muscle groups working together.
In a push up, for example, your shoulder and elbow joints are moving together. This targets the muscles in the chest, shoulder and triceps.
When you do a squat, you’re using your thigh and butt muscles, your back, and even the muscles in your core.
It can help to think about compound movements by grouping them by primary movement patterns.
For example, some lower body compound exercises follow a “squat pattern”. Examples include bodyweight squats, weighted squats, lunges and split squats.
A Bulgarian split squat is a type of compound movement exercise. Evelin Montero/Shutterstock We also have “hinge patterns”, where you hinge from a point on your body (such as the hips). Examples include deadlifts, hip thrusts and kettle bell swings.
Upper body compounded exercises can be grouped into “push patterns” (such as vertical barbell lifts) or “pull patterns” (such as weighted rows, chin ups or lat pull downs, which is where you use a pulley system machine to lift weights by pulling a bar downwards).
In contrast, isolation exercises are movements that occur at a single joint.
For instance, bicep curls only require movement at the elbow joint and work your bicep muscles. Tricep extensions and lateral raises are other examples of isolation exercises.
Many compound exercises mimic movements we do every day. Photo by Ketut Subiyanto/Pexels Compound exercises can make daily life easier
Many compound exercises mimic movements we do every day.
Hinge patterns mimic picking something off the floor. A vertical press mimics putting a heavy box on a high shelf. A squat mimics standing up from the couch or getting on and off the toilet.
That might sound ridiculous to a young, fit person (“why would I need to practise getting on and off a toilet?”).
Unfortunately, we lose strength and muscle mass as we age. Men lose about 5% of their muscle mass per decade, while for women the figure is about 4% per decade.
When this decline begins can vary widely. However, approximately 30% of an adult’s peak muscle mass is lost by the time they are 80.
The good news is resistance training can counteract these age-related changes in muscle size and strength.
So building strength through compound exercise movements may help make daily life feel a bit easier. In fact, our ability to perform compound movements are a good indicator how well we can function as we age.
Want to be able to get stuff down from high shelves when you’re older? Practising compound exercises like a vertical press could help. Galina_Lya/Shutterstock What about strength and athletic ability?
Compound exercises use multiple joints, so you can generally lift heavier weights than you could with isolation exercises. Lifting a heavier weight means you can build muscle strength more efficiently.
One study divided a group of 36 people into two. Three times a week, one group performed isolation exercises, while the other group did compound exercises.
After eight weeks, both groups had lost fat. But the compound exercises group saw much better results on measures of cardiovascular fitness, bench press strength, knee extension strength, and squat strength.
If you play a sport, compound movements can also help boost athletic ability.
Squat patterns require your hip, knee, and ankle to extend at the same time (also known as triple extension).
Our bodies use this triple extension trick when we run, sprint, jump or change direction quickly. In fact, research has found squat strength is strongly linked to being able to sprint faster and jump higher.
Isolation exercises are still good
What if you’re unable to do compound movements, or you just don’t want to?
Don’t worry, you’ll still build strength and muscle with isolation exercises.
Isolation exercises are also typically easier to learn as there is no skill required. They are an easy and low risk way to add extra exercise at the end of the workout, where you might otherwise be too tired to do more compound exercises safely and with correct form.
In fact, both isolation and compound exercises seem to be equally effective in helping us lose body fat and increase fat-free muscle mass when total intensity and volume of exercises are otherwise equal.
Some people also do isolation exercises when they want to build up a particular muscle group for a certain sport or for a bodybuilding competition, for example.
Isolation exercises have their role to play. Photo by Kampus Production/Pexels I just want a time efficient workout
Considering the above factors, you could consider prioritising compound exercises if you’re:
- time poor
- keen to lift heavier weights
- looking for an efficient way to train many muscles in the one workout
- interested in healthy ageing.
That said, most well designed workout programs will include both compound and isolation movements.
Correction: This article has been amended to reflect the fact a weighted row is a pull pattern, not a push pattern.
Mandy Hagstrom, Senior Lecturer, Exercise Physiology. School of Health Sciences, UNSW Sydney and Anurag Pandit, PhD Candidate in Exercise Physiology, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: