Never Too Old?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Age Limits On Exercise?
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion on whether we should exercise less as we get older, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
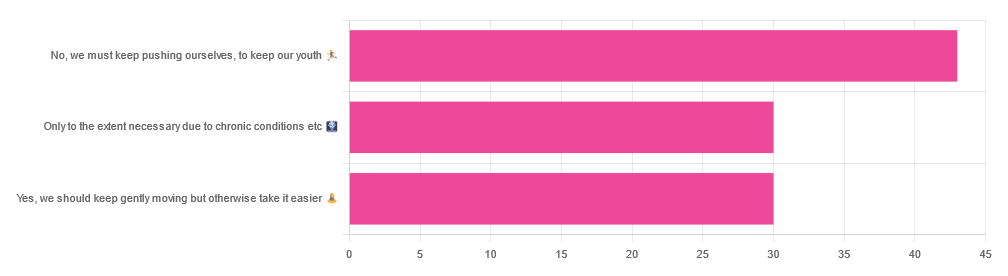
- About 42% said “No, we must keep pushing ourselves, to keep our youth“
- About 29% said “Only to the extent necessary due to chronic conditions etc”
- About 29% said “Yes, we should keep gently moving but otherwise take it easier”
One subscriber who voted for “No, we must keep pushing ourselves, to keep our youth“ wrote to add:
❝I’m 71 and I push myself. I’m not as fast or strong as I used to be but, I feel great when I push myself instead of going through the motions. I listen to my body!❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
One subscriber who voted for “Only to the extent necessary due to chronic conditions etc” wrote to add:
❝It’s never too late to get stronger. Important to keep your strength and balance. I am a Silver Sneakers instructor and I see first hand how helpful regular exercise is for seniors.❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
One subscriber who voted to say “Yes, we should keep gently moving but otherwise take it easier” wrote to add:
❝Keep moving but be considerate and respectful of your aging body. It’s a time to find balance in life and not put yourself into a positon to damage youself by competing with decades younger folks (unless you want to) – it will take much longer to bounce back.❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
These will be important, because we’ll come back to them at the end.
So what does the science say?
Endurance exercise is for young people only: True or False?
False! With proper training, age is no barrier to serious endurance exercise.
Here’s a study that looked at marathon-runners of various ages, and found that…
- the majority of middle-aged and elderly athletes have training histories of less than seven years of running
- there are virtually no relevant running time differences (p<0.01) per age in marathon finishers from 20 to 55 years
- after 55 years, running times did increase on average, but not consistently (i.e. there were still older runners with comparable times to the younger age bracket)
The researchers took this as evidence of aging being indeed a biological process that can be sped up or slowed down by various lifestyle factors.
See also:
Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
this covers the many aspects of biological aging (it’s not one number, but many!) and how our various different biological ages are often not in sync with each other, and how we can optimize each of them that can be optimized
Resistance training is for young people only: True or False?
False! In fact, it’s not only possible for older people, but is also associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality.
Specifically, those who reported strength-training at least once per week enjoyed longer lives than those who did not.
You may be thinking “is this just the horse-riding thing again, where correlation is not causation and it’s just that healthier people (for other reasons) were able to do strength-training more, rather than the other way around?“
…which is a good think to think of, so well-spotted if you were thinking that!
But in this case no; the benefits remained when other things were controlled for:
❝Adjusted for demographic variables, health behaviors and health conditions, a statistically significant effect on mortality remained.
Although the effects on cardiac and cancer mortality were no longer statistically significant, the data still pointed to a benefit.
Importantly, after the physical activity level was controlled for, people who reported strength exercises appeared to see a greater mortality benefit than those who reported physical activity alone.❞
See the study: Is strength training associated with mortality benefits? A 15 year cohort study of US older adults
And a pop-sci article about it: Strength training helps older adults live longer
Closing thoughts
As it happens… All three of the subscribers we quoted all had excellent points!
Because in this case it’s less a matter of “should”, and more a selection of options:
- We (most of us, at least) can gain/regain/maintain the kind of strength and fitness associated with much younger people, and we need not be afraid of exercising accordingly (assuming having worked up to such, not just going straight from couch to marathon, say).
- We must nevertheless be mindful of chronic conditions or even passing illnesses/injuries, but that goes for people of any age
- We also can’t argue against a “safety first” cautious approach to exercise. After all, sure, maybe we can run marathons at any age, but that doesn’t mean we have to. And sure, maybe we can train to lift heavy weights, but if we’re content to be able to carry the groceries or perhaps take our partner’s weight in the dance hall (or the bedroom!), then (if we’re also at least maintaining our bones and muscles at a healthy level) that’s good enough already.
Which prompts the question, what do you want to be able to do, now and years from now? What’s important to you?
For inspiration, check out: Train For The Event Of Your Life!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
More research shows COVID-19 vaccines are safe for young adults
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- Myocarditis, or inflammation of the heart muscle, is most commonly caused by a viral infection like COVID-19, not by vaccination.
- In line with previous research, a recent CDC study found no association between COVID-19 vaccination and sudden cardiac death in previously healthy young people.
- A COVID-19 infection is much more likely to cause inflammation of the heart muscle than a COVID-19 vaccine, and those cases are typically more severe.
Since the approval of the first COVID-19 vaccines, anti-vaccine advocates have raised concerns about heart muscle inflammation, also called myocarditis, after vaccination to suggest that vaccines are unsafe. They’ve also used concerns about myocarditis to spread false claims that vaccines cause sudden deaths, which is not true.
Research has consistently shown that cases of myocarditis after vaccination are extremely rare and usually mild, and a new study from the CDC found no association between sudden cardiac death and COVID-19 vaccination in young adults.
Read on to learn more about myocarditis and what the latest research says about COVID-19 vaccine safety.
What is myocarditis?
Myocarditis is inflammation of the myocardium, or the middle muscular layer of the heart wall. This inflammation weakens the heart’s ability to pump blood. Symptoms may include fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid or irregular heartbeat, and flu-like symptoms.
Myocarditis may resolve on its own. In rare cases, it may lead to stroke, heart failure, heart attack, or death.
What causes myocarditis?
Myocarditis is typically caused by a viral infection like COVID-19. Bacteria, parasites, fungi, chemicals, and certain medications can also cause myocarditis.
In very rare cases, some people develop myocarditis after receiving a COVID-19 vaccine, but these cases are usually mild and resolve on their own. In contrast, a COVID-19 infection is much more likely to cause myocarditis, and those cases are typically more severe.
Staying up to date on vaccines reduces your risk of developing myocarditis from a COVID-19 infection.
Are COVID-19 vaccines safe for young people?
Yes. COVID-19 vaccines have been rigorously tested and monitored over the past three years and have been determined to be safe for everyone 6 months and older. A recent CDC study found no association between COVID-19 vaccination and sudden cardiac death in previously healthy young adults.
The benefits of vaccination outweigh any potential risks. Staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines reduces your risk of severe illness, hospitalization, death, long COVID, and COVID-19-related complications, such as myocarditis.
The CDC recommends people 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring—if at least four months have passed since they received a COVID-19 vaccine.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Nudge – by Richard Thaler & Cass Sunstein
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How often in life do we make a suboptimal decision that ends up plaguing us for a long time afterwards? Sometimes, a single good or bad decision can even directly change the rest of our life.
So, it really is important that we try to optimize the decisions we do make.
Professors Richard Thaler and Cass Sunstein look at all kinds of decision-making in this book. Their goal, as per the subtitle, is “improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness”.
For the most part, the book concentrates on “nudges”. Small factors that influence our decisions one way or another.
Most importantly: that some of them are very good reasons to be nudged; others, very bad ones. And they often look similar.
Where this book excels is in highlighting the many ways we make decisions without even thinking about it… or we think about it, but only down a prescribed, foreseen track, to an externally expected conclusion (for example, an insurance company offering three packages, but two of them exist only to direct you to the “correct” choice).
A weakness of the book is that in some aspects it’s a little inconsistent. The authors describe their economic philosophy as “libertarian paternalism”, and as libertarians they’re against mandates, except when as paternalists they’re for them. But, if we take away their labels, this boils down to “some mandates can be good and some can be bad”, which would not be so inconsistent after all.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand your own decision-making processes through the eyes of policy-setting economists (especially Sunstein, who worked for the White House Office of Information & Regulatory Affairs) whose job it is to make sure you make the “right” decisions, then this is a very enlightening book.
Click here to check out Nudge and improve your decision-making clarity!
Share This Post
-
Recognize The Early Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Parkinson’s disease is a degenerative condition with wide-reaching implications for health. While there is currently no known cure, there are treatments, so knowing about it sooner rather than later is important.
Spot The Signs
There are two main kinds of symptoms, motor and non-motor.
Motor symptoms include:
- trembling that occurs when muscles are relaxed; often especially visible in the fingers
- handwriting changes—not just because of the above, but also often getting smaller
- blank expression, on account of fewer instruction signals getting through to the face
- frozen gait—especially difficulty starting walking, and a reduced arm swing
Non-motor symptoms include:
- loss of sense of smell—complete, or a persistent reduction of
- sleepwalking, or sleep-talking, or generally acting out dreams while asleep
- constipation—on an ongoing basis
- depression/anxiety, especially if there was no prior history of these conditions
For more detail on each of these, as well as what steps you might want to take, check out what Dr. Luis Zayas has to say:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Citicoline vs Parkinson’s (And More)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
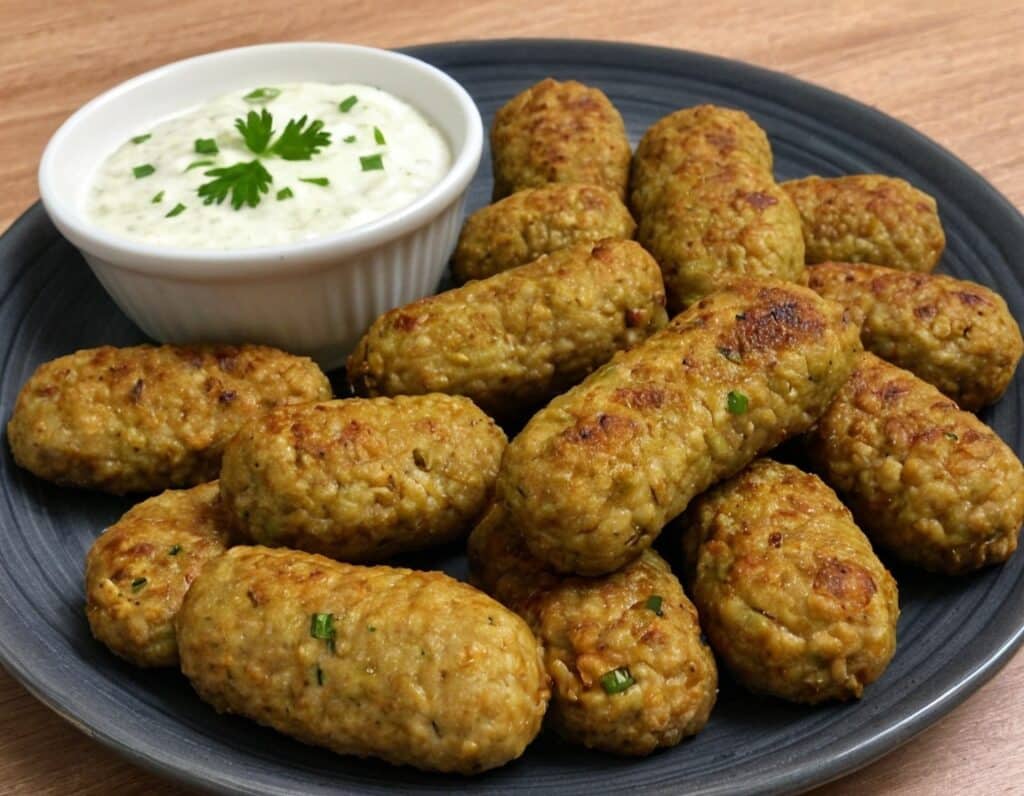
Zucchini & Oatmeal Koftas
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These vegetarian (and with one tweak, vegan) koftas are delicious as a snack, light lunch, or side to a larger meal. Healthwise, they contain the healthiest kind of fiber, as well as omega-3 fatty acids, and beneficial herbs and spices.
You will need
- ¼ cup oatmeal
- 1 large zucchini, grated
- 1 small carrot, grated
- ¼ cup cheese (your preference; vegan is also fine)
- 2 tbsp ground flaxseed
- 2 tbsp nutritional yeast
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Small handful fresh parsley, chopped
- Extra virgin olive oil, for frying
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Soak the flaxseed in 2 oz hot water for at least 5 minutes
2) Combine all of the ingredients except the olive oil (and including the water that the flax has been soaking in) in a big bowl, mixing thoroughly
3) Shape into small balls, patties, or sausage shapes, and fry until the color is golden and the structural integrity is good. If doing patties, you’ll need to gently flip them to cook both sides; otherwise, rolling them to get all sides is fine.
4) Serve! Traditional is with some kind of yogurt dip, but we’re not the boss of you, so enjoy them how you like:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health? ← it’s β-glucan, as found in oats
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us ← as in the flax
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk? ← it’s healthier than table salt
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
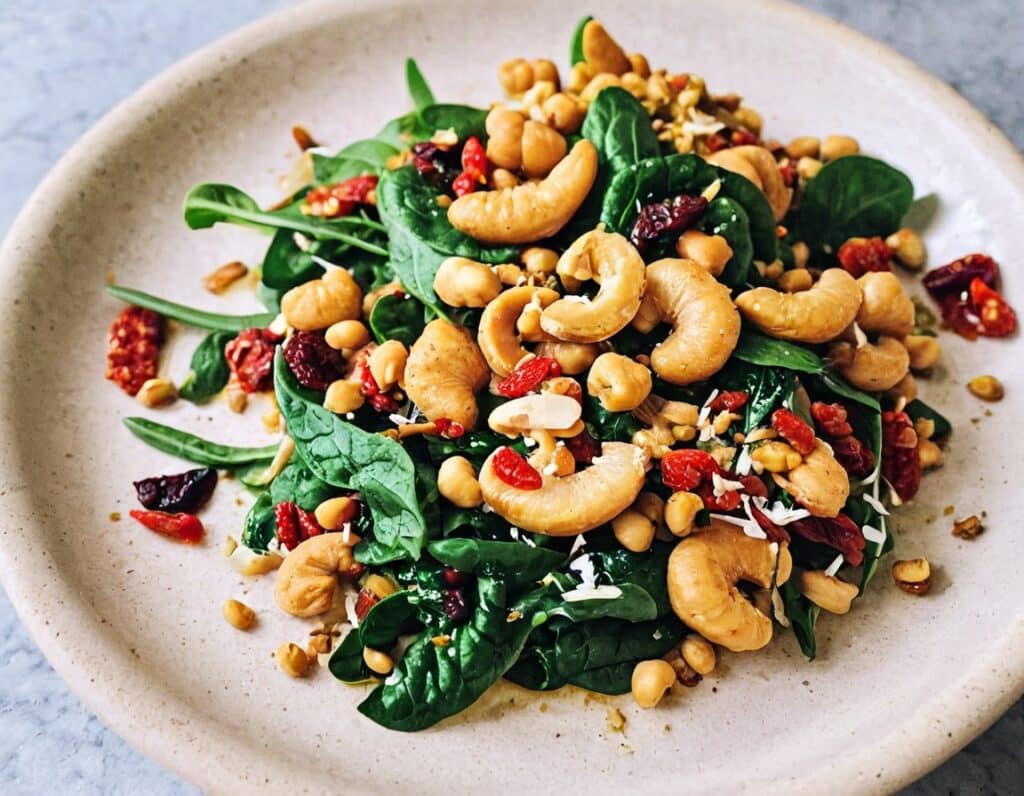
Protein Immune Support Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How to get enough protein from a salad, without adding meat? Cashews and chickpeas have you more than covered! Along with the leafy greens and an impressive array of minor ingredients full of healthy phytochemicals, this one’s good for your muscles, bones, skin, immune health, and more.
You will need
- 1½ cups raw cashews (if allergic, omit; the chickpeas and coconut will still carry the dish for protein and healthy fats)
- 2 cans (2x 14oz) chickpeas, drained
- 1½ lbs baby spinach leaves
- 2 large onions, finely chopped
- 3 oz goji berries
- ½ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 2 tbsp dessicated coconut
- 1 tbsp dried cumin
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp chili flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil, for cooking
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat a little oil in a pan; add the onions and cook for about 3 minutes.
2) Add the garlic and cook for a further 2 minutes.
3) Add the spinach, and cook until it wilts.
4) Add the remaining ingredients except the coconut, and cook for another three minutes.
5) Heat another pan (dry); add the coconut and toast for 1–2 minutes, until lightly golden. Add it to the main pan.
6) Serve hot as a main, or an attention-grabbing side:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- What Matters Most For Your Heart?
- Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Who Initiates Sex & Why It Matters
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In an ideal world, it wouldn’t matter any more than who first says “let’s get something to eat” when hungry. But in reality, it can cause serious problems on both sides:
Fear and loathing?
The person who initiates gets the special prize of an n% chance of experiencing rejection, and then what? Try again, and again, and risk seeming pushy? Or leave the ball in the other person’s court, where it may then go untouched for the next few months, because (in the most positive scenario) they were waiting for you to initiate at a better time for them?
The person who does not initiate, and/but does not want sex at that time, gets the special prize of either making their partner feel unwanted, insecure, and perhaps unloved, or else grudgingly consenting to sex that’s going to be no fun while your heart’s not in it, and thus create the same end result plus you had an extra bad experience?
So, that sucks all around:
- Initiating touch (sex or cuddling) can feel like a test of being wanted, whereupon a lack of initiation or response may be misinterpreted as a lack of love or appreciation.
- Meanwhile, non-reciprocation might stem from exhaustion or unrelated issues. For many, it’s a physiological lottery.
10almonds note: not discussed in this video, but for many couples, problems can also arise because one partner or another just isn’t showing up with the expected physical signs of physiological arousal, so even if they say (and mean!) an enthusiastic “yes”, their body’s signs get misread as a “not really, though”, resulting in one partner feeling rejected, and both feeling inadequate—on account of something that was completely unrelated to how the person actually felt about the prospect of sex*.
*Sometimes, physiological arousal will simply not accompany psychological arousal, no matter how sincere the latter. And on the flipside, sometimes the signs of physiological arousal will just show up without psychological arousal. The human body is just like that sometimes. We all must listen to our partners’ words, not their genitals!
The solution to this problem is thus the same as the solution to the rest of the problem that is discussed in the video, and it’s: good communication.
That can be easier said than done, of course—not everyone is at their most eloquent in such situations! Which is why it can be important to have those conversations first outside of the bedroom when the stakes are low/non-existent.
Even with the best communication, a more general, overarching non-reciprocity (real or perceived) of sexual desire can cause bitterness, resentment, and can ultimately be relationship-ending if a resolution that’s acceptable to everyone involved is not found.
Ultimately, the work as a couple must begin from within as individuals—addressing self-worth issues to better navigate love and intimacy.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Relationships: When To Stick It Out & When To Call It Quits
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: