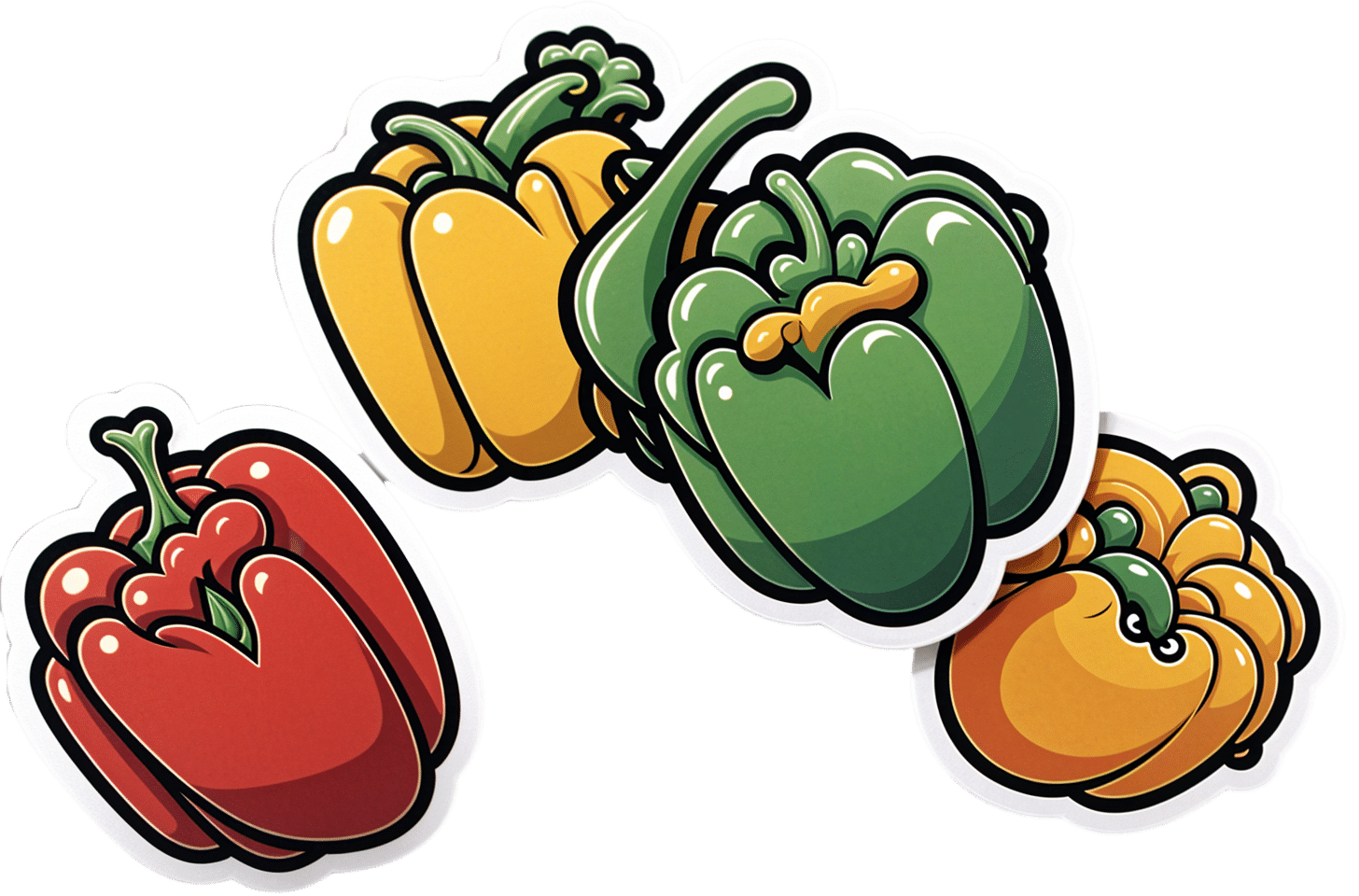
Which Bell Peppers To Pick?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bell Peppers: A Spectrum Of Specialties
We were going to do this as part of our ongoing “This Or That?” challenge, but as there are four main types all with many different benefits, we thought this bunch of fruits deserved a main feature.
And yes, they’re botanically fruits, even if culinarily used as vegetables—much like tomatoes, famously!
They’re all the same (but also very much not)
A thing to know is that whether bell peppers be green, yellow, orange, or red, they’re all the same plant, Capiscum anuum. All that differs is how early or late they’re harvested.
Notwithstanding the “Capiscum” genus, they don’t contain capsaicin (as is found in hot peppers). Capsaicin’s a wonderful phytochemical:
Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
…but today we’re all about the bell peppers.
So, let’s see how they stack up!
💚 Green for lutein
Lutein is especially important for the eyes and [the rest of the] brain, to the point that there’s now an Alzheimer’s test that measures lutein concentration in the eye:
Green peppers have most of this important carotenoid, though the others all have some too. See also:
💛 Yellow for vitamin C
Yellow peppers are technically highest in vitamin C, but all of them contain far more than the daily dose per fruit already, so if there’s any color of pepper that’s nutritionally the most expendable, it’s yellow, since any other color pepper can take its place.
Watch out, though! Cooking destroys vitamin C, so if you want to get your Cs in, you’re going to want to do it raw.
🧡 Orange for zeaxanthin and cryptoxanthins
Similar in their benefits to lutein, these antioxidant carotenoids are found most generously in orange peppers (20x as much as in yellow, 10x as much as in red, and slightly more than in green).
❤️ Red for vitamins A & B6
Red peppers are richest by far in vitamin A, with one fruit giving the daily dose already. The others have about 10% of that, give or take.
Red peppers also have the most vitamin B6, though the others also have nearly as much.
❤️ Red for lycopene
We must do a main feature for lycopene sometime, as unlike a lot of antioxidant carotenoids, lycopene is found in comparatively very few foods (most famously it’s present in tomatoes).
Red is the only color of pepper to have lycopene.
10almonds tip: to get the most out of your lycopene, cook these ones!
Lycopene becomes 4x more bioavailable when cooked:
Lycopene in tomatoes: chemical and physical properties affected by food processing ← this paper is about tomatoes but lycopene is lycopene and this applies to the lycopene in red peppers, too
And the overall winner is…
You! Because you get to eat all four of them
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Plant-Based Athlete – by Matt Frazier and Robert Cheeke
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’re already a seasoned plant-based athlete yourself, you can probably skip this book; the 60 recipes at the end would still provide value, but there is the “No Meat Athlete Cookbook” that you could hop straight to, in any case.
For most readers, there will be plenty of value from start to finish. We get a quick ground-up tour of nutrition basics, before getting into restructuring diet to optimize it for performance.
There is less in the way of “Vegans struggle with…” and more in the way of “People think vegans struggle with…” and explanations of what vegan athletes actually eat. The book does include science, but isn’t too science-heavy, and relies more on modelling what plant-based superathletes enjoy on a daily basis.
To that end,if the book has a weak point, it’s perhaps that it could have stood to include more science. The book comes recommended by Dr. Michael Greger, whose nutritional approach is incredibly science-heavy and well-referenced, and this book is obviously compatible with that (so they could have!), but in this case Frazier and Cheeke leave us to take their word for it.
Nevertheless, the science is good whether they cite it or not, and this book is quite a comprehensive primer of plant-based athleticism.
Bottom line: if you’re wondering how to optimize the two goals of “eating plants” and “being a powerful athlete”, then this one’s the book for you.
Click here to check out The Plant-Based Athlete and upgrade your health and athletic performance!
Share This Post
-
Menopause can bring increased cholesterol levels and other heart risks. Here’s why and what to do about it
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years, typically between 45 and 55. As women approach or experience menopause, common “change of life” concerns include hot flushes, sweats and mood swings, brain fog and fatigue.
But many women may not be aware of the long-term effects of menopause on the heart and blood vessels that make up the cardiovascular system. Heart disease accounts for 35% of deaths in women each year – more than all cancers combined.
What should women – and their doctors – know about these risks?
Hormones protect hearts – until they don’t
As early as 1976, the Framingham Heart Study reported more than twice the rates of cardiovascular events in postmenopausal than pre-menopausal women of the same age. Early menopause (younger than age 40) also increases heart risk.
Before menopause, women tend to be protected by their circulating hormones: oestrogen, to a lesser extent progesterone and low levels of testosterone.
These sex hormones help to relax and dilate blood vessels, reduce inflammation and improve lipid (cholesterol) levels. From the mid-40s, a decline in these hormone levels can contribute to unfavourable changes in cholesterol levels, blood pressure and weight gain – all risk factors for heart disease.
Speedkingz/Shutterstock 4 ways hormone changes impact heart risk
1. Dyslipidaemia– Menopause often involves atherogenic changes – an unhealthy imbalance of lipids in the blood, with higher levels of total cholesterol, triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C), dubbed the “bad” cholesterol. There are also reduced levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C) – the “good” cholesterol that helps remove LDL-C from blood. These changes are a major risk factor for heart attack or stroke.
2. Hypertension – Declines in oestrogen and progesterone levels during menopause contribute to narrowing of the large blood vessels on the heart’s surface, arterial stiffness and raise blood pressure.
3. Weight gain – Females are born with one to two million eggs, which develop in follicles. By the time they stop ovulating in midlife, fewer than 1,000 remain. This depletion progressively changes fat distribution and storage, from the hips to the waist and abdomen. Increased waist circumference (greater than 80–88 cm) has been reported to contribute to heart risk – though it is not the only factor to consider.
4. Comorbidities – Changes in body composition, sex hormone decline, increased food consumption, weight gain and sedentary lifestyles impair the body’s ability to effectively use insulin. This increases the risk of developing metabolic syndromes such as type 2 diabetes.
While risk factors apply to both genders, hypertension, smoking, obesity and type 2 diabetes confer a greater relative risk for heart disease in women.
So, what can women do?
Every woman has a different level of baseline cardiovascular and metabolic risk pre-menopause. This is based on their genetics and family history, diet, and lifestyle. But all women can reduce their post-menopause heart risk with:
- regular moderate intensity exercise such as brisk walking, pushing a lawn mower, riding a bike or water aerobics for 30 minutes, four or five times every week
- a healthy heart diet with smaller portion sizes (try using a smaller plate or bowl) and more low-calorie, nutrient-rich foods such as vegetables, fruit and whole grains
- plant sterols (unrefined vegetable oil spreads, nuts, seeds and grains) each day. A review of 14 clinical trials found plant sterols, at doses of at least 2 grams a day, produced an average reduction in serum LDL-C (bad cholesterol) of about 9–14%. This could reduce the risk of heart disease by 25% in two years
- less unhealthy (saturated or trans) fats and more low-fat protein sources (lean meat, poultry, fish – especially oily fish high in omega-3 fatty acids), legumes and low-fat dairy
- less high-calorie, high-sodium foods such as processed or fast foods
- a reduction or cessation of smoking (nicotine or cannabis) and alcohol
- weight-gain management or prevention.
Exercise can reduce post-menopause heart disease risk. Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock What about hormone therapy medications?
Hormone therapy remains the most effective means of managing hot flushes and night sweats and is beneficial for slowing the loss of bone mineral density.
The decision to recommend oestrogen alone or a combination of oestrogen plus progesterone hormone therapy depends on whether a woman has had a hysterectomy or not. The choice also depends on whether the hormone therapy benefit outweighs the woman’s disease risks. Where symptoms are bothersome, hormone therapy has favourable or neutral effects on coronary heart disease risk and medication risks are low for healthy women younger than 60 or within ten years of menopause.
Depending on the level of stroke or heart risk and the response to lifestyle strategies, some women may also require medication management to control high blood pressure or elevated cholesterol levels. Up until the early 2000s, women were underrepresented in most outcome trials with lipid-lowering medicines.
The Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration analysed 27 clinical trials of statins (medications commonly prescribed to lower cholesterol) with a total of 174,000 participants, of whom 27% were women. Statins were about as effective in women and men who had similar risk of heart disease in preventing events such as stroke and heart attack.
Every woman approaching menopause should ask their GP for a 20-minute Heart Health Check to help better understand their risk of a heart attack or stroke and get tailored strategies to reduce it.
Treasure McGuire, Assistant Director of Pharmacy, Mater Health SEQ in conjoint appointment as Associate Professor of Pharmacology, Bond University and as Associate Professor (Clinical), The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How Healthy People Regulate Their Emotions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some people seem quite unflappable, while others are consistently on the edge of a breakdown or outburst. So, how does a person regulate emotions, without suppressing them?
Eight things mentally healthy people do
Doing these things is hardest when one is actually in a disrupted emotional state, so they are all good things to get in the habit of doing at all times:
- Recognize and label emotions: identify specific emotions like anxiety, excitement, frustration, and so forth. You can track them for better emotional management, but it suffices even to recognize in the moment such things as “ok, I’m feeling anxious” etc.
- Embrace self-awareness: acknowledge emotions without judgment, using mindfulness and meditation to enhance emotional awareness and reduce reactivity—view your emotions neutrally, with a detached curiosity.
- Reframe negative thoughts: use cognitive reappraisal to change your perspective on situations, viewing setbacks as opportunities for growth.
- Express emotions constructively: use outlets like writing, or talking to someone to process emotions, preventing emotional build-up. Creating expressive art can also help many.
- Seek social support: cultivate strong relationships that provide emotional support and perspective, helping to manage stress and emotions.
- Maintain physical health: exercise, sleep, and a balanced diet support emotional resilience by improving overall well-being and brain function. It’s harder to be in the best mental health if your body is collapsing from exhaustion.
- Use stress management techniques: practice deep breathing, meditation, or other (non-chemical) relaxation methods to reduce stress and calm the mind and body.
- Seek professional help when needed: when emotions become overwhelming, consider therapy to develop personalized coping mechanisms and emotional regulation strategies.
For more details on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- How Are You, Really? (Alexithymia & Emotional Regulation)
- How To Manage Chronic Stress
- How To Set Anxiety Aside
- A Selection Of CBT & DBT Tools For Emotional Regulation
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Doctor’s Kitchen – by Dr. Rupy Aujla
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve featured Dr. Aujla before as an expert-of-the-week, and now it’s time to review a book by him. What’s his deal, and what should you expect?
Dr. Aujla first outlines the case for food as medicine. Not just “eat nutritionally balanced meals”, but literally, “here are the medicinal properties of these plants”. Think of some of the herbs and spices we’ve featured in our Monday Research Reviews, and add in medicinal properties of cancer-fighting cruciferous vegetables, bananas with dopamine and dopamine precursors, berries full of polyphenols, hemp seeds that fight cognitive decline, and so forth.
Most of the book is given over to recipes. They’re plant-centric, but mostly not vegan. They’re consistent with the Mediterranean diet, but mostly Indian. They’re economically mindful (favoring cheap ingredients where reasonable) while giving a nod to where an extra dollar will elevate the meal. They don’t give calorie values etc—this is a feature not a bug, as Dr. Aujla is of the “positive dieting” camp that advocates for us to “count colors, not calories”. Which, we have to admit, makes for very stress-free cooking, too.
Dr. Aujla is himself an Indian Brit, by the way, which gives him two intersecting factors for having a taste for spices. If you don’t share that taste, just go easier on the pepper etc.
As for the medicinal properties we mentioned up top? Four pages of references at the back, for any who are curious to look up the science of them. We at 10almonds do love references!
Bottom line: if you like tasty food and you’re looking for a one-stop, well-rounded, food-as-medicine cookbook, this one is a top-tier choice.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Miss Diagnosis: Anxiety, ADHD, & Women
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Why is ADHD so often misdiagnosed as anxiety in women?❞
A great question! A short and slightly flippant answer could be “it’s the medical misogyny”:
Women and Minorities Bear the Brunt of Medical Misdiagnosis
…and if you’d like to learn more in-depth about this, we recommend this excellent book:
Unwell Women: Misdiagnosis and Myth in a Man-Made World – by Dr. Elinor Cleghorn ← you can read our review here
However, in this case there is more going on too!
Part of this is because ADHD is, like many psychiatric issues, a collection of symptoms that may or may not all always be present. Since clinical definitions are decided by clinicians, rather than some special natural law of the universe, sometimes this results in “several small conditions in a trenchcoat”, and if one symptom is or isn’t present, it can make things look quite different:
What’s The Difference Between ADD and ADHD?
There are two things at hand here: as in the above example, there’s the presence or absence of hyperactivity, but also, that “attention deficit”?
It’s often not really a deficit of attention, so much as the attention is going somewhere else—an example of naming psychiatric disorders for how they affect other people, rather than the person in question.
Sidenote: personality disorders really get the worst of this!
“You have a deep insecurity about never being good enough, and you constantly mess up in your attempt to overcompensate? You may have Evil Bastard Disorder!”
“You have a crippling fear of abandonment and that you are fundamentally unloveable, so you do all you can to try to keep people close? You must have Manipulative Bitch Disorder!”
etc
See also: Why Everyone You Don’t Like Is A Narcissist
In the case of ADHD and anxiety and women, a lot of this comes down to how the redirection of focus is perceived:
❝For some time, it has been held that women with ADHD are more likely to internalize symptoms and become anxious and depressed and to suffer emotional dysregulation❞
This internalization of symptoms, vs the externalization more generally perceived in boys and men, is more likely to be seen as anxiety.
Double standards also abound for social reasons, e.g:
- He is someone who thinks ten steps ahead and covers all bases
- She is anxious and indecisive and unable to settle on one outcome
Here’s a very good overview of how this double-standard makes its way into diagnostic processes, along with other built-in biases:
Miss. Diagnosis: A Systematic Review of ADHD in Adult Women
Want to learn more?
We’ve reviewed quite a few books about ADHD, but if we had to pick one to spotlight, we’d recommend this one:
The Silent Struggle: Taking Charge of ADHD in Adults – by L. William Ross-Child, MLC
Enjoy! And while we have your attention… Would you like this section to be bigger? If so, send us more questions!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Intermittent Fasting for Women Over 50 – by Emma Sanchez
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Intermittent fasting is promoted as a very healthful (evidence-based!) way to trim the fat and slow aging, along with other health benefits. But, physiologically and especially metabolically, the average woman is quite different from the average man! And most resources are aimed at men. So, what’s the difference?
Emma Sanchez gives an overview not just of intermittent fasting, but also, how it goes with specifically female physiology. From hormonal cycles, to different body composition and fat distribution, to how we simply retain energy better—which can be a mixed blessing!
We’re given advice about how to optimize all those things and more.
She also covers issues that many writers on the topic of intermittent fasting will tend to shy away from, such as:
- mood swings
- risk of eating disorder
- impact on cognitive thinking
…and she does this evenly and fairly, making the case for intermittent fasting while acknowledging potential pitfalls that need to be recognized in order to be managed.
Lastly, the “over 50” thing. This is covered in detail quite late in the book, but there are a lot of changes that occur (beyond the obvious!), and once again, Sanchez has tips and tricks for holding back the clock where possible, and working with it rather than against it, when appropriate.
All in all, a great book for any woman over 50, or really also for women under 50, especially if that particular milestone is on the horizon.
Get your copy of Intermittent Fasting for Women over 50 from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: