Stop Checking Your Likes – by Susie Moore
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You might think this one’s advice is summed up sufficiently by the title, that there’s no need for a book! But…
There’s a lot more to this than “stop comparing the worst out-takes of your life to someone else’s highlight reel”, and there’s a lot more to this than “just unplug”.
Instead, Susie Moore discusses the serious underlying real emotional considerations of the need for approval (and even just acceptance) by our community, as well the fear of missing out.
It’s not just about how social media is designed to hijack various parts of our brain, or how The Alogorithm™ is out to personally drag your soul through Hell for a few more clicks; it’s also about the human element that would exist even without that. Who remembers MySpace? No algorithm in those days, but oh the drama potential for those “top 8 friends” places. And if you think that kind of problem is just for young people 20 years ago, you have mercifully missed the drama that older generations can get into on Facebook.
Along with the litany of evil, though, Moore also gives practical advice on how to overcome those things, how to “see the world through comedy-colored glasses”, how to ask “what’s missing, really?”, and how to make your social media experience work for you, rather than it merely using you as fuel. ← link is to our own related article!
Bottom line: if social media sucks a lot of your time, there may be more to it than just “social media sucks in general”, and there are ways to meet your emotional needs without playing by corporations’ rules to do so.
Click here to check out Stop Checking Your Likes, and breathe easy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Early Bird Or Night Owl? Genes vs Environment
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A Sliding Slope?

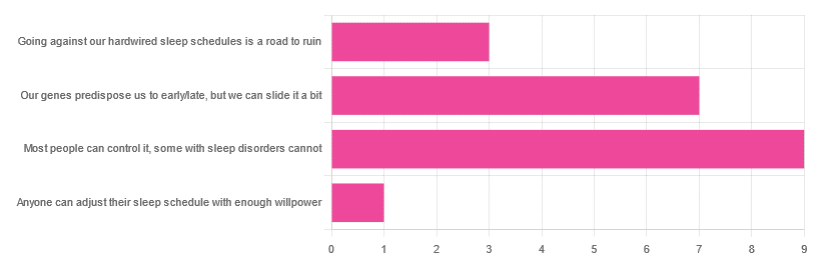
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you how much control you believe we have over our sleep schedule, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- 45% said “most people can control it; some people with sleep disorders cannot
- 35% said “our genes predispose us to early/late, but we can slide it a bit
- 15% said: “going against our hardwired sleep schedules is a road to ruin”
- 5% said “anyone can adjust their sleep schedule with enough willpower”
You may be wondering: what’s with those single-digit numbers in the graph there? And the answer is: Tuesday’s email didn’t go out at the usual time due to a scheduling mistake (sorry!), which is probably what affected the number of responses (poll response levels vary, but are usually a lot higher than this).
Note: yes, this does mean most people who read our newsletter don’t vote. So, not to sound like a politician on the campaign trail, but… Your vote counts! We always love reading your comments when you add those, too—often they provide context that allow us to tailor what we focus on in our articles
However, those are the responses we got, so here we are!
What does the science say?
Anyone can adjust their sleep with enough willpower: True or False?
False, simply. It’s difficult for most people, but for many people with sleep disorders, it is outright impossible.
In a battle of narcolepsy vs willpower, for example, no amount of willpower will stop the brain from switching to sleep mode when it thinks it’s time to sleep:
❝Narcolepsy is the most common neurological cause of chronic sleepiness. The discovery about 20 years ago that narcolepsy is caused by selective loss of the neurons producing orexins sparked great advances in the field
[There is also] developing evidence that narcolepsy is an autoimmune disorder that may be caused by a T cell-mediated attack on the orexin neurons and explain how these new perspectives can inform better therapeutic approaches.❞
~ Dr. Carrie Mahoney et al. (lightly edited for brevity)
Source: The neurobiological basis of narcolepsy
For further reading, especially if this applies to you or a loved one:
Our genes predispose us to early/late, but we can slide it a bit: True or False?
True! First, about our genes predisposing us:
…and also:
Gene distinguishes early birds from night owls and helps predict time of death
Now, as for the “can slide it a bit”, this is really just a function of the general categories of “early bird” and “night owl” spanning periods of time that allow for a few hours’ wiggle-room at either side.
However, it is recommended to make any actual changes more gradually, with the Sleep Foundation going so far as to recommend 30 minutes, or even just 15 minutes, of change per day:
Sleep Foundation | How to Fix Your Sleep Schedule
Going against our hardwired sleep schedule is a road to ruin: True or False?
False, contextually. By this we mean: our “hardwired” sleep schedule is (for most of us), genetically predisposed but not predetermined.
Also, genetic predispositions are not necessarily always good for us; one would not argue, for example, for avoiding going against a genetic predisposition to addiction.
Some genetic predispositions are just plain bad for us, and genes can be a bit of a lottery.
That said, we do recommend getting some insider knowledge (literally), by getting personal genomics tests done, if that’s a viable option for you, so you know what’s really a genetic trait (and what to do with that information) and what’s probably caused by something else (and what to do with that information):
Genetic Testing: Health Benefits & Methods
Take care!
Share This Post

The Comfort Zone – by Kristen Butler
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are you sitting comfortably? Then we’ll begin. Funny, how being comfortable can be a good starting point, then we are advised “You have to get out of your comfort zone”.
And yet, when we think of our personal greatest moments in life, they were rarely uncomfortable moments. Why is that?
Kristen Butler wants us to resolve this paradox, with a reframe:
The comfort zone? That’s actually the “flow” zone.
Just as “slow and steady wins the race”, we can—like the proverbial tortoise—take our comfort with us as we go.
The discomfort zone? That’s the stress zone, the survival zone, the “putting out fires” zone. From the outside, it looks like we’re making a Herculean effort, and perhaps we are, but is it actually so much better than peaceful consistent productivity?
Butler writes in a way that will be relatable for many, and may be a welcome life-ring if you feel like you’ve been playing catch-up for a while.
Is she advocating for complacency, then? No, and she discusses this too. That “complacency zone” is really the “burnout zone” after being in the “survival zone” for too long.
She lays out for us, therefore, a guide for growing in comfort, expanding the comfort zone yes, but by securely pushing it from the inside, not by making a mad dash out and hoping it follows us.
Bottom line: if you’ve been (perhaps quietly) uncomfortable for a little too long for comfort, this book can reframe your approach to get you to a position of sustainable, stress-free growth.
Click here to check out The Comfort Zone, and start building yours!
Share This Post

Survival of the Prettiest – by Dr. Nancy Etcoff
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Beauty is in the eye of the beholder, right? And what does it matter, in this modern world, especially if we are already in a happy stable partnership?
The science of it, as it turns out, is less poetic. Not only is evolutionary psychology still the foundation of our perception of human beauty (yes, even if we have zero possibility of further procreation personally), but also, its effects are far, far wider than partner selection.
From how nice people are to you, to how much they trust you, to how easily they will forgive a (real or perceived) misdeed, to what kind of medical care you get (or don’t), your looks shape your experiences.
In this very easy-reading work that nevertheless contains very many references, Dr. Etcoff explores the science of beauty. Not just what traits are attractive and why, but also, what they will do for (or against) us—in concrete terms, with numbers.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand the subconscious biases held by yourself and others, this book is a top-tier primer.
Share This Post
Related Posts

How Much Does A Vegan Diet Affect Biological Aging?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Slow Your Aging, One Meal At A Time
This one’s a straightforward one today, and the ““life hack” can be summed up:
Enjoy a vegan diet to enjoy younger biological age.
First, what is biological age?
Biological age is not one number, but a collection of numbers, as per different biomarkers of aging, including:
- Visual markers of aging (e.g. wrinkles, graying hair)
- Performative markers of aging (e.g. mobility tests)
- Internal functional markers of aging (e.g. tests for cognitive decline, eyesight, hearing, etc)
- Cellular markers of aging (e.g. telomere length)
We wrote more about this here:
Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
A vegan diet may well impact multiple of those categories of aging, but today we’re highlighting a study (hot off the press; published only a few days ago!) that looks at its effect on that last category: cellular markers of aging.
There’s an interesting paradox here, because this category is:
- the most easily ignorable; because we all feel it if our knees are giving out or our skin is losing elasticity, but who notices if telomeres’ T/S ratio changed by 0.0407? ← the researchers, that’s who, as this difference is very significant
- the most far-reaching in its impact, because cellular aging in turn has an effect on all the other markers of aging
Second, how much difference does it make, and how do we know?
The study was an eight-week interventional identical twin study. This means several things, to start with:
- Eight weeks is a rather short period of time to accumulate cellular aging, let alone for an intervention to accumulate a significant difference in cellular aging—but it did. So, just imagine what difference it might make in a year or ten!
- Doing an interventional study with identical twin pairs already controlled for a lot of factors, that are usually confounding variables in population / cohort / longitudinal / observational studies.
Factors that weren’t controlled for by default by using identical twins, were controlled for in the experiment design. For example, twin pairs were rejected if one or more twin in a given pair already had medical conditions that could affect the outcome:
❝Inclusion criteria involved participants aged ≥18, part of a willing twin pair, with BMI <40, and LDL-C <190 mg/dL. Exclusions included uncontrolled hypertension, metabolic disease, diabetes, cancer, heart/renal/liver disease, pregnancy, lactation, and medication use affecting body weight or energy.
Eligibility was determined via online screening, followed by an orientation meeting and in-person clinic visit. Randomization occurred only after completing baseline visits, dietary recalls, and questionnaires for both twins❞
~ Dr. Varun Dwaraka et al. ← there’s a lot of “et al.” to this one; the paper had 16 collaborating authors!
As to the difference it made over the course of the 8 weeks…
❝Various measures of epigenetic age acceleration (PC GrimAge, PC PhenoAge, DunedinPACE) were assessed, along with system-specific effects (Inflammation, Heart, Hormone, Liver, and Metabolic).
Distinct responses were observed, with the vegan cohort exhibiting significant decreases in overall epigenetic age acceleration, aligning with anti-aging effects of plant-based diets. Diet-specific shifts were noted in the analysis of methylation surrogates, demonstrating the influence of diet on complex trait prediction through DNA methylation markers.❞
~ Ibid.
You can read the whole paper here (it goes into a lot more detail than we have room to here, and also gives infographics, charts, numbers, the works):
Were they just eating more healthily, though?
Well, arguably yes, as the results show, but to be clear:
The omnivorous diet compared to the vegan diet in this study was also controlled; both groups were given a healthy meal plan for their respective diet. So this wasn’t a case of “any omnivorous diet vs healthy vegan diet”, but rather “healthy omnivorous diet vs healthy vegan diet”.
Again, the paper itself has the full details—a short version is that it involved a healthy meal kit delivery service, followed by ongoing dietician involvement in an equal and carefully-controlled fashion.
So, aside from that one group had an omnivorous meal plan and the other vegan, both groups received the same level of “healthy eating” support, guidance, and oversight.
But isn’t [insert your preferred animal product here] healthy?
Quite possibly! For general health, general scientific consensus is that eating at least mostly plants is best, red meat is bad, poultry is neutral in moderation, fish is good in moderation, dairy is good in moderation if fermented, eggs are good in moderation if not fried.
This study looked at the various biomarkers of aging that we listed, and not every possible aspect of health—there’s more science yet to be done, and the researchers themselves are calling for it.
It also bears mentioning that for some (relatively few, but not insignificantly few) people, extant health conditions may make a vegan diet unhealthy or otherwise untenable. Do speak with your own doctor and/or dietician if unsure.
See also: Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy?
We would hypothesize, by the way, that the anti-aging benefits of a vegan diet are probably proportional to abstention from animal products—meaning that even if you simply have some “vegan days”, while still consuming animal products other days, you’ll still get benefit for the days you abstained. That’s just our hypothesis though.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

The Sun Exposure Dilemma
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Sun Exposure Dilemma

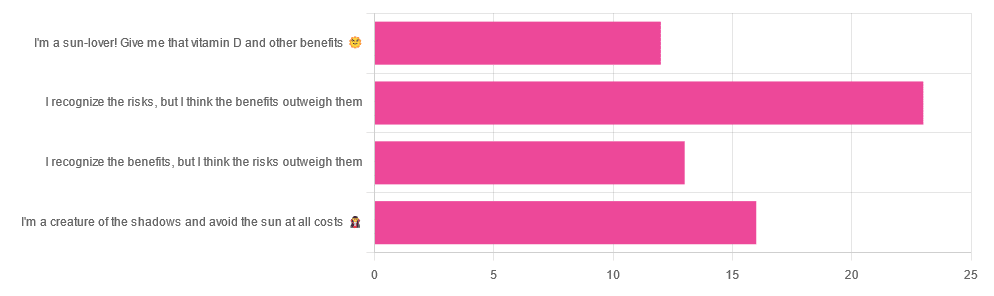
Yesterday, we asked you about your policy on sun exposure, and got the above-pictured, below-described, set of answers:
- A little over a third of respondents chose “I recognize the risks, but I think the benefits outweigh them”
- A quarter of respondents chose “I am a creature of the shadows and I avoid the sun at all costs”
- A little over a fifth of respondents chose “I recognize the benefits, but I think the risks outweigh them”
- A little under a fifth of respondents chose “I’m a sun-lover! Give me that vitamin D and other benefits!”
All in all, this is perhaps the most even spread of answers we’ve had for Friday mythbuster polls—though the sample size was smaller than it often is.
Of those who added comments, common themes were to mention your local climate, and the importance of sunscreen and/or taking vitamin D supplements.
One subscriber mentioned having lupus and living in Florida, which is a particularly unfortunate combination:
Lupus Foundation | Lupus & UV exposure: What you need to know
Another subscriber wrote:
❝Use a very good sunscreen with a high SPF all the time. Reapply after swimming or as needed! I also wear polarized sunglasses anytime I’m outside.❞
…which are important things to note too, and a lot of people forget!
See also: Who Screens The Sunscreens? (on fearing chemical dangers, vs the protection given)
But, onto today’s science for the topic at hand…
We need to get plenty of sun to get plenty of vitamin D: True or False?
True or False, depending on so many factors—to the point that many people get it wildly wrong in either direction.
Whether we are getting enough vitamin D depends on many circumstances, including:
- The climate (and depending on latitude, time of year) where we live
- Our genes, and especially (but not only) our skintone
- The clothes we wear (or don’t)
- Our diet (and not just “how much vitamin D do we consume”)
- Chronic diseases that affect vitamin D metabolism and/or requirements and/or sensitivity to the sun
For a rundown on these factors and more, check out:
Should I be getting my vitamin D levels checked?
Notably, on the topic of whether you should stay in the sun for longer to get more vitamin D…
❝The body can only produce a certain amount of vitamin D at the time, so staying in the sun any longer than needed (which could be just a few minutes, in a sunny climate) is not going to help increase your vitamin D levels, while it will increase your risk of skin cancer.❞
In contrast, she does also note:
❝During winter, catching enough sun can be difficult, especially if you spend your days confined indoors. Typically, the required exposure increases to two to three hours per week in winter. This is because sunlight exposure can only help produce vitamin D if the UVB rays reach us at the correct angle. So in winter we should regularly spend time outside in the middle of the day to get our dose of vitamin D.❞
See also: Vitamin D & Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
We can skip the sun and get our vitamin D from diet/supplements: True or False?
True! However, vitamin D is not the only health benefit of sun exposure.
Not only is sunlight-induced serotonin production important for many things ranging from mood to circadian rhythm (which in turn affects many other aspects of health), but also…
While too much sun can cause skin cancer, too little sun could cause other kinds of cancer:
Benefits of Sunlight: A Bright Spot for Human Health
Additionally, according to new research, the circadian rhythm benefits we mentioned above may also have an impact on type 2 diabetes:
Can catching some rays help you fight off type 2 diabetes?
Which way to jump?
A lot of it depends on who you are, ranging from the factors we mentioned earlier, to even such things as “having many moles” or “having blonde hair”.
This latter item, blonde hair, is a dual thing: it’s a matter of genetic factors that align with being prone to being more sensitive to the sun, as well as being a lesser physical barrier to the sun’s rays than dark hair (that can block some UV rays).
So for example, if two people have comparably gray hair now, but one of them used to have dark hair and the other blonde, there will still be a difference in how they suffer damage, or don’t—and yes, even if their skin is visually of the same approximate skintone.
You probably already know for yourself whether you are more likely to burn or tan in the sun, and the former group are less resistant to the sun’s damage… But the latter group are more likely to spend longer in the sun, and accumulate more damage that way.
If you’d like a very comprehensive downloadable, here are the guidelines issued by the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence:
NICE Guidelines | Sunlight exposure: risks and benefits
…and skip to “At risk groups”, if you don’t want to read the whole thing; “Skin type” is also an important subsection, which also uses your hair and eye color as indicators.
Writer’s note: genetics are complicated and not everyone will fall neatly into categories, which is why it’s important to know the individual factors.
For example, I am quite light-skinned with slightly graying dark hair and gray-blue eyes, and/but also have an obscure Sámi gene that means my skin makes vitamin D easily, while simultaneously being unusually resistant to burning (I just tan). Basically: built for the midnight sun of the Arctic circle.
And yet! My hobbies include not getting skin cancer, so I tend to still be quite mindful of UV levels in different weathers and times of day, and make choices (schedule, clothing, sunscreen or not) accordingly.
Bottom line:
That big self-perpetuating nuclear explosion in the sky is responsible for many things, good and bad for our health, so be aware of your own risk factors, especially for vitamin D deficiency, and skin cancer.
- If you have a predisposition to both, that’s unfortunate, but diet and supplementation at least can help with the vitamin D while getting modest amounts of sun at most.
- Remember that you can only make so much vitamin D at once, so sunbathing for health benefits need only take a few minutes
- Remember that sunlight is important for our circadian rhythm, which is important for many things.
- That’s governed by specific photoreceptor cells, though, so we don’t need our skin to be exposed for that; we just need to be able to see sunlight.
- If you’re going to be out in the sun, and not covered up, sunscreen is your friend, and yes, that goes for clear cold days under the winter sun too.
- Most phone weather apps these days have a UV index score as part of the data they give. Get used to checking it as often as you’d check for rain.
Stay safe, both ways around!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Clean Needles Save Lives. In Some States, They Might Not Be Legal.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Kim Botteicher hardly thinks of herself as a criminal.
On the main floor of a former Catholic church in Bolivar, Pennsylvania, Botteicher runs a flower shop and cafe.
In the former church’s basement, she also operates a nonprofit organization focused on helping people caught up in the drug epidemic get back on their feet.
The nonprofit, FAVOR ~ Western PA, sits in a rural pocket of the Allegheny Mountains east of Pittsburgh. Her organization’s home county of Westmoreland has seen roughly 100 or more drug overdose deaths each year for the past several years, the majority involving fentanyl.
Thousands more residents in the region have been touched by the scourge of addiction, which is where Botteicher comes in.
She helps people find housing, jobs, and health care, and works with families by running support groups and explaining that substance use disorder is a disease, not a moral failing.
But she has also talked publicly about how she has made sterile syringes available to people who use drugs.
“When that person comes in the door,” she said, “if they are covered with abscesses because they have been using needles that are dirty, or they’ve been sharing needles — maybe they’ve got hep C — we see that as, ‘OK, this is our first step.’”
Studies have identified public health benefits associated with syringe exchange services. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says these programs reduce HIV and hepatitis C infections, and that new users of the programs are more likely to enter drug treatment and more likely to stop using drugs than nonparticipants.
This harm-reduction strategy is supported by leading health groups, such as the American Medical Association, the World Health Organization, and the International AIDS Society.
But providing clean syringes could put Botteicher in legal danger. Under Pennsylvania law, it’s a misdemeanor to distribute drug paraphernalia. The state’s definition includes hypodermic syringes, needles, and other objects used for injecting banned drugs. Pennsylvania is one of 12 states that do not implicitly or explicitly authorize syringe services programs through statute or regulation, according to a 2023 analysis. A few of those states, but not Pennsylvania, either don’t have a state drug paraphernalia law or don’t include syringes in it.
Those working on the front lines of the opioid epidemic, like Botteicher, say a reexamination of Pennsylvania’s law is long overdue.
There’s an urgency to the issue as well: Billions of dollars have begun flowing into Pennsylvania and other states from legal settlements with companies over their role in the opioid epidemic, and syringe services are among the eligible interventions that could be supported by that money.
The opioid settlements reached between drug companies and distributors and a coalition of state attorneys general included a list of recommendations for spending the money. Expanding syringe services is listed as one of the core strategies.
But in Pennsylvania, where 5,158 people died from a drug overdose in 2022, the state’s drug paraphernalia law stands in the way.
Concerns over Botteicher’s work with syringe services recently led Westmoreland County officials to cancel an allocation of $150,000 in opioid settlement funds they had previously approved for her organization. County Commissioner Douglas Chew defended the decision by saying the county “is very risk averse.”
Botteicher said her organization had planned to use the money to hire additional recovery specialists, not on syringes. Supporters of syringe services point to the cancellation of funding as evidence of the need to change state law, especially given the recommendations of settlement documents.
“It’s just a huge inconsistency,” said Zoe Soslow, who leads overdose prevention work in Pennsylvania for the public health organization Vital Strategies. “It’s causing a lot of confusion.”
Though sterile syringes can be purchased from pharmacies without a prescription, handing out free ones to make drug use safer is generally considered illegal — or at least in a legal gray area — in most of the state. In Pennsylvania’s two largest cities, Philadelphia and Pittsburgh, officials have used local health powers to provide legal protection to people who operate syringe services programs.
Even so, in Philadelphia, Mayor Cherelle Parker, who took office in January, has made it clear she opposes using opioid settlement money, or any city funds, to pay for the distribution of clean needles, The Philadelphia Inquirer has reported. Parker’s position signals a major shift in that city’s approach to the opioid epidemic.
On the other side of the state, opioid settlement funds have had a big effect for Prevention Point Pittsburgh, a harm reduction organization. Allegheny County reported spending or committing $325,000 in settlement money as of the end of last year to support the organization’s work with sterile syringes and other supplies for safer drug use.
“It was absolutely incredible to not have to fundraise every single dollar for the supplies that go out,” said Prevention Point’s executive director, Aaron Arnold. “It takes a lot of energy. It pulls away from actual delivery of services when you’re constantly having to find out, ‘Do we have enough money to even purchase the supplies that we want to distribute?’”
In parts of Pennsylvania that lack these legal protections, people sometimes operate underground syringe programs.
The Pennsylvania law banning drug paraphernalia was never intended to apply to syringe services, according to Scott Burris, director of the Center for Public Health Law Research at Temple University. But there have not been court cases in Pennsylvania to clarify the issue, and the failure of the legislature to act creates a chilling effect, he said.
Carla Sofronski, executive director of the Pennsylvania Harm Reduction Network, said she was not aware of anyone having faced criminal charges for operating syringe services in the state, but she noted the threat hangs over people who do and that they are taking a “great risk.”
In 2016, the CDC flagged three Pennsylvania counties — Cambria, Crawford, and Luzerne — among 220 counties nationwide in an assessment of communities potentially vulnerable to the rapid spread of HIV and to new or continuing high rates of hepatitis C infections among people who inject drugs.
Kate Favata, a resident of Luzerne County, said she started using heroin in her late teens and wouldn’t be alive today if it weren’t for the support and community she found at a syringe services program in Philadelphia.
“It kind of just made me feel like I was in a safe space. And I don’t really know if there was like a come-to-God moment or come-to-Jesus moment,” she said. “I just wanted better.”
Favata is now in long-term recovery and works for a medication-assisted treatment program.
At clinics in Cambria and Somerset Counties, Highlands Health provides free or low-cost medical care. Despite the legal risk, the organization has operated a syringe program for several years, while also testing patients for infectious diseases, distributing overdose reversal medication, and offering recovery options.
Rosalie Danchanko, Highlands Health’s executive director, said she hopes opioid settlement money can eventually support her organization.
“Why shouldn’t that wealth be spread around for all organizations that are working with people affected by the opioid problem?” she asked.
In February, legislation to legalize syringe services in Pennsylvania was approved by a committee and has moved forward. The administration of Gov. Josh Shapiro, a Democrat, supports the legislation. But it faces an uncertain future in the full legislature, in which Democrats have a narrow majority in the House and Republicans control the Senate.
One of the bill’s lead sponsors, state Rep. Jim Struzzi, hasn’t always supported syringe services. But the Republican from western Pennsylvania said that since his brother died from a drug overdose in 2014, he has come to better understand the nature of addiction.
In the committee vote, nearly all of Struzzi’s Republican colleagues opposed the bill. State Rep. Paul Schemel said authorizing the “very instrumentality of abuse” crossed a line for him and “would be enabling an evil.”
After the vote, Struzzi said he wanted to build more bipartisan support. He noted that some of his own skepticism about the programs eased only after he visited Prevention Point Pittsburgh and saw how workers do more than just hand out syringes. These types of programs connect people to resources — overdose reversal medication, wound care, substance use treatment — that can save lives and lead to recovery.
“A lot of these people are … desperate. They’re alone. They’re afraid. And these programs bring them into someone who cares,” Struzzi said. “And that, to me, is a step in the right direction.”
At her nonprofit in western Pennsylvania, Botteicher is hoping lawmakers take action.
“If it’s something that’s going to help someone, then why is it illegal?” she said. “It just doesn’t make any sense to me.”
This story was co-reported by WESA Public Radio and Spotlight PA, an independent, nonpartisan, and nonprofit newsroom producing investigative and public-service journalism that holds power to account and drives positive change in Pennsylvania.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: