These Signs Often Mean These Nutrient Deficiencies (Do You Have Any?)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These are not a necessary “if this then this” equation, but rather a “if this, then probably this”, and it’s a cue to try upping that thing in your diet, and if that doesn’t quickly fix it, get some tests done:
- White bumps on the skin: vitamin A, omega 3
- Craving sour foods: vitamin C
- Restless leg syndrome: iron, magnesium
- Cracked lips: vitamin B2
- Tingling hands and feet: vitamin B12
- Easy bruising: vitamin K and vitamin C
- Canker sores: vitamin B9 (folate), vitamin B12, iron
- Brittle or misshapen nails: vitamin B7 (biotin)
- Craving salty foods: sodium, potassium
- Prematurely gray hair: copper, vitamin B9 (folate), vitamin B12
- Dandruff: omega 3, zinc, vitamin B6
- Craving ice: iron
Dr. LeGrand Peterson has more to say about these though, as well as a visual guide to symptoms, so do check out the video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to know more?
You might like this previous main feature about supplements vs nutrients from food
Do We Need Supplements, And Do They Work?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Toxic Gas That Sterilizes Medical Devices Prompts Safety Rule Update
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Over the past two years, Madeline Beal has heard frustration and even bewilderment during public meetings about ethylene oxide, a cancer-causing gas that is used to sterilize half of the medical devices in the U.S.
Beal, senior risk communication adviser for the Environmental Protection Agency, has fielded questions about why the agency took so long to alert people who live near facilities that emit the chemical about unusually high amounts of the carcinogenic gas in their neighborhoods. Residents asked why the EPA couldn’t close those facilities, and they wanted to know how many people had developed cancer from their exposure.
“If you’re upset by the information you’re hearing tonight, if you’re angry, if it scares you to think about risk to your family, those are totally reasonable responses,” Beal told an audience in Laredo, Texas, in September 2022. “We think the risk levels near this facility are too high.”
There are about 90 sterilizing plants in the U.S. that use ethylene oxide, and for decades companies used the chemical to sterilize medical products without drawing much attention. Many medical device-makers send their products to the plants to be sterilized before they are shipped, typically to medical distribution companies.
But people living around these facilities have been jolted in recent years by a succession of warnings about cancer risk from the federal government and media reports, an awareness that has also spawned protests and lawsuits alleging medical harm.
The EPA is expected to meet a March 1 court-ordered deadline to finalize tighter safety rules around how the toxic gas is used. The proposed changes come in the wake of a 2016 agency report that found that long-term exposure to ethylene oxide is more dangerous than was previously thought.
But the anticipated final rules — the agency’s first regulatory update on ethylene oxide emissions in more than a decade — are expected to face pushback. Medical device-makers worry stricter regulation will increase costs and may put patients at higher risk of infection from devices, ranging from surgical kits to catheters, due to deficient sterilization. The new rules are also not likely to satisfy the concerns of environmentalists or members of the public, who already have expressed frustration about how long it took the federal government to sound the alarm.
“We have been breathing this air for 40 years,” said Connie Waller, 70, who lives with her husband, David, 75, within two miles of such a sterilizing plant in Covington, Georgia, east of Atlanta. “The only way to stop these chemicals is to hit them in their pocketbook, to get their attention.”
The EPA says data shows that long-term exposure to ethylene oxide can increase the risk of breast cancer and cancers of the white blood cells, such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma, myeloma, and lymphocytic leukemia. It can irritate the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs, and has been linked to damage to the brain and nervous and reproductive systems. Children are potentially more vulnerable, as are workers routinely exposed to the chemical, EPA officials say. The agency calculates the risk based on how much of the gas is in the air or near the sterilizing facility, the distance a person is from the plant, and how long the person is exposed.
Waller said she was diagnosed with breast cancer in 2004 and that her husband was found to have non-Hodgkin lymphoma eight years later.
A 2022 study of communities living near a sterilization facility in Laredo found the rates of acute lymphocytic leukemia and breast cancer were greater than expected based on statewide rates, a difference that was statistically significant.
Beal, the EPA risk adviser, who regularly meets with community members, acknowledges the public’s concerns. “We don’t think it’s OK for you to be at increased risk from something that you have no control over, that’s near your house,” she said. “We are working as fast as we can to get that risk reduced with the powers that we have available to us.”
In the meantime, local and state governments and industry groups have scrambled to defuse public outcry.
Hundreds of personal injury cases have been filed in communities near sterilizing plants. In 2020, New Mexico’s then-attorney general filed a lawsuit against a plant in Santa Teresa, and that case is ongoing. In a case that settled last year in suburban Atlanta, a company agreed to pay $35 million to 79 people who alleged ethylene oxide used at the plant caused cancer and other injuries.
In Cook County, Illinois, a jury in 2022 awarded $363 million to a woman who alleged exposure to ethylene oxide gas led to her breast cancer diagnosis. But, in another Illinois case, a jury ruled that the sterilizing company was not liable for a woman’s blood cancer claim.
Greg Crist, chief advocacy officer for the Advanced Medical Technology Association, a medical device trade group that says ethylene oxide is an effective and reliable sterilant, attributes the spate of lawsuits to the litigious nature of trial attorneys.
“If they smell blood in the water, they’ll go after it,” Crist said.
Most states have at least one sterilizing plant. According to the EPA, a handful, like California and North Carolina, have gone further than the agency and the federal Clean Air Act to regulate ethylene oxide emissions. After a media and political firestorm raised awareness about the metro Atlanta facilities, Georgia started requiring sterilizing plants that use the gas to report all leaks.
The proposed rules the EPA is set to finalize would set lower emissions limits for chemical plants and commercial sterilizers and increase some safety requirements for workers within these facilities. The agency is expected to set an 18-month deadline for commercial sterilizers to come into compliance with the emissions rules.
That would help at facilities that “cut corners,” with lax pollution controls that allow emissions of the gas into nearby communities, said Richard Peltier, a professor of environmental health sciences at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst. Stronger regulation also prevents the plants from remaining under the radar. “One of the dirty secrets is that a lot of it is self-regulated or self-policed,” Peltier added.
But the proposed rules did not include protections for workers at off-site warehouses that store sterilized products, which can continue to emit ethylene oxide. They also did not require air testing around the facilities, prompting debate about how effective they would be in protecting the health of nearby residents.
Industry officials also don’t expect an alternative that is as broadly effective as ethylene oxide to be developed anytime soon, though they support researching other methods. Current alternatives include steam, radiation, and hydrogen peroxide vapor.
Increasing the use of alternatives can reduce industry dependence on “the crutch of ethylene oxide,” said Darya Minovi, senior analyst with the Union of Concerned Scientists, an advocacy group.
But meeting the new guidelines will be disruptive to the industry, Crist said. He estimates companies will spend upward of $500 million to comply with the new EPA rules and could struggle to meet the agency’s 18-month timetable. Sterilization companies will also have difficulty adjusting to new rules on how workers handle the gas without a dip in efficiency, Crist said.
The Food and Drug Administration, which regulates drugs and medical devices, is also watching the regulatory moves closely and worries the updated emissions rule could “present some unique challenges” if implemented as proposed, said Audra Harrison, an FDA spokesperson. “The FDA is concerned about the rule’s effects on the availability of medical devices,” she added.
Other groups, like the American Chemistry Council and the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, the state’s environmental agency, assert that ethylene oxide use isn’t as dangerous as the EPA says. The EPA’s toxicity assessment has “severe flaws” and is “overly conservative,” the council said in an emailed statement. Texas, which has several sterilizing plants, has said ethylene oxide isn’t as high a cancer risk as the agency claims, an assessment that the EPA has rejected.
Tracey Woodruff, a researcher at the University of California-San Francisco who previously worked at the EPA, said it can be hard for the agency to keep up with regulating chemicals like ethylene oxide because of constrained resources, the technical complications of rulemaking, and industry lobbying.
But she’s hopeful the EPA can strike a balance between its desire to reduce exposure and the desire of the FDA not to disrupt medical device sterilization. And scrutiny can also help the device sterilization industry think outside the box.
“We continue to discover these chemicals that we’ve already been exposed to were toxic, and we have high exposures,” she said. “Regulation is an innovation forcer.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
Tranquility by Tuesday?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
I Know How She Does It: How Successful Women Make The Most of Their Time
This is Laura Vanderkam, author of “Tranquility By Tuesday” (amongst other books). Her “thing” is spending more time on what’s important, and less on what isn’t. Sounds simple, but she’s made a career out of it, so condensed here for you are…
Laura’s 7 Keys To Productivity
Key One: Plan your weeks on Fridays
You don’t want your Monday morning to be a “James Bond intro” (where everything is already in action and you’re just along for the ride, trying to figure out what’s going on). So, take some time last thing each Friday, to plan ahead for the following week!
Key Two: Measure what matters
Whatever that means to you. Laura tracks her use of time in half-hour blocks, and likes keeping track of streaks. For her, that means running daily and keeping a log of it. She also keeps track of the books she reads. For someone else it could be music practice, or a Duolingo streak, or eating fruit each day.
On which note…
“Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen” is simpler than most nutrition trackers (where you must search for everything you eat, or scan barcodes for all ingredients).
Instead, it keeps track of whether you are having certain key health-giving foods often enough to maintain good health.
We might feature his method in a future edition of 10almonds, but for now, check the app out for yourself here:
Get Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen on iOS / Get Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen on Android
Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen @ Nutrition Facts
Key Three: Figure out 2–3 “anchor” events for the weekend
Otherwise, it can become a bit of a haze and on Monday you find yourself thinking “where did the weekend go?”. So, plan some stuff! It doesn’t have to be anything out-of-this-world, just something that you can look forward to in advance and remember afterwards. It could be a meal out with your family, or a session doing some gardening, or a romantic night in with your partner. Whatever makes your life “living” and not passing you by!
Key Four: Tackle the toughest work first
You’ve probably heard about “swallowing frogs”. If not, there are various versions, usually attributed to Mark Twain.
Here’s one:
“If it’s your job to eat a frog, it’s best to do it first thing in the morning. And if it’s your job to eat two frogs, it’s best to eat the biggest one first.”
Top Productivity App “ToDoist” has an option for this, by the way!
Laura’s key advice here is: get the hard stuff done now! Before you get distracted or tired and postpone it to tomorrow (and then lather rinse repeat, so it never gets done)
10almonds Tip:
“But what if something’s really important but not as pressing as some less important, but more urgent tasks?”
Simple!
Set a timer (we love the Pomodoro method, by the way) and do one burst of the important-but-not-urgent task first. Then you can get to the more urgent stuff.
Repeat each day until the important-but-not-urgent task is done!
The 10almonds Team
Key Five: Use bits of time well
If, like many of us, you’ve a neverending “to read” list, use the 5–10 minute breaks that get enforced upon us periodically through the day!
- Use those few minutes before a meeting/phonecall!
- Use the time you spend waiting for public transport or riding on it!
- Use the time you spent waiting for a family member to finish doing a thing!
All those 5–10 minute bits soon add up… You might as well spend that time reading something you know will add value to your life, rather than browsing social media, for example.
Key Six: Make very short daily to-do lists
By “short”, Laura considers this “under 10 items”. Do this as the last part of your working day, ready for tomorrow. Not at bedtime! Bedtime is for winding down, not winding up
Key Seven: Have a bedtime
Laura shoots for 10:30pm, but whatever works for you and your morning responsibilities. Your morning responsibilities aren’t tied to a specific time? Lucky you, but try to keep a bedtime anyway. Otherwise, your daily rhythm can end up sliding around the clock, especially if you work from home!
Share This Post
-
How Love Changes Your Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When we fall in love, have a romantic attachment, or have a sad breakup, there’s a lot going on neurochemically, and also with different parts of the brain taking the wheel. Dr. Shannon Odell explains:
The neurochemistry of love
Of course, not every love will follow this exact pattern, but here’s perhaps the most common one:
Infatuation stage: This early phase is characterized by obsessive thoughts and a strong desire to be with the person. The ventral tegmental area (VTA), the brain’s reward center, becomes highly active, releasing dopamine, one of the feel-good neurotransmitters, which makes love feel intoxicating, similar to addictive substances. Additionally, activity in the prefrontal cortex, responsible for critical thinking and judgment, decreases, causing people to see their partners through “rose-tinted glasses”. However, this intense stage usually lasts only a few months.
Attachment stage: As the relationship progresses, it shifts into a more stable and long-lasting phase. This stage is driven by oxytocin and vasopressin, hormones that promote trust/bonding and arousal, respectively. These same hormones also play a role in family and friendship connections. Oxytocin, in particular, reduces stress hormones, which is why spending time with a loved one can feel so calming.
Heartbreak stage: When a relationship ends, the insular cortex processes emotional and physical pain, making heartbreak feel as painful as a physical injury. Meanwhile, the VTA remains active, leading to intense longing and cravings for the lost partner, similar to withdrawal symptoms. The stress axis also activates, causing distress and restlessness. Over time, higher brain regions help regulate these emotions. Healing strategies such as exercise, socializing, and listening to music can help by triggering dopamine release and easing the pain of heartbreak.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
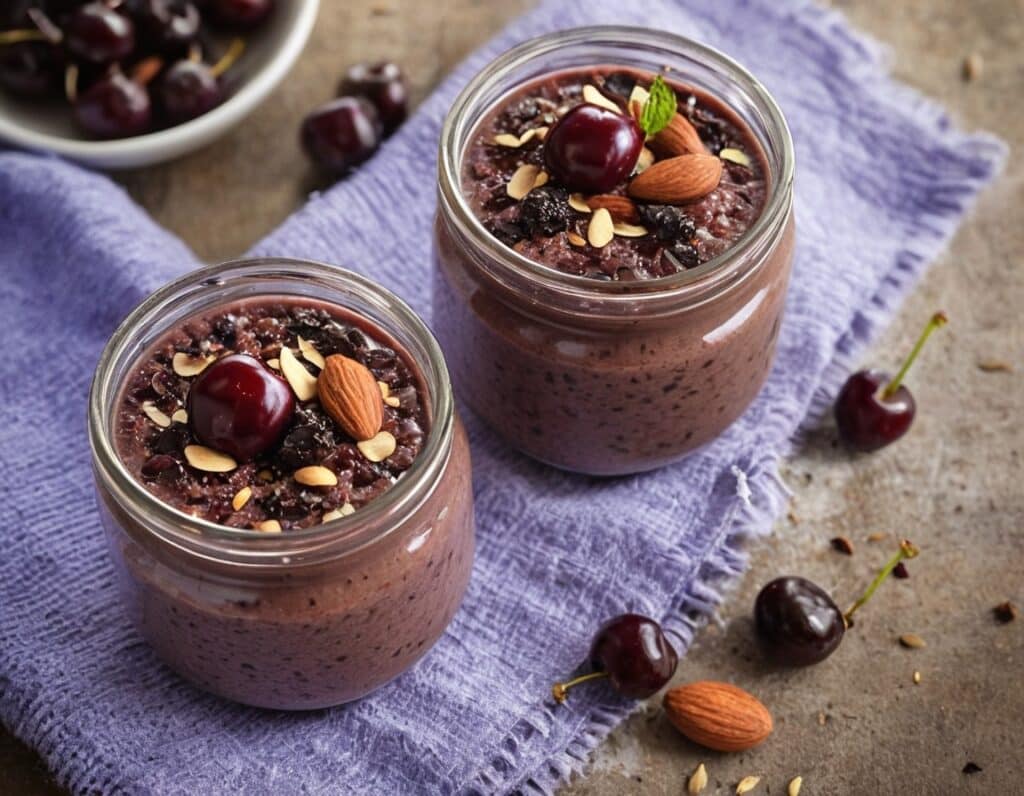
Black Forest Chia Pudding
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This pudding tastes so decadent, it’s hard to believe it’s so healthy, but it is! Not only is it delicious, it’s also packed with nutrients including protein, carbohydrates, healthy fats (including omega-3s), fiber, vitamins, minerals, and assorted antioxidant polyphenols. Perfect dessert or breakfast!
You will need
- 1½ cups pitted fresh or thawed-from-frozen cherries
- ½ cup mashed banana
- 3 tbsp unsweetened cocoa powder
- 2 tbsp chia seeds, ground
- Optional: 2 pitted dates, soaked in hot water for 10 minutes and then drained (include these if you prefer a sweeter pudding)
- Garnish: a few almonds, and/or berries, and/or cherries and/or cacao nibs
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the ingredients except for the chia seeds and the garnish, with ½ cup of water, until completely smooth
2) Divide into two small bowls or glass jars
3) Add 1 tbsp ground chia seeds to each, and stir until evenly distributed
4) Add the garnish and refrigerate overnight or at least for some hours. There’s plenty of wiggle-room here, so make it at your convenience and serve at your leisure.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Cherries’ Very Healthy Wealth Of Benefits!
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
America Worries About Health Costs — And Voters Want to Hear From Biden and Republicans
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
President Joe Biden is counting on outrage over abortion restrictions to help drive turnout for his reelection. Former President Donald Trump is promising to take another swing at repealing Obamacare.
But around America’s kitchen tables, those are hardly the only health topics voters want to hear about in the 2024 campaigns. A new KFF tracking poll shows that health care tops the list of basic expenses Americans worry about — more than gas, food, and rent. Nearly 3 in 4 adults — and majorities of both parties — say they’re concerned about paying for unexpected medical bills and other health costs.
“Absolutely health care is something on my mind,” Rob Werner, 64, of Concord, New Hampshire, said in an interview at a local coffee shop in January. He’s a Biden supporter and said he wants to make sure the Affordable Care Act, also known as Obamacare, is retained and that there’s more of an effort to control health care costs.
The presidential election is likely to turn on the simple question of whether Americans want Trump back in the White House. (Nikki Haley, the former South Carolina governor and U.S. ambassador to the United Nations, remained in the race for the Republican nomination ahead of Super Tuesday, though she had lost the first four primary contests.) And neither major party is basing their campaigns on health care promises.
But in the KFF poll, 80% of adults said they think it’s “very important” to hear presidential candidates talk about what they’d do to address health care costs — a subject congressional and state-level candidates can also expect to address.
“People are most concerned about out-of-pocket expenses for health care, and rightly so,” said Andrea Ducas, vice president of health policy at the Center for American Progress, a Washington, D.C.-based progressive think tank.
Here’s a look at the major health care issues that could help determine who wins in November.
Abortion
Less than two years after the Supreme Court overturned the constitutional right to an abortion, it is shaping up to be the biggest health issue in this election.
That was also the case in the 2022 midterm elections, when many voters rallied behind candidates who supported abortion rights and bolstered Democrats to an unexpectedly strong showing. Since the Supreme Court’s decision, voters in six states — including Kansas, Kentucky, and Ohio, where Republicans control the legislatures — have approved state constitutional amendments protecting abortion access.
Polls show that abortion is a key issue to some voters, said Robert Blendon, a public opinion researcher and professor emeritus at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. He said up to 30% across the board see it as a “personal” issue, rather than policy — and most of those support abortion rights.
“That’s a lot of voters, if they show up and vote,” Blendon said.
Proposals to further protect — or restrict — abortion access could drive voter turnout. Advocates are working to put abortion-related measures on the ballot in such states as Arizona, Florida, Missouri, and South Dakota this November. A push in Washington toward a nationwide abortion policy could also draw more voters to the polls, Blendon said.
A surprise ruling by the Alabama Supreme Court in February that frozen embryos are children could also shake up the election. It’s an issue that divides even the anti-abortion community, with some who believe that a fertilized egg is a unique new person deserving of full legal rights and protections, and others believing that discarding unused embryos as part of the in vitro fertilization process is a morally acceptable way for couples to have children.
Pricey Prescriptions
Drug costs regularly rank high among voters’ concerns.
In the latest tracking poll, more than half — 55% — said they were very worried about being able to afford prescription drugs.
Biden has tried to address the price of drugs, though his efforts haven’t registered with many voters. While its name doesn’t suggest landmark health policy, the Inflation Reduction Act, or IRA, which the president signed in August 2022, included a provision allowing Medicare to negotiate prices for some of the most expensive drugs. It also capped total out-of-pocket spending for prescription drugs for all Medicare patients, while capping the price of insulin for those with diabetes at $35 a month — a limit some drugmakers have extended to patients with other kinds of insurance.
Drugmakers are fighting the Medicare price negotiation provision in court. Republicans have promised to repeal the IRA, arguing that forcing drugmakers to negotiate lower prices on drugs for Medicare beneficiaries would amount to price controls and stifle innovation. The party has offered no specific alternative, with the GOP-led House focused primarily on targeting pharmacy benefit managers, the arbitrators who control most Americans’ insurance coverage for medicines.
Costs of Coverage
Health care costs continue to rise for many Americans. The cost of employer-sponsored health plans have hit new highs in the past few months, raising costs for employers and workers alike. Experts have attributed the increase to high demand and expensive prices for certain drugs and treatments, notably weight loss drugs, as well as to medical inflation.
Meanwhile, the ACA is popular. The KFF poll found that more adults want to see the program expanded than scaled back. And a record 21.3 million people signed up for coverage in 2024, about 5 million of them new customers.
Enrollment in Republican-dominated states has grown fastest, with year-over-year increases of 80% in West Virginia, nearly 76% in Louisiana, and 62% in Ohio, according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
Public support for Obamacare and record enrollment in its coverage have made it politically perilous for Republicans to pursue the law’s repeal, especially without a robust alternative. That hasn’t stopped Trump from raising that prospect on the campaign trail, though it’s hard to find any other Republican candidate willing to step out on the same limb.
“The more he talks about it, the more other candidates have to start answering for it,” said Jarrett Lewis, a partner at Public Opinion Strategies, a GOP polling firm.
“Will a conversation about repeal-and-replace resonate with suburban women in Maricopa County?” he said, referring to the populous county in Arizona known for being a political bellwether. “I would steer clear of that if I was a candidate.”
Biden and his campaign have pounced on Trump’s talk of repeal. The president has said he wants to make permanent the enhanced premium subsidies he signed into law during the pandemic that are credited with helping to increase enrollment.
Republican advisers generally recommend that their candidates promote “a market-based system that has the consumer much more engaged,” said Lewis, citing short-term insurance plans as an example. “In the minds of Republicans, there is a pool of people that this would benefit. It may not be beneficial for everyone, but attractive to some.”
Biden and his allies have criticized short-term insurance plans — which Trump made more widely available — as “junk insurance” that doesn’t cover care for serious conditions or illnesses.
Entitlements Are Off-Limits
Both Medicaid and Medicare, the government health insurance programs that cover tens of millions of low-income, disabled, and older people, remain broadly popular with voters, said the Democratic pollster Celinda Lake. That makes it unlikely either party would pursue a platform that includes outright cuts to entitlements. But accusing an opponent of wanting to slash Medicare is a common, and often effective, campaign move.
Although Trump has said he wouldn’t cut Medicare spending, Democrats will likely seek to associate him with other Republicans who support constraining the program’s costs. Polls show that most voters oppose reducing any Medicare benefits, including by raising Medicare’s eligibility age from 65. However, raising taxes on people making more than $400,000 a year to shore up Medicare’s finances is one idea that won strong backing in a recent poll by The Associated Press and NORC Center for Public Affairs Research.
Brian Blase, a former Trump health adviser and the president of Paragon Health Institute, said Republicans, if they win more control of the federal government, should seek to lower spending on Medicare Advantage — through which commercial insurers provide benefits — to build on the program’s efficiencies and ensure it costs taxpayers less than the traditional program.
So far, though, Republicans, including Trump, have expressed little interest in such a plan. Some of them are clear-eyed about the perils of running on changing Medicare, which cost $829 billion in 2021 and is projected to consume nearly 18% of the federal budget by 2032.
“It’s difficult to have a frank conversation with voters about the future of the Medicare program,” said Lewis, the GOP pollster. “More often than not, it backfires. That conversation will have to happen right after a major election.”
Addiction Crisis
Many Americans have been touched by the growing opioid epidemic, which killed more than 112,000 people in the United States in 2023 — more than gun deaths and road fatalities combined. Rural residents and white adults are among the hardest hit.
Federal health officials have cited drug overdose deaths as a primary cause of the recent drop in U.S. life expectancy.
Republicans cast addiction as largely a criminal matter, associating it closely with the migration crisis at the U.S. southern border that they blame on Biden. Democrats have sought more funding for treatment and prevention of substance use disorders.
“This affects the family, the neighborhood,” said Blendon, the public opinion researcher.
Billions of dollars have begun to flow to states and local governments from legal settlements with opioid manufacturers and retailers, raising questions about how to best spend that money. But it isn’t clear that the crisis, outside the context of immigration, will emerge as a campaign issue.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I have a stuffy nose, how can I tell if it’s hay fever, COVID or something else?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hay fever (also called allergic rhinitis) affects 24% of Australians. Symptoms include sneezing, a runny nose (which may feel blocked or stuffy) and itchy eyes. People can also experience an itchy nose, throat or ears.
But COVID is still spreading, and other viruses can cause cold-like symptoms. So how do you know which one you’ve got?
Lysenko Andrii/Shutterstock Remind me, how does hay fever cause symptoms?
Hay fever happens when a person has become “sensitised” to an allergen trigger. This means a person’s body is always primed to react to this trigger.
Triggers can include allergens in the air (such as pollen from trees, grasses and flowers), mould spores, animals or house dust mites which mostly live in people’s mattresses and bedding, and feed on shed skin.
When the body is exposed to the trigger, it produces IgE (immunoglobulin E) antibodies. These cause the release of many of the body’s own chemicals, including histamine, which result in hay fever symptoms.
People who have asthma may find their asthma symptoms (cough, wheeze, tight chest or trouble breathing) worsen when exposed to airborne allergens. Spring and sometimes into summer can be the worst time for people with grass, tree or flower allergies.
However, animal and house dust mite symptoms usually happen year-round.
Ryegrass pollen is a common culprit. bangku ceria/Shutterstock What else might be causing my symptoms?
Hay fever does not cause a fever, sore throat, muscle aches and pains, weakness, loss of taste or smell, nor does it cause you to cough up mucus.
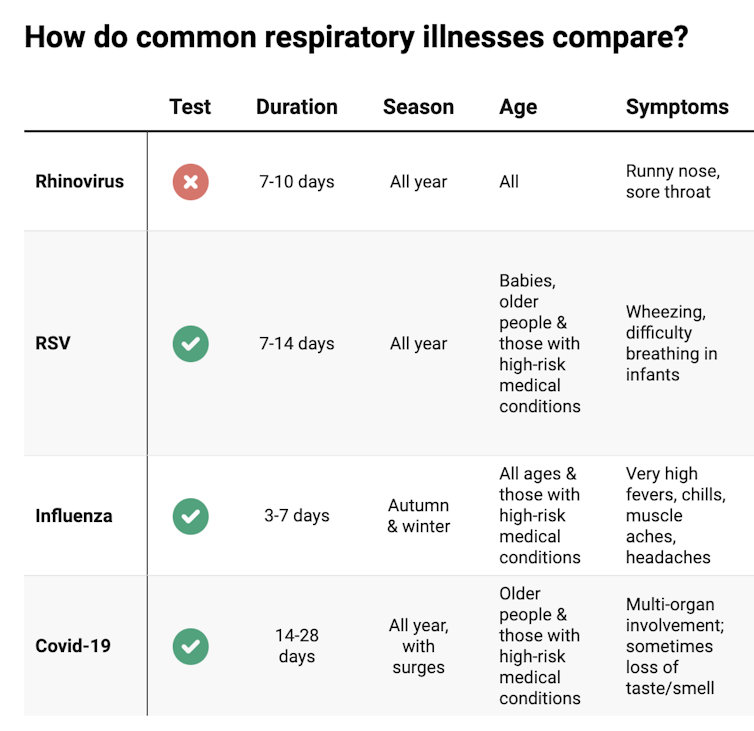
These symptoms are likely to be caused by a virus, such as COVID, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or a “cold” (often caused by rhinoviruses). These conditions can occur all year round, with some overlap of symptoms:
Natasha Yates/The Conversation COVID still surrounds us. RSV and influenza rates appear higher than before the COVID pandemic, but it may be due to more testing.
So if you have a fever, sore throat, muscle aches/pains, weakness, fatigue, or are coughing up mucus, stay home and avoid mixing with others to limit transmission.
People with COVID symptoms can take a rapid antigen test (RAT), ideally when symptoms start, then isolate until symptoms disappear. One negative RAT alone can’t rule out COVID if symptoms are still present, so test again 24–48 hours after your initial test if symptoms persist.
You can now test yourself for COVID, RSV and influenza in a combined RAT. But again, a negative test doesn’t rule out the virus. If your symptoms continue, test again 24–48 hours after the previous test.
If it’s hay fever, how do I treat it?
Treatment involves blocking the body’s histamine release, by taking antihistamine medication which helps reduce the symptoms.
Doctors, nurse practitioners and pharmacists can develop a hay fever care plan. This may include using a nasal spray containing a topical corticosteroid to help reduce the swelling inside the nose, which causes stuffiness or blockage.
Nasal sprays need to delivered using correct technique and used over several weeks to work properly. Often these sprays can also help lessen the itchy eyes of hay fever.
Drying bed linen and pyjamas inside during spring can lessen symptoms, as can putting a smear of Vaseline in the nostrils when going outside. Pollen sticks to the Vaseline, and gently blowing your nose later removes it.
People with asthma should also have an asthma plan, created by their doctor or nurse practitioner, explaining how to adjust their asthma reliever and preventer medications in hay fever seasons or on allergen exposure.
People with asthma also need to be alert for thunderstorms, where pollens can burst into tinier particles, be inhaled deeper in the lungs and cause a severe asthma attack, and even death.
What if it’s COVID, RSV or the flu?
Australians aged 70 and over and others with underlying health conditions who test positive for COVID are eligible for antivirals to reduce their chance of severe illness.
Most other people with COVID, RSV and influenza will recover at home with rest, fluids and paracetamol to relieve symptoms. However some groups are at greater risk of serious illness and may require additional treatment or hospitalisation.
For RSV, this includes premature infants, babies 12 months and younger, children under two who have other medical conditions, adults over 75, people with heart and lung conditions, or health conditions that lessens the immune system response.
For influenza, people at higher risk of severe illness are pregnant women, Aboriginal people, people under five or over 65 years, or people with long-term medical conditions, such as kidney, heart, lung or liver disease, diabetes and decreased immunity.
If you’re concerned about severe symptoms of COVID, RSV or influenza, consult your doctor or call 000 in an emergency.
If your symptoms are mild but persist, and you’re not sure what’s causing them, book an appointment with your doctor or nurse practitioner. Although hay fever season is here, we need to avoid spreading other serious infectious.
For more information, you can call the healthdirect helpline on 1800 022 222 (known as NURSE-ON-CALL in Victoria); use the online Symptom Checker; or visit healthdirect.gov.au or the Australian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy.
Deryn Thompson, Eczema and Allergy Nurse; Lecturer, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: