How community health screenings get more people of color vaccinated
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
U.S. preventive health screening rates dropped drastically at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. They have yet to go back to pre-pandemic levels, especially for Black and Latine communities.
Screenings, or routine medical checkups, are important ways to avoid and treat disease. They’re key to finding problems early on and can even help save people’s lives.
Community health workers say screenings are also a key to getting more people vaccinated. Screening fairs provide health workers the chance to build rapport and trust with the communities they serve, while giving their clients the chance to ask questions and get personalized recommendations according to their age, gender, and family history.
But systemic barriers to health care can often keep people from marginalized communities from accessing recommended screenings, exacerbating racial health disparities.
Public Good News spoke with Dr. Marie-Jose Francois, president and chief executive officer, and April Johnson, outreach coordinator, at the Center for Multicultural Wellness and Prevention (CMWP), in Central Florida, to learn how they promote the benefits of screening and leverage screenings for vaccination outreach among their diverse communities.
Here’s what they said.
[Editor’s note: This content has been edited for clarity and length.]
PGN: What is CMWP’s mission? How does vaccine outreach fit into the work you do in the communities you serve?
Dr. Marie-Jose Francois: Since 1995, our mission has been to enhance the health, wellness, and quality of life for diverse populations in Central Florida. At the beginning, our main focus was education, wellness, and screening for HIV/AIDS, and we continue to do case management for HIV screening and testing.
When the issue of COVID-19 came into the picture, we included COVID-19 information and education and stressed the importance of screening and receiving vaccinations during all of our outreach activities.
We try to meet the community where they are. Because there is so much misconception—and taboo—in regard to immunization.
April Johnson: So our job is to disperse accurate information. And how we do that is we go into rural communities. We build partnerships with local apartment complexes, hair salons, nail salons, laundromats, and provide a little community engagement, where people just hang out in different areas.
We build gatekeepers in those communities because you first have to get in there. You have to know that they trust you. Being in this field for about 30 years, I’ve [learned that] flexibility is key. Because sometimes you can’t get them from 9 to 5, or [from] Monday through Friday. So, you have to be very flexible in doing the outreach portion in order to get what you need.
I’ve built collaborations with senior citizen centers, community centers, schools, clinics, churches in Orlando and [in] different areas in Orange, Osceola, Seminole, and Lake counties. And we also partner with other community-based organizations to try to make it like a one-stop shop. So, partnership is a big thing.
PGN: How do you promote the importance of preventive screenings in the communities you serve?
M.F.: We try to make them view their health in a more comprehensive way, for them to understand the importance of screening. [That] self care is key, and for them to not be afraid.
We empower them to know what to ask when they go to the doctor. We ask them, ‘Do you know your status? Do you know your numbers?’
For example, if you go to the doctor, do you know your blood pressure? If you’re diabetic? Do you know your hemoglobin (A1C)? Do you know your cholesterol levels?
And now, [we also ask them]: ‘Have you received your flu shot for the year? Have you received all of your vaccine doses for COVID-19?’ We are even adding the mpox vaccine now, based on risk factors.
[We recommend they] ask their provider. For women, [we ask], ‘When do you need to have your mammogram?’ For the men, ‘You need to ask about your PSA and also about when and when to have your colonoscopy based on your age.’
We also try to explain to the community that the more they know their family history, the more they can engage in their own health. Because sometimes you have mom and dad who have a history of cancer. They have a history of diabetes or blood pressure—and they don’t talk to their children. So, we try to [recommend they] talk to their children. Your own family needs to know what’s going on so they can be proactive in their screenings.
PGN: What strategies or methods have you found most effective in getting people screened?
M.F.: Not everybody wants to be screened, not everybody wants to receive vaccines.
But with patience, just give them the facts. It goes right back to education, people have to be assured.
When you talk to them about COVID, or even HIV, you may hear them say, ‘Oh, I don’t see myself at risk for HIV.’ But we have to repeat to them that the more they get screened to make sure they’re OK, the better it is for them. ‘The more you use condoms, [the] safer it is for you.’
In Haitian culture, they listen to the radio. So we use the radio as a tool to educate and deliver information [to] get vaccinated, wash your hands. ‘If you’re coughing, cover your mouth. If you have a fever, wear your masks. Call your doctor.’
In our target population, we have people who have chronic conditions. We have people with HIV. So, we have to motivate them to receive the flu vaccine, to receive the COVID vaccine, to receive that RSV [vaccine], or to get the mpox vaccine. We have people with diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, depressed immune systems. We have people with lupus, we have people with sickle cell disease.
So, this is a way to [ensure that] whomever you’re talking to one-on-one understands the value of being safe.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Cherries’ Very Healthy Wealth Of Benefits!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cherry’s Health Benefits Simply Pop
We wrote recently about some of the health benefits of cherries, in our “This or That” challenge, pitting them against strawberries:
Strawberries vs Cherries – Which is Healthier?
We said there that we’d do a main feature on cherries sometime soon, so here it is!
Sweet & Sour
Cherries can be divided into sweet vs sour. These are mostly nutritionally similar, though sour ones do have some extra benefits.
Sweet and sour cherries are closely related but botanically different plants; it’s not simply a matter of ripeness (or preparation).
These can mostly be sorted into varieties of Prunus avium and Prunus cerasus, respectively:
Cherry Antioxidants: From Farm to Table
Sour cherry varieties include morello and montmorency, so look out for those names in particular when doing your grocery-shopping.
You may remember that it’s a good rule of thumb that foods that are more “bitter, astringent, or pungent” will tend to have a higher polyphenol content (that’s good):
Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Juiced up
Almost certainly for reasons of budget and convenience, as much as for standardization, most studies into the benefits of cherries have been conducted using concentrated cherry juice as a supplement.
At home, we need not worry so much about standardization, and our budget and convenience are ours to manage. To this end, as a general rule of thumb, whole fruits are pretty much always better than juice:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Antioxidant & anti-inflammatory!
Cherries are a very good source of antioxidants, and as such they also reduce inflammation, which in turn means ameliorating autoimmune diseases, from common things like arthritis…
…to less common things like gout:
Cherry Consumption and the Risk of Recurrent Gout Attacks
This can also be measured by monitoring uric acid metabolites:
Consumption of cherries lowers plasma urate in healthy women
Anti-diabetic effect
Most of the studies on this have been rat studies, and the human studies have been less “the effect of cherry consumption on diabetes” and more a matter of separate studies adding up to this conclusion in, the manner of “cherries have this substance, this substance has this effect, therefore cherries will have this effect”. You can see an example of this discussed over the course of 15 studies, here:
A Review of the Health Benefits of Cherries ← skip to section 2.2.1: “Cherry Intake And Diabetes”
In short, the jury is out on cherry juice, but eating cherries themselves (much like getting plenty of fruit in general) is considered good against diabetes.
Good for healthy sleep
For this one, the juice suffices (actual cherries are still recommended, but the juice gave clear significant positive results):
Pilot Study of the Tart Cherry Juice for the Treatment of Insomnia and Investigation of Mechanisms ← this was specifically in people over the age of 50
Importantly, it’s not that cherries have a sedative effect, but rather they support the body’s ability to produce melatonin adequately when the time comes:
Effect of tart cherry juice (Prunus cerasus) on melatonin levels and enhanced sleep quality
Post-exercise recovery
Cherries are well-known for boosting post-exercise recovery, though they may actually improve performance during exercise too, if eaten beforehand/
For example, these marathon-runners who averaged 13% compared to placebo control:
As for its recovery benefits, we wrote about this before:
How To Speed Up Recovery After A Workout (According To Actual Science)
Want to get some?
We recommend your local supermarket (or farmer’s market!), but if for any reason you prefer to take a supplement, here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post

Saunas: Health Benefits (& Caveats)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Heat Is On
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your (health-related) opinion on saunas, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:

- About 53% said it is “a healthful activity with many benefits”
- About 25% said it is “best avoided; I feel like I’m dying in there”
- About 12% said “it feels good and therefore can’t be all bad”
So what does the science say?
The heat of saunas carries a health risk: True or False?
False, generally speaking, for any practical purposes. Of course, anything in life comes with a health risk, but statistically speaking, your shower at home is a lot more dangerous than a sauna (risk of slipping with no help at hand).
It took a bit of effort to find a paper on the health risks of saunas, because all the papers on PubMed etc coming up for those keywords were initially papers with “reduces the risk of…”, i.e. ways in which the sauna is healthy.
However, we did find one:
❝Contraindications to sauna bathing include unstable angina pectoris, recent myocardial infarction, and severe aortic stenosis.
Sauna bathing is safe, however, for most people with coronary heart disease with stable angina pectoris or old myocardial infarction.
Very few acute myocardial infarctions and sudden deaths occur in saunas, but alcohol consumption during sauna bathing increases the risk of hypotension, arrhythmia, and sudden death, and should be avoided. ❞
~ Dr. Matti Hannuksela & Dr. Samer Ellahham
Source: Benefits and risks of sauna bathing
So, very safe for most people, safe even for most people with heart disease, but there are exceptions so check with your own doctor of course.
And drinking alcohol anywhere is bad for the health, but in a sauna it’s a truly terrible idea. As an aside, please don’t drink alcohol in the shower, either (risk of slipping with no help at hand, and this time, broken glass too).
On the topic of it being safe for most people’s hearts, see also:
Beneficial effects of sauna bathing for heart failure patients
As an additional note, those who have a particular sensitivity to the heat, may (again please check with your own doctor, as your case may vary) actually benefit from moderate sauna use, to reduce the cardiovascular strain that your body experiences during heatwaves (remember, you can get out of a sauna more easily than you can get out of a heatwave, so for many people it’s a lot easier to do moderation and improve thermoregulatory responses):
Sauna usage can bring many health benefits: True or False?
True! Again, at least for most people. As well as the above-discussed items, here’s one for mortality rates in healthy Finnish men:
Not only that, also…
❝The Finnish saunas have the most consistent and robust evidence regarding health benefits and they have been shown to decrease the risk of health outcomes such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, thromboembolism, dementia, and respiratory conditions; may improve the severity of musculoskeletal disorders, COVID-19, headache and flu, while also improving mental well-being, sleep, and longevity.
Finnish saunas may also augment the beneficial effects of other protective lifestyle factors such as physical activity.
The beneficial effects of passive heat therapies may be linked to their anti-inflammatory, cytoprotective and anti-oxidant properties and synergistic effects on neuroendocrine, circulatory, cardiovascular and immune function.
Passive heat therapies, notably Finnish saunas, are emerging as potentially powerful and holistic strategies to promoting health and extending the healthspan in all populations. ❞
~ Dr. Jari Laukkanen & Dr. Setor Kunutsor
(the repeated clarification of “Finnish sauna” is not a matter of fervent nationalism, by the way, but rather a matter of disambiguating it from Swedish sauna, which has some differences, most notably a lack of steam)
That reminds us: in Scandinavia, it is usual to use a sauna naked, and in Finland in particular, it is a common social activity amongst friends, coworkers, etc. In the US, many people are not so comfortable with nudity, and indeed, many places that provide saunas, may require the wearing of swimwear. But…
Just one problem: if you’re wearing swimwear because you’ve just been swimming in a pool, you now have chlorinated water soaked into your swimwear, which in the sauna, will become steam + chlorine gas. That’s not so good for your health (and is one reason, beyond tradition and simple normalization, for why swimwear is usually not permitted in Finnish saunas).
Want to read more?
You might like our previous main feature,
Turning Up The Heat Against Diabetes & Alzheimer’s ← you guessed it, sauna may be beneficial against these too
Take care!
Share This Post

Chicken or Fish – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing chicken to fish, we picked the fish.
Why?
To understand the choice, we have to start a bit earlier on the decision tree. For most people most of the time, when it comes to a diet high in plants or high in animals, the plant-centric diet will generally be best:
Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy?
When it comes to animal meats, red meat is a fairly uncontroversial first thing to strike off the list:
…with pork and some other meats not being much better.
But chicken? Poultry in general appears to be quite health-neutral. The jury is out and the science has mixed results, but the data is leaning towards “it’s probably fine”.
See for example this huge (n=29,682) study:
this same paper shows that…
❝higher intake of processed meat, unprocessed red meat, or poultry, but not fish, was significantly associated with a small increased risk of incident CVD, whereas higher intake of processed meat or unprocessed red meat, but not poultry or fish, was significantly associated with a small increased risk of all-cause mortality❞
So, since poultry isn’t significantly increasing all-cause mortality, and fish isn’t significantly increasing all-cause mortality or cardiovascular disease, fish comes out as the hands-down (fins-down?) winner.
One more (this time, easy) choice to make, though!
While fish in general (please, not fried, though!) is generally considered quite healthy, there is a big difference (more than you might think, and for reasons that are quite alarming), between…
Health Risks & Nutrition: Farmed Fish vs Wild-Caught
Enjoy, and take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts

Can We Drink To Good Health?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Can we drink to good health?
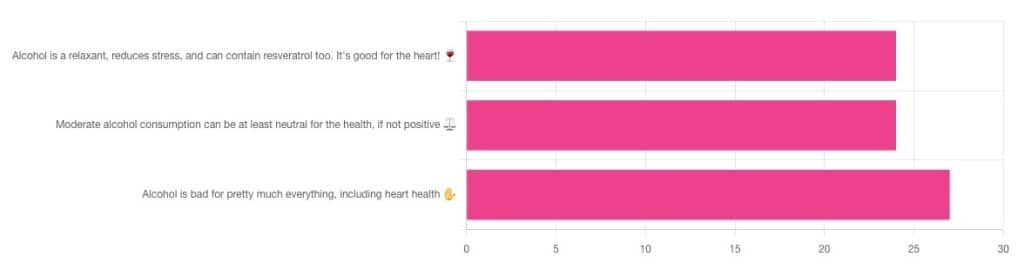
We asked you for your thoughts on alcohol and heart health, and we got quite an even spread of results!

If perchance that’s too tiny to read, the figures were:
- 32% voted for “Alcohol is a relaxant, reduces stress, and can contain resveratrol too. It’s good for the heart!”
- 32% voted for: “Moderate alcohol consumption can be at least neutral for the health, if not positive ⚖️”
- 36% voted for: “Alcohol is bad for pretty much everything, including heart health ✋”
One subscriber who voted for “Alcohol is a relaxant, reduces stress, and can contain resveratrol too. It’s good for the heart!” added the following thoughts:
❝While it isn’t necessary to consume alcohol, moderate amounts can be beneficial and contribute to well-being through social activity, celebrations, etc.❞
That’s an interesting point, and definitely many people do see alcohol that way! Of course, that does not mean that one will find no social activities, celebrations, etc, in parts of the world where alcohol consumption is uncommon. Indeed, in India, wedding parties where no alcohol is consumed can go on for days!
But, “we live in a society” and all that, and while we’re a health newsletter not a social issues newsletter, it’d be remiss of us to not acknowledge the importance of socialization for good mental health—and thus the rest of our health too.
So, if indeed all our friends and family drink alcohol, it can certainly make abstaining more of a challenge.
On that note, let’s take a moment to consider “The French Paradox” (an observation of a low prevalence of ischemic heart disease despite high intakes of saturated fat, a phenomenon accredited to the consumption of red wine).
As it happens, a comprehensive review in “Circulation”, a cardiovascular health journal, has suggested the French Paradox may not be so paradoxical after all.
Research suggests it has more to do with other lifestyle factors (and historic under-reporting of cardiovascular disease by French doctors), which would explain why Japan has lower rates of heart disease, despite drinking little wine, and more beer and spirits.
So, our subscriber’s note may not be completely without reason! It’s just about the party, not the alcohol.
One subscriber who voted for “Moderate alcohol consumption can be at least neutral for the health, if not positive ⚖️” wrote:
❝Keeping in mind, moderate means one glass of wine for women a day and two for men. Hard alcohol doesn’t have the same heart benefits as wine❞
That is indeed the guideline according to some health bodies!
In other places with different guiding advisory bodies, that’s been dropped down to one a day for everyone (the science may be universal, but how government institutions interpret that is not).
About that wine… Specifically, red wine, for its resveratrol content:
While there are polyphenols such as resveratrol in red wine that could boost heart health, there’s so little per glass that you may need 100–1000 glasses to get the dosage that provides benefits in mouse studies. If you’re not a mouse, you might even need more.
To this end, many people prefer resveratrol supplementation. ← link is to an example product, but there are plenty more so feel free to shop around
A subscriber who voted for “Alcohol is bad for pretty much everything, including heart health ✋” says:
❝New guidelines suggest 1 to 2 drinks a week are okay but the less the better.❞
If you haven’t heard these new guidelines, we’ll mention again: every government has its own official bodies and guidelines so perhaps your local guidelines differ, but for example here’s what that World Health Organization has to say (as of January this year):
WHO: No level of alcohol consumption is safe for our health
So, whom to believe? The governments who hopefully consider the welfare of their citizenry more important than the tax dollars from alcohol sales, or the World Health Organization?
It’s a tough one, but we’ll always err on the side of the science.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

One More Resource Against Osteoporosis!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Your Bones Were Made For Moving Too!
We know that to look after bone health, resistance training is generally what’s indicated. Indeed, we mentioned it yesterday, and we’ve talked about it before:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
We also know that if you have osteoporosis already, some exercises are a better or worse idea than others:
Osteoporosis & Exercises: Which To Do (And Which To Avoid)
However! New research suggests that also getting in your recommended 150 minutes per week of moderate exercise slows bone density loss.
The study by Dr. Tiina Savikangas et al. looked at 299 people in their 70s (just over half being women) and found that, over the course of a year, bone mineral density loss was inversely correlated with moderate exercise as recorded by an accelerometer (as found in most fitness-tracking wearables and smartphones).
In other words: those who got more minutes of exercise, kept more bone mineral density.
As well as monitoring bone mineral density, the study also looked at cross-sectional area, but that remained stable throughout.
As for how much is needed:
❝Even short bursts of activity can be significant for the skeleton, so we also looked at movement in terms of the number and intensity of individual impacts. For example, walking and running cause impacts of different intensities.
We found that impacts that were comparable to at least brisk walking were associated with better preservation of bone mineral density.❞
Read more: Impacts during everyday physical activity can slow bone loss ← pop-science source, interviewing the lead researcher
On which note, we’ve a small bone to pick…
As a small correction, the pop-science source says that the subjects’ ages ranged from 70 to 85 years; the paper, meanwhile, clearly shows that the age-range was 74.4±3.9 years (shown in the “Results” table), rounded to 74.4 ± 4 years, in the abstract. So, certainly no participant was older than 78 years and four months.
Why this matters: the age range itself may be critical or it might not, but what is important is that this highlights how we shouldn’t just believe figures cited in pop-science articles, and it’s always good to click through to the source!
This paper is a particularly fascinating read if you have time, because—unlike a lot of studies—they really took great care to note what exactly can and cannot be inferred from the data, and how and why.
Especially noteworthy was the diligence with which they either controlled for, or recognized that they could not control for, far more variables than most studies even bother to mention.
This kind of transparency is critical for good science, and we’d love to see more of it!
Want to apply this to your life?
Tracking minutes-of-movement is one of the things that fitness trackers are best at, so connect your favourite app (one of these days we’ll do a fitness tracker comparison article) and get moving!
And as for the other things that fitness trackers do? As it turns out, they do have their strengths and weaknesses, which are good to bear in mind:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Fully Present – by Dr. Susan Smalley and Diana Winston
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“The Science and the Art of…” tends to be a bit of a fuzzy obfuscation, but in this case, it’s accurate, especially in this presentation. The authors are, indeed, a scientist and an artist—and both practitioners, meeting in the middle.
As such, we get the clinical insights of a researcher and professor of psychiatry, and the grounded-yet-spiritual insights of an erstwhile Buddhist nun.
While the book is pop psychology in essence, the format is much more that of a textbook than a self-help book. Will it be useful for helping yourself anyway, though? Yes, absolutely, if you apply the information contained within.
Don’t be fooled into thinking that a textbook format makes it dry, though—the writing is very compelling, and you’ll find yourself turning pages eagerly. There’s no time like the present, after all!
Bottom line: if you find the scientific evidence-base for the usefulness of mindfulness appealing, but find a lot of guides a little fluffy, this one is perfectly balanced—and very well written, too.
Click here to check out Fully Present, bring yourself into the moment, always!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: