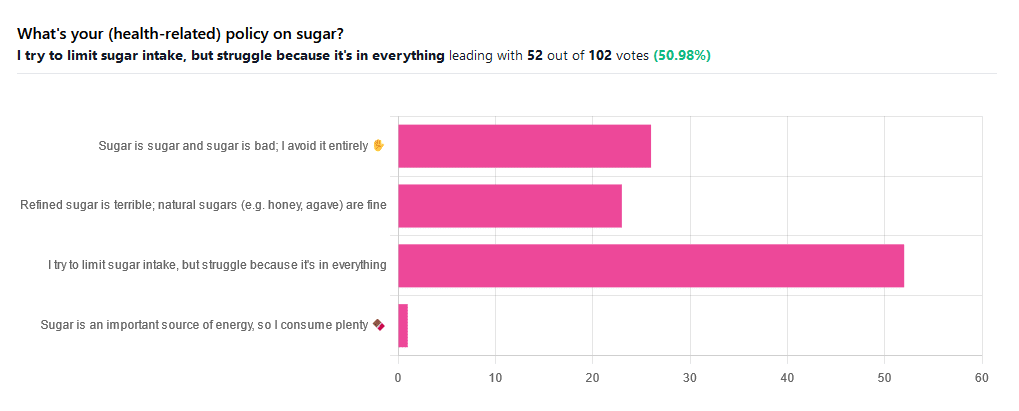Somatic Exercises For Nervous System Regulation – by Rose Kilian
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about the vagus nerve, its importance, and how to make use of it, but it’s easy to let it slip from one’s mind when it comes to exercises. This book fixes that!
The promised 35 exercises are quite a range, and are organized into sections:
- Revitalizing through breath
- Stress and tension release
- Spinal and postural health
- Mindfulness and grounding
- Movements for flexibility
- Graceful balance and focus
While it’s not necessary to do all 35 exercises, it’s recommended to do at least some from each section, to “cover one’s bases”, and enjoy the best of all worlds.
The exercises are drawn from many sources, but tai chi and yoga are certainly the most well-represented. Others, meanwhile, are straight from physiotherapy or are things one might expect to be advised at a neurology consultation.
Bottom line: if you’d like to take better care of your vagus nerve, the better for it to take care of you, this book can certainly help with that.
Click here to check out Somatic Exercises For Nervous System Regulation, and take care of yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose C’s

We asked you for your (health-related) policy on sugar. The trends were as follows:
- About half of all respondents voted for “I try to limit sugar intake, but struggle because it’s in everything”
- About a quarter of all respondents voted for “Refined sugar is terrible; natural sugars (e.g. honey, agave) are fine”
- About a quarter of all respondents voted for “Sugar is sugar and sugar is bad; I avoid it entirely”
- One (1) respondent voted for “Sugar is an important source of energy, so I consume plenty”
Writer’s note: I always forget to vote in these, but I’d have voted for “I try to limit sugar intake, but struggle because it’s in everything”.
Sometimes I would like to make my own [whatever] to not have the sugar, but it takes so much more time, and often money too.
So while I make most things from scratch (and typically spend about an hour cooking each day), sometimes store-bought is the regretfully practical timesaver/moneysaver (especially when it comes to condiments).
So, where does the science stand?
There has, of course, been a lot of research into the health impact of sugar.
Unfortunately, a lot of it has been funded by sugar companies, which has not helped. Conversely, there are also studies funded by other institutions with other agendas to push, and some of them will seek to make sugar out to be worse than it is.
So for today’s mythbusting overview, we’ve done our best to quality-control studies for not having financial conflicts of interest. And of course, the usual considerations of favoring high quality studies where possible Large sample sizes, good method, human subjects, that sort of thing.
Sugar is sugar and sugar is bad: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
- Sucrose is sucrose, and is generally bad.
- Fructose is fructose, and is worse.
Both ultimately get converted into glycogen (if not used immediately for energy), but for fructose, this happens mostly* in the liver, which a) taxes it b) goes very unregulated by the pancreas, causing potentially dangerous blood sugar spikes.
This has several interesting effects:
- Because fructose doesn’t directly affect insulin levels, it doesn’t cause insulin insensitivity (yay)
- Because fructose doesn’t directly affect insulin levels, this leaves hyperglycemia untreated (oh dear)
- Because fructose is metabolized by the liver and converted to glycogen which is stored there, it’s one of the main contributors to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (at this point, we’re retracting our “yay”)
Read more: Fructose and sugar: a major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
*”Mostly” in the liver being about 80% in the liver. The remaining 20%ish is processed by the kidneys, where it contributes to kidney stones instead. So, still not fabulous.
Fructose is very bad, so we shouldn’t eat too much fruit: True or False?
False! Fruit is really not the bad guy here. Fruit is good for you!
Fruit does contain fructose yes, but not actually that much in the grand scheme of things, and moreover, fruit contains (unless you have done something unnatural to it) plenty of fiber, which mitigates the impact of the fructose.
- A medium-sized apple (one of the most sugary fruits there is) might contain around 11g of fructose
- A tablespoon of high-fructose corn syrup can have about 27g of fructose (plus about 3g glucose)
Read more about it: Effects of high-fructose (90%) corn syrup on plasma glucose, insulin, and C-peptide in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and normal subjects
However! The fiber content (in fruit) mitigates the impact of the fructose almost entirely anyway.
And if you take fruits that are high in sugar and/but high in polyphenols, like berries, they now have a considerable net positive impact on glycemic health:
- Polyphenols and Glycemic Control
- Polyphenols and their effects on diabetes management: A review
- Dietary polyphenols as antidiabetic agents: Advances and opportunities
You may be wondering: what was that about “unless you have done something unnatural to it”?
That’s mostly about juicing. Juicing removes much (or all) of the fiber, and if you do that, you’re basically back to shooting fructose into your veins:
- Effect of Fruit Juice on Glucose Control and Insulin Sensitivity in Adults: A Meta-Analysis of 12 Randomized Controlled Trials
- Intake of Fruit, Vegetables, and Fruit Juices and Risk of Diabetes in Women
Natural sugars like honey, agave, and maple syrup, are healthier than refined sugars: True or False?
True… Sometimes, and sometimes marginally.
This is partly because of the glycemic index and glycemic load. The glycemic index scores tail off thus:
- table sugar = 65
- maple syrup = 54
- honey = 46
- agave syrup = 15
So, that’s a big difference there between agave syrup and maple syrup, for example… But it might not matter if you’re using a very small amount, which means it may have a high glycemic index but a low glycemic load.
Note, incidentally, that table sugar, sucrose, is a disaccharide, and is 50% glucose and 50% fructose.
The other more marginal health benefits come from that fact that natural sugars are usually found in foods high in other nutrients. Maple syrup is very high in manganese, for example, and also a fair source of other minerals.
But… Because of its GI, you really don’t want to be relying on it for your nutrients.
Wait, why is sugar bad again?
We’ve been covering mostly the more “mythbusting” aspects of different forms of sugar, rather than the less controversial harms it does, but let’s give at least a cursory nod to the health risks of sugar overall:
- Obesity and associated metabolic risk
- Main contributor to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Increased risk of heart disease
- Insulin resistance and diabetes risk
- Cellular aging (shortened telomeres)
- 95% increased cancer risk
That last one, by the way, was a huge systematic review of 37 large longitudinal cohort studies. Results varied depending on what, specifically, was being examined (e.g. total sugar, fructose content, sugary beverages, etc), and gave up to 200% increased cancer risk in some studies on sugary beverages, but 95% increased risk is a respectable example figure to cite here, pertaining to added sugars in foods.
And finally…
The 56 Most Common Names for Sugar (Some Are Tricky)
How many did you know?
Share This Post

What Most People Don’t Know About HIV
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What To Know About HIV This World AIDS Day

Yesterday, we asked you to engage in a hypothetical thought experiment with us, and putting aside for a moment any reason you might feel the scenario wouldn’t apply for you, asked:
❝You have unprotected sex with someone who, afterwards, conversationally mentions their HIV+ status. Do you…❞
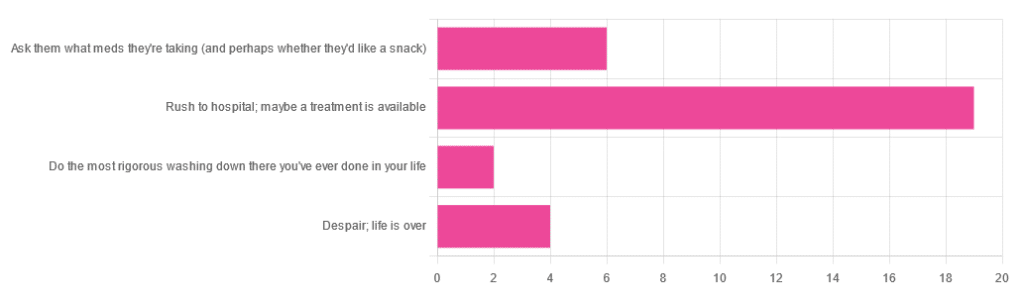
…and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses. Of those who responded…
- Just over 60% said “rush to hospital; maybe a treatment is available”
- Just under 20% said “ask them what meds they’re taking (and perhaps whether they’d like a snack)”
- Just over 10% said “despair; life is over”
- Two people said “do the most rigorous washing down there you’ve ever done in your life”
So, what does science say about it?
First, a quick note on terms
- HIV is the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. It does what it says on the tin; it gives humans immunodeficiency. Like many viruses that have become epidemic in humans, it started off in animals (called SIV, because there was no “H” involved yet), which were then eaten by humans, passing the virus to us when it one day mutated to allow that.
- It’s technically two viruses, but that’s beyond the scope of today’s article; for our purposes they are the same. HIV-1 is more virulent and infectious than HIV-2, and is the kind more commonly found in most of the world.
- AIDS is Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, and again, is what it sounds like. When a person is infected with HIV, then without treatment, they will often develop AIDS.
- Technically AIDS itself doesn’t kill people; it just renders people near-defenseless to opportunistic infections (and immune-related diseases such as cancer), since one no longer has a properly working immune system. Common causes of death in AIDS patients include cancer, influenza, pneumonia, and tuberculosis.
People who contract HIV will usually develop AIDS if untreated. Untreated life expectancy is about 11 years.
HIV/AIDS are only a problem for gay people: True or False?
False, unequivocally. Anyone can get HIV and develop AIDS.
The reason it’s more associated with gay men, aside from homophobia, is that since penetrative sex is more likely to pass it on…
- If a man penetrates a woman and passes on HIV, that woman will probably not go on to penetrate someone else
- If a man penetrates a man and passes on HIV, that man could go on to penetrate someone else—and so on
- This means that without any difference in safety practices or promiscuity, it’s going to spread more between men on average, by simple mathematics.
- This is why “men who have sex with men” is the generally-designated higher-risk category.
There is medication to cure HIV/AIDS: True or False?
False (though there have been individual case studies of gene treatments that may have cured people—time will tell).
But! There are medications that can prevent HIV from being a life-threatening problem:
- PrEP (Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis) is a medication that one can take in advance of potential exposure to HIV, to guard against it.
- This is a common choice for people aren’t sure about their partners’ statuses, or people working in risky environments.
- PEP (Post-Exposure Prophylaxis) is a medication that one can take after potential exposure to HIV, to “nip it in the bud”.
- Those of you who were rushing to hospital in our poll, this is what you’re rushing there for.
- ARVs (Anti-RetroVirals) are a class of medications (there are different options; we don’t have room to distinguish them) that reduce an HIV+ person’s viral load to undetectable levels.
- Those of you who were asking what meds your partner was taking, these will be those meds. Also, most of them are to be taken in the morning with food, so that’s what the snack was for.
If someone is HIV+, the risk of transmission in unprotected sex is high: True or False?
True or False, with false being the far more likely. It depends on their medications, and this is why you were asking. If someone is on ARVs and their viral load is undetectable (as is usual once someone has been on ARVs for 6 months), they cannot transmit HIV to you.
U=U is not a fancy new emoticon, it means “undetectable = untransmittable”, which is a mathematically true statement in the case of HIV viral loads.
See: NIH | HIV Undetectable=Untransmittable (U=U)
If you’re thinking “still sounds risky to me”, then consider this:
You are safer having unprotected sex with someone who is HIV+ and on ARVs with an undetectable viral load, than you are with someone you are merely assuming is HIV- (perhaps you assume it because “surely this polite blushing young virgin of a straight man won’t give me cooties” etc)
Note that even your monogamous partner of many decades could accidentally contract HIV due to blood contamination in a hospital or an accident at work etc, so it’s good practice to also get tested after things that involve getting stabbed with needles, cut in a risky environment, etc.
If you’re concerned about potential stigma associated with HIV testing, you can get kits online:
CDC | How do I find an HIV self-test?
(these are usually fingerprick blood tests, and you can either see the results yourself at home immediately, or send it in for analysis, depending on the kit)
If I get HIV, I will get AIDS and die: True or False?
False, assuming you get treatment promptly and keep taking it. So those of you who were at “despair; life is over” can breathe a sigh of relief now.
However, if you get HIV, it does mean you will have to take those meds every day for the rest of your (no reason it shouldn’t be long and happy) life.
So, HIV is definitely still something to avoid, because it’s not great to have to take a life-saving medication every day. For a little insight as to what that might be like:
HIV.gov | Taking HIV Medication Every Day: Tips & Challenges
(as you’ll see there, there are also longer-lasting injections available instead of daily pulls, but those are much less widely available)
Summary
Some quick take-away notes-in-a-nutshell:
- Getting HIV may have been a death sentence in the 1980s, but nowadays it’s been relegated to the level of “serious inconvenience”.
- Happily, it is very preventable, with PrEP, PEP, and viral loads so low that they can’t transmit HIV, thanks to ARVs.
- Washing will not help, by the way. Safe sex will, though!
- As will celibacy and/or monogamy in seroconcordant relationships, e.g. you both have the same (known! That means actually tested recently! Not just assumed!) HIV status.
- If you do get it, it is very manageable with ARVs, but prevention is better than treatment
- There is no certain cure—yet. Some people (small number of case studies) may have been cured already with gene therapy, but we can’t know for sure yet.
Want to know more? Check out:
Take care!
Share This Post

Black Tea or Green Tea – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing black tea to green tea, we picked the black tea.
Why?
It was close! Ultimately we picked the black tea as the “best all-rounder”.
Both teas are great for the health, insofar as tea in general is a) a very good way to hydrate (better absorption than plain water) and b) an excellent source of beneficial phytochemicals—mostly antioxidants of various kinds, but there’s a lot in there.
We did a run-down previously of the relative benefits of each of four kinds of tea (black, white, green, red):
Which Tea Is Best, By Science?
Which concluded in its final summary:
Black, white, green, and red teas all have their benefits, and ultimately the best one for you will probably be the one you enjoy drinking, and thus drink more of.
If trying to choose though, we offer the following summary:
- Black tea: best for total beneficial phytochemicals
- White tea:best for your oral health
- Green tea: best for your brain
- ❤️ Red tea: best if you want naturally caffeine-free
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts

Parsnips vs Potatoes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing parsnips to potatoes, we picked the parsnips.
Why?
To be more specific, we’re looking at russet potatoes, and in both cases we’re looking at cooked without fat or salt, skin on. In other words, the basic nutritional values of these plants in edible form, without adding anything. With this in mind, once we get to the root of things, there’s a clear winner:
Looking at the macros first, potatoes have more carbs while parsnips have more fiber. Potatoes do have more protein too, but given the small numbers involved when it comes to protein we don’t think this is enough of a plus to outweigh the extra fiber in the parsnips.
In the category of vitamins, again a champion emerges: parsnips have more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B9, C, E, and K, while potatoes have more of vitamins B3, B6, and choline. So, a 7:3 win for parsnips.
When it comes to minerals, parsnips have more calcium copper, manganese, selenium, and zinc, while potatoes have more iron and potassium. Potatoes do also have more sodium, but for most people most of the time, this is not a plus, healthwise. Disregarding the sodium, this category sees a 5:2 win for parsnips.
In short: as with most starchy vegetables, enjoy both in moderation if you feel so inclined, but if you’re picking one, then parsnips are the nutritionally best choice here.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Are Waist Trainers Just A Waste, And Are Posture Fixers A Quick Fix?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are Waist Trainers Just A Waste, And Are Posture Fixers A Quick Fix?

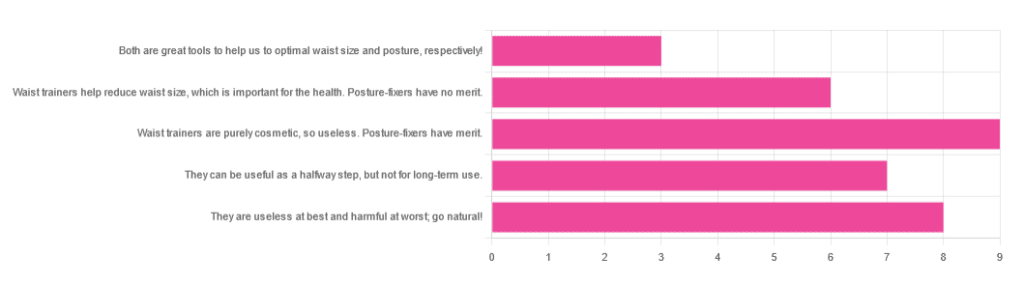
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on waist trainers and posture-fixing harnesses, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of results:
- The most popular response was “Waist trainers are purely cosmetic, so useless. Posture-fixers have merit”, with a little over a quarter of the votes.
- The least popular response was “Both are great tools to help us to optimal waist size and posture, respectively!”
- The other three answers each got a little under a quarter of the vote. In terms of discrete data, these were all 7±1, so basically, there was nothing in it.
The sample size was smaller than usual—perhaps the cluster of American holiday dates yesterday and today kept people busy! But, pressing on…
What does the science say?
Waist trainers are purely cosmetic, so, useless. True or False?
True, simply. Honestly, they’re not even that great for cosmetic purposes. They will indeed cinch in your middle, and this shape will be retained for a (very) short while after uncinching, because your organs have been squished inwards and may take a short while to get back to where they are supposed to be.
The American Board of Cosmetic Surgery may not be an unbiased source, but we’re struggling to find scientists who will even touch one of these, so, let’s see what these doctors have to say:
- Waist training can damage vital organs
- You will be slowly suffocating yourself
- Waist training simply doesn’t work
- You cannot drastically change your body shape with a piece of fabric*
Read: ABCS | 4 Reasons to Throw Your Waist Trainer in the Trash
*”But what about foot-binding?”—feet have many bones, whose growth can be physically restricted. Your waist has:
- organs: necessary! (long-term damage possible, but they’re not going away)
- muscles: slightly restrictable! (temporary restriction; no permanent change)
- fat: very squeezable! (temporary muffin; no permanent change)
Posture correctors have merit: True or False?
True—probably, and as a stepping-stone measure only.
The Ergonomics Health Association (a workplace health & safety organization) says:
❝Looking at the clinical evidence of posture correctors, we can say without a doubt that they do work, just not for everyone and not in the same way for all patients.❞
Source: Do Posture Correctors Work? Here’s What Our Experts Think
That’s not very compelling, so we looked for studies, and found… Not much, actually. However, what we did find supported the idea that “they probably do help, but we seriously need better studies with less bias”:
That is also not a compelling title, but here is where it pays to look at the studies and not just the titles. Basically, they found that the results were favorable to the posture-correctors—the science itself was just trash:
❝ The overall findings were that posture-correcting shirts change posture and subjectively have a positive effect on discomfort, energy levels and productivity.
The quality of the included literature was poor to fair with only one study being of good quality. The risk of bias was serious or critical for the included studies. Overall, this resulted in very low confidence in available evidence.❞
Since the benefit of posture correctors like this one is due to reminding the wearer to keep good posture, there is a lot more (good quality!) science for wearable biofeedback tech devices, such as this one:
Spine Cop: Posture Correction Monitor and Assistant
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Sesame Seeds vs Poppy Seeds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sesame seeds to poppy seeds, we picked the poppy seeds.
Why?
It’s close, and they’re both very respectable seeds!
In terms of macros, their protein content is the same, while poppy seeds have a little less fat and more carbs, as well as slightly more fiber. A moderate win for poppy seeds on this one.
About that fat… The lipid profiles here see poppy seeds with (as a percentage of total fat, so notwithstanding that poppy seeds have a little less fat overall) more polyunsaturated fat and less saturated fat. Another win for poppy seeds in this case.
In the category of vitamins, poppy seeds contain a lot more vitamins B5 & E while sesame seeds contain notably more vitamins B3, B6 and choline. Marginal win for sesame this time.
When it comes to minerals, poppy seeds contain rather more calcium, phosphorus, potassium, and manganese, while sesame seeds contain more copper, iron, and selenium. Marginal win for poppies here.
Note: it is reasonable to wonder about poppy seeds’ (especially unwashed poppy seeds’) opiate content. Indeed, they do contain opiates, and levels do vary, but to give you an idea: you’d need to eat, on average, 1kg (2.2lbs) of poppy seeds to get the same opiate content as a 30mg codeine tablet.
All in all, adding up the wins in each section, this one’s a moderate win for poppy seeds, but of course, enjoy both in moderation!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Chia Seeds vs Flax Seeds – Which is Healthier?
- Sunflower Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier?
- Hemp Seeds vs Flax Seeds – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: