Half of Australians in aged care have depression. Psychological therapy could help
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While many people maintain positive emotional wellbeing as they age, around half of older Australians living in residential aged care have significant levels of depression. Symptoms such as low mood, lack of interest or pleasure in life and difficulty sleeping are common.
Rates of depression in aged care appear to be increasing, and without adequate treatment, symptoms can be enduring and significantly impair older adults’ quality of life.
But only a minority of aged care residents with depression receive services specific to the condition. Less than 3% of Australian aged care residents access Medicare-subsidised mental health services, such as consultations with a psychologist or psychiatrist, each year.

Cochrane Australia
Instead, residents are typically prescribed a medication by their GP to manage their mental health, which they often take for several months or years. A recent study found six in ten Australian aged care residents take antidepressants.
While antidepressant medications may help many people, we lack robust evidence on whether they work for aged care residents with depression. Researchers have described “serious limitations of the current standard of care” in reference to the widespread use of antidepressants to treat frail older people with depression.
Given this, we wanted to find out whether psychological therapies can help manage depression in this group. These treatments address factors contributing to people’s distress and provide them with skills to manage their symptoms and improve their day-to-day lives. But to date researchers, care providers and policy makers haven’t had clear information about their effectiveness for treating depression among older people in residential aged care.
The good news is the evidence we published today suggests psychological therapies may be an effective approach for people living in aged care.
We reviewed the evidence
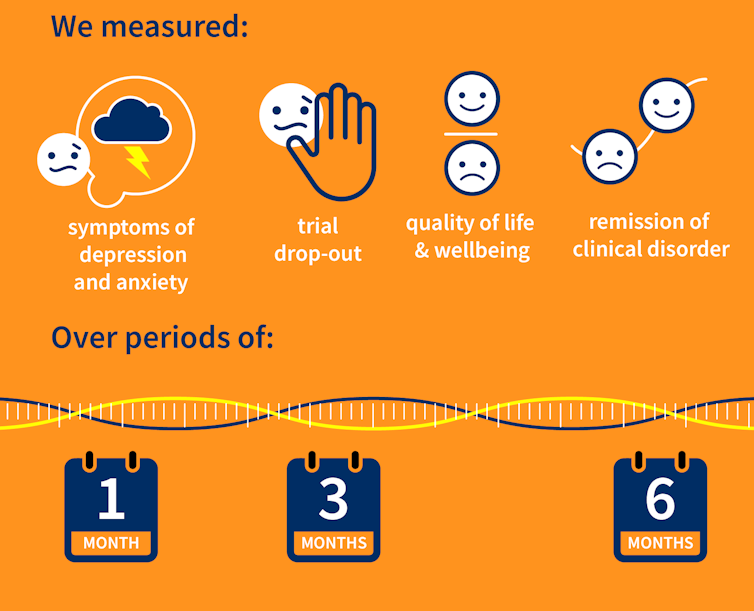
Our research team searched for randomised controlled trials published over the past 40 years that were designed to test the effectiveness of psychological therapies for depression among aged care residents 65 and over. We identified 19 trials from seven countries, including Australia, involving a total of 873 aged care residents with significant symptoms of depression.
The studies tested several different kinds of psychological therapies, which we classified as cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), behaviour therapy or reminiscence therapy.
CBT involves teaching practical skills to help people re-frame negative thoughts and beliefs, while behaviour therapy aims to modify behaviour patterns by encouraging people with depression to engage in pleasurable and rewarding activities. Reminiscence therapy supports older people to reflect on positive or shared memories, and helps them find meaning in their life history.
The therapies were delivered by a range of professionals, including psychologists, social workers, occupational therapists and trainee therapists.
Cochrane Australia
In these studies, psychological therapies were compared to a control group where the older people did not receive psychological therapy. In most studies, this was “usual care” – the care typically provided to aged care residents, which may include access to antidepressants, scheduled activities and help with day-to-day tasks.
In some studies psychological therapy was compared to a situation where the older people received extra social contact, such as visits from a volunteer or joining in a discussion group.
What we found
Our results showed psychological therapies may be effective in reducing symptoms of depression for older people in residential aged care, compared with usual care, with effects lasting up to six months. While we didn’t see the same effect beyond six months, only two of the studies in our review followed people for this length of time, so the data was limited.
Our findings suggest these therapies may also improve quality of life and psychological wellbeing.
Psychological therapies mostly included between two and ten sessions, so the interventions were relatively brief. This is positive in terms of the potential feasibility of delivering psychological therapies at scale. The three different therapy types all appeared to be effective, compared to usual care.
However, we found psychological therapy may not be more effective than extra social contact in reducing symptoms of depression. Older people commonly feel bored, lonely and socially isolated in aged care. The activities on offer are often inadequate to meet their needs for stimulation and interest. So identifying ways to increase meaningful engagement day-to-day could improve the mental health and wellbeing of older people in aged care.
Some limitations
Many of the studies we found were of relatively poor quality, because of small sample sizes and potential risk of bias, for example. So we need more high-quality research to increase our confidence in the findings.
Many of the studies we reviewed were also old, and important gaps remain. For example, we are yet to understand the effectiveness of psychological therapies for people from diverse cultural or linguistic backgrounds.
Separately, we need better research to evaluate the effectiveness of antidepressants among aged care residents.
What needs to happen now?
Depression should not be considered a “normal” experience at this (or any other) stage of life, and those experiencing symptoms should have equal access to a range of effective treatments. The royal commission into aged care highlighted that Australians living in aged care don’t receive enough mental health support and called for this issue to be addressed.
While there have been some efforts to provide psychological services in residential aged care, the unmet need remains very high, and much more must be done.
The focus now needs to shift to how to implement psychological therapies in aged care, by increasing the competencies of the aged care workforce, training the next generation of psychologists to work in this setting, and funding these programs in a cost-effective way.
Tanya Davison, Adjunct professor, Health & Ageing Research Group, Swinburne University of Technology and Sunil Bhar, Professor of Clinical Psychology, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Rewire Your OCD Brain – by Dr. Catherine Pittman & Dr. William Youngs
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
OCD is just as misrepresented in popular media as many other disorders, and in this case, it’s typically not “being a neat freak” or needing to alphabetize things, so much as having uncontrollable obsessive intrusive thoughts, and often in response to those, unwanted compulsions. This can come from unchecked spiralling anxiety, and/or PTSD, for example.
What Drs. Pittman & Young offer is an applicable set of solutions, to literally rewire the brain (insofar as synapses can be considered neural wires). Leveraging neuroplasticity to work with us rather than against us, the authors talk us through picking apart the crossed wires, and putting them back in more helpful ways.
This is not, by the way, a book of CBT, though it does touch on that too.
Mostly, the book explains—clearly and simply and sometimes with illustrations—what is going wrong for us neurologically, and how to neurologically change that.
Bottom line: whether you have OCD or suffer from anxiety or just need help dealing with obsessive thoughts, this book can help a lot in, as the title suggests, rewiring that.
Click here to check out Rewire Your OCD Brain, and banish obsessive thoughts!
Share This Post
-
What does it mean to be immunocompromised?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our immune systems help us fight off disease, but certain health conditions and medications can weaken our immune systems. People whose immune systems don’t work as well as they should are considered immunocompromised.
Read on to learn more about how the immune system works, what causes people to be immunocompromised, and how we can protect ourselves and the immunocompromised people around us from illness.
What is the immune system?
The immune system is a network of cells, organs, and chemicals that helps our bodies fight off infections caused by invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
Some important parts of the immune system include:
- White blood cells, which attack and kill germs that don’t belong inside our bodies.
- Lymph nodes, which help our bodies filter out germs.
- Antibodies, which help our bodies recognize invaders.
- Cytokines, which tell our immune cells what to do.
What causes people to be immunocompromised?
Some health conditions and medications can prevent our immune systems from functioning optimally, which makes us more vulnerable to infection. Health conditions that compromise the immune system fall into two categories: primary immunodeficiency and secondary immunodeficiency.
Primary immunodeficiency
People with primary immunodeficiency are born with genetic mutations that prevent their immune systems from functioning as they should. There are hundreds of types of primary immunodeficiencies. Since these mutations affect the immune system to varying degrees, some people may experience symptoms and get diagnosed early in life, while others may not know they’re immunocompromised until adulthood.
Secondary immunodeficiency
Secondary immunodeficiency happens later in life due to an infection like HIV, which weakens the immune system over time, or certain types of cancer, which prevent the body from producing enough white blood cells to adequately fight off infection. Studies have also shown that getting infected with COVID-19 may cause immunodeficiency by reducing our production of “killer T-cells,” which help fight off infections.
Sometimes necessary treatments for certain medical conditions can also cause secondary immunodeficiency. For example, people with autoimmune disorders—which cause the immune system to become overactive and attack healthy cells—may need to take immunosuppressant drugs to manage their symptoms. However, the drugs can make them more vulnerable to infection.
People who receive organ transplants may also need to take immunosuppressant medications for life to prevent their body from rejecting the new organ. (Given the risk of infection, scientists continue to research alternative ways for the immune system to tolerate transplantation.)
Chemotherapy for cancer patients can also cause secondary immunodeficiency because it kills the immune system’s white blood cells as it’s trying to kill cancer cells.
What are the symptoms of a compromised immune system?
People who are immunocompromised may become sick more frequently than others or may experience more severe or longer-term symptoms than others who contract the same disease.
Other symptoms of a compromised immune system may include fatigue; digestive problems like cramping, nausea, and diarrhea; and slow wound healing.
How can I find out if I’m immunocompromised?
If you think you may be immunocompromised, talk to your health care provider about your medical history, your symptoms, and any medications you take. Blood tests can determine whether your immune system is producing adequate proteins and cells to fight off infection.
I’m immunocompromised—how can I protect myself from infection?
If you’re immunocompromised, take precautions to protect yourself from illness.
Wash your hands regularly, wear a well-fitting mask around others to protect against respiratory viruses, and ensure that you’re up to date on recommended vaccines.
Immunocompromised people may need more doses of vaccines than people who are not immunocompromised—including COVID-19 vaccines. Talk to your health care provider about which vaccines you need.
How can I protect the immunocompromised people around me?
You never know who may be immunocompromised. The best way to protect immunocompromised people around you is to avoid spreading illnesses.
If you know you’re sick, isolate whenever possible. Wear a well-fitting mask around others—especially if you know that you’re sick or that you’ve been exposed to germs. Make sure you’re up to date on recommended vaccines, and practice regular hand-washing.
If you’re planning to spend time with someone who is immunocompromised, ask them what steps you can take to keep them safe.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Bananas vs Grapes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing bananas to grapes, we picked the bananas.
Why?
In terms of macros, bananas have more fiber and carbs, the ratio of which gives them the (very slightly) lower glycemic index. The difference in GI is marginal enough that it’d be tied on that point alone, but looking at total fiber figures, we say that having nearly 3x the fiber counts for a win here.
In the category of vitamins, bananas have more of vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, and choline, while grapes have more of vitamins A, B1, E, and K. Thus, an 8:4 win for bananas (and with considerable margins of difference, too).
When it comes to minerals, bananas have more copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium*, selenium, and zinc, while grapes have more calcium and manganese. Thus, a 6:2 win for bananas this time.
*because of some popular mentions in TV shows, people get hung up on bananas being a good source of potassium. Which they are, but they’re not even in the top 10 of fruits for potassium. Here’s a non-exhaustive list of fruits that have more potassium than bananas, portion for portion:
- Honeydew melon
- Papaya
- Mango
- Prunes
- Figs
- Dates
- Nectarine
- Cantaloupe melon
- Kiwi
- Orange
See also: The Other “Special K”: The Top Micronutrient Deficiency In High Blood Pressure
It’s worth mentioning polyphenols: black/red grapes do have more abundant polyphenols than bananas, and this is very much a point in their favor; however, we don’t think it’s enough to compensate for bananas beating them in every other category, so we still declare bananas the winner.
Of course, the solution to this dilemma is to enjoy both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Can We Drink To Good Health? ← while there are polyphenols such as resveratrol in red wine that per se would boost heart health, there’s so little per glass that you may need 100–1000 glasses per day to get the dosage that provides benefits in mouse studies.
If you’re not a mouse, you might even need more than that!
To this end, many people prefer resveratrol supplementation ← link is to an example product on Amazon, but there are plenty more so feel free to shop around 😎
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Welcoming the Unwelcome – by Pema Chödrön
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a lot in life that we don’t get to choose. Some things we have zero control over, like the weather. Others, we can only influence, like our health. Still yet others might give us an illusion of control, only to snatch it away, like a financial reversal or a bereavement.
How, then, to suffer those “slings and arrows of outrageous fortune” and come through the other side with an even mind and a whole heart?
Author Pema Chödrön has a guidebook for us.
Quick note: this book does not require the reader to have any particular religious faith to enjoy its benefits, but the author is a nun. As such, the way she describes things is generally within the frame of her religion. So that’s a thing to be aware of in case it might bother you. That said…
The largest part of her approach is one that psychology might describe as rational emotive behavioral therapy.
As such, we are encouraged to indeed “meet with triumph and disaster, and treat those two imposters just the same”, and more importantly, she lays out the tools for us to do so.
Does this mean not caring? No! Quite the opposite. It is expected, and even encouraged, that we might care very much. But: this book looks at how to care and remain compassionate, to others and to ourselves.
For Chödrön, welcoming the unwelcome is about de-toothing hardship by accepting it as a part of the complex tapestry of life, rather than something to be endured.
Bottom line: this book can greatly increase the reader’s ability to “go placidly amid the noise and haste” and bring peace to an often hectic world—starting with our own.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ageless Aging – by Maddy Dychtwald
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Maddy Dychtwald, herself 73, has spent her career working in the field of aging. She’s not a gerontologist or even a doctor, but she’s nevertheless been up-to-the-ears in the industry for decades, mostly as an organizer, strategist, facilitator, and so forth. As such, she’s had her finger on the pulse of the healthy longevity movement for a long time.
This book was written to address a problem, and the problem is: lifespan is increasing (especially for women), but healthspan has not been keeping up the pace.
In other words: people (especially women) are living longer, but often with more health problems along the way than before.
And mostly, it’s for lack of information (or sometimes: too much competing incorrect information).
Fortunately, information is something that a woman in Dychtwald’s position has an abundance of, because she has researchers and academics in many fields on speed-dial and happy to answer her questions (we get a lot of input from such experts throughout the book—which is why this book is so science-based, despite the author not being a scientist).
The book answers a lot of important questions beyond the obvious “what diet/exercise/sleep/supplements/etc are best for healthy aging” (spoiler: it’s quite consistent with the things we recommend here, because guess what, science is science), questions like how best to prepare for this that or the other, how to get a head start on preventative healthcare for some things, how to avoid being a burden to our families (one can argue that families are supposed to look after each other, but still, it’s a legitimate worry for many, and understandably so), and even how to balance the sometimes conflicting worlds of health and finances.
Unlike many authors, she also talks about the different kinds of aging, and tackles each of them separately and together. We love to see it!
Bottom line: this book is a very good one-stop-shop for all things healthy aging. It’s aimed squarely at women, but most advice goes for men the same too, aside from the section on hormones and such.
Click here to check out Ageless Aging, and plan your future!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Blueberries vs Banana – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing blueberries to banana, we picked the banana.
Why?
Surprise, that which is more expensive is not always commensurately more healthy! A lot of the price difference between bananas and blueberries comes down to:
- ease of transport (unripe bananas can be transported quite easily without too much risk of bruising; unripe blueberries can’t even be usefully picked)
- shelf-life (unripe bananas will take their time to ripen; the already-ripe blueberries will often go bad very quickly)
For this reason, frozen blueberries are a great option for budget-friendly berries. But, onto the comparisons:
In terms of macros, bananas have slightly more protein, carbs, and fiber, and the slightly lower glycemic index. Really, both are good, but by the numbers, bananas win.
When it comes to vitamins, blueberries have more of vitamins B1, C, E, and K, while bananas have more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, and choline. Another win for bananas, though of course we could quibble which vitamins are most likely to be not found in sufficient abundance in the rest of one’s diet, but as it is, we just compared the nutrients head-to-head without trying to guess the rest of someone’s diet.
In the category of minerals, blueberries have more calcium and manganese, while bananas have more copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. Another win for bananas.
As for polyphenols, this is where blueberries shine, with a lot more than bananas (difficult to calculate exactly due to variations, but, in the order of hundreds of times more). A win for blueberries this time.
Adding up the section gives us an overall win for bananas, but by all means enjoy either or both; perhaps even together!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Blueberry & Banana Collagen Baked Oats ← You will love this recipe! And… Good news for vegans/vegetarians: while we include an optional tablespoon of collagen powder in this recipe, the whole recipe is already geared around collagen synthesis, so it’s very collagen-boosting even with just the plants, providing collagen’s building blocks of protein, zinc, and vitamins C and D (your miraculous body will use these to assemble the collagen inside you).
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: