What you need to know about menopause
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Menopause describes the time when a person with ovaries has gone one full year without a menstrual period. Reaching this phase is a natural aging process that marks the end of reproductive years.
Read on to learn more about the causes, stages, signs, and management of menopause.
What causes menopause?
As you age, your ovaries begin making less estrogen and progesterone—two of the hormones involved in menstruation—and your fertility declines, causing menopause.
Most people begin perimenopause, the transitional time that ends in menopause, in their late 40s, but it can start earlier. On average, people in the U.S. experience menopause in their early 50s.
Your body may reach early menopause for a variety of reasons, including having an oophorectomy, a surgery that removes the ovaries. In this case, the hormonal changes happen abruptly rather than gradually.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer patients may also induce menopause, as these treatments may impact ovary function.
What are the stages of menopause?
There are three stages:
- Perimenopause typically occurs eight to 10 years before menopause happens. During this stage, estrogen production begins to decline and ovaries release eggs less frequently.
- Menopause marks the point when you have gone 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period. This means the ovaries have stopped releasing eggs and producing estrogen.
- Postmenopause describes the time after menopause. Once your body reaches this phase, it remains there for the rest of your life.
How do the stages of menopause affect fertility?
Your ovaries still produce eggs during perimenopause, so it is still possible to get pregnant during that stage. If you do not wish to become pregnant, continue using your preferred form of birth control throughout perimenopause.
Once you’ve reached menopause, you can no longer get pregnant naturally. People who would like to become pregnant after that may pursue in vitro fertilization (IVF) using eggs that were frozen earlier in life or donor eggs.
What are the signs of menopause?
Hormonal shifts result in a number of bodily changes. Signs you are approaching menopause may include:
- Hot flashes (a sudden feeling of warmth).
- Irregular menstrual periods, or unusually heavy or light menstrual periods.
- Night sweats and/or cold flashes.
- Insomnia.
- Slowed metabolism.
- Irritability, mood swings, and depression.
- Vaginal dryness.
- Changes in libido.
- Dry skin, eyes, and/or mouth.
- Worsening of premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
- Urinary urgency (a sudden need to urinate).
- Brain fog.
How can I manage the effects of menopause?
You may not need any treatment to manage the effects of menopause. However, if the effects are disrupting your life, your doctor may prescribe hormone therapy.
If you have had a hysterectomy, your doctor may prescribe estrogen therapy (ET), which may be administered via a pill, patch, cream, spray, or vaginal ring. If you still have a uterus, your doctor may prescribe estrogen progesterone/progestin hormone therapy (EPT), which is sometimes called “combination therapy.”
Both of these therapies work by replacing the hormones your body has stopped making, which can reduce the physical and mental effects of menopause.
Other treatment options may include antidepressants, which can help manage mood swings and hot flashes; prescription creams to alleviate vaginal dryness; or gabapentin, an anti-seizure medication that has been shown to reduce hot flashes.
Lifestyle changes may help alleviate the effects on their own or in combination with prescription medication. Those changes include:
- Incorporating movement into your daily life.
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol.
- Quitting smoking.
- Maintaining a regular sleep schedule.
- Practicing relaxation techniques, such as meditation.
- Consuming foods rich in plant estrogens, such as grains, beans, fruits, vegetables, and seeds.
- Seeking support from a therapist and from loved ones.
What health risks are associated with menopause?
Having lower levels of estrogen may put you at greater risk of certain health complications, including osteoporosis and coronary artery disease.
Osteoporosis occurs when bones lose their density, increasing the risk of fractures. A 2022 study found that the prevalence of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women was 82.2 percent.
Coronary artery disease occurs when the arteries that send blood to your heart become narrow or blocked with fatty plaque.
Estrogen therapy can reduce your risk of osteoporosis and coronary artery disease by preserving bone mass and maintaining cardiovascular function.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Studies of Parkinson’s disease have long overlooked Pacific populations – our work shows why that must change
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A form of Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in a gene known as PINK1 has long been labelled rare. But our research shows it’s anything but – at least for some populations.
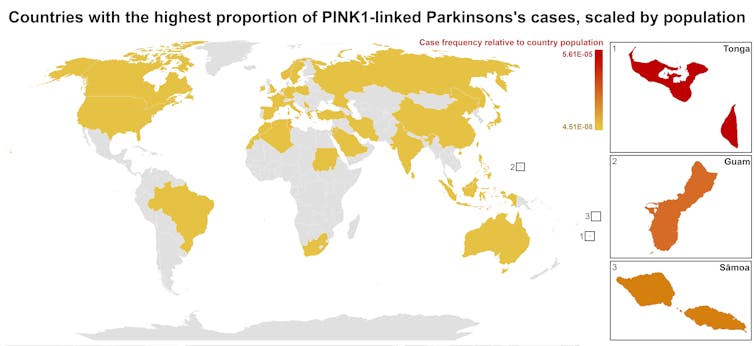
Our meta-analysis revealed that people in specific Polynesian communities have a much higher rate of PINK1-linked Parkinson’s than expected. This finding reshapes not only our understanding of who is most at risk, but also how soon symptoms may appear and what that might mean for treatment and testing.
Parkinson’s disease is often thought of as a single condition. In reality, it is better understood as a group of syndromes caused by different factors – genetic, environmental or a combination of both.
These varying causes lead to differences in disease patterns, progression and subsequent diagnosis. Recognising this distinction is crucial as it paves the way for targeted interventions and may even help prevent the disease altogether.
Shutterstock/sfam_photo Why we focus on PINK1-linked Parkinson’s
We became interested in this gene after a 2021 study highlighted five people of Samoan and Tongan descent living in New Zealand who shared the same PINK1 mutation.
Previously, this mutation had been spotted only in a few more distant places –Malaysia, Guam and the Philippines. The fact it appeared in people from Samoan and Tongan backgrounds suggested a historical connection dating back to early Polynesian migrations.
One person in 1,300 West Polynesians carries this mutation. This is a frequency well above what scientists usually classify as rare (below one in 2,200). This discovery means we may be overlooking entire communities in Parkinson’s research if we continue to assume PINK1-linked cases are uncommon.
This world map shows people in some Polynesian communities have a much higher rate of PINK1-linked Parkinson’s than the global population. Eden Yin, CC BY-SA Traditional understanding says PINK1-linked Parkinson’s is both rare and typically strikes younger people, mostly in their 30s or 40s, if they inherit two faulty copies of the gene. In other words, it’s considered a recessive condition, needing two matching puzzle pieces before the disease can unfold.
Our work challenges this view. We show that even one defective PINK1 gene can cause Parkinson’s at an average age of 43, much earlier than the typical onset after 65. That’s a significant departure from the standard belief that only people with two defective gene copies are at risk.
Why this matters for people with the disease
It’s not just genetics that challenge long-held views. Historically, PINK1-linked Parkinson’s was thought to lack some of the classic features of the disease, such as toxic clumps of alpha-synuclein protein.
In typical Parkinson’s, alpha-synuclein builds up in the brain, forming sticky clumps known as Lewy bodies. Our results, contrary to prior beliefs, show that alpha-synuclein pathology is present in 87.5% of PINK1 cases. This finding opens up a promising new avenue for future treatment development.
The biggest concern is early onset. PINK1-linked Parkinson’s can begin as early as 11 years old, although a more common starting point is around the mid-30s. This early onset means living longer with the disease, which can profoundly affect education, work opportunities and family life.
Current treatments (such as levodopa, a precursor of dopamine) help manage symptoms, but they’re not designed to address the root cause. If we know someone has a PINK1 mutation, scientists and clinicians can explore therapies for specific genetic pathways, potentially delivering relief beyond symptom management.
Sex differences add a layer of complexity
In Parkinson’s, generally, men are at higher risk and tend to develop symptoms earlier. However, our findings suggest the opposite pattern for PINK1-linked cases. Particularly, women with two defective copies of the gene experience onset earlier than men.
This highlights the need to consider sex-related factors in Parkinson’s research. Overlooking them risks missing key elements of the disease.
Genetic testing could be a game-changer for PINK1-linked Parkinson’s. Because it often appears earlier, doctors may not recognise it immediately, especially if they are more familiar with the common, later-onset form of Parkinson’s.
Early genetic testing could lead to a faster, more accurate diagnosis, allowing treatment to begin when interventions are most effective. It would help families understand how the disease is inherited, enabling relatives to get tested.
In some cases, where appropriate and culturally acceptable, embryo screening may be considered to prevent the passing of the faulty gene.
Knowing you have a PINK1 mutation could also make finding the right treatment more efficient. Instead of a lengthy trial-and-error process with different medications, doctors could use emerging therapies designed to target the underlying PINK1 mutation rather than relying on general Parkinson’s treatments meant for the broader population.
Addressing research gaps
These findings underscore how crucial it is to include diverse populations in health research.
Many communities, such as those in Samoa, Tonga and other Pacific nations, have had little to no involvement in global Parkinson’s genetics studies. This has created gaps in knowledge and real-world consequences for people who may not receive timely or accurate diagnoses.
Researchers, funding bodies and policymakers must prioritise projects beyond the usual focus on European or industrialised countries to ensure research findings and treatments are relevant to all affected populations.
To better diagnose and treat Parkinson’s, we need a more inclusive approach. Recognising that PINK1-linked Parkinson’s is not as rare as previously thought – and that genetics, sex differences and cultural factors all play a role – allows us to improve care for everyone.
By expanding genetic testing, refining treatments and ensuring research reflects the full spectrum of Parkinson’s, we can move closer to more precise diagnoses, targeted therapies and better support systems for all.
Victor Dieriks, Research Fellow in Health Sciences, University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau and Eden Paige Yin, PhD candidate in Health Sciences, University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Emperor’s New Klotho, Or Something More?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Unzipping The Genes Of Aging?
Klotho is an enzyme encoded in humans’ genes—specifically, in the KL gene.
It’s found throughout all living parts of the human body (and can even circulate about in its hormonal form, or come to rest in its membranaceous form), and its subgroups are especially found:
- α-klotho: in the brain
- β-klotho: in the liver
- γ-klotho: in the kidneys
Great! Why do we care?
Klotho, its varieties and variants, its presence or absence, are very important in aging.
Almost every biological manifestation of aging in humans has some klotho-related indicator; usually the decrease or mutation of some kind of klotho.
Which way around the cause and effect go has been the subject of much debate and research: do we get old because we don’t have enough klotho, or do we make less klotho because we’re getting old?
Of course, everything has to be tested per variant and per system, so that can take a while (punctuated by research scientists begging for more grants to do the next one). Given that it’s about aging, testing in humans would take an incredibly long while, so most studies so far have been rodent studies.
The general gist of the results of rodent studies is “reduced klotho hastens aging; increased klotho slows it”.
(this can be known by artificially increasing or decreasing the level of klotho expression, again something easier in mice as it is harder to arrange transgenic humans for the studies)
Here’s one example of many, of that vast set of rodent studies:
Suppression of Aging in Mice by the Hormone Klotho
Relevance for Alzheimer’s, and a science-based advice
A few years ago (2020), an Alzheimer’s study was undertaken; they noted that the famous apolipoprotein E4 (apoE4) allele is the strongest genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s, and that klotho may be another. FGF21 (secreted by the liver, mostly during fasting) binds to its own receptor (FGFR1) and its co-receptor β-klotho. Since this is a known neuroprotective factor, they wondered whether klotho itself may interact with β-amyloid (Aβ), and found:
❝Aβ can enhance the ability of klotho to draw FGF21 to regions of incipient neurodegeneration in AD❞
In other words: β-amyloid, the substance whose accumulation is associated with neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease, is a mediator in klotho bringing a known neuroprotective factor, FGF21, to the areas of neurodegeneration
In fewer words: klotho calls the firefighters to the scene of the fire
Read more: Alignment of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid β-peptide and klotho
The advice based on this? Consider practicing intermittent fasting, if that is viable for you, as it will give your liver more FGF21-secreting time, and the more FGF21, the more firefighters arrive when klotho sounds the alarm.
See also: Intermittent Fasting: What’s the truth?
…and while you’re at it:
Does intermittent fasting have benefits for our brain?
A more recent (2023) study with a slightly different (but connected) purpose, found results consistent with this:
Longevity factor klotho enhances cognition in aged nonhuman primates
…and, for that matter this (2023) study that found:
Associations between klotho and telomere biology in high stress caregivers
…which looks promising, but we’d like to see it repeated with a sounder method (they sorted caregiving into “high-stress” and “low-stress” depending on whether a child was diagnosed with ASD or not, which is by no means a reliable way of sorting this). They did ask for reported subjective stress levels, but to be more objective, we’d like to see clinical markers of stress (e.g. cortisol levels, blood pressure, heart rate changes, etc).
A very recent (April 2024) study found that it has implications for more aspects of aging—and this time, in humans (but using a population-based cohort study, rather than lab conditions):
Can I get it as a supplement?
Not with today’s technology and today’s paucity of clinical trials, you can’t. Maybe in the future!
However… The presence of senescent (old, badly copied, stumbling and staggering onwards when they should have been killed and eaten and recycled already) cells actively reduces klotho levels, which means that taking supplements that are senolytic (i.e., that kill those senescent cells) can increase serum klotho levels:
Orally-active, clinically-translatable senolytics restore α-Klotho in mice and humans
Ok, what can I take for that?
We wrote about a senolytic supplement that you might enjoy, recently:
Fisetin: The Anti-Aging Assassin
Want to know more?
If you have the time, Dr. Peter Attia interviews Dr. Dena Dubal (researcher in several of the above studies) here:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
PFAS Exposure & Cancer: The Numbers Are High
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
PFAS & Cancer Risk: The Numbers Are High
Image Credits Mount Sinai This is Dr. Maaike van Gerwen. Is that an MD or a PhD, you wonder? It’s both.
She’s also Director of Research in the Department of Otolaryngology at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, Scientific Director of the Program of Personalized Management of Thyroid Disease, and Member of the Institute for Translational Epidemiology and the Transdisciplinary Center on Early Environmental Exposures.
What does she want us to know?
She’d love for us to know about her latest research published literally today, about the risks associated with PFAS, such as the kind widely found in non-stick cookware:
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exposure and thyroid cancer risk
Dr. van Gerwen and her team tested this several ways, and the very short and simple version of the findings is that per doubling of exposure, there was a 56% increased rate of thyroid cancer diagnosis.
(The rate of exposure was not just guessed based on self-reports; it was measured directly from PFAS levels in the blood of participants)
- PFAS exposure can come from many sources, not just non-stick cookware, but that’s a “biggie” since it transfers directly into food that we consume.
- Same goes for widely-available microwaveable plastic food containers.
- Relatively less dangerous exposures include waterproofed clothing.
To keep it simple and look at the non-stick pans and microwavable plastic containers, doubling exposure might mean using such things every day vs every second day.
Practical take-away: PFAS may be impossible to avoid completely, but even just cutting down on the use of such products is already reducing your cancer risk.
Isn’t it too late, by this point in life? Aren’t they “forever chemicals”?
They’re not truly “forever”, but they do have long half-lives, yes.
See: Can we take the “forever” out of forever chemicals?
The half-lives of PFOS and PFOA in water are 41 years and 92 years, respectively.
In the body, however, because our body is constantly trying to repair itself and eliminate toxins, it’s more like 3–7 years.
That might seem like a long time, and perhaps it is, but the time will pass anyway, so might as well get started now, rather than in 3–7 years time!
Read more: National Academies Report Calls for Testing People With High Exposure to “Forever Chemicals”
What should we use instead?
In place of non-stick cookware, cast iron is fantastic. It’s not everyone’s preference, though, so you might also like to know that ceramic cookware is a fine option that’s functionally non-stick but without needing a non-stick coating. Check for PFAS-free status; they should advertise this.
In place of plastic microwaveable containers, Pyrex (or equivalent) glass dishes (you can get them with lids) are a top-tier option. Ceramic containers (without metallic bits!) are also safely microwaveable.
See also:
Here’s a List of Products with PFAS (& How to Avoid Them)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What Weston Price Got Right (And Wrong)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Weston Price: What Stood The Test of Time?
This is Dr. Weston Price, a dentist. You may guess from the photo, or perhaps already knew, his work is not new in 2023. We usually feature current health experts here, but we’re taking a day to do a blast from the past, because his ideas endure today, and inform a lot of people’s health views. So, he’s a good one to at least know about.
What was his deal?
Dr. Price (1870–1948) wanted to study focal infection theory—the idea that repairing root canals allowed bacterial infections that caused everything from heart disease to arthritis. His solution was that the teeth should be extracted instead.
This theory was popular in the 1920s, was challenged in the 1930s, ignored in the 1940s (the world was a bit busy), and by broad medical consensus anyway, rejected in the 1950s. But, while it was being challenged in the 1930s, Dr. Price decided to find more evidence for its support.
The result was his famous world tour of peoples living traditional lifestyles without the influence of “modern” diet. His findings, and the conclusions he drew from them, extended to far more than just dental health.
What did he find?
Dr. Price found that people living traditional lifestyles, with their traditional diets based on locally-sourced foods, had much better overall health. Of course, he was a dentist and not a general practitioner, so aside from examining their teeth, he largely relied on self-reported diagnoses of illness, or lack thereof.
In short: he found that people in places without modern medical institutions had fewer diagnoses of disease. From this, he concluded that incidence of disease was much lower.
There was also an unexamined element of survivorship bias—an undiagnosed disease is more likely to be fatal, and he questioned only living people, which skewed the stats rather. Nor did he examine infant mortality rate nor adult life expectancy, both of which were not great.
Was it all useless, then?
Actually no! He did hit upon some observations that have stood the test of time:
- He correctly concluded that modern diets with sugar and white flour were ruinous to the health.
- He correctly concluded that locally-sourced food, and grass-fed in the case of pastoral farming, tended to have much more nutritional value than the mass-produced results of intensive farming.
- He correctly concluded that many modern preservation methods robbed foods of their nutrients.
- He correctly concluded that many grains and seeds are more nutritions when fermented/soaked/sprouted.
About that “locally-sourced food”: the reason locally-sourced food tends to be more nutritious is that it has required less in the way of preservation for a long trip around the world, and will also tend to be fresher.
On the other hand, this does mean a lot of the foods that Dr. Price recommends are very much subject to availability. It may well be true that the Inuit people do not eat a lot of fruit and veg (which mostly do not grow there), but if you live in Nevada, maybe locally-sourced whale fat is just as difficult to find.
One person’s “this fatty organ meat contains the vitamin C we need” may be another person’s “that’s great; I have an apple tree in my garden though”.
Want to learn more?
Dr. Price’s most influential work is his magnum opus, “Nutrition and Physical Degeneration”. It’s a fascinating book in its historical context, but do be warned, it was written by a rich white man in 1939 and the writing is as racist as you might expect. Even when making favourable comparisons, the tone is very much “and here is what these savages are doing well”.
If you don’t fancy reading all that, here are two other sources about Weston Price’s work and conclusions, presented for balance:
- The Weston A. Price Foundation (Official Website)
- Weston Price’s Appalling Legacy (Science-Based Medicine.org)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Vaping: A Lot Of Hot Air?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Vaping: A Lot Of Hot Air?
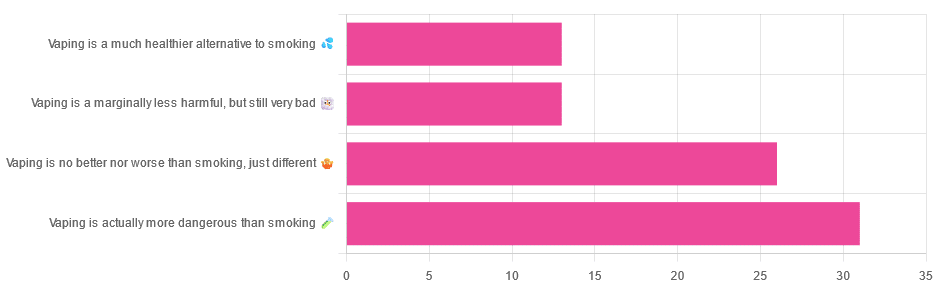
Yesterday, we asked you for your (health-related) opinions on vaping, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- A little over a third of respondents said it’s actually more dangerous than smoking
- A little under a third of respondents said it’s no better nor worse, just different
- A little over 10% of respondents said it’s marginally less harmful, but still very bad
- A little over 10% of respondents said it’s a much healthier alternative to smoking
So what does the science say?
Vaping is basically just steam inhalation, plus the active ingredient of your choice (e.g. nicotine, CBD, THC, etc): True or False?
False! There really are a lot of other chemicals in there.
And “chemicals” per se does not necessarily mean evil green glowing substances that a comicbook villain would market, but there are some unpleasantries in there too:
- Potential harmful health effects of inhaling nicotine-free shisha-pen vapor: a chemical risk assessment of the main components propylene glycol and glycerol
- Inflammatory and Oxidative Responses Induced by Exposure to Commonly Used e-Cigarette Flavoring Chemicals and Flavored e-Liquids without Nicotine
So, the substrate itself can cause irritation, and flavorings (with cinnamaldehyde, the cinnamon flavoring, being one of the worst) can really mess with our body’s inflammatory and oxidative responses.
Vaping can cause “popcorn lung”: True or False?
True and False! Popcorn lung is so-called after it came to attention when workers at a popcorn factory came down with it, due to exposure to diacetyl, a chemical used there.
That chemical was at that time also found in most vapes, but has since been banned in many places, including the US, Canada, the EU and the UK.
Vaping is just as bad as smoking: True or False?
False, per se. In fact, it’s recommended as a means of quitting smoking, by the UK’s famously thrifty NHS, that absolutely does not want people to be sick because that costs money:
Of course, the active ingredients (e.g. nicotine, in the assumed case above) will still be the same, mg for mg, as they are for smoking.
Vaping is causing a health crisis amongst “kids nowadays”: True or False?
True—it just happens to be less serious on a case-by-case basis to the risks of smoking.
However, it is worth noting that the perceived harmlessness of vapes is surely a contributing factor in their widespread use amongst young people—decades after actual smoking (thankfully) went out of fashion.
On the other hand, there’s a flipside to this:
Flavored vape restrictions lead to higher cigarette sales
So, it may indeed be the case of “the lesser of two evils”.
Want to know more?
For a more in-depth science-ful exploration than we have room for here…
BMJ | Impact of vaping on respiratory health
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I’m iron deficient. Which supplements will work best for me and how should I take them?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Iron deficiency is common and can be debilitating. It mainly affects women. One in three premenopausal women are low in iron compared to just 5% of Australian men. Iron deficiency particularly affects teenage girls, women who do a lot of exercise and those who are pregnant.
The body needs iron to make new red blood cells, and to support energy production, the immune system and cognitive function. If you’re low, you may experience a range of symptoms including fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, headache, irregular heartbeat and reduced concentration.
If a blood test shows you’re iron deficient, your doctor may recommend you start taking an oral iron supplement. But should you take a tablet or a liquid? With food or not? And when is the best time of day?
Here are some tips to help you work out how, when and what iron supplement to take.
LittlePigPower/Shutterstock How do I pick the right iron supplement?
The iron in your body is called “elemental iron”. Choosing the right oral supplement and dose will depend on how much elemental iron it has – your doctor will advise exactly how much you need.
The sweet spot is between 60-120 mg of elemental iron. Any less and the supplement won’t be effective in topping up your iron levels. Any higher and you risk gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhoea, cramping and stomach pain.
Low iron can especially affect people during pregnancy and women who do a lot of sport. Kamil Macniak/Shutterstock In Australia, iron salts are the most common oral supplements because they are cheap, effective and come in different delivery methods (tablets, capsules, liquid formulas). The iron salts you are most likely to find in your local chemist are ferrous sulfate (~20% elemental iron), ferrous gluconate (~12%) and ferrous fumarate (~33%).
These formulations all work similarly, so your choice should come down to dose and cost.
Many multivitamins may look like an iron supplement, but it’s important to note they usually have too little iron – usually less than 20 mg – to correct an iron deficiency.
Should I take tablets or liquid formulas?
Iron contained within a tablet is just as well absorbed as iron found in a liquid supplement. Choosing the right one usually comes down to personal preference.
The main difference is that liquid formulas tend to contain less iron than tablets. That means you might need to take more of the product to get the right dose, so using a liquid supplement could work out to be more expensive in the long term.
What should I eat with my iron supplement?
Research has shown you will absorb more of the iron in your supplement if you take it on an empty stomach. But this can cause more gastrointestinal issues, so might not be practical for everyone.
If you do take your supplement with meals, it’s important to think about what types of food will boost – rather than limit – iron absorption. For example, taking the supplement alongside vitamin C improves your body’s ability to absorb it.
Some supplements already contain vitamin C. Otherwise you could take the supplement along with a glass of orange juice, or other vitamin C-rich foods.
Taking your supplement alongside foods rich in vitamin C, like orange juice or kiwifruit, can help your body absorb the iron. Anete Lusina/Pexels On the other hand, tea, coffee and calcium all decrease the body’s ability to absorb iron. So you should try to limit these close to the time you take your supplement.
Should I take my supplement in the morning or evening?
The best time of day to take your supplement is in the morning. The body can absorb significantly more iron earlier in the day, when concentrations of hepcidin (the main hormone that regulates iron) are at their lowest.
Exercise also affects the hormone that regulates iron. That means taking your iron supplement after exercising can limit your ability to absorb it. Taking your supplement in the hours following exercise will mean significantly poorer absorption, especially if you take it between two and five hours after you stop.
Our research has shown if you exercise every day, the best time to take your supplement is in the morning before training, or immediately after (within 30 minutes).
My supplements are upsetting my stomach. What should I do?
If you experience gastrointestinal side effects such as diarrhoea or cramps when you take iron supplements, you may want to consider taking your supplement every second day, rather than daily.
Taking a supplement every day is still the fastest way to restore your iron levels. But a recent study has shown taking the same total dose can be just as effective when it’s taken on alternate days. For example, taking a supplement every day for three months works as well as every second day for six months. This results in fewer side effects.
Oral iron supplements can be a cheap and easy way to correct an iron deficiency. But ensuring you are taking the right product, under the right conditions, is crucial for their success.
It’s also important to check your iron levels prior to commencing iron supplementation and do so only under medical advice. In large amounts, iron can be toxic, so you don’t want to be consuming additional iron if your body doesn’t need it.
If you think you may be low on iron, talk to your GP to find out your best options.
Alannah McKay, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Sports Nutrition, Australian Catholic University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: