Severe Complications for Pregnant Veterans Nearly Doubled in the Last Decade, a GAO Report Finds
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ProPublica is a Pulitzer Prize-winning investigative newsroom. Sign up for The Big Story newsletter to receive stories like this one in your inbox.
Series: Post-Roe America:Abortion Access Divides the Nation
After the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade, ending nearly 50 years of federal protection for abortion, some states began enforcing strict abortion bans while others became new havens for the procedure. ProPublica is investigating how sweeping changes to reproductive health care access in America are affecting people, institutions and governments.
Over the past decade, the rate of veterans suffering severe pregnancy complications has risen dramatically, a new federal report found.
Veterans have raced to the hospital with dangerous infections, kidney failure, aneurysms or blood loss. They’ve required hysterectomies, breathing machines and blood transfusions to save their lives. Between 2011 and 2020, 13 veterans died after such complications.
The report found that among people getting health care benefits through the Department of Veterans Affairs, the rate of severe complications nearly doubled during that time, from about 93 per 10,000 hospitalizations in 2011 to just over 184 per 10,000 hospitalizations in 2020. Black veterans had the highest rates.
The report, which was put together by the Government Accountability Office, also made recommendations for reducing the problem, which focus on conducting more routine screenings throughout pregnancy and in the postpartum period.
“It is imperative that the VA help ensure veterans have the healthiest pregnancy outcomes possible,” the report said, highlighting the increasing number of veterans using the agency’s maternity benefits as well as the troublesome complication rates faced by Black women.
The report’s findings are an unfortunate trend, said Alyssa Hundrup, director of health care at the GAO. The office analyzed data on 40,000 hospitalizations related to deliveries paid for by the VA. It captures a time period before 21 states banned or greatly restricted abortion and the military was thrust into a political battle over whether it would pay for active service members to travel for abortion care if a pregnancy was a risk to their health.
Hundrup, who led the review, said the analysis included hospital records from days after delivery to a year postpartum. The report was mandated after Congress passed a law in 2021 that aimed to address the maternal health crisis among veterans. The law led to a $15 million investment in maternity care coordination programs for veterans.
The report recommended that the VA analyze and collect more data on severe complications as well as data on the mental health, race and ethnicity of veterans who experience complications to understand the causes behind the increase and the reasons for the disparity. The report also states that oversight is needed to ensure screenings are being completed.
Studies show there’s a connection between mental health conditions and pregnancy-related complications, VA officials said.
The report recommended expanding the screening questions that providers ask patients at appointments to glean more information about their mental health, including anxiety and PTSD symptoms. It urged the VA to review the data more regularly.
“You don’t know what you don’t measure,” Hundrup said in an interview with ProPublica.
The VA health system, which historically served a male population, does not provide maternity care at its facilities. Instead, the agency has outsourced maternity care. But when patients were treated by those providers, the VA failed to track whether they were getting screened for other health issues and mental health problems.
Officials hope the improved data collection will help the VA study underlying issues that may lead to complications. For example, do higher rates of anxiety have a connection to rates of high blood pressure in pregnant people?
VA officials are working with a maternal health review committee to monitor the data as it is gathered. The agency recently conducted its first review of data going back five years about pregnancy-related complications, said Dr. Amanda Johnson, acting head of the VA’s Office of Women’s Health, who is overseeing the implementation of the report’s recommendations.
The VA has created a dashboard to monitor pregnant veterans’ health outcomes. The VA’s data analysis team will also examine the impact of veterans’ ages on complications and whether they differ for people who live in urban and rural areas.
VA officials will begin to review mental health screenings conducted by maternal care coordinators in March. The coordinators advocate for veterans, helping them between health care visits, whether their providers are inside or outside the VA.
Johnson said that reducing racial and ethnic disparities is a priority for the agency. In 2018, ProPublica published “Lost Mothers,” a series that shed light on the country’s maternal health crisis. Studies have shown that in the general population, Black women are three times more likely than white women to die from pregnancy-related complications. While deaths made up only a small portion of the bad outcomes for Black veterans cited in the report, VA care could not spare them from elevated rates of severe complications. Johnson said the maternal health crisis also persists within the VA.
“There is a disparity,” Johnson said. “We are not immune to that.”
Research shows pregnant people who have used the VA’s coverage have higher rates of trauma and mental conditions that can increase their risks of complications and bad outcomes.
This may be because many people who join the military enter it having already faced trauma, said Dr. Laura Miller, a psychiatrist and the medical director of reproductive mental health at the VA.
She said veterans with PTSD have higher rates of complications such as preeclampsia, a potentially fatal condition related to high blood pressure, gestational diabetes and postpartum depression. If untreated during pregnancy, depression also increases the likelihood of preterm birth and lingering problems for babies.
Hundrup said she hopes this proactive work will improve maternal health.
“We want these numbers trending in the other direction,” Hundrup said.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Menopause Manifesto – by Dr. Jen Gunter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From the subtitle, you may wonder: with facts and feminism? Is this book about biology or sociology?
And the answer is: both. It’s about biology, principally, but without ignoring the context. We do indeed “live in a society”, and that affects everything from our healthcare options to what is expected of us as women.
So, as a warning: if you dislike science and/or feminism, you won’t like this book.
Dr. Jen Gunter, herself a gynaecologist, is here to arm us with science-based facts, to demystify an important part of life that is commonly glossed over.
She talks first about the what/why/when/how of menopause, and then delivers practical advice. She also talks about the many things we can (and can’t!) usefully do about symptoms we might not want, and how to look after our health overall in the context of menopause. We learn what natural remedies do or don’t work and/or can be actively harmful, and we learn the ins and outs of different hormone therapy options too.
Bottom line: no matter whether you are pre-, peri-, or post-menopausal, this is the no-BS guide you’ve been looking for. Same goes if you’re none of the above but spend any amount of time close to someone who is.
Share This Post
-
Ras El-Hanout
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a spice blend, and its name (رأس الحانوت) means “head of the shop”. It’s popular throughout Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia, but can often be found elsewhere. The exact blend will vary a little from place to place and even from maker to maker, but the general idea is the same. The one we provide here today is very representative (and for an example of its use, see our Marrakesh Sorghum Salad recipe!).
Note: we’re giving all the quantities in whole tsp today, to make multiplying/dividing easier if you want to make more/less ras el-hanout.
You will need
- 6 tsp ground ginger
- 6 tsp ground coriander seeds
- 4 tsp ground turmeric
- 4 tsp ground sweet cinnamon
- 4 tsp ground cumin
- 2 tsp ground allspice ← not a spice mix! This is the name of a spice!
- 2 tsp ground cardamom
- 2 tsp ground anise
- 2 tsp ground black pepper
- 1 tsp ground cayenne pepper
- 1 tsp ground cloves
Note: you may notice that garlic and salt are conspicuous by their absence. The reason for this is that they are usually added separately per dish, if desired.
Method
1) Mix them thoroughly
That’s it! Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- A Tale Of Two Cinnamons ← this is important, to understand why it’s critical to use sweet cinnamon specifically
- Sweet Cinnamon vs Regular Cinnamon – Which is Healthier? ← not even exaggerating; one is health-giving and the other contains a compound that is toxic at 01.mg/kg; guess which one is easier to find in the US and Canada?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Semaglutide for Weight Loss?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Semaglutide for weight loss?
Semaglutide is the new kid on the weight-loss block, but it’s looking promising (with some caveats!).
Most popularly by brand names Ozempic and Wegovy, it was first trialled to help diabetics*, and is now sought-after by the rest of the population too. So far, only Wegovy is FDA-approved for weight loss. It contains more semaglutide than Ozempic, and was developed specifically for weight loss, rather than for diabetes.
*Specifically: diabetics with type 2 diabetes. Because it works by helping the pancreas to make insulin, it’s of no help whatsoever to T1D folks, sadly. If you’re T1D and reading this though, today’s book of the day is for you!
First things first: does it work as marketed for diabetes?
It does! At a cost: a very common side effect is gastrointestinal problems—same as for tirzepatide, which (like semaglutide) is a GLP-1 agonist, meaning it works the same way. Here’s how they measure up:
- Head-to-head study: Effects of subcutaneous tirzepatide versus placebo or semaglutide on pancreatic islet function and insulin sensitivity in adults with type 2 diabetes
- Head-to-head systematic review: Semaglutide for the treatment of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of safety and efficacy outcomes
As you can see, both of them work wonders for pancreatic function and insulin sensitivity!
And, both of them were quite unpleasant for around 20% of participants:
❝Tirzepatide, oral and SC semaglutide has a favourable efficacy in treating T2DM. Gastrointestinal adverse events were highly recorded in tirzepatide, oral and SC semaglutide groups.❞
What about for weight loss, if not diabetic?
It works just the same! With just the same likelihood of gastro-intestinal unpleasantries, though. There’s a very good study that was done with 1,961 overweight adults; here it is:
Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity
The most interesting things here are the positive results and the side effects:
❝The mean change in body weight from baseline to week 68 was −14.9% in the semaglutide group as compared with −2.4% with placebo, for an estimated treatment difference of −12.4 percentage points (95% confidence interval [CI], −13.4 to −11.5; P<0.001).❞
In other words: if you take this, you’re almost certainly going to get something like 6x better weight loss results than doing the same thing without it.
❝Nausea and diarrhea were the most common adverse events with semaglutide; they were typically transient and mild-to-moderate in severity and subsided with time. More participants in the semaglutide group than in the placebo group discontinued treatment owing to gastrointestinal events (59 [4.5%] vs. 5 [0.8%])❞
~ ibid.
In other words: you have about a 3% chance of having unpleasant enough side effects that you don’t want to continue treatment (contrast this with the 20%ish chance of unpleasant side effects of any extent)!
Any other downsides we should know about?
If you stop taking it, weight regain is likely. For example, a participant in one of the above-mentioned studies who lost 22% of her body weight with the drug’s help, says:
❝Now that I am no longer taking the drug, unfortunately, my weight is returning to what it used to be. It felt effortless losing weight while on the trial, but now it has gone back to feeling like a constant battle with food. I hope that, if the drug can be approved for people like me, my [doctor] will be able to prescribe the drug for me in the future.❞
~ Jan, a trial participant at UCLH
Is it injection-only, or is there an oral option?
An oral option exists, but (so far) is on the market only in the form of Rybelsus, another (slightly older) drug containing semaglutide, and it’s (so far) only FDA-approved for diabetes, not for weight loss. See:
A new era for oral peptides: SNAC and the development of oral semaglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes ← for the science
FDA approves first oral GLP-1 treatment for type 2 diabetes ← For the FDA statement
Where can I get these?
Availability and prescribing regulations vary by country (because the FDA’s authority stops at the US borders), but here is the website for each of them if you’d like to learn more / consider if they might help you:
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Under Pressure: A Guide To Controlling High Blood Pressure – by Dr. Frita Fisher
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hypertension kills a lot of people, and does so with little warning—it can be asymptomatic before it gets severe enough to cause harm, and once it causes harm, well, one heart attack or stroke is already one too many.
Aimed more squarely at people in the 35–45 danger zone (young enough to not be getting regular blood pressure checks, old enough that it may have been building up for decades), this is a very good primer on blood pressure, factors affecting it, what goes wrong, what to do about it, and how to make a good strategy for managing it for life.
The style is easy-reading, making this short (91 pages) book a very quick read, but an informative one.
Bottom line: if you are already quite knowledgeable about blood pressure and blood pressure management, this one’s probably not for you. But if you’re in the category of “what do those numbers mean again?”, then this is a very handy book to have, to get you up to speed so that you can handle things as appropriate.
Click here to check out Under Pressure, and get/keep yours under control!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Alpha, beta, theta: what are brain states and brain waves? And can we control them?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s no shortage of apps and technology that claim to shift the brain into a “theta” state – said to help with relaxation, inward focus and sleep.
But what exactly does it mean to change one’s “mental state”? And is that even possible? For now, the evidence remains murky. But our understanding of the brain is growing exponentially as our methods of investigation improve.
Brain-measuring tech is evolving
Currently, no single approach to imaging or measuring brain activity gives us the whole picture. What we “see” in the brain depends on which tool we use to “look”. There are myriad ways to do this, but each one comes with trade-offs.
We learnt a lot about brain activity in the 1980s thanks to the advent of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Eventually we invented “functional MRI”, which allows us to link brain activity with certain functions or behaviours in real time by measuring the brain’s use of oxygenated blood during a task.
We can also measure electrical activity using EEG (electroencephalography). This can accurately measure the timing of brain waves as they occur, but isn’t very accurate at identifying which specific areas of the brain they occur in.
Alternatively, we can measure the brain’s response to magnetic stimulation. This is very accurate in terms of area and timing, but only as long as it’s close to the surface.
What are brain states?
All of our simple and complex behaviours, as well as our cognition (thoughts) have a foundation in brain activity, or “neural activity”. Neurons – the brain’s nerve cells – communicate by a sequence of electrical impulses and chemical signals called “neurotransmitters”.
Neurons are very greedy for fuel from the blood and require a lot of support from companion cells. Hence, a lot of measurement of the site, amount and timing of brain activity is done via measuring electrical activity, neurotransmitter levels or blood flow.
We can consider this activity at three levels. The first is a single-cell level, wherein individual neurons communicate. But measurement at this level is difficult (laboratory-based) and provides a limited picture.
As such, we rely more on measurements done on a network level, where a series of neurons or networks are activated. Or, we measure whole-of-brain activity patterns which can incorporate one or more so-called “brain states”.
According to a recent definition, brain states are “recurring activity patterns distributed across the brain that emerge from physiological or cognitive processes”. These states are functionally relevant, which means they are related to behaviour.
Brain states involve the synchronisation of different brain regions, something that’s been most readily observed in animal models, usually rodents. Only now are we starting to see some evidence in human studies.
Various kinds of states
The most commonly-studied brain states in both rodents and humans are states of “arousal” and “resting”. You can picture these as various levels of alertness.
Studies show environmental factors and activity influence our brain states. Activities or environments with high cognitive demands drive “attentional” brain states (so-called task-induced brain states) with increased connectivity. Examples of task-induced brain states include complex behaviours such as reward anticipation, mood, hunger and so on.
In contrast, a brain state such as “mind-wandering” seems to be divorced from one’s environment and tasks. Dropping into daydreaming is, by definition, without connection to the real world.
We can’t currently disentangle multiple “states” that exist in the brain at any given time and place. As mentioned earlier, this is because of the trade-offs that come with recording spatial (brain region) versus temporal (timing) brain activity.
Brain states vs brain waves
Brain state work can be couched in terms such as alpha, delta and so forth. However, this is actually referring to brain waves which specifically come from measuring brain activity using EEG.
EEG picks up on changing electrical activity in the brain, which can be sorted into different frequencies (based on wavelength). Classically, these frequencies have had specific associations:
- gamma is linked with states or tasks that require more focused concentration
- beta is linked with higher anxiety and more active states, with attention often directed externally
- alpha is linked with being very relaxed, and passive attention (such as listening quietly but not engaging)
- theta is linked with deep relaxation and inward focus
- and delta is linked with deep sleep.
Brain wave patterns are used a lot to monitor sleep stages. When we fall asleep we go from drowsy, light attention that’s easily roused (alpha), to being relaxed and no longer alert (theta), to being deeply asleep (delta).
Can we control our brain states?
The question on many people’s minds is: can we judiciously and intentionally influence our brain states?
For now, it’s likely too simplistic to suggest we can do this, as the actual mechanisms that influence brain states remain hard to detangle. Nonetheless, researchers are investigating everything from the use of drugs, to environmental cues, to practising mindfulness, meditation and sensory manipulation.
Controversially, brain wave patterns are used in something called “neurofeedback” therapy. In these treatments, people are given feedback (such as visual or auditory) based on their brain wave activity and are then tasked with trying to maintain or change it. To stay in a required state they may be encouraged to control their thoughts, relax, or breathe in certain ways.
The applications of this work are predominantly around mental health, including for individuals who have experienced trauma, or who have difficulty self-regulating – which may manifest as poor attention or emotional turbulence.
However, although these techniques have intuitive appeal, they don’t account for the issue of multiple brain states being present at any given time. Overall, clinical studies have been largely inconclusive, and proponents of neurofeedback therapy remain frustrated by a lack of orthodox support.
Other forms of neurofeedback are delivered by MRI-generated data. Participants engaging in mental tasks are given signals based on their neural activity, which they use to try and “up-regulate” (activate) regions of the brain involved in positive emotions. This could, for instance, be useful for helping people with depression.
Another potential method claimed to purportedly change brain states involves different sensory inputs. Binaural beats are perhaps the most popular example, wherein two different wavelengths of sound are played in each ear. But the evidence for such techniques is similarly mixed.
Treatments such as neurofeedback therapy are often very costly, and their success likely relies as much on the therapeutic relationship than the actual therapy.
On the bright side, there’s no evidence these treatment do any harm – other than potentially delaying treatments which have been proven to be beneficial.
Susan Hillier, Professor: Neuroscience and Rehabilitation, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Viruses aren’t always harmful. 6 ways they’re used in health care and pest control
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We tend to just think of viruses in terms of their damaging impacts on human health and lives. The 1918 flu pandemic killed around 50 million people. Smallpox claimed 30% of those who caught it, and survivors were often scarred and blinded. More recently, we’re all too familiar with the health and economic impacts of COVID.
But viruses can also be used to benefit human health, agriculture and the environment.
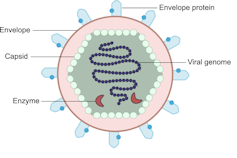
Viruses are comparatively simple in structure, consisting of a piece of genetic material (RNA or DNA) enclosed in a protein coat (the capsid). Some also have an outer envelope.
Viruses get into your cells and use your cell machinery to copy themselves.
Here are six ways we’ve harnessed this for health care and pest control.1. To correct genes
Viruses are used in some gene therapies to correct malfunctioning genes. Genes are DNA sequences that code for a particular protein required for cell function.
If we remove viral genetic material from the capsid (protein coat) we can use the space to transport a “cargo” into cells. These modified viruses are called “viral vectors”.
Viruses consist of a piece of RNA or DNA enclosed in a protein coat called the capsid.
DEXiViral vectors can deliver a functional gene into someone with a genetic disorder whose own gene is not working properly.
Some genetic diseases treated this way include haemophilia, sickle cell disease and beta thalassaemia.
2. Treat cancer
Viral vectors can be used to treat cancer.
Healthy people have p53, a tumour-suppressor gene. About half of cancers are associated with the loss of p53.
Replacing the damaged p53 gene using a viral vector stops the cancerous cell from replicating and tells it to suicide (apoptosis).
Viral vectors can also be used to deliver an inactive drug to a tumour, where it is then activated to kill the tumour cell.
This targeted therapy reduces the side effects otherwise seen with cytotoxic (cell-killing) drugs.
We can also use oncolytic (cancer cell-destroying) viruses to treat some types of cancer.
Tumour cells have often lost their antiviral defences. In the case of melanoma, a modified herpes simplex virus can kill rapidly dividing melanoma cells while largely leaving non-tumour cells alone.
3. Create immune responses
Viral vectors can create a protective immune response to a particular viral antigen.
One COVID vaccine uses a modified chimp adenovirus (adenoviruses cause the common cold in humans) to transport RNA coding for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein into human cells.
The RNA is then used to make spike protein copies, which stimulate our immune cells to replicate and “remember” the spike protein.
Then, when you are exposed to SARS-CoV-2 for real, your immune system can churn out lots of antibodies and virus-killing cells very quickly to prevent or reduce the severity of infection.
4. Act as vaccines
Viruses can be modified to act directly as vaccines themselves in several ways.
We can weaken a virus (for an attenuated virus vaccine) so it doesn’t cause infection in a healthy host but can still replicate to stimulate the immune response. The chickenpox vaccine works like this.
The Salk vaccine for polio uses a whole virus that has been inactivated (so it can’t cause disease).
Others use a small part of the virus such as a capsid protein to stimulate an immune response (subunit vaccines).
An mRNA vaccine packages up viral RNA for a specific protein that will stimulate an immune response.
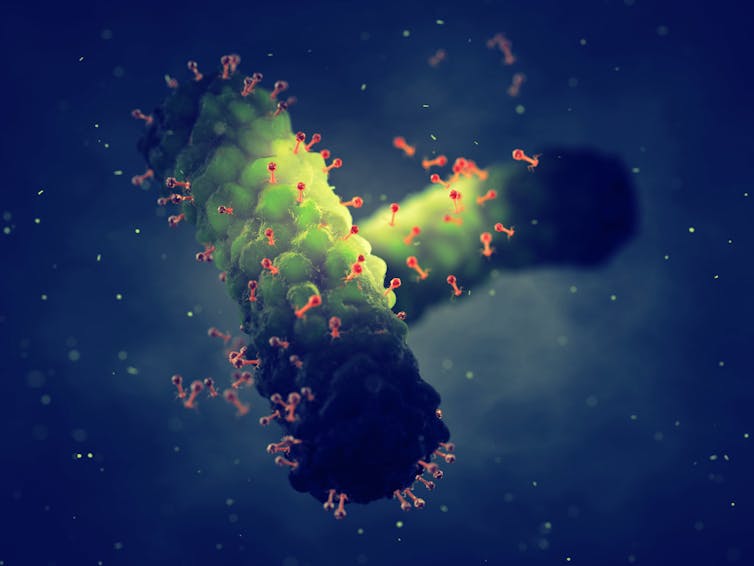
5. Kill bacteria
Viruses can – in limited situations in Australia – be used to treat antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections.
Bacteriophages are viruses that kill bacteria. Each type of phage usually infects a particular species of bacteria.
Unlike antibiotics – which often kill “good” bacteria along with the disease-causing ones – phage therapy leaves your normal flora (useful microbes) intact.
Bacteriophages (red) are viruses that kill bacteria (green).
Shutterstock6. Target plant, fungal or animal pests
Viruses can be species-specific (infecting one species only) and even cell-specific (infecting one type of cell only).
This occurs because the proteins viruses use to attach to cells have a shape that binds to a specific type of cell receptor or molecule, like a specific key fits a lock.
The virus can enter the cells of all species with this receptor/molecule. For example, rabies virus can infect all mammals because we share the right receptor, and mammals have other characteristics that allow infection to occur whereas other non-mammal species don’t.
When the receptor is only found on one cell type, then the virus will infect that cell type, which may only be found in one or a limited number of species. Hepatitis B virus successfully infects liver cells primarily in humans and chimps.
We can use that property of specificity to target invasive plant species (reducing the need for chemical herbicides) and pest insects (reducing the need for chemical insecticides). Baculoviruses, for example, are used to control caterpillars.
Similarly, bacteriophages can be used to control bacterial tomato and grapevine diseases.
Other viruses reduce plant damage from fungal pests.
Myxoma virus and calicivirus reduce rabbit populations and their environmental impacts and improve agricultural production.
Just like humans can be protected against by vaccination, plants can be “immunised” against a disease-causing virus by being exposed to a milder version.
Thea van de Mortel, Professor, Nursing, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Griffith University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: