Stay off My Operating Table – by Dr. Philip Ovadia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
With heart disease as the #1 killer worldwide, and 88% of adults being metabolically unhealthy (leading cause of heart disease), this is serious!
Rather than taking a “quick fix” advise-and-go approach, Dr. Ovadia puts the knowledge and tools in our hands to do better in the long term.
As a heart surgeon himself, his motto here is:
❝What foods to put on your table so you don’t end up on mine❞
There’s a lot more to this book than the simple “eat the Mediterranean diet”:
- While the Mediterranean diet is generally considered the top choice for heart health, he also advises on how to eat healthily on all manner of diets… Carnivore, Keto, Paleo, Atkins, Gluten-Free, Vegan, you-name-it.
- A lot of the book is given to clearing up common misconceptions, things that sounded plausible but are just plain dangerous. This information alone is worth the price of the book, we think.
- There’s also a section given over to explaining the markers of metabolic health, so you can monitor yourself effectively
- Rather than one-size-fits-all, he also talks about common health conditions and medications that may change what you need to be doing
- He also offers advice about navigating the health system to get what you need—including dealing with unhelpful doctors!
Bottom line: A very comprehensive (yet readable!) manual of heart health.
Get your copy of Stay Off My Operating Table from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cashew Nuts vs Macadamia Nuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cashews to macadamias, we picked the cashews.
Why?
In terms of macros, cashews have more than 2x the protein, while macadamias have nearly 2x the fat. The fats are mostly monounsaturated, so it’s still healthy in moderation, but still, we’re going to prize the protein over it and call this category a nominal win for cashews.
When it comes to vitamins, things are fairly even; cashews have more of vitamins B5, B6, B9, and E, while macadamias have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, and C.
In the category of minerals, cashews take the clear lead; cashews have more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while macadamias have more calcium and manganese.
In short, enjoy both (as macadamias have their benefits too), but cashews win in total nutrient density.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Come Together – by Dr. Emily Nagoski
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From Dr. Emily Nagoski, author of the bestseller “Come As You Are” (which we reviewed very favorably before) we now present: Come Together.
What it is not about: simultaneous orgasms. The title is just a play on words.
What it is about: improving sexual wellbeing, particularly in long-term relationships where one or more partner(s) may be experiencing low desire.
Hence: come together, in the closeness sense.
A lot of books (or advice articles) out there take the Cosmo approach of “spicing things up”, and that can help for a night perhaps, but relying on novelty is not a sustainable approach.
Instead, what Dr. Nagoski outlines here is a method for focusing on shared comfort and pleasure over desire, creating the right state of mind that’s more conducive to sexuality, and reducing things that put the brakes on sexuality.
She also covers things whereby sexuality can often be obliged to change (for example, with age and/or disability), but that with the right attitude, change can sometimes just be growth in a different way, as you explore the new circumstances together, and continue to find shared pleasure in the ways that best suit your changing circumstances,
Bottom line: if you and/or your partner(s) would like to foster and maintain intimacy and pleasure, then this is a top-tier book for you.
Click here to check out Come Together, and, well, come together!
Share This Post
-
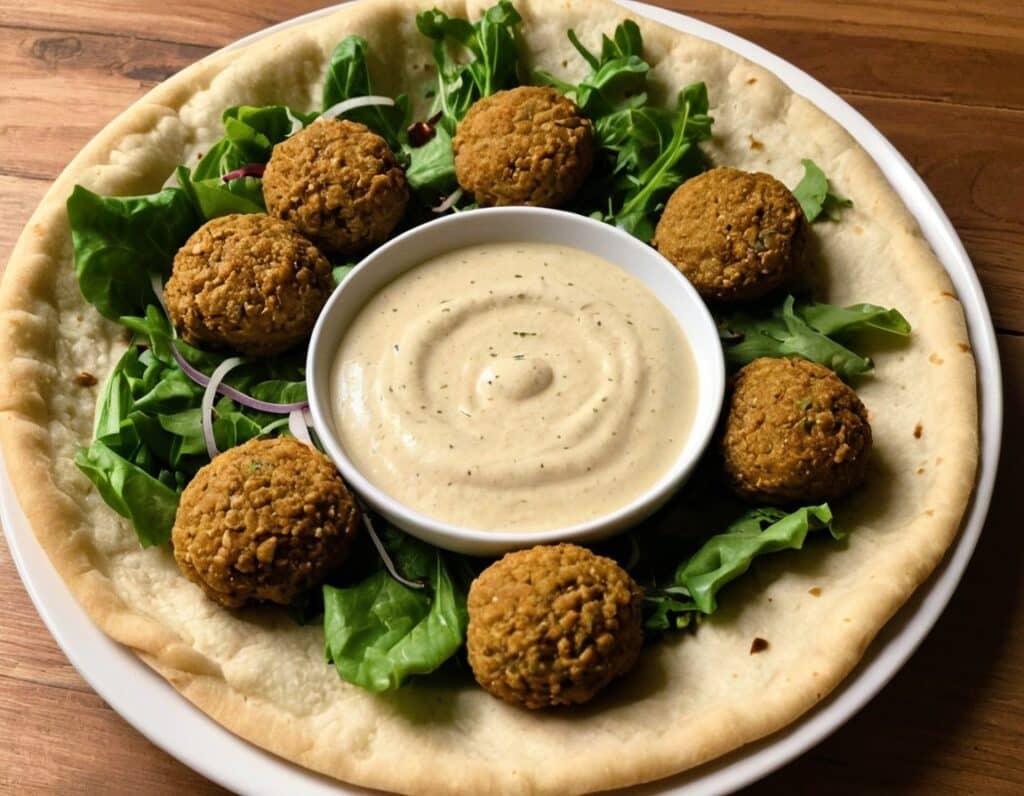
Mouthwatering Protein Falafel
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Baking falafel, rather than frying it, has a strength and a weakness. The strength: it is less effort and you can do more at once. The weakness: it can easily get dry. This recipe calls for baking them in a way that won’t get dry, and the secret is one of its protein ingredients: peas! Add to this the spices and a tahini sauce, and you’ve a mouthwatering feast that’s full of protein, fiber, polyphenols, and even healthy fats.
You will need
- 1 cup peas, cooked
- 1 can chickpeas, drained and rinsed (keep the chickpea water—also called aquafaba—aside, as we’ll be using some of it later)
- ½ small red onion, chopped
- 1 handful fresh mint, chopped
- 1 tbsp fresh parsley, chopped
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 tbsp chickpea flour (also called gram flour, besan flour, or garbanzo bean flour) plus more for dusting
- 2 tsp red chili flakes (adjust per heat preferences)
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
For the tahini sauce:
- 2 tbsp tahini
- 2 tbsp lemon juice
- ¼ bulb garlic, crushed
- 5 tbsp aquafaba (if for some reason you don’t have it, such as for example you substituted 1 cup chickpeas that you cooked yourself, substitute with water here)
To serve:
- Flatbreads (you can use our Healthy Homemade Flatbreads recipe if you like)
- Leafy salad
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 350℉ / 180℃.
2) Blend the peas and chickpeas in a food processor for a few seconds. You want a coarse mixture, not a paste.
3) Add the rest of the main section ingredients except the olive oil, and blend again for a few more seconds. It should still have a chunky texture, or else you will have made hummus. If you accidentally make hummus, set your hummus aside and start again on the falafels.
4) Shape the mixture into balls; if it lacks structural integrity, fold in a little more chickpea flour until the balls stay in shape. Either way, once you have done that, dust the balls in chickpea flour.
5) Brush the balls in a little olive oil, as you put them on a baking tray lined with baking paper. Bake for 15–18 minutes until golden, turning partway through.
6) While you are waiting, making the tahini sauce by combining the tahini sauce ingredients in a high-speed blender and processing on high until smooth. If you do not have a small enough blender (a bullet-style blender should work for this), then do it manually, which means you’ll have to crush the garlic all the way into a smooth paste, such as with a pestle and mortar, or alternatively, use ready-made garlic paste—and then simply whisk the ingredients together until smooth.
7) Serve the falafels warm or cold, on flatbreads with leafy salad and the tahini sauce.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tahini vs Hummus – Which is Healthier?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we scored 4/5 today!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
ADHD medication – can you take it long term? What are the risks and do benefits continue?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a condition that can affect all stages of life. Medication is not the only treatment, but it is often the treatment that can make the most obvious difference to a person who has difficulties focusing attention, sitting still or not acting on impulse.
But what happens once you’ve found the medication that works for you or your child? Do you just keep taking it forever? Here’s what to consider.
What are ADHD medications?
The mainstay of medication for ADHD is stimulants. These include methylphenidate (with brand names Ritalin, Concerta) and dexamfetamine. There is also lisdexamfetamine (branded Vyvanse), a “prodrug” of dexamfetamine (it has a protein molecule attached, which is removed in the body to release dexamfetamine).
There are also non-stimulants, in particular atomoxetine and guanfacine, which are used less often but can also be highly effective. Non-stimulants can be prescribed by GPs but this may not always be covered by the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme and could cost more.
How stimulants work
Some stimulants prescribed for ADHD are “short acting”. This means the effect comes on after around 20 minutes and lasts around four hours.
Longer-acting stimulants give a longer-lasting effect, usually by releasing medication more slowly. The choice between the two will be guided by whether the person wants to take medication once a day or prefers to target the medication effect to specific times or tasks.
For the stimulants (with the possible exception of lisdexamfetamine) there is very little carry-over effect to the next day. This means the symptoms of ADHD may be very obvious until the first dose of the morning takes effect.
One of the main aims of treatment is the person with ADHD should live their best life and achieve their goals. In young children it is the parents who have to consider the risks and benefits on behalf of the child. As children mature, their role in decision making increases.
What about side effects?
The most consistent side effects of the stimulants are they suppress appetite, resulting in weight loss. In children this is associated with temporary slowing of the growth rate and perhaps a slight delay in pubertal development. They can also increase the heart rate and may cause a rise in blood pressure. Stimulants often cause insomnia.
These changes are largely reversible on stopping medication. However, there is concern the small rises in blood pressure could accelerate the rate of heart disease, so people who take medication over a number of years might have heart attacks or strokes slightly sooner than would have happened otherwise.
This does not mean older adults should not have their ADHD treated. Rather, they should be aware of the potential risks so they can make an informed decision. They should also make sure high blood pressure and attacks of chest pain are taken seriously.
Stimulants can be associated with stomach ache or headache. These effects may lessen over time or with a reduction in dose. While there have been reports about stimulants being misused by students, research on the risks of long-term prescription stimulant dependence is lacking.
Will medication be needed long term?
Although ADHD can affect a person’s functioning at all stages of their life, most people stop medication within the first two years.
People may stop taking it because they don’t like the way it makes them feel, or don’t like taking medication at all. Their short period on medication may have helped them develop a better understanding of themselves and how best to manage their ADHD.
In teenagers the medication may lose its effectiveness as they outgrow their dose and so they stop taking it. But this should be differentiated from tolerance, when the dose becomes less effective and there are only temporary improvements with dose increases.
Tolerance may be managed by taking short breaks from medication, switching from one stimulant to another or using a non-stimulant.
Medication is usually prescribed by a specialist but rules differ around Australia.
Ground Picture/ShutterstockToo many prescriptions?
ADHD is becoming increasingly recognised, with more people – 2–5% of adults and 5–10% of children – being diagnosed. In Australia stimulants are highly regulated and mainly prescribed by specialists (paediatricians or psychiatrists), though this differs from state to state. As case loads grow for this lifelong diagnosis, there just aren’t enough specialists to fit everyone in.
In November, a Senate inquiry report into ADHD assessment and support services highlighted the desperation experienced by people seeking treatment.
There have already been changes to the legislation in New South Wales that may lead to more GPs being able to treat ADHD. Further training could help GPs feel more confident to manage ADHD. This could be in a shared-care arrangement or independent management of ADHD by GPs like a model being piloted at Nepean Blue Mountains Local Health District, with GPs training within an ADHD clinic (where I am a specialist clinician).
Not every person with ADHD will need or want to take medication. However, it should be more easily available for those who could find it helpful.
Alison Poulton, Senior Lecturer, Brain Mind Centre Nepean, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Reduce The Harm Of Festive Drinking (Without Abstaining)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Reduce The Harm Of Festive Drinking
Not drinking alcohol is—of course—the best way to avoid the harmful effects of alcohol. However, not everyone wants to abstain, especially at this time of year, so today we’re going to be focusing on harm reduction without abstinence.
If you do want to quit (or even reduce) drinking, you might like our previous article about that:
For everyone else, let’s press on with harm reduction:
Before You Drink
A common (reasonable, but often unhelpful) advice is “set yourself a limit”. The problem with this is that when we’re sober, “I will drink no more than n drinks” is easy. After the first drink, we start to feel differently about it.
So: delay your first drink of the day for as long as possible
That’s it, that’s the tip. The later you start drinking, not only will you likely drink less, but also, your liver will have had longer to finish processing whatever you drank last night, so it’s coming at the new drink(s) fresh.
On that note…
Watch your meds! Often, especially if we are taking medications that also tax our liver (acetaminophen / paracetamol / Tylenol is a fine example of this), we are at risk of having a bit of a build-up, like an office printer that still chewing on the last job while you’re trying to print the next.
Additionally: do indeed eat before you drink.
While You Drink
Do your best to drink slowly. While this can hit the same kind of problem as the “set yourself a limit” idea, in that once you start drinking you forget to drink slowly, it’s something to try for.
If your main reason for drinking is the social aspect, then merely having a drink in your hand is generally sufficient. You don’t need to be keeping pace with anyone.
It is further good to alternate your drinks with water. As in, between each alcoholic drink, have a glass of water. This helps in several ways:
- Hydrates you, which is good for your body’s recovery abilities
- Halves the amount of time you spend drinking
- Makes you less thirsty; it’s easy to think “I’m thirsty” and reach for an alcoholic drink that won’t actually help. So, it may slow down your drinking for that reason, too.
At the dinner table especially, it’s very reasonable to have two glasses, one filled with water. Nobody will be paying attention to which glass you drink from more often.
After You Drink
Even if you are not drunk, assume that you are.
Anything you wouldn’t let a drunk person in your care do, don’t do. Now is not the time to drive, have a shower, or do anything you wouldn’t let a child do in the kitchen.
Hospital Emergency Rooms, every year around this time, get filled up with people who thought they were fine and then had some accident.
The biggest risks from alcohol are:
- Accidents
- Heart attacks
- Things actually popularly associated with alcohol, e.g. alcohol poisoning etc
So, avoiding accidents is as important as, if not more important than, avoiding damage to your liver.
Drink some water, and eat something.
Fruit is great, as it restocks you on vitamins, minerals, and water, while being very easy to digest.
Go to bed.
There is a limit to how much trouble you can get into there. Sleep it off.
In the morning, do not do “hair of the dog”; drinking alcohol will temporarily alleviate a hangover, but only because it kicks your liver back into an earlier stage of processing the alcohol—it just prolongs the inevitable.
Have a good breakfast, instead. Remember, fruit is your friend (as explained above).
Want to know more?
Here’s a great service with a lot of further links to a lot more resources:
With You | How to safely detox from alcohol at home
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
To Pee Or Not To Pee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is it “strengthening” to hold, or are we doing ourselves harm if we do? Dr. Heba Shaheed explains in this short video:
A flood of reasons not to hold
Humans should urinate 4–6 times daily, but for many people, the demands of modern life often lead to delaying urination, raising questions about its effects on the body.
So first, let’s look at how it all works: the bladder is part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, urethra, and sphincters. Urine is produced by the kidneys and transported via the ureters into the bladder, a hollow organ with a muscular wall. This muscle (called the detrusor) allows the bladder to inflate as it fills with urine (bearing in mind, the main job of any muscle is to be able to stretch and contract).
As the bladder fills, stretch receptors in that muscle signal fullness to the spinal cord. This triggers the micturition reflex, causing the detrusor to contract and the internal urethral sphincter to open involuntarily. Voluntary control over the external urethral sphincter allows a person to delay or release urine as needed.
So, at what point is it best to go forth and pee?
For most people, bladder fullness is first noticeable at around 150-200ml, with discomfort occurring at 400-500ml (that’s about two cups*). Although the bladder can stretch to hold up to a liter, exceeding this capacity can cause it to rupture, a rare but serious condition requiring surgical intervention.
*note, however, that this doesn’t necessarily mean that drinking two cups will result in two cups being in your bladder; that’s not how hydration works. Unless you are already perfectly hydrated, most if not all of the water will be absorbed into the rest of your body where it is needed. Your bladder gets filled when your body has waste products to dispose of that way, and/or is overhydrated (though overhydration is not very common).
Habitually holding urine and/or urinating too quickly (note: not “too soon”, but literally, “too quickly”, we’re talking about the velocity at which it exits the body) can weaken pelvic floor muscles over time. This can lead to bladder pain, urgency, incontinence, and/or a damaged pelvic floor.
In short: while the body’s systems are equipped to handle occasional delays, holding it regularly is not advisable. For the good of your long-term urinary health, it’s best to avoid straining the system and go whenever you feel the urge.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Keeping your kidneys happy: it’s more than just hydration!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: