Exercise with Type 1 Diabetes – by Ginger Vieira
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you or a loved one has Type 1 Diabetes, you’ll know that exercise can be especially frustrating…
- If you don’t do it, you risk weight gain and eventual insulin resistance.
- If you do it, you risk dangerous hypos, or perhaps hypers if you took off your pump or skipped a bolus.
Unfortunately, the popular medical advice is “well, just do your best”.
Ginger Vieira is Type 1 Diabetic, and writes with 20+ experience of managing her diabetes while being a keen exerciser. As T1D folks out there will also know, comorbidities are very common; in her case, fibromyalgia was the biggest additional blow to her ability to exercise, along with an underactive thyroid. So when it comes to dealing with the practical nuts and bolts of things, she (while herself observing she’s not a doctor, let alone your doctor) has a lot more practical knowledge than an endocrinologist (without diabetes) behind a desk.
Speaking of nuts and bolts, this book isn’t a pep talk.
It has a bit of that in, but most of it is really practical information, e.g: using fasted exercise (4 hours from last meal+bolus) to prevent hypos, counterintuitive as that may seem—the key is that timing a workout for when you have the least amount of fast-acting insulin in your body means your body can’t easily use your blood sugars for energy, and draws from your fat reserves instead… Win/Win!
That’s just one quick tip because this is a 1-minute review, but Vieira gives:
- whole chapters, with example datasets (real numbers)
- tech-specific advice, e.g. pump, injection, etc
- insulin-specific advice, e.g. fast vs slow, and adjustments to each in the context of exercise
- timing advice re meal/bolus/exercise for different insulins and techs
- blood-sugar management advice for different exercise types (aerobic/anaerobic, sprint/endurance, etc)
…and lots more that we don’t have room to mention here
Basically… If you or a loved one has T1D, we really recommend this book!
Order a copy of “Exercise with Type 1 Diabetes” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
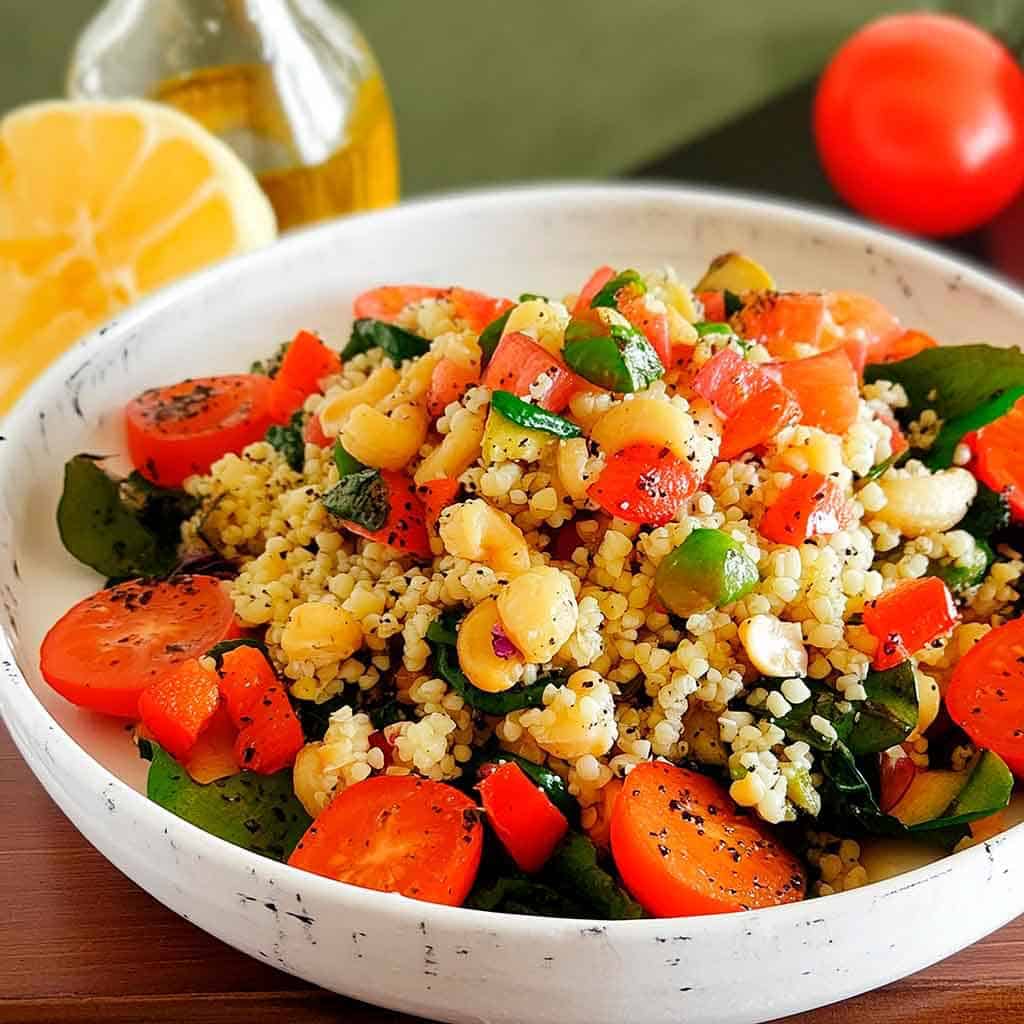
Tasty Tabbouleh with Tahini
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tabbouleh is a salad, but it’s not “just a salad”. It’s a special kind of salad that’s as exciting for the tastebuds as it is healthy for the body and brain. Its core ingredients have been traditional for about a dozen generations, and seasonings are always a personal matter (not to mention that Lebanese tabbouleh-makers centuries ago might not have used miso and nooch, as we will today), but the overall feel of the Gestalt of tabbouleh seasonings remains the same, and this recipe is true to that.
You will need
For the tabbouleh:
- 1 cup bulgur wheat
- 1 cup plum tomatoes, chopped
- 1 cucumber, peeled and chopped (add the peel to a jug of water and put it in the fridge; this will be refreshing cucumber water later!)
- 1 cup chickpeas, cooked without salt
- 1/2 cup parsley, chopped
- 1/2 cup mint, chopped
- 2 spring onions, finely chopped
- 2oz fresh lemon juice
- 1 tsp white miso paste
- 1 tsp garlic powder
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp ground celery seeds
- 1 tsp ground nigella seeds
- 1 tsp ground black pepper
- 1 tsp MSG, or 1/2 tsp low sodium salt (you can find it in supermarkets, the sodium chloride is cut with potassium chloride to make it have less sodium and more potassium)
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast (nooch), ground (it comes in flakes; you will have to grind it in a spice grinder or with a pestle and mortar)
For the tahini sauce:
- 3 garlic cloves, crushed
- 3 tbsp tahini
- 1 tbsp fresh lemon juice
- 1 tbsp white miso paste
- 1 tsp ground cumin
To serve:
- A generous helping of leafy greens; we recommend collard greens, but whatever works for you is good; just remember that dark green is best. Consider cavolo nero, or even kale if that’s your thing, but to be honest this writer doesn’t love kale
- 1 tsp coarsely ground nigella seeds
- Balsamic vinegar, ideally aged balsamic vinegar (this is thicker and sweeter, but unlike most balsamic vinegar reductions, doesn’t have added sugar).
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Rinse the bulgur wheat and then soak it in warm water. There is no need to boil it; the warm water is enough to soften it and you don’t need to cook it (bulgur wheat has already been parboiled before it got to you).
2) While you wait, take a small bowl and mix the rest of the ingredients from the tabbouleh section (so, the lemon juice, miso paste, and all those ground spices and MSG/salt and ground nutritional yeast); you’re making a dressing out of all the ingredients here.
3) When the bulgur wheat is soft (expect it to take under 15 minutes), drain it and put it in a big bowl. Add the tomatoes, cucumber, chickpeas, parsley, mint, and spring onions. This now technically qualifies as tabbouleh already, but we’re not done.
4) Add the dressing to the tabbouleh and mix thoroughly but gently (you don’t want to squash the tomatoes, cucumber, etc). Leave it be for at least 15 minutes while the flavors blend.
5) Take the “For the tahini sauce” ingredients (all of them) and blend them with 4 oz water, until smooth. You’re going to want to drizzle this sauce, so if the consistency is too thick for drizzling, add a little more water and/or lemon juice (per your preference), 1 tbsp at a time.
6) Roughly chop the leafy greens and put them in a bowl big enough for the tabbouleh to join them there. The greens will serve as a bed for the tabbouleh itself.
7) Drizzle the tahini over the tabbouleh, and drizzle a little of the aged balsamic vinegar too.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Make Your Negativity Work For You
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s The Right Balance?
We’ve written before about positivity the pitfalls and perils of toxic positivity:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
…as well as the benefits that can be found from selectively opting out of complaining:
A Bone To Pick… Up And Then Put Back Where We Found It
So… What place, if any, does negativity usefully have in our lives?
Carrot and Stick
We tend to think of “carrot and stick” motivation being extrinsic, i.e. there is some authority figure offering is reward and/or punishment, in response to our reactions.
In those cases when it really is extrinsic, the “stick” can still work for most people, by the way! At least in the short term.
Because in the long term, people are more likely to rebel against a “stick” that they consider unjust, and/or enter a state of learned helplessness, per “I’ll never be good enough to satisfy this person” and give up trying to please them.
But what about when you have your own carrot and stick? What about when it comes to, for example, your own management of your own healthy practices?
Here it becomes a little different—and more effective. We’ll get to that, but first, bear with us for a touch more about extrinsic motivation, because here be science:
We will generally be swayed more easily by negative feelings than positive ones.
For example, a study was conducted as part of a blood donation drive, and:
- Group A was told that their donation could save a life
- Group B was told that their donation could prevent a death
The negative wording given to group B boosted donations severalfold:
Read the paper: Life or Death Decisions: Framing the Call for Help
We have, by the way, noticed a similar trend—when it comes to subject lines in our newsletters. We continually change things up to see if trends change (and also to avoid becoming boring), but as a rule, the response we get from subscribers is typically greater when a subject line is phrased negatively, e.g. “how to avoid this bad thing” rather than “how to have this good thing”.
How we can all apply this as individuals?
When we want to make a health change (or keep up a healthy practice we already have)…
- it’s good to note the benefits of that change/practice!
- it’s even better to note the negative consequences of not doing it
For example, if you want to overcome an addiction, you will do better for your self-reminders to be about the bad consequences of using, more than the good consequences of abstinence.
See also: How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
This goes even just for things like diet and exercise! Things like diet and exercise can seem much more low-stakes than substance abuse, but at the end of the day, they can add healthy years onto our lives, or take them off.
Because of this, it’s good to take time to remember, when you don’t feel like exercising or do feel like ordering that triple cheeseburger with fries, the bad outcomes that you are planning to avoid with good diet and exercise.
Imagine yourself going in for that quadruple bypass surgery, asking yourself whether the unhealthy lifestyle was worth it. Double down on the emotions; imagine your loved ones grieving your premature death.
Oof, that was hard-hitting
It was, but it’s effective—if you choose to do it. We’re not the boss of you! Either way, we’ll continue to send the same good health advice and tips and research and whatnot every day, with the same (usually!) cheery tone.
One last thing…
While it’s good to note the negative, in order to avoid the things that lead to it, it’s not so good to dwell on the negative.
So if you get caught in negative thought spirals or the like, it’s still good to get yourself out of those.
If you need a little help with that sometimes, check out these:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
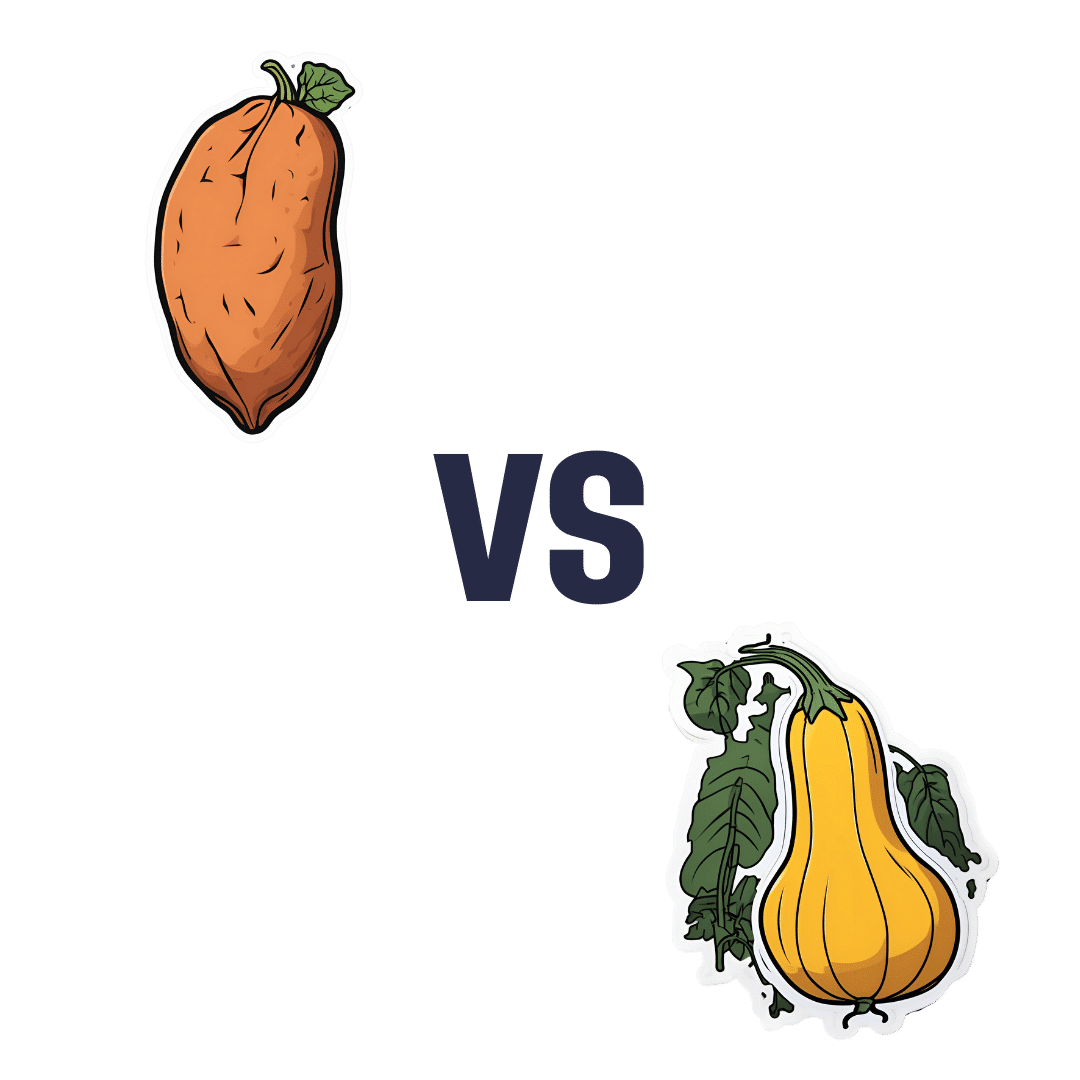
Sweet Potato vs Winter Squash – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sweet potato to winter squash, we picked the sweet potato.
Why?
In terms of macros, the sweet potato has 2x the protein, 2x the carbs, and slightly more fiber. Because the protein numbers are small, the carb:fiber ratio is the deciding factor here, and has winter squash has the lower glycemic index (assuming cooking them both on a like-for-like basis), we’re going with that on macros, but it’s subjective.
In the category of vitamins, sweet potato has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, C, E, and choline, while winter squash has more of vitamins B9 and K. It’s interesting to note that while sweet potato is rightly famous for its vitamin A content, winter squash is actually very good for that too. Still, by the numbers, it’s a clear 9:2 victory for sweet potato here.
When it comes to minerals, sweet potato has more calcium copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while winter squash has more selenium, meaning an 8:1 victory for sweet potato this time.
In short, enjoy either or both, but sweet potato is the more nutritionally dense option for sure.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Carb-Strong or Carb-Wrong? Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Workout Advice For Busy People
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hampton at Hybrid Calisthenics always has very sound advice in his uplifting videos, and this one’s no exception:
Key tips for optimizing workouts without burning out
“We all have the same 24 hours” is a folly when in fact, some of us have more responsibilities and/or other impediments to getting things done (e.g. disabilities).
A quick word on disabilities first: sometimes people are quick to point out Paralympian athletes, and “if they can do it, so can you!” and forget that these people are in the top percentile of the top percentile of the top percentile of human performance. If you wouldn’t disparagingly say “if Simone Biles/Hussein Bolt/Michael Phelps can do it, so can you”, then don’t for Paralympians either 😉
Now, as for Hampton’s advice, he recommends:
Enjoy short, intense workouts:
- You can get effective results in under 30 minutes (or even just a few minutes per day) with compound exercises (e.g., squats, pull-ups).
- Focus on full-body movements also saves time!
- Push closer to failure when possible to maximize efficiency. It’s the last rep where most of the strength gains are made! Same deal with cardiovascular fitness, too. Nevertheless, do take safety into account in both cases, of course.
Time your rest periods:
- Resting for 2–3 minutes between sets ensures optimal recovery.
- Avoid getting distracted during rest by setting a timer to stay focused.
- 10almonds tip: use this time to practice a mindfulness meditation. That will greatly reduce the chance of you becoming distracted.
Remember holistic fitness:
- Fitness isn’t just about exercise; diet, sleep, and stress management are equally important for your fitness as much as for the rest of your health.
- Better sleep and reduced stress will help you exercise more consistently and avoid junk food.
Address burnout:
- If feeling too exhausted to apply these tips, focus on getting better rest and reducing stress first.
- Taking a short break to reset can help in the long run.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- How To Do High Intensity Interval Training (Without Wrecking Your Body)
- How To Rest More Efficiently (Yes, Really)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Loss, Trauma, and Resilience – by Dr. Pauline Boss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most books about bereavement are focused on grieving healthily and then moving on healthily. And, while it may be said “everyone’s grief is on their own timescale”… society’s expectation is often quite fixed:
“Time will heal”, they say.
But what if it doesn’t? What happens when that’s not possible?
Ambiguous loss occurs when someone is on the one hand “gone”, but on the other hand, not necessarily.
This can be:
- Someone was lost in a way that didn’t leave a body to 100% confirm it
- (e.g. disaster, terrorism, war, murder, missing persons)
- Someone remains physically present but in some ways already “gone”
- (e.g. Alzheimer’s disease or other dementia, brain injury, coma)
These things stop us continuing as normal, and/but also stop us from moving on as normal.
When either kind of moving forward is made impossible, everything gets frozen in place. How does one deal with that?
Dr. Boss wrote this book for therapists, but its content is equally useful for anyone struggling with ambiguous loss—or who has a loved one who is, in turn, struggling with that.
The book looks at the impact of ambiguous loss on continuing life, and how to navigate that:
- How to be resilient, in the sense of when life tries to break you, to have ways to bend instead.
- How to live with the cognitive dissonance of a loved one who is a sort of “Schrödinger’s person”.
- How, and this is sometimes the biggest one, to manage ambiguous loss in a society that often pushes toward: “it’s been x period of time, come on, get over it now, back to normal”
Will this book heal your heart and resolve your grief? No, it won’t. But what it can do is give a roadmap for nonetheless thriving in life, while gently holding onto whatever we need to along the way.
Click here to check out “Ambiguous loss, Trauma, and Resilience” on Amazon—it can really help
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Someone was lost in a way that didn’t leave a body to 100% confirm it
-
Your Science-Based Guide To Losing Fat & Toning Up
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This health coach researched the science and crunched the numbers so that you don’t have to:
Body by the numbers
Let’s get mathematical:
Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) consists of:
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): 70% of daily calorie burn (basic body functions, of which the brain is the single biggest calorie-burner)
- Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT): 15% (the normal movements that occur as you go about your daily life)
- Exercise Activity: 5% (actual workouts, often overestimated)
- Thermic Effect of Food (TEF): 10% (energy needed for digestion)
Basic BMR estimate:
- Women: body weight (kg) × 0.9 × 24
- Men: body weight (kg) × 24
But yours may differ, so if you have a fitness tracker or other gadget that estimates it for you, go with that!
Note: muscle burns calories just to maintain it, making muscle mass crucial to increasing one’s BMR.
And now some notes about running a caloric deficit:
- Safe caloric deficit: no more than 500 calories/day.
- Absolute minimum daily intake: 1,200 calories (women), 1,500 calories (men) (not sustainable long-term).
- Tracking calories is useful but not always accurate.
- Extreme calorie restriction slows metabolism and can lead to binge-eating.
- Your body will adjust to calorie deficits over time, making long-term drastic deficits ineffective.
Diet for fat loss & muscle gain:
- Protein Intake: 1.5–2g per pound of body weight.
- Aim for 30g of protein per meal (supports muscle & satiety).
- Protein has a higher thermic effect (20-30%) than carbs (5-10%) & fats (2-4%), meaning more calories are burned digesting protein.
- Fats are essential for hormone health & satiety (0.5–1g per kg of body weight).
- Carbs should be complex (whole grains, vegetables, fruits, etc.).
- Avoid excessive simple carbs (sugar, white bread, white pasta, etc) to maintain stable hunger signals.
- Hydration is key for appetite control & metabolism (often mistaken for hunger).
Exercise for fat loss & muscle gain:
- Resistance training (3-5x per week) is essential for toning & metabolism.
- Cardio is NOT necessary for fat loss but good for overall health.
- NEAT (non-exercise movement) burns significant calories (walking, taking stairs, fidgeting, etc.).
- “Hot girl walks” & daily movement can significantly aid weight loss.
- Women won’t get “bulky” from weight training unless they eat like a bodybuilder (i.e. several times the daily caloric requirement).
Some closing words in addition:
Poor sleep reduces fat loss by 50% and increases hunger. High stress levels lead to fat retention and cravings for unhealthy foods. Thus, managing stress & sleep is as important as diet & exercise for body transformation!
For more on all of this (plus the sources for the science), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Lose Weight (Healthily) ← our own main feature about such; we took a less numbers-based, more principles-based, approach. Both approaches work, so go with whichever suits your personal preference more!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: