The Comfort Zone – by Kristen Butler
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are you sitting comfortably? Then we’ll begin. Funny, how being comfortable can be a good starting point, then we are advised “You have to get out of your comfort zone”.
And yet, when we think of our personal greatest moments in life, they were rarely uncomfortable moments. Why is that?
Kristen Butler wants us to resolve this paradox, with a reframe:
The comfort zone? That’s actually the “flow” zone.
Just as “slow and steady wins the race”, we can—like the proverbial tortoise—take our comfort with us as we go.
The discomfort zone? That’s the stress zone, the survival zone, the “putting out fires” zone. From the outside, it looks like we’re making a Herculean effort, and perhaps we are, but is it actually so much better than peaceful consistent productivity?
Butler writes in a way that will be relatable for many, and may be a welcome life-ring if you feel like you’ve been playing catch-up for a while.
Is she advocating for complacency, then? No, and she discusses this too. That “complacency zone” is really the “burnout zone” after being in the “survival zone” for too long.
She lays out for us, therefore, a guide for growing in comfort, expanding the comfort zone yes, but by securely pushing it from the inside, not by making a mad dash out and hoping it follows us.
Bottom line: if you’ve been (perhaps quietly) uncomfortable for a little too long for comfort, this book can reframe your approach to get you to a position of sustainable, stress-free growth.
Click here to check out The Comfort Zone, and start building yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Colloidal Gold’s Impressive Claims
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
All That Glitters…
Today we’ll be examining colloidal gold supplementation.
This issue of 10almonds brought to you by the writer suddenly getting lots of advertisements for this supplement. It’s not a new thing though, and has been around in one form or another since pretty much forever.
Colloidal gold is…
- Gold, as in the yellow metal
- Colloidal, as in “very tiny insoluble particles dispersed though another substance (such as water)”
What are the claims made for it?
Honestly, just about everything is claimed for it. But to go with some popular claims:
- Reduces inflammation
- Supports skin health
- Boosts immune function
- Combats aging
- Improves cognitive function
So, what does the science say?
Does it do those things?
The short and oversimplified answer is: no
However, there is a little bit of tangential merit, so we’re going to talk about the science of it, and how the leap gets made between what the science says and what the advertisements say.
First… What makes gold so special, in general? Historically, three things:
- It’s quite rare
- It’s quite shiny
- It’s quite unreactive
- The first is about supply and demand, so that’s not very important to us in this article.
- The second is an aesthetic quality, which actually will have a little bit of relevance, but not much.
- The third has been important historically (because it meant that shiny gold stayed shiny, because it didn’t tarnish), and now also important industrially too, as gold can be used in many processes where we basically need for nothing to happen (i.e., a very inert component is needed)
That third quality—its unreactivity—has become important in medicine.
When scientists need a way to deliver something (without the delivering object getting eaten by the body’s “eat everything” tendencies), or otherwise not interact chemically with anything around, gold is an excellent choice.
Hence gold teeth, and gold fillings, by the way. They’re not just for the bling factor; they were developed because of their unreactivity and thus safety.
So, what about those health claims we mentioned above?
Here be science (creative interpretations not included)
The most-backed-by-science claim from that list is “reduces inflammation”.
Websites selling colloidal gold cite studies such as:
Gold nanoparticles reduce inflammation in cerebral microvessels of mice with sepsis
A promising title!The results of the study showed:
❝20 nm cit-AuNP treatment reduced leukocyte and platelet adhesion to cerebral blood vessels, prevented BBB failure, reduced TNF- concentration in brain, and ICAM-1 expression both in circulating polymorphonuclear (PMN) leukocytes and cerebral blood vessels of mice with sepsis. Furthermore, 20 nm cit-AuNP did not interfere with the antibiotic effect on the survival rate of mice with sepsis.❞
That “20 nm cit-AuNP” means “20 nm citrate-covered gold nanoparticles”
So it is not so much the antioxidant powers of gold being tested here, as the antioxidant powers of citrate, a known antioxidant. The gold was the carrying agent, whose mass and unreactivity allowed it to get where it needed to be.
The paper does say the words “Gold nanoparticles have been demonstrated to own important anti-inflammatory properties“ in the abstract, but does not elaborate on that, reference it, or indicate how.
Websites selling colloidal gold also cite papers such as:
Anti-inflammatory effect of gold nanoparticles supported on metal oxides
Another promising title! However the abstract mentions:
❝The effect was dependent on the MOx NPs chemical nature
[…]
The effect of Au/TiO2 NPs was not related to Au NPs size❞
MOx NPs = mineral oxide nanoparticles. In this case, the gold was a little more than a carrying agent, though, because the gold is described and explained as being a catalytic agent (i.e., its presence helps the attached mineral oxides react more quickly).
We said that was the most-backed claim, and as you can see, it has some basis but is rather tenuous since the gold by itself won’t do anything; it just helps the mineral oxides.
Next best-backed claim builds from that, which is “supports skin health”.
Sometimes colloidal gold is sold as a facial tonic. By itself it’ll distribute (inert) gold nanoparticles across your skin, and may “give you a healthy glow”, because that’s what happens when you put shiny wet stuff on your face.
Healthwise, if the facial tonic also contains some of the minerals we mentioned above, then it may have an antioxidant effect. But again, no minerals, no effect.
The claim that it “combats aging” is really a tag-on to the “antioxidant” claim.
As for the “supports immune health” claim… Websites selling colloid gold cite studies such as:
To keep things brief: gold can fight infectious diseases in much the same way that forks can fight hunger. It’s an inert carrying agent.
As for “improves cognitive function”? The only paper we could find cited was that mouse sepsis study again, this time with the website saying “researchers found that rats treated with colloidal gold showed improved spatial memory and learning ability“ whereas the paper cited absolutely did not claim that, not remotely, not even anything close to that. It wasn’t even rats, it was mice, and they did not test their memory or learning.
Is it safe?
Colloidal gold supplementation is considered very safe, precisely because gold is one of the least chemically reactive substances you could possibly consume. It is special precisely because it so rarely does anything.
However, impurities could be introduced in the production process, and the production process often involves incredibly harsh reagents to get the gold ions, and if any of those reagents are left in the solution, well, gold is safe but sodium borohydride and chloroauric acid aren’t!
Where can I get some?
In the unlikely event that our research review has given you an urge to try it, here’s an example product on Amazon
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Reduce Your Stroke Risk
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
❝Each year in the U.S., over half a million people have a first stroke; however, up to 80% of strokes may be preventable.❞
~ American Stroke Association
Source: New guideline: Preventing a first stroke may be possible with screening, lifestyle changes
So, what should we do?
Some of the risk factors are unavoidable or not usefully avoidable, like genetic predispositions and old age, respectively (i.e. it is possible to avoid old age—by dying young, which is not a good approach).
Some of the risk factors are avoidable. Let’s look at the most obvious first:
You cannot drink to your good health
While overall, the World Health Organization has declared that “the only safe amount of alcohol is zero”, when it comes to stroke risk specifically, it seems that low consumption is not associated with stroke, while moderate to high consumption is associated with a commensurately increased risk of stroke:
Alcohol Intake as a Risk Factor for Acute Stroke
Note: there are some studies out there that say that a low to moderate consumption may decrease the risk compared to zero consumption. However, any such study that this writer has seen has had the methodological flaw of not addressing why those who do not drink alcohol, do not drink it. In many cases, someone who drinks no alcohol at all does so because either a) it would cause problems with some medication(s) they are taking, or b) they used to drink heavily, and quit. In either case, their reasons for not drinking alcohol may themselves be reasons for an increased stroke risk—not the lack of alcohol itself.
Smoke now = stroke later
This one is straightforward; smoking is bad for pretty much everything, and that includes stroke risk, as it’s bad for your heart and brain both, increasing stroke risk by 200–400%:
Smoking and stroke: the more you smoke the more you stroke
So, the advice here of course is: don’t smoke
Diet matters
The American Stroke Association’s guidelines recommend, just for a change, the Mediterranean Diet. This does not mean just whatever is eaten in the Mediterranean region though, and there are specifically foods that are included and excluded, and the ratios matter, so here’s a run-down of what the Mediterranean Diet does and doesn’t include:
The Mediterranean Diet: What Is It Good For? ← what isn’t it good for?!
You can outrun stroke
Or out-walk it; that’s fine too. Most important here is frequency of exercise, more than intensity. So basically, getting those 150 minutes moderate exercise per week as a minimum.
See also: The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less & Move More
Which is good, because it means we can get a lot of exercise in that doesn’t feel like “having to do” exercise, for example:
Do You Love To Go To The Gym? No? Enjoy These “No-Exercise Exercises”!
Your brain needs downtime too
Your brain (and your heart) both need you to get good regular sleep:
Sleep Disorders in Stroke: An Update on Management
We sometimes say that “what’s good for your heart is good for your brain” (because the heart feeds the brain, and also ultimately clears away detritus), and that’s true here too, so we might also want to prioritize sleep regularity over other factors, even over duration:
How Regularity Of Sleep Can Be Even More Important Than Duration ← this is about adverse cardiovascular events, including ischemic stroke
Keep on top of your blood pressure
High blood pressure is a very modifiable risk factor for stroke. Taking care of the above things will generally take care of this, especially the DASH variation of the Mediterranean diet:
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
However, it’s still important to actually check your blood pressure regularly, because sometimes an unexpected extra factor can pop up for no obvious reason. As a bonus, you can do this improved version of the usual blood pressure test, still using just a blood pressure cuff:
Try This At Home: ABI Test For Clogged Arteries
Consider GLP-1 receptor agonists (or…)
GLP-1 receptor agonists (like Ozempic et al.) seem to have cardioprotective and neuroprotective (thus: anti-stroke) activity independent of their weight loss benefits:
Of course, GLP-1 RAs aren’t everyone’s cup of tea, and they do have their downsides (including availability, cost, and the fact benefits reverse themselves if you stop taking them), so if you want a similar effect from a natural approach, there are some foods that work on the body’s incretin responses in the same way as GLP-1 RAs do:
5 Foods That Naturally Mimic The “Ozempic Effect”
Better to know sooner rather than too late
Rather than waiting until one half of our face is drooping to know that there was a stroke risk, here are things to watch out for to know about it before it’s too late:
6 Signs Of Stroke (One Month In Advance)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
You Are the One You’ve Been Waiting For – by Dr. Richard Schwartz
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As self-therapy approaches go, the title here could be read two ways: as pop-psychology fluff, or a suggestion of something deeper. And, while written in a way to make it accessible to all, we’re happy to report the content consists of serious therapeutic ideas, presented clearly.
Internal Family Systems (IFS) is a large, internationally recognized, and popular therapeutic approach. It’s also an approach that lends itself quite well to self-therapy, as this book illustrates.
Dr. Schwartz kicks off by explaining not IFS, but the problem that it solves… We (most of us, anyway) have over the course of our lives tried to plug the gaps in our own unmet psychological needs. And, that can cause resentment, strain, and can even be taken out on others if we’re not careful.
The real meat of the book, however, is in its illustrative explanations of how IFS works, and can be applied by an individual. The goal is to recognize all the parts that make us who we are, understand what they need in order to be at peace, and give them that. Spoiler: most what they will need is just being adequately heard, rather than locked in a box untended.
One of the benefits of using this book for self-therapy, of course, is that it requires a lot less vulnerability with a third party.
But, speaking of which, what of these intimate relationships the subtitle of the book referenced? Mostly the benefits to such come from a “put your own oxygen mask on first” angle… but the book does also cover discussions between intimate partners, and approaches to love, including what the author calls “courageous love”.
Bottom line: this is a great book if you want to do some “spring-cleaning of the soul” and live a little more lightly as a result.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
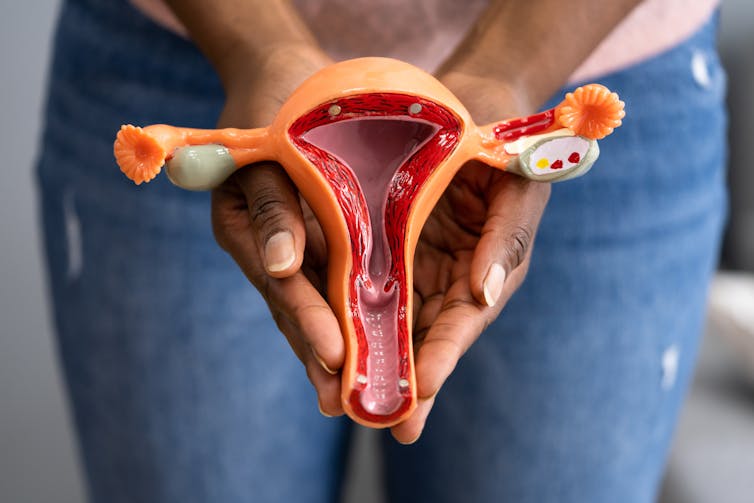
What’s the difference between period pain and endometriosis pain?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Menstruation, or a period, is the bleeding that occurs about monthly in healthy people born with a uterus, from puberty to menopause. This happens when the endometrium, the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus, is shed.
Endometriosis is a condition that occurs when endometrium-like tissue is found outside the uterus, usually within the pelvic cavity. It is often considered a major cause of pelvic pain.
Pelvic pain significantly impacts quality of life. But how can you tell the difference between period pain and endometriosis?
Polina Zimmerman/Pexels Periods and period pain
Periods involve shedding the 4-6 millimetre-thick endometrial lining from the inside of the uterus.
As the lining detaches from the wall of the uterus, the blood vessels which previously supplied the lining bleed. The uterine muscles contract, expelling the blood and crumbled endometrium.
The crumbled endometrium and blood mostly pass through the cervix and vagina. But almost everyone back-bleeds via their fallopian tubes into their pelvic cavity. This is known as “retrograde menstruation”.
Most of the lining is shed through the vagina. Andrey_Popov/Shutterstock The process of menstrual shedding is caused by inflammatory substances, which also cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, headaches, aches, pains, dizziness, feeling faint, as well as stimulating pain receptors.
These inflammatory substances are responsible for the pain and symptoms in the week before a period and the first few days.
For women with heavy periods, their worst days of pain are usually the heaviest days of their period, coinciding with more cramps to expel clots and more retrograde bleeding.
Many women also have pain when they are releasing an egg from their ovary at the time of ovulation. Ovulation or mid-cycle pain can be worse in those who bleed more, as those women are more likely to bleed into the ovulation follicle.
Around 90% of adolescents experience period pain. Among these adolescents, 20% will experience such severe period pain they need time off from school and miss activities. These symptoms are too often normalised, without validation or acknowledgement.
What about endometriosis?
Many symptoms have been attributed to endometriosis, including painful periods, pain with sex, bladder and bowel-related pain, low back pain and thigh pain.
Other pain-related conditions such migraines and chronic fatigue have also been linked to endometriosis. But these other pain-related symptoms occur equally often in people with pelvic pain who don’t have endometriosis.
One in five adolescents who menstrate experience severe symptoms. CGN089/Shutterstock Repeated, significant period and ovulation pain can eventually lead some people to develop persistent or chronic pelvic pain, which lasts longer than six months. This appears to occur through a process known as central sensitisation, where the brain becomes more sensitive to pain and other sensory stimuli.
Central sensitisation can occur in people with persistent pain, independent of the presence or absence of endometriosis.
Eventually, many people with period and/or persistent pelvic pain will have an operation called a laparoscopy, which allows surgeons to examine organs in the pelvis and abdomen, and diagnose and treat endometriosis.
Yet only 50% of those with identical pain symptoms who undergo a laparoscopy will end up having endometriosis.
Endometriosis is also found in pain-free women. So we cannot predict who does and doesn’t have endometriosis from symptoms alone.
How is this pain managed?
Endometriosis surgery usually involves removing lesions and adhesions. But at least 30% of people return to pre-surgery pain levels within six months or have more pain than before.
After surgery, emergency department presentations for pain are unchanged and 50% have repeat surgery within a few years.
Suppressing periods using hormonal therapies (such as continuous oral contraceptive pills or progesterone-only approaches) can suppress endometriosis and reduce or eliminate pain, independent of the presence or absence of endometriosis.
Not every type or dose of hormonal medications suits everyone, so medications need to be individualised.
The current gold-standard approach to manage persistent pelvic pain involves a multidisciplinary team approach, with the aim of achieving sustained remission and improving quality of life. This may include:
- physiotherapy for pelvic floor and other musculoskeletal problems
- management of bladder and bowel symptoms
- support for self-managing pain
- lifestyle changes including diet and exercise
- psychological or group therapy, as our moods, stress levels and childhood events can affect how we feel and experience pain.
Whether you have period pain, chronic pelvic pain or pain you think is associated with endometriosis, if you feel pain, it’s real. If it’s disrupting your life, you deserve to be taken seriously and treated as the whole person you are.
Sonia R. Grover, Senior Research Fellow, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute; Clinical Professor of Gynaecology, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are plant-based burgers really bad for your heart? Here’s what’s behind the scary headlines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re hearing a lot about ultra-processed foods and the health effects of eating too many. And we know plant-based foods are popular for health or other reasons.
So it’s not surprising new research out this week including the health effects of ultra-processed, plant-based foods is going to attract global attention.
And the headlines can be scary if that research and the publicity surrounding it suggests eating these foods increases your risk of heart disease, stroke or dying early.
Here’s how some media outlets interpreted the research. The Daily Mail ran with:
Vegan fake meats are linked to increase in heart deaths, study suggests: Experts say plant-based diets can boost health – but NOT if they are ultra-processed
The New York Post’s headline was:
Vegan fake meats linked to heart disease, early death: study
But when we look at the study itself, it seems the media coverage has focused on a tiny aspect of the research, and is misleading.
So does eating supermarket plant-based burgers and other plant-based, ultra-processed foods really put you at greater risk of heart disease, stroke and premature death?
Here’s what prompted the research and what the study actually found.
Nina Firsova/Shutterstock Remind me, what are ultra-processed foods?
Ultra-processed foods undergo processing and reformulation with additives to enhance flavour, shelf-life and appeal. These include everything from packet macaroni cheese and pork sausages, to supermarket pastries and plant-based mince.
There is now strong and extensive evidence showing ultra-processed foods are linked with an increased risk of many physical and mental chronic health conditions.
Although researchers question which foods should be counted as ultra-processed, or if all of them are linked to poorer health, the consensus is that, generally, we should be eating less of them.
We also know plant-based diets are popular. These are linked with a reduced risk of chronic health conditions such as heart disease and stroke, cancer and diabetes. And supermarkets are stocking more plant-based, ultra-processed food options.
How about the new study?
The study looked for any health differences between eating plant-based, ultra-processed foods compared to eating non-plant based, ultra-processed foods. The researchers focused on the risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease and stroke) and deaths from it.
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods in this study included mass-produced packaged bread, pastries, buns, cakes, biscuits, cereals and meat alternatives (fake meats). Ultra-processed foods that were not plant-based included milk-based drinks and desserts, sausages, nuggets and other reconstituted meat products.
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank. This is a large biomedical database that contains de-identified genetic, lifestyle (diet and exercise) and health information and biological samples from half a million UK participants. This databank allows researchers to determine links between this data and a wide range of diseases, including heart disease and stroke.
They used data from nearly 127,000 people who provided details of their diet between 2009 and 2012. The researchers linked this to their hospital records and death records. On average, the researchers followed each participant’s diet and health for nine years.
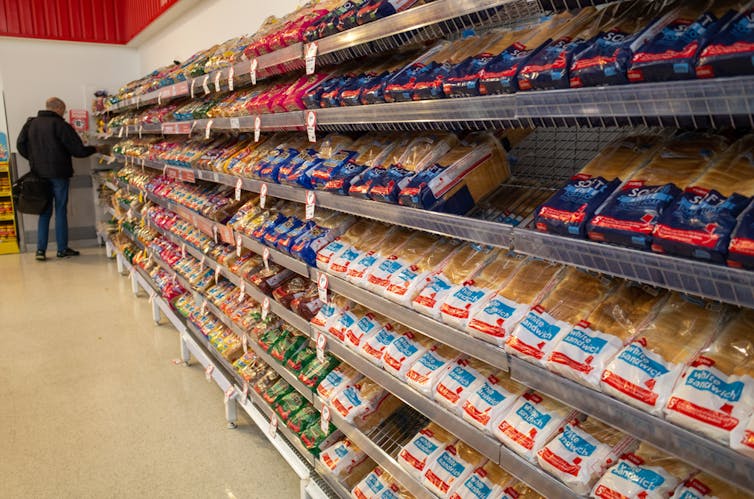
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods included in this study included packaged supermarket bread. doublelee/Shutterstock What did the study find?
With every 10% increase of total energy from plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods there was an associated 5% increased risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease or stroke) and a 12% higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
But for every 10% increase in plant-sourced, non-ultra-processed foods consumed there was an associated 7% lower risk of cardiovascular disease and a 13% lower risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
The researchers found no evidence for an association between all plant-sourced foods (whether or not they were ultra-processed) and either an increased or decreased risk of cardiovascular disease or dying from it.
This was an observational study, where people recalled their diet using questionnaires. When coupled with other data, this can only tell us if someone’s diet is associated with a particular risk of a health outcome. So we cannot say that, in this case, the ultra-processed foods caused the heart disease and deaths from it.
Why has media coverage focused on fake meats?
Much of the media coverage has focused on the apparent health risks associated with eating fake meats, such as sausages, burgers, nuggets and even steaks.
These are considered ultra-processed foods. They are made by deconstructing whole plant foods such as pea, soy, wheat protein, nuts and mushrooms, and extracting the protein. They are then reformulated with additives to make the products look, taste and feel like traditional red and white meats.
However this was only one type of plant-based, ultra-processed food analysed in this study. This only accounted for an average 0.2% of the dietary energy intake of all the participants.
Compare this to bread, pastries, buns, cakes and biscuits, which are other types of plant-based, ultra-processed foods. These accounted for 20.7% of total energy intake in the study.
This image was at the top of the media release. Screenshot/Imperial It’s hard to say why the media focused on fake meat. But there is one clue in the media release issued to promote the research.
Although the media release did not mention the words “fake meat”, an image of plant-based burgers, sausages and meat balls or rissoles featured prominently.
The introduction of the study itself also mentions plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods, such as sausages, nuggets and burgers.
So it’s no wonder people can be confused.
Does this mean fake meats are fine?
Not necessarily. This study analysed the total intake of plant-based, ultra-processed foods, which included fake meats, albeit a very small proportion of people’s diets.
From this study alone we cannot tell if there would be a different outcome if someone ate large amounts of fake meats.
In fact, a recent review of fake meats found there was not enough evidence to determine their impact on health.
We also need more recent data to reflect current eating patterns of fake meats. This study used dietary data collected from 2009 to 2012, and fake meats have become more popular since.
What if I really like fake meat?
We have known for a while that ultra-processed foods can harm our health. This study tells us that regardless if an ultra-processed food is plant-based or not, it may still be harmful.
We know fake meat can contain large amounts of saturated fats (from coconut or palm oil), salt and sugar.
So like other ultra-processed foods, they should be eaten infrequently. The Australian Dietary Guidelines currently recommends people should only consume foods like this sometimes and in small amounts.
Are some fake meats healthier than others?
Check the labels and nutrition information panels. Look for those lowest in fat and salt. Burgers and sausages that are a “pressed cake” of minced ingredients such as nuts, beans and vegetables will be preferable to reformulated products that look identical to meat.
You can also eat whole plant-based protein foods such as legumes. These include beans, lentils, chickpeas and soy beans. As well as being high in protein and fibre, they also provide essential nutrients such as iron and zinc. Using spices and mushrooms alongside these in your recipes can replicate some of the umami taste associated with meat.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Brain As A Work-In-Progress
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
And The Brain Goes Marching On!
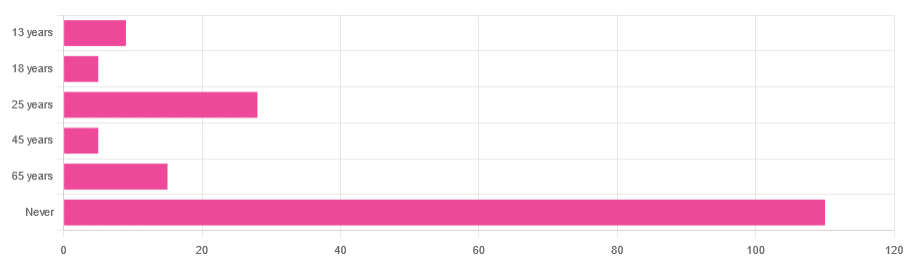
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you “when does the human brain stop developing?” and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 64% of people said “Never”
- About 16% of people said “25 years”
- About 9% of people said “65 years”
- About 5% of people said “13 years”
- About 3% of people said “18 years”
- About 3% of people said “45 years”
Some thoughts, before we get into the science:
An alternative wording for the original question was “when does the human brain finish developing”; the meaning is the same but the feeling is slightly different:
- “When does the human brain stop developing?” focuses attention on the idea of cessation, and will skew responses to later ages
- When does the human brain finish developing?” focuses on attention on a kind of “is it done yet?” and will skew responses to earlier ages
Ultimately, since we had to chose one word or another, we picked the shortest one, but it would have been interesting if we could have done an A/B test, and asked half one way, and half the other way!
Why we picked those ages
We picked those ages as poll options for reasons people might be drawn to them:
- 13 years: in English-speaking cultures, an important milestone of entering adolescence (note that the concept of a “teenager” is not precisely universal as most languages do not have “-teen” numbers in the same way; the concept of “adolescent” may thus be tied to other milestones)
- 18 years: age of legal majority in N. America and many other places
- 25 years: age popularly believed to be when the brain is finished developing, due to a study that we’ll talk about shortly (we guess that’s why there’s a spike in our results for this, too!)
- 45 years: age where many midlife hormonal changes occur, and many professionals are considered to have peaked in competence and start looking towards retirement
- 65 years: age considered “senior” in much of N. America and many other places, as well as the cut-off and/or starting point for a lot of medical research
Notice, therefore, how a lot of things are coming from places they really shouldn’t. For example, because there are many studies saying “n% of people over 65 get Alzheimer’s” or “n% of people over 65 get age-related cognitive decline”, etc, 65 becomes the age where we start expecting this—because of an arbitrary human choice of where to draw the cut-off for the study enrollment!
Similarly, we may look at common ages of legal majority, or retirement pensions, and assume “well it must be for a good reason”, and dear reader, those reasons are more often economically motivated than they are biologically reasoned.
So, what does the science say?
Our brains are never finished developing: True or False?
True! If we define “finished developing” as “we cease doing neurogenesis and neuroplasticity is no longer in effect”.
Glossary:
- Neurogenesis: the process of creating new brain cells
- Neuroplasticity: the process of the brain adapting to changes by essentially rebuilding itself to suit our perceived current needs
We say “perceived” because sometimes neuroplasticity can do very unhelpful things to us (e.g: psychological trauma, or even just bad habits), but on a biological level, it is always doing its best to serve our overall success as an organism.
For a long time it was thought that we don’t do neurogenesis at all as adults, but this was found to be untrue:
How To Grow New Brain Cells (At Any Age)
Summary of conclusions of the above: we’re all growing new brain cells at every age, even if we be in our 80s and with Alzheimer’s disease, but there are things we can do to enhance our neurogenic potential along the way.
Neuroplasticity will always be somewhat enhanced by neurogenesis (after all, new neurons get given jobs to do), and we reviewed a great book about the marvels of neuroplasticity including in older age:
Our brains are still developing up to the age of 25: True or False?
True! And then it keeps on developing after that, too. Now this is abundantly obvious considering what we just talked about, but see what a difference the phrasing makes? Now it makes it sound like it stops at 25, which this statement doesn’t claim at all—it only speaks for the time up to that age.
A lot of the popular press about “the brain isn’t fully mature until the age of 25” stems from a 2006 study that found:
❝For instance, frontal gray matter volume peaks at about age 11.0 years in girls and 12.1 years in boys, whereas temporal gray matter volume peaks at about age at 16.7 years in girls and 16.2 years in boys. The dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex, important for controlling impulses, is among the latest brain regions to mature without reaching adult dimensions until the early 20s.❞
Source: Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Adolescent Brain
There are several things to note here:
- The above statement is talking about the physical size of the brain growing
- Nowhere does he say “and stops developing at 25”
However… The study only looked at brains up to the age of 25. After that, they stopped looking, because the study was about “the adolescent brain” so there has to be a cut-off somewhere, and that was the cut-off they chose.
This is the equivalent of saying “it didn’t stop raining until four o’clock” when the reality is that four o’clock is simply when you gave up on checking.
The study didn’t misrepresent this, by the way, but the popular press did!
Another 2012 study looked at various metrics of brain development, and found:
- Synapse overproduction into the teens
- Cortex pruning into the late 20s
- Prefrontal pruning into middle age at least (they stopped looking)
- Myelination beyond middle age (they stopped looking)
Source: Experience and the developing prefrontal cortex ← check out figure 1, and make sure you’re looking at the human data not the rat data
So how’s the most recent research looking?
Here’s a 2022 study that looked at 123,984 brain scans spanning the age range from mid-gestation to 100 postnatal years, and as you can see from its own figure 1… Most (if not all) brain-things keep growing for life, even though most slow down at some point, they don’t stop:
Brain charts for the human lifespan ← check out figure 1; don’t get too excited about the ventricular volume column as that is basically “brain that isn’t being a brain”. Do get excited about the rest, though!
Want to know how not to get caught out by science being misrepresented by the popular press? Check out:
How Science News Outlets Can Lie To You (Yes, Even If They Cite Studies!)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: