Fast Burn – by Dr. Ian K. Smith
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Intermittent fasting seems simple enough: how complicated can “stop eating for a bit” be? Well, there are nuances and tweaks and hacks and “if you do this bit wrong it will sabotage your benefits” things to know about, too.
Dr. Smith takes us through the basic essentials first, and covers each of the main kinds of intermittent fasting, for example:
- Time-restricted eating; 12:12, 16:8, etc, with those being hours fasting vs hours eating
- Caloric restriction models; for example 5:2, where one eats “normally” for 5 days a week, and on two non-consecutive days, eats only 500 calories
- Day off models and more; for example, “no eating on Sundays” that can, depending on your schedule, be anything from a 24-hour fast to 36 hours or more.
…and, most notably, what they each do metabolically.
Then, the real meat of the book is his program. Taking into account the benefits of each form of fasting, he weaves together a 9-week program to first ease us gently into intermittent fasting, and then enjoy the maximum benefits with minimum self-sabotage.
Which is the biggest stumbling-block for many trying intermittent fasting for the first time, so it’s a huge help that he takes care of this here.
He also includes meal plans and recipes; readers can use those or not; the fasting plan stands on its own two feet without them too.
Bottom line: if you’ve been thinking of trying intermittent fasting but have been put off by all the kinds or have had trouble sticking to it, this book may be just what you need.
Click here to check out Fast Burn on Amazon and see what you can achieve!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why Do We Have Pores, And Could We Not?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Do we really need pores, and why are they bigger on the face?❞
Pores secrete sweat or sebum (there are different kinds of pores for each).
If we didn’t have sweat pores, we’d be unable to sweat, which superficially may seem like a bonus, but it’d make us prone to overheating (like dogs, pigs, and other mammals that cannot sweat).
If we didn’t have sebum pores (usually called hair follicles, which are supplied by a sebaceous gland), we’d be completely hairless, and also unable to supply our skin with natural oils that keep it healthy. So we’d have no hair and very unhappy skin.
Which is ironic, because to believe beauty magazines, we must at all costs minimize our pores (and indeed, interventions like botox* can kill them).
*Let’s give that its full name though:
Suffice it to say, we do not recommend getting injected with neurotoxins unless it is truly necessary to ward off a greater harm.
As for being bigger on the face, they need not be, but sebaceous glands are more active and numerous there, being most active and numerous in the face/forehead—which is why oily skin is more likely to appear there than other parts of the body.
If your facial sebaceous glands are too active for your liking…
…there are ways to reduce that, a simple and relatively gentle way (relative, for example, botox) is with retinoids, including retinols or retinoic acids. Here’s some of the science of that; the paper is about treating acne, but the mechanism of action is the same (down-regulating the sebaceous glands’ action):
The potential side-effects, however were noted as:
- Cheilitis
- Desquamation of the skin
- Pruritus
Which, in translation from sciencese, means:
- Chapped lips
- Flaky skin
- Itchiness
Which aren’t necessarily fun, which is why with retinoids are best taken in very small doses at first to see how your skin reacts.
Remember when we said what your skin would be like without pores? This is what would happen, only much worse.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Knee Pain Won’t Get Better Unless You Fix This First
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most knee pain is mechanical, caused by excessive stress or strain on specific parts of the knee joint. However, it’s weak glutes that are often the root cause of excess knee strain, because when glutes are weak, they fail to keep the pelvis level and legs aligned, leading to improper knee movement.
The seat of the problem
Weak glutes cause the pelvis to drop and the thigh bone to roll inwards (called “valgus knee”). This misalignment creates shearing forces and excessive pressure on different parts of the knee. However, it can usually be fixed, and the following exercises are recommended:
- Seated band abductions: use a resistance band around the thighs while seated. Push your knees apart, and hold for a few seconds.
- Glute bridge with resistance band: lie on your back with your feet flat and a resistance band around your thighs. Push your hips up into a bridge position, then press your knees outward against the band.
- Clamshell exercise: lie on your side, with your knees bent at 90°. Keep your body slightly tilted forward, then lift the top knee while keeping your heels together.
- Hip abductions (lateral leg raises): lie on your side, keeping your legs straight. Lift the top leg slightly backward and upward, leading with your heel.
- Standing hip abductions: stand upright, using a wall for support. Lift one leg sideways and slightly backward while keeping your spine straight. Unlike the other exercises, this one has the benefit of being doable almost anywhere.
For more on each of these plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
The Secret to Better Squats: Foot, Knee, & Ankle Mobility
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Fix Your Upper Back With These Three Steps
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to back pain, the lower back gets a lot of attention, but what about when it’s nearer the neck and shoulders?
Reaching for better health
In this short video, Liv describes and shows three exercises:
Exercise 1: Thoracic Pullover (Dumbbell Pullover)
Purpose: Improves overhead reach and shoulder mobility.
Equipment: light weight, yoga block, or foam roller.
Steps:- Lie on the floor with the foam roller/block beneath the upper back.
- Hold the weight in both hands, arms extended upward.
- Inhale deeply and reach the weight toward the ceiling.
- Exhale and arc your spine over the block, moving the weight backward.
- Keep core tension to maintain a neutral lower back position.
- Perform 10 repetitions.
Exercise 2: Rotational Mobility Stretch
Purpose: enhances torso rotation, core strength, and hip mobility.
Equipment: none (or a mat)
Steps:- Lie on your side with knees stacked at 90° and arms extended in front.
- Hold a weight in the top hand.
- Inhale and lift the top arm toward the ceiling, extending the shoulder blade.
- Exhale and twist your torso, allowing the arm to move toward the floor.
- Modify by extending the bottom leg for a deeper twist if needed.
- Perform 6 reps per side, switching legs and repeating on the other side.
Exercise 3: Doorway/Pole Side Stretch
Purpose: targets multiple areas for a deep, satisfying stretch.
Equipment: door frame, pole, or wall.
Steps:- Stand at arm’s length from the wall or frame.
- Cross the outer leg (furthest from the wall) behind the inner leg.
- Place the closest hand on the wall and reach the other arm overhead.
- Grip the wall or frame with the top hand, pressing away with the bottom hand.
- Lean into a banana-shaped curve and rotate your chest upward for a deeper stretch.
- Hold for 20–30 seconds per side and repeat 2–3 times.
For more on all of these, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Semaglutide for Weight Loss?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Semaglutide for weight loss?
Semaglutide is the new kid on the weight-loss block, but it’s looking promising (with some caveats!).
Most popularly by brand names Ozempic and Wegovy, it was first trialled to help diabetics*, and is now sought-after by the rest of the population too. So far, only Wegovy is FDA-approved for weight loss. It contains more semaglutide than Ozempic, and was developed specifically for weight loss, rather than for diabetes.
*Specifically: diabetics with type 2 diabetes. Because it works by helping the pancreas to make insulin, it’s of no help whatsoever to T1D folks, sadly. If you’re T1D and reading this though, today’s book of the day is for you!
First things first: does it work as marketed for diabetes?
It does! At a cost: a very common side effect is gastrointestinal problems—same as for tirzepatide, which (like semaglutide) is a GLP-1 agonist, meaning it works the same way. Here’s how they measure up:
- Head-to-head study: Effects of subcutaneous tirzepatide versus placebo or semaglutide on pancreatic islet function and insulin sensitivity in adults with type 2 diabetes
- Head-to-head systematic review: Semaglutide for the treatment of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of safety and efficacy outcomes
As you can see, both of them work wonders for pancreatic function and insulin sensitivity!
And, both of them were quite unpleasant for around 20% of participants:
❝Tirzepatide, oral and SC semaglutide has a favourable efficacy in treating T2DM. Gastrointestinal adverse events were highly recorded in tirzepatide, oral and SC semaglutide groups.❞
What about for weight loss, if not diabetic?
It works just the same! With just the same likelihood of gastro-intestinal unpleasantries, though. There’s a very good study that was done with 1,961 overweight adults; here it is:
Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity
The most interesting things here are the positive results and the side effects:
❝The mean change in body weight from baseline to week 68 was −14.9% in the semaglutide group as compared with −2.4% with placebo, for an estimated treatment difference of −12.4 percentage points (95% confidence interval [CI], −13.4 to −11.5; P<0.001).❞
In other words: if you take this, you’re almost certainly going to get something like 6x better weight loss results than doing the same thing without it.
❝Nausea and diarrhea were the most common adverse events with semaglutide; they were typically transient and mild-to-moderate in severity and subsided with time. More participants in the semaglutide group than in the placebo group discontinued treatment owing to gastrointestinal events (59 [4.5%] vs. 5 [0.8%])❞
~ ibid.
In other words: you have about a 3% chance of having unpleasant enough side effects that you don’t want to continue treatment (contrast this with the 20%ish chance of unpleasant side effects of any extent)!
Any other downsides we should know about?
If you stop taking it, weight regain is likely. For example, a participant in one of the above-mentioned studies who lost 22% of her body weight with the drug’s help, says:
❝Now that I am no longer taking the drug, unfortunately, my weight is returning to what it used to be. It felt effortless losing weight while on the trial, but now it has gone back to feeling like a constant battle with food. I hope that, if the drug can be approved for people like me, my [doctor] will be able to prescribe the drug for me in the future.❞
~ Jan, a trial participant at UCLH
Is it injection-only, or is there an oral option?
An oral option exists, but (so far) is on the market only in the form of Rybelsus, another (slightly older) drug containing semaglutide, and it’s (so far) only FDA-approved for diabetes, not for weight loss. See:
A new era for oral peptides: SNAC and the development of oral semaglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes ← for the science
FDA approves first oral GLP-1 treatment for type 2 diabetes ← For the FDA statement
Where can I get these?
Availability and prescribing regulations vary by country (because the FDA’s authority stops at the US borders), but here is the website for each of them if you’d like to learn more / consider if they might help you:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hazelnuts vs Pistachios – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing hazelnuts to pistachios, we picked the hazelnuts.
Why?
An argument could be made for either, depending on what we prioritize! So there was really no wrong answer here today, but it is good to know what each nut’s strengths are:
In terms of macros, pistachios have more fiber, carbs, protein, and (mostly healthy) fat. That does make them the “more food per food” option, but it’s worth noting that while hazelnuts have more fiber, they also have a higher margin of difference when it comes to their greater carb count, and resultantly, hazelnuts do have the lower glycemic index. That said, they’re still both low-GI foods, so we’ll call this section a win for pistachios overall.
When it comes to vitamins, hazelnuts have more of vitamins B3, B5, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while pistachios have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, and B6. So, a fair 7:4 win for hazelnuts here.
In the category of minerals, hazelnuts have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, and zinc, while pistachios have more phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. A clear 6:3 win for hazelnuts.
In short, both are good sources of many nutrients, so choose according to what you want to prioritize, or better yet, enjoy both.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
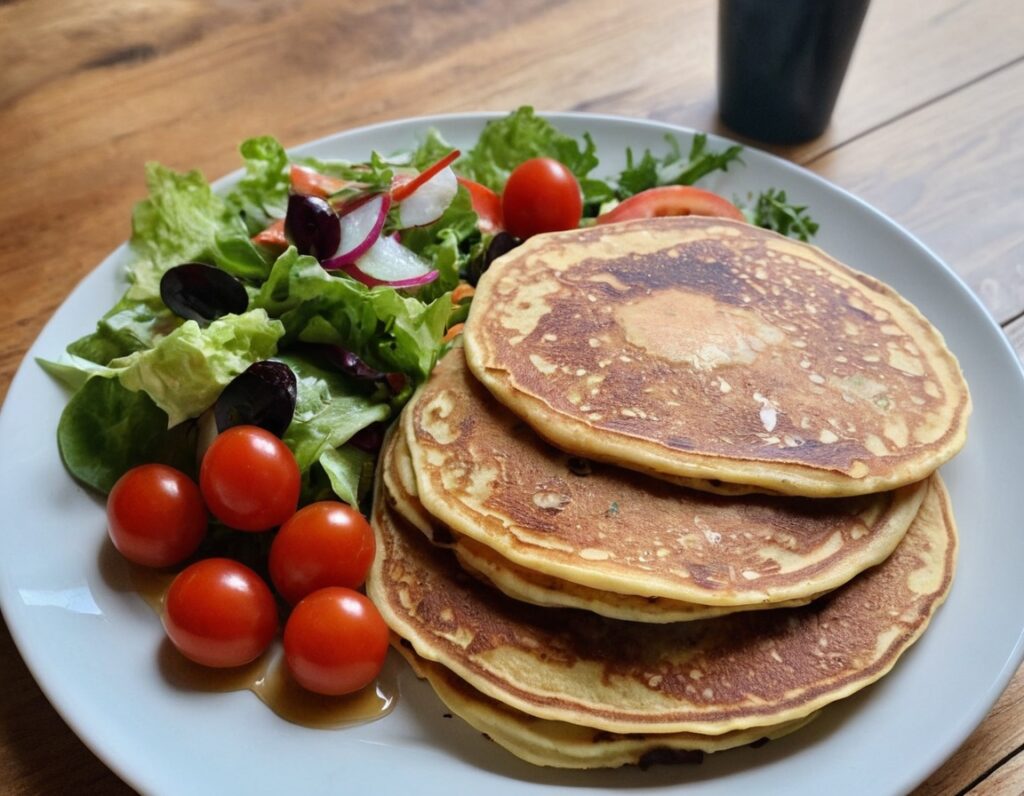
Mineral-Rich Mung Bean Pancakes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mung beans are rich in an assortment of minerals, especially iron, copper, phosphorus, and magnesium. They’re also full of protein and fiber! What better way to make pancakes healthy?
You will need
- ½ cup dried green mung beans
- ½ cup chopped fresh parsley
- ½ cup chopped fresh dill
- ¼ cup uncooked wholegrain rice
- ¼ cup nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp MSG, or 2 tsp low-sodium salt
- 2 green onions, finely sliced
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Soak the mung beans and rice together overnight.
2) Drain and rinse, and blend them in a blender with ¼ cup of water, to the consistency of regular pancake batter, adding more water (sparingly) if necessary.
3) Transfer to a bowl and add the rest of the ingredients except for the olive oil, which latter you can now heat in a skillet over a medium-high heat.
4) Add a few spoonfuls of batter to the pan, depending on how big you want the pancakes to be. Cook on both sides until you get a golden-brown crust, and repeat for the rest of the pancakes.
5) Serve! As these are savory pancakes, you might consider serving them with a little salad—tomatoes, olives, and cucumbers go especially well.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- What’s The Deal With MSG?
- All About Olive Oils: Is “Extra Virgin” Worth It?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: