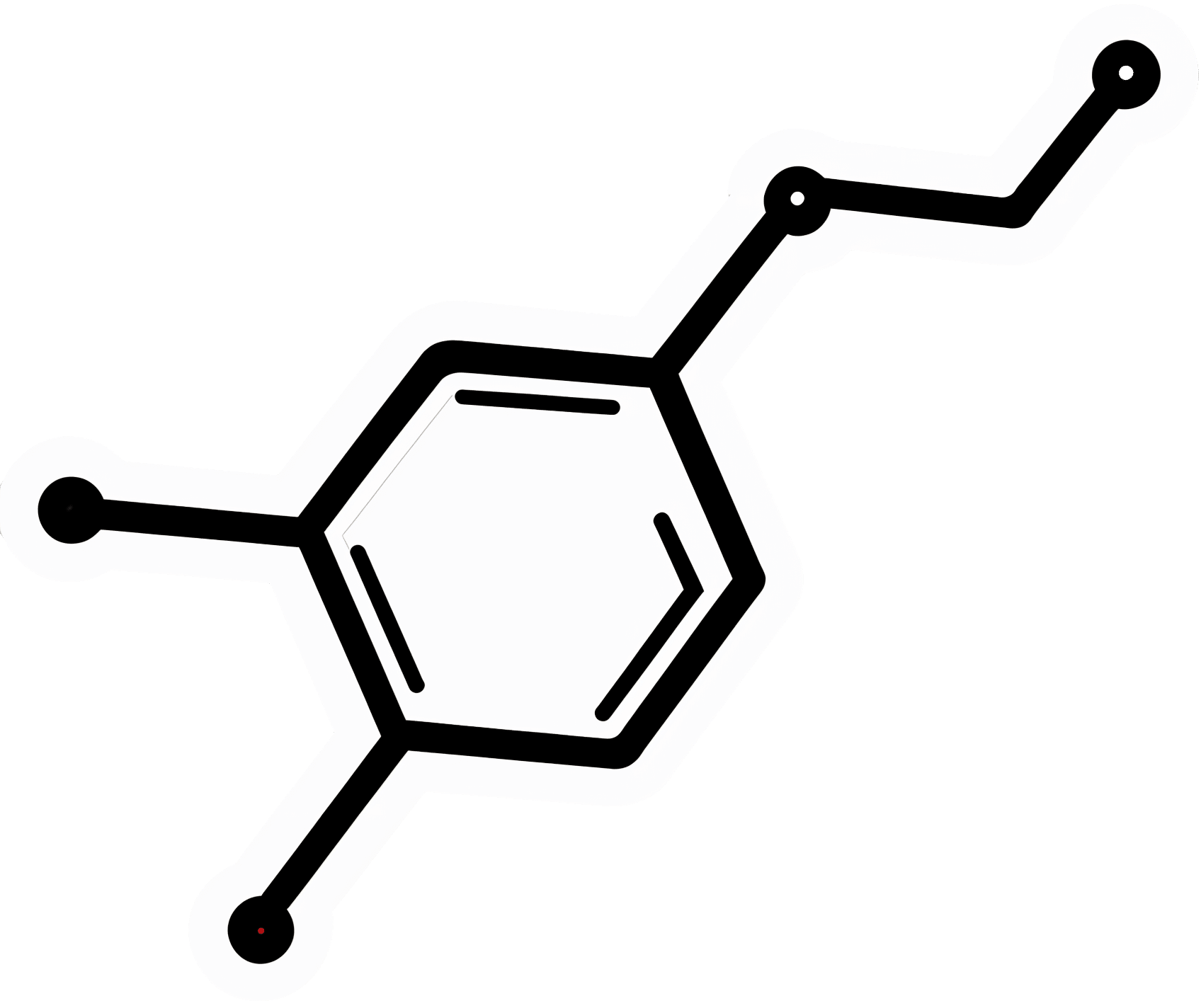
The Circadian Code – by Dr. Satchin Panda
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a lot more to circadian rhythm than “sleep during these hours”. And there’s a lot more to bear in mind than “don’t have blue/white light at night”.
In fact, Dr. Satchin Panda explains, there’s a whole daily symphony of movements in our body as different biochemical processes wax and wane according to what time of day it is.
There are several important things he wants us to know about this:
- Our body needs to know what time it is, for those processes to work correctly
- Because of these daily peaks and troughs of various physiological functions, we get “correct” times for things we do every day. Not just sleeping/waking, but also:
- The best time to eat
- The best time to exercise
- The best time to do mental work
- The best times to take different kinds of supplements/medications
Dr. Panda also looks at what things empower, or disempower, our body to keep track of what time it is.
Bottom line: if you’d like to optimize your days and your health, this book has a lot of very valuable practicable tips.
Click here to check out The Circadian Code, and make the most of yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dried Apricots vs Dried Prunes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dried apricots to dried prunes, we picked the prunes.
Why?
First, let’s talk hydration. We’ve described both of these as “dried”, but prunes are by default dried plums, usually partially rehydrated. So, for fairness, on the other side of things we’re also looking at dried apricots, partially rehydrated. Otherwise, it would look (mass for mass or volume for volume) like one is seriously outstripping the other even if some metric were actually equal, just because of water-weight in one and not the other.
Illustrative example: consider, for example, that the sugar in a bunch of grapes or a handful of raisins can be the same, not because they magically got more sugary, but because the water was dried out, so per mass and per volume, there’s more sugar, proportionally.
Back to dried apricots and dried prunes…
You’ll often see these two next to each other in the heath food store, which is why we’re comparing them here.
Of course, if it is practical, please by all means enjoy fresh apricots and fresh plums. But we know that life is not always convenient, fruits are not in season growing in abundance in our gardens all year round, and sometimes we’re stood in the aisle of a grocery store, weighing up the dried fruit options.
- Apricots are well-known for their zinc, potassium, and vitamin A.
- Prunes are well-known for their fiber.
But that’s not the whole story…
- Apricots outperform prunes for vitamin A, and also vitamins C and E.
- Prunes take first place for vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and K, and also for minerals calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, and zinc.
- Prunes also have about 3x the fiber, which at the very least offsets the fact that they have 3x the sugar.
Once again, sugar in fruit is healthy (sugar in fruit juices is not*, though, so enjoy prunes rather than just prune juice, if you can) and can take its rightful place as providing a significant portion of our daily energy needs, if we let it.
*It’s the same sugar, just the manner of delivery changes what it does to our liver and our pancreas; see:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
In summary…
Dried apricots are great (fresh are even better), and yet prunes outperform them by most metrics on a like-for-like basis.
Prunes have, on balance, a lot more vitamins and minerals, as well as more fiber and energy.
Want to get some?
Your local supermarket probably has them, and if you prefer having them delivered to your door, then here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Wakefulness, Cognitive Enhancement, AND Improved Mood?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Old Drug, New Tricks?
Modafinil (also known by brand names including Modalert and Provigil) is a dopamine uptake inhibitor.
What does that mean? It means it won’t put any extra dopamine in your brain, but it will slow down the rate at which your brain removes naturally-occuring dopamine.
The result is that your brain will get to make more use of the dopamine it does have.
(dopamine is a neutrotransmitter that allows you to feel wakeful and happy, and perform complex cognitive tasks)
Modafinil is prescribed for treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness. Often that’s caused by shift work sleep disorder, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or narcolepsy.
Read: Overview of the Clinical Uses, Pharmacology, and Safety of Modafinil
Many studies done on humans (rather than rats) have been military experiments to reduce the effects of sleep deprivation:
Click Here To See A Military Study On Modafinil!
They’ve found modafinil to be helpful, and more effective and more long-lasting than caffeine, without the same “crash” later. This is for two reasons:
1) while caffeine works by blocking adenosine (so you don’t feel how tired you are) and by constricting blood vessels (so you feel more ready-for-action), modafinil works by allowing your brain to accumulate more dopamine (so you’re genuinely more wakeful, and you get to keep the dopamine)
2) the biological half-life of modafinil is 12–15 hours, as opposed to 4–8 hours* for caffeine.
*Note: a lot of sources quote 5–6 hours for caffeine, but this average is misleading. In reality, we are each genetically predetermined to be either a fast caffeine metabolizer (nearer 4 hours) or a slow caffeine metabolizer (nearer 8 hours).
What’s a biological half-life (also called: elimination half-life)?
A substance’s biological half-life is the time it takes for the amount in the body to be reduced by exactly half.
For example: Let’s say you’re a fast caffeine metabolizer and you have a double-espresso (containing 100mg caffeine) at 8am.
By midday, you’ll have 50mg of caffeine left in your body. So far, so simple.
By 4pm you might expect it to be gone, but instead you have 25mg remaining (because the amount halves every four hours).
By 8pm, you have 12.5mg remaining.
When midnight comes and you’re tucking yourself into bed, you still have 6.25mg of caffeine remaining from your morning coffee!
Use as a nootropic
Many healthy people who are not sleep-deprived use modafinil “off-label” as a nootropic (i.e., a cognitive enhancer).
Read: Modafinil for cognitive neuroenhancement in healthy non-sleep-deprived subjects: A systematic review
Important Note: modafinil is prescription-controlled, and only FDA-approved for sleep disorders.
To get around this, a lot of perfectly healthy biohackers describe the symptoms of sleep pattern disorder to their doctor, to get a prescription.
We do not recommend lying to your healthcare provider, and nor do we recommend turning to the online “grey market”.
Such websites often use anonymized private doctors to prescribe on an “informed consent” basis, rather than making a full examination. Those websites then dispense the prescribed medicines directly to the patient with no further questions asked (i.e. very questionable practices).
Caveat emptor!
A new mood-brightener?
Modafinil was recently tested head-to-head against Citalapram for the treatment of depression, and scored well:
See its head-to-head scores here!
How does it work? Modafinil does for dopamine what a lot of anti-depressants do for serotonin. Both dopamine and serotonin promote happiness and wakefulness.
This is very promising, especially as modafinil (in most people, at least) has fewer unwanted side-effects than a lot of common anti-depressant medications.
Share This Post
-
Pasteurization: What It Does And Doesn’t Do
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pasteurization’s Effect On Risks & Nutrients
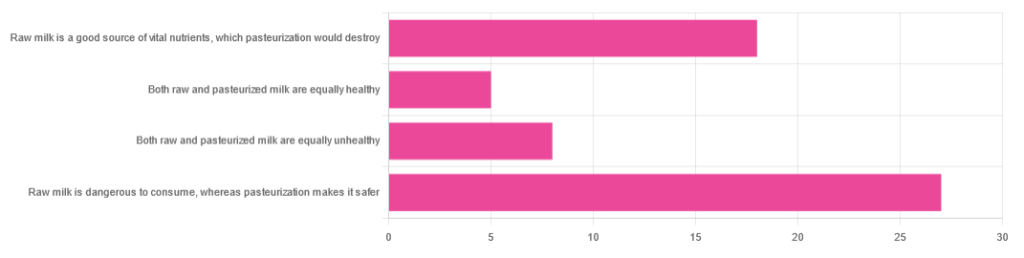
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your health-related opinions of raw (cow’s) milk, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 47% said “raw milk is dangerous to consume, whereas pasteurization makes it safer”
- About 31% said “raw milk is a good source of vital nutrients which pasteurization would destroy”
- About 14% said “both raw milk and pasteurized milk are equally unhealthy”
- About 9% said “both raw milk and pasteurized milk are equally healthy”
Quite polarizing! So, what does the science say?
“Raw milk is dangerous to consume, whereas pasteurization makes it safer: True or False?”
True! Coincidentally, the 47% who voted for this are mirrored by the 47% of the general US population in a similar poll, deciding between the options of whether raw milk is less safe to drink (47%), just as safe to drink (15%), safer to drink (9%), or not sure (30%):
Public Fails to Appreciate Risk of Consuming Raw Milk, Survey Finds
As for what those risks are, by the way, unpasteurized dairy products are estimated to cause 840x more illness and 45x more hospitalizations than pasteurized products.
This is because unpasteurized milk can (and often does) contain E. coli, Listeria, Salmonella, Cryptosporidium, and other such unpleasantries, which pasteurization kills.
Source for both of the above claims:
(we know the title sounds vague, but all this information is easily visible in the abstract, specifically, the first two paragraphs)
Raw milk is a good source of vital nutrients which pasteurization would destroy: True or False?
False! Whether it’s a “good” source can be debated depending on other factors (e.g., if we considered milk’s inflammatory qualities against its positive nutritional content), but it’s undeniably a rich source. However, pasteurization doesn’t destroy or damage those nutrients.
Incidentally, in the same survey we linked up top, 16% of the general US public believed that pasteurization destroys nutrients, while 41% were not sure (and 43% knew that it doesn’t).
Note: for our confidence here, we are skipping over studies published by, for example, dairy farming lobbies and so forth. Those do agree, by the way, but nevertheless we like sources to be as unbiased as possible. The FDA, which is not completely unbiased, has produced a good list of references for this, about half of which we would consider biased, and half unbiased; the clue is generally in the journal names. For example, Food Chemistry and the Journal of Food Science and Journal of Nutrition are probably less biased than the International Dairy Association and the Journal of Dairy Science:
FDA | Raw Milk Misconceptions and the Danger of Raw Milk Consumption
this page covers a lot of other myths too, more than we have room to “bust” here, but it’s very interesting reading and we recommend to check it out!
Notably, we also weren’t able to find any refutation by counterexample on PubMed, with the very slight exception that some studies sometimes found that in the case of milks that were of low quality, pasteurization can reduce the vitamin E content while increasing the vitamin A content. For most milks however, no significant change was found, and in all cases we looked at, B-vitamins were comparable and vitamin D, popularly touted as a benefit of cow’s milk, is actually added later in any case. And, importantly, because this is a common argument, no change in lipid profiles appears to be findable either.
In science, when something has been well-studied and there aren’t clear refutations by counterexample, and the weight of evidence is clearly very much tipped into one camp, that usually means that camp has it right.
Milk generally is good/bad for the health: True or False?
True or False, depending on what we want to look at. It’s definitely not good for inflammation, but the whole it seems to be cancer-neutral and only increases heart disease risk very slightly:
- Keep Inflammation At Bay ← short version is milk is bad, fermented milk products are fine in moderation
- Is Dairy Scary? ← short version is that milk is neither good nor terrible; fermented dairy products however are health-positive in numerous ways when consumed in moderation
You may be wondering…
…how this goes for the safety of dairy products when it comes to the bird flu currently affecting dairy cows, so:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The China Study – by Dr. T Colin Campbell and Dr. Thomas M. Campbell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is not the newest book we’ve reviewed (originally published 2005; this revised and expanded edition 2016), but it is a seminal one.
You’ve probably heard it referenced, and maybe you’ve wondered what the fuss is about. Now you can know!
The titular study itself was huge. We tend to think “oh there was one study” and look to discount it, but it literally looked at the population of China. That’s a large study.
And because China is relatively ethnically homogenous, especially per region, it was easier to isolate what dietary factors made what differences to health. Of course, that did also create a limitation: follow-up studies would be needed to see if the results were the same for non-Chinese people. But even for the rest of us (this reviewer is not Chinese), it already pointed science in the right direction. And sure enough, smaller follow-up studies elsewhere found the same.
But enough about the research; what about the book? This is a book review, not a research review, after all.
The book itself is easy for a lay reader to understand. It explains how the study was conducted (no small feat), and how the data was examined. It also discusses the results, and the conclusions drawn from those results.
In light of all this, it also offers simple actionable advices, on how to eat to avoid disease in general, and cancer in particular. In especially that latter case, one take-home conclusion was: get more of your protein from plants for a big reduction in cancer risk, for example.
Bottom line: this book is an incredible blend of “comprehensive” and “readable” that we don’t often find in the same book! It contains not just a lot of science, but also an insight into how the science works, on a research level. And, of course, its results and conclusions have strong implications for all our lives.
Click here to check out The China Study, to know more about it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Gut Health 2.0
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Gene Expression & Gut Health
This is Dr. Tim Spector. After training in medicine and becoming a consultant rheumatologist, he’s turned his attention to medical research, and is these days a specialist in twin studies, genetics, epigenetics, microbiome, and diet.
What does he want us to know?
For one thing: epigenetics are for more than just getting your grandparents’ trauma.
More usefully: there are things we can do to improve epigenetic factors in our body
DNA is often seen as the script by which our body does whatever it’s going to do, but it’s only part of the story. Thinking of DNA as some kind of “magical immutable law of reality” overlooks (to labor the metaphor) script revisions, notes made in the margins, directorial choices, and ad-lib improvizations, as well as the quality of the audience’s hearing and comprehension.
Hence the premise of one of Dr. Spector’s older books, “Identically Different: Why We Can Change Our Genes”
(*in fact, it was his first, from all the way back in 2013, when he’d only been a doctor for 34 years)
Gene expression will trump genes every time, and gene expression is something that can often be changed without getting in there with CRISPR / a big pair of scissors and some craft glue.
How this happens on the micro level is beyond the scope of today’s article; part of it has to do with enzymes that get involved in the DNA transcription process, and those enzymes in turn are despatched or not depending on hormonal messaging—in the broadest sense of “hormonal”; all the body’s hormonal chemical messengers, not just the ones people think of as hormones.
However, hormonal messaging (of many kinds) is strongly influenced by something we can control relatively easily with a little good (science-based) knowledge: the gut.
The gut, the SAD, and the easy
In broad strokes: we know what is good for the gut. We’ve written about it before at 10almonds:
Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
This is very much in contrast with what in scientific literature is often abbreviated “SAD”, the Standard American Diet, which is very bad for the gut.
However, Dr. Spector (while fully encouraging everyone to enjoy an evidence-based gut-healthy diet) wanted to do one better than just a sweeping one-size-fits-all advice, so he set up a big study with 15,000 identical twins; you can read about it here: TwinsUK
The information that came out of that was about a lot more than just gene expression and gut health, but it did provide the foundation for Dr. Spector’s next project, ZOE.
ZOE crowdsources huge amounts of data including individual metabolic responses to standardized meals in order to predict personalized food responses based on individual biology and unique microbiome profile.
In other words, it takes the guesswork out of a) knowing what your genes mean for your food responses b) tailoring your food choices with your genetic expression in mind, and c) ultimately creating a positive feedback loop to much better health on all levels.
Now, this is not an ad for ZOE, but if you so wish, you can…
- Get the free ZOE gut health guide (this is good, but generic, gut health information)
- Take the ZOE home gut health test (quiz followed by offers of lab tests)
- Browse the ZOE Health Academy, its education wing
Want to know more?
Dr. Spector has a bunch of books out, including some that we’ve reviewed previously:
- Spoon-Fed: Why Almost Everything We’ve Been Told About Food Is Wrong
- The Diet Myth: The Real Science Behind What We Eat
- Food for Life: The New Science of Eating Well
You can also check out our own previous main feature, which wasn’t about Dr. Spector’s work but was very adjacent:
The Brain-Gut Highway: A Two-Way Street
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why are tall people more likely to get cancer? What we know, don’t know and suspect
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
People who are taller are at greater risk of developing cancer. The World Cancer Research Fund reports there is strong evidence taller people have a higher chance of of developing cancer of the:
- pancreas
- large bowel
- uterus (endometrium)
- ovary
- prostate
- kidney
- skin (melanoma) and
- breast (pre- and post-menopausal).
But why? Here’s what we know, don’t know and suspect.
Pexels/Andrea Piacquadio Height does increase your cancer risk – but only by a very small amount. Christian Vinces/Shutterstock A well established pattern
The UK Million Women Study found that for 15 of the 17 cancers they investigated, the taller you are the more likely you are to have them.
It found that overall, each ten-centimetre increase in height increased the risk of developing a cancer by about 16%. A similar increase has been found in men.
Let’s put that in perspective. If about 45 in every 10,000 women of average height (about 165 centimetres) develop cancer each year, then about 52 in each 10,000 women who are 175 centimetres tall would get cancer. That’s only an extra seven cancers.
So, it’s actually a pretty small increase in risk.
Another study found 22 of 23 cancers occurred more commonly in taller than in shorter people.
Why?
The relationship between height and cancer risk occurs across ethnicities and income levels, as well as in studies that have looked at genes that predict height.
These results suggest there is a biological reason for the link between cancer and height.
While it is not completely clear why, there are a couple of strong theories.
The first is linked to the fact a taller person will have more cells. For example, a tall person probably has a longer large bowel with more cells and thus more entries in the large bowel cancer lottery than a shorter person.
Scientists think cancer develops through an accumulation of damage to genes that can occur in a cell when it divides to create new cells.
The more times a cell divides, the more likely it is that genetic damage will occur and be passed onto the new cells.
The more damage that accumulates, the more likely it is that a cancer will develop.
A person with more cells in their body will have more cell divisions and thus potentially more chance that a cancer will develop in one of them.
Some research supports the idea having more cells is the reason tall people develop cancer more and may explain to some extent why men are more likely to get cancer than women (because they are, on average, taller than women).
However, it’s not clear height is related to the size of all organs (for example, do taller women have bigger breasts or bigger ovaries?).
One study tried to assess this. It found that while organ mass explained the height-cancer relationship in eight of 15 cancers assessed, there were seven others where organ mass did not explain the relationship with height.
It is worth noting this study was quite limited by the amount of data they had on organ mass.
Is it because tall people have more cells? Halfpoint/Shutterstock Another theory is that there is a common factor that makes people taller as well as increasing their cancer risk.
One possibility is a hormone called insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). This hormone helps children grow and then continues to have an important role in driving cell growth and cell division in adults.
This is an important function. Our bodies need to produce new cells when old ones are damaged or get old. Think of all the skin cells that come off when you use a good body scrub. Those cells need to be replaced so our skin doesn’t wear out.
However, we can get too much of a good thing. Some studies have found people who have higher IGF-1 levels than average have a higher risk of developing breast or prostate cancer.
But again, this has not been a consistent finding for all cancer types.
It is likely that both explanations (more cells and more IGF-1) play a role.
But more research is needed to really understand why taller people get cancer and whether this information could be used to prevent or even treat cancers.
I’m tall. What should I do?
If you are more LeBron James than Lionel Messi when it comes to height, what can you do?
Firstly, remember height only increases cancer risk by a very small amount.
Secondly, there are many things all of us can do to reduce our cancer risk, and those things have a much, much greater effect on cancer risk than height.
We can take a look at our lifestyle. Try to:
- eat a healthy diet
- exercise regularly
- maintain a healthy weight
- be careful in the sun
- limit alcohol consumption.
And, most importantly, don’t smoke!
If we all did these things we could vastly reduce the amount of cancer.
You can also take part in cancer screening programs that help pick up cancers of the breast, cervix and bowel early so they can be treated successfully.
Finally, take heart! Research also tells us that being taller might just reduce your chance of having a heart attack or stroke.
Susan Jordan, Associate Professor of Epidemiology, The University of Queensland and Karen Tuesley, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, School of Public Health, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: