Why We Get Fat: And What to Do About It – by Gary Taubes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Taubes’ “The Case Against Sugar“. What does this one bring differently?
Mostly, it’s a different focus. Unsurprisingly, Taubes’ underlying argument is the same: sugar is the biggest dietary health hazard we face. However, this book looks at it specifically through the lens of weight loss, or avoiding weight gain.
Taubes argues for low-carb in general; he doesn’t frame it specifically as the ketogenic diet here, but that is what he is advocating. However, he also acknowledges that not all carbs are created equal, and looks at several categories that are relatively better or worse for our insulin response, and thus, fat management.
If the book has a fault it’s that it does argue a bit too much for eating large quantities of meat, based on Weston Price’s outdated and poorly-conducted research. However, if one chooses to disregard that, the arguments for a low-carb diet for weight management remain strong.
Bottom line: if you’d like to cut some fat without eating less (or exercising more), this book offers a good, well-explained guide for doing so.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
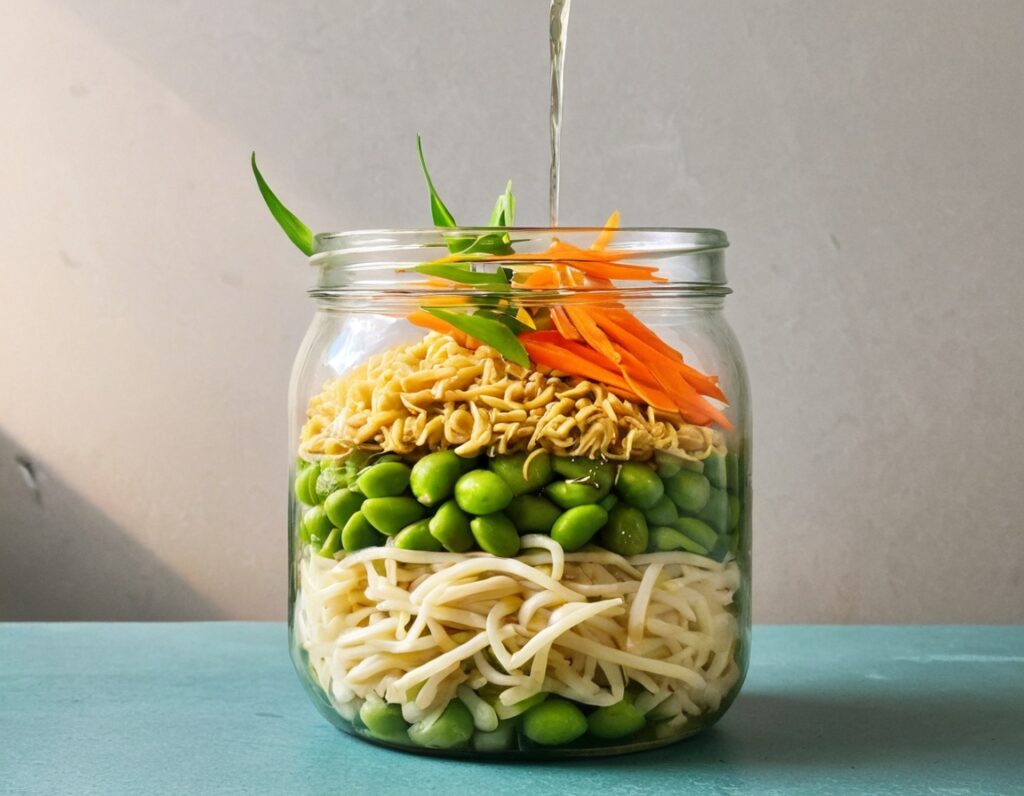
Gut-Positive Pot Noodles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Everything we consume either improves our health a little or worsens it. Pot noodles aren’t generally the healthiest foods, but these ones sure are! There’s quite a range of fiber in this, including the soluble fiber of the noodles themselves (which are, in fact, mostly fiber and water). As a bonus, the glucomannan in the noodles promotes feelings of fullness, notwithstanding its negligible carb count. Of course, the protein in the edamame beans also counts for satiety!
You will need
- ½ cup konjac noodles (also called shirataki), tossed in 1 tsp avocado oil (or sesame oil, if you don’t have avocado)
- 2 oz mangetout, thinly sliced
- 1 oz edamame beans
- ¼ carrot, grated
- 2 baby sweetcorn, cut in half lengthways
- 1 scallion, finely diced
- 1 heaped tsp crunchy peanut butter (omit if allergic)
- 1 tsp miso paste
- 1 tsp chili oil
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp peeled-and-grated ginger
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Layer a heat-resistant jar (mason jars are usually quite resistant to temperature changes) with the noodles and vegetables.
2) Combine the peanut butter, miso paste, and chili oil, black pepper, and ginger in a small bowl. Pour this dressing over the layered vegetables and noodles, and screw the lid on. Refrigerate until needed.
3) Add hot water to the jar and stir, to serve. If you prefer the vegetables to be more cooked, you can microwave (without the lid!) for a minute or two.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars ← today’s recipe makes a perfect high-fiber, low-carb starter, per the hacks here
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Unprocessed 10th Anniversary Edition – by Abbie Jay
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The main premise of this book is cooking…
- With nutritious whole foods
- Without salt, oil, sugar (“SOS”)
It additionally does it without animal products and without gluten, and (per “nutritious whole foods”), and, as the title suggests, avoiding anything that’s more than very minimally processed. Remember, for example, that if something is fermented, then that fermentation is a process, so the food has been processed—just, minimally.
This is a revised edition, and it’s been adjusted to, for example, strip some of the previous “no salt” low-sodium options (such as tamari with 233mg/tsp sodium, compared to salt’s 2,300mg/tsp sodium).
You may be wondering: what’s left? Tasty, well-seasoned, plant-based food, that leans towards the “comfort food” culinary niche.
Enough to sate the author, after her own battles with anorexia and obesity (in that order) and finally, after various hospital trips, getting her diet where it needed to be for the healthy lifestyle that she lives now, while still getting to eat such dishes as “Chef AJ’s Disappearing Lasagna” and peanut butter fudge truffles and 151 more.
Bottom line: if you want whole-food plant-based comfort-food cooking that’s healthy in general and especially heart-healthy, this book has plenty of that.
Click here to check out Unprocessed: 10th Anniversary Edition, and… Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Want to sleep longer? Adding mini-bursts of exercise to your evening routine can help – new study
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Exercising before bed has long been discouraged as the body doesn’t have time to wind down before the lights go out.
But new research has found breaking up a quiet, sedentary evening of watching television with short bursts of resistance exercise can lead to longer periods of sleep.
Adults spend almost one third of the 24-hour day sleeping. But the quality and length of sleep can affect long-term health. Sleeping too little or waking often in the night is associated with an increased risk of heart disease and diabetes.
Physical activity during the day can help improve sleep. However, current recommendations discourage intense exercise before going to bed as it can increase a person’s heart rate and core temperature, which can ultimately disrupt sleep.
Nighttime habits
For many, the longest period of uninterrupted sitting happens at home in the evening. People also usually consume their largest meal during this time (or snack throughout the evening).
Insulin (the hormone that helps to remove sugar from the blood stream) tends to be at a lower level in the evening than in the morning.
Together these factors promote elevated blood sugar levels, which over the long term can be bad for a person’s health.
Our previous research found interrupting evening sitting every 30 minutes with three minutes of resistance exercise reduces the amount of sugar in the bloodstream after eating a meal.
But because sleep guidelines currently discourage exercising in the hours before going to sleep, we wanted to know if frequently performing these short bursts of light activity in the evening would affect sleep.
Activity breaks for better sleep
In our latest research, we asked 30 adults to complete two sessions based in a laboratory.
During one session the adults sat continuously for a four-hour period while watching streaming services. During the other session, they interrupted sitting by performing three minutes of body-weight resistance exercises (squats, calf raises and hip extensions) every 30 minutes.
After these sessions, participants went home to their normal life routines. Their sleep that evening was measured using a wrist monitor.
Our research found the quality of sleep (measured by how many times they woke in the night and the length of these awakenings) was the same after the two sessions. But the night after the participants did the exercise “activity breaks” they slept for almost 30 minutes longer.
Identifying the biological reasons for the extended sleep in our study requires further research.
But regardless of the reason, if activity breaks can extend sleep duration, then getting up and moving at regular intervals in the evening is likely to have clear health benefits.
Time to revisit guidelines
These results add to earlier work suggesting current sleep guidelines, which discourage evening exercise before bed, may need to be reviewed.
As the activity breaks were performed in a highly controlled laboratory environment, future research should explore how activity breaks performed in real life affect peoples sleep.
We selected simple, body-weight exercises to use in this study as they don’t require people to interrupt the show they may be watching, and don’t require a large space or equipment.
If people wanted to incorporate activity breaks in their own evening routines, they could probably get the same benefit from other types of exercise. For example, marching on the spot, walking up and down stairs, or even dancing in the living room.
The key is to frequently interrupt evening sitting time, with a little bit of whole-body movement at regular intervals.
In the long run, performing activity breaks may improve health by improving sleep and post-meal blood sugar levels. The most important thing is to get up frequently and move the body, in a way the works best for a person’s individual household.
Jennifer Gale, PhD candidate, Department of Human Nutrition, University of Otago and Meredith Peddie, Senior Lecturer, Department of Human Nutrition, University of Otago
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Five Supplements That Actually Work Vs Arthritis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Diana Girnita, a double board-certified physician (internal medicine & rheumatology) who, in addition to her MD, also has a PhD in immunology—bearing in mind that rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition.
Her mission is to help people with any form of arthritis (rheumatoid or otherwise) and those with many non-arthritic autoimmune conditions (ranging from tendonitis to lupus) to live better.
Today, we’ll be looking at her recommendations of 5 supplements that actually help alleviate arthritis:
Collagen
Collagen famously supports skin, nails, bones, and joint cartilage; Dr. Girnita advises that it’s particularly beneficial for osteoarthritis.
Specifically, she recommends either collagen peptides or hydrolyzed collagen, as they are most absorbable. However, collagen can also be sourced from foods like bone broth, fish with skin and bones, and gelatin-based foods.
If you’re vegetarian/vegan, then it becomes important to simply consume the ingredients for collagen, because like most animals, we can synthesize it ourselves provided we get the necessary nutrients. For more on that, see:
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
Glucosamine & chondroitin
Technically two things, but almost always sold/taken together. Naturally found in joint cartilage, it can slow cartilage breakdown and reduce pain in osteoarthritis.
Studies show pain relief, especially in moderate-to-severe cases; best taken long-term. Additionally, it’s a better option than NSAIDs for patients with heart or gastrointestinal issues.
10almonds tip: something that’s tricker to find as a supplement than glucosamine and chondroitin, but you might want to check it out:
Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?!
Omega-3 fatty acids
Dr. Girnita recommends this one because unlike the above recommendations that mainly help reduce/reverse the joint damage itself, omega-3 reduces inflammation, pain, and stiffness, and can decrease or eliminate the need for NSAIDs in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis.
She recommends 2-4g EPA/DHA daily; ideally taken with a meal for better absorption.
She also recommends to look for mercury-free options—algae-derived are usually better than fish-derived, but check for certification either way! See also:
What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
Boswellia serrata (frankincense)
Popularly enjoyed as an incense but also available in supplement form, it contains boswellic acid, which reduces inflammation and cartilage damage.
Dr. Girnita recommends 100 mg daily, but advises that it may interact with some antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and NSAIDs—so speak with your pharmacist/doctor if unsure.
We also wrote about this one here:
Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief
Curcumin (turmeric)
Well-known for its potent anti-inflammatory properties, it’s comparable to NSAIDs in pain relief for most common forms of arthritis.
Dr. Girnita recommends 1–1.5g of curcumin daily, ideally combined with black pepper for better absorption:
Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
Lastly…
Dr. Girnita advises to not blindly trust supplements, but rather, to test them for 2–3 months while keeping a journal of your symptoms. If it improves things for you, keep it up, if not, discontinue. Humans can be complicated and not everything will work exactly the same way for everyone!
For more on dealing with chronic pain specifically, by the way, check out:
Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Just One Heart – by Dr. Jonathan Fisher
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this is not: a book to say eat fiber, go easy on the salt, get some exercise, and so forth.
What this rather is: a book about the connection between the heart and mind; often written poetically, the simple biological reality is that our emotional state does have a genuine impact on our heart health, and as such, any effort to look after our heart (healthwise) would be incomplete without an effort to look after our heart (emotionally).
Dr. Fisher talks about the impact of stress and uncertainty, as well as peace and security, on heart health—and then, having sorted emotional states into “heart breakers” and “heart wakers”, he goes about laying out a plan for what is, emotionally and thus also physiologically, good for our heart.
Chapter by chapter, he walks us through the 7 principles to live by:
- Steadiness: how to steady your heart amid chaos
- Wisdom: how to develop a wise heart in uncertain times
- Openness: how to safely open your heart in a threatening world
- Wholeness: how to show up with your whole heart without going to pieces
- Courage: how to lead with a courageous heart when fear surrounds you
- Lightness: how to live with a light heart in a heavy world
- Warmth: how to love with a warm heart when life feels cold
The style is anything but clinical; it’s well-written, certainly, and definitely informed in part by his medical understanding of the heart, but it’s entirely the raw human element that shines throughout, and that makes the ideas a lot more tangible.
Bottom line: if you’d like your heart to be healthy (cardiac health) and your heart to be healthy (emotional health), this book is a very worthwhile read.
Click here to check out Just One Heart, and take care of yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Whole-Body Approach to Osteoporosis – by Keith McCormick
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You probably already know to get enough calcium and vitamin D, and do some resistance training. What does this book offer beyond that advice?
It’s pretty comprehensive, as it turns out. It covers the above, plus the wide range of medications available, what supplements help or harm or just don’t have enough evidence either way yet, things like that.
Amongst the most important offerings are the signs and symptoms that can help monitor your bone health (things you can do at home! Like examinations of your fingernails, hair, skin, tongue, and so forth, that will reveal information about your internal biochemical make-up), as well as what lab tests to ask for. Which is important, as osteoporosis is one of those things whereby we often don’t learn something is wrong until it’s too late.
The author is a chiropractor, which doesn’t always have a reputation as the most robustly science-based of physical therapy options, but he…
- doesn’t talk about chiropractic
- did confer with a flock of experts (osteopaths, nutritionists, etc) to inform/check his work
- does refer consistently to good science, and explains it well
- includes 16 pages of academic references, and yes, they are very reputable publications
Bottom line: this one really does give what the subtitle promises: a whole body approach to avoiding (or reversing) osteoporosis.
Click here to check out The Whole Body Approach To Osteoporosis; sooner is better than later!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: