52 Small Changes – by Brett Blumenthal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We see a lot of books that exhort us to get a six-pack in a month, change our life in 7 days, learn Japanese in 24 hours. The reality is, things take time!
Brett Blumenthal is more realistic while being just as motivational:
The idea is simple… Make one small change per week for 52 weeks, and at the end of the year, you’ll be healthier and happier.
At 10almonds, we’re big fans of small changes that add up (or rather: compound!) to make big differences, so this one’s absolutely our style!
Best of all, she offers us not just “do this” advice, but also “and here’s the information and resources you’ll need to make this change work the best it can for you”
The advices range in topic from nutrition to exercise to sleep to mental wellness to interpersonal stuff and more. The biggest focus is on personal health, though, with small changes to exercise and nutrition making up the lion’s share of the changes.
Bottom line: this is a book you’ll want to grab once a week. Consider setting a reminder on your phone to check in with it each Sunday, for example!
Take the first step and order “52 Small Changes” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
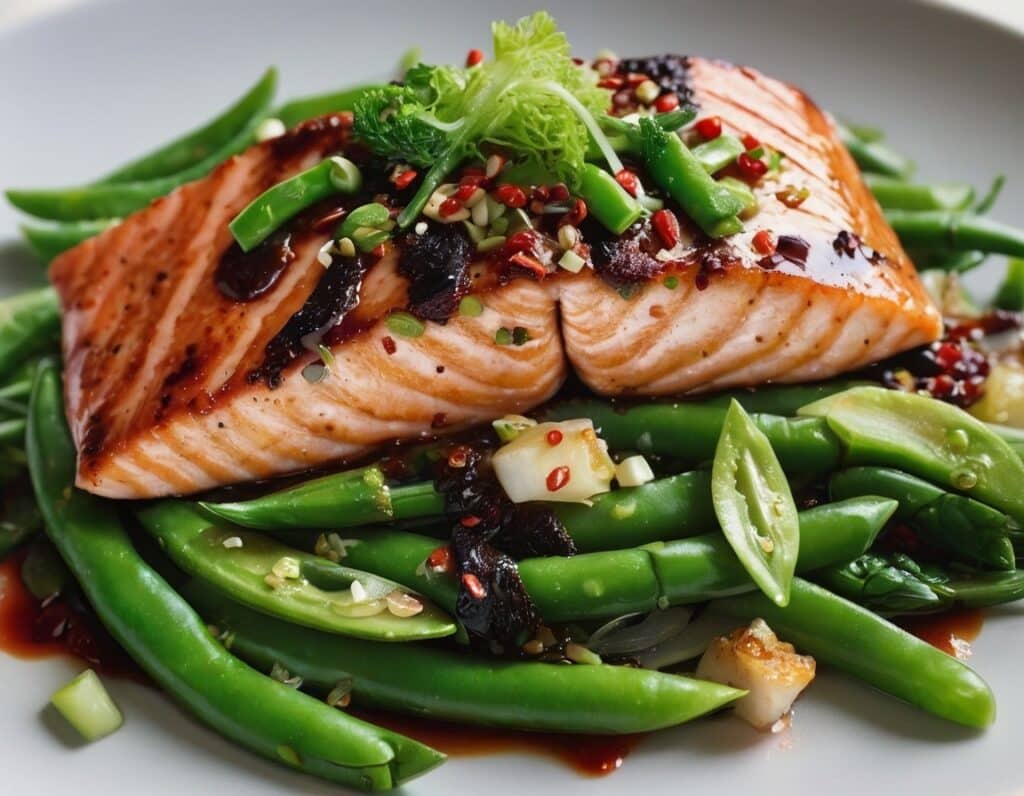
Chili Hot-Bedded Salmon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one can be made in less time than it takes to order and receive a Chinese take-out! The principle is simple: it’s a bed of greens giving pride of place to a salmon fillet in a deliciously spicy marinade. So healthwise, we have greens-and-beans, healthy protein and fats, and tasty polyphenols. Experientially, we have food that tastes a lot more decadent than it is!
You will need
- 4 salmon fillets (if vegan, substitute firm tofu; see also how to make this no-salmon salmon)
- 2 bok choy, washed and stems trimmed
- 7 oz green beans, trimmed
- 4 oz sugar snap peas
- 4 spring onions, sliced
- 2 tbsp chili oil*
- 1 tbsp soy sauce
- 1 tsp garlic paste
- 1 tsp ginger paste
- 1 tsp black pepper
*this can be purchased as-is, but if you want to make your own in advance, simply take extra virgin olive oil and infuse it with [finely chopped, red] chili. This is a really good thing to do for commonly-used flavored oils, by the way—chili oil and garlic oil are must-haves in this writer’s opinion; basil oil, sage oil, and rosemary oil, are all excellent things to make and have in, too. Just know, infusing is not quick, so it’s good to do these in batch and make plenty well before you need it. For now, if you don’t have any homemade already, then store-bought is fine 🙂
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 360℉/180℃/gas mark 6
2) Lay out 4 large squares of foil, and put the bok choy, green beans, and sugar snap peas in a little pile in the middle of each one. Put a salmon fillet on top of each (if it has skin, score the skin first, so that juices will be able to penetrate, and put it skin-side down), and then top with the spring onions.
3) Mix the rest of the ingredients in a small bowl, and then spoon this marinade evenly over each of the fillets (alternatively, if you have occasion to marinade the fillets in advance and let them sit in the marinade in the fridge for some hours before, do so, in which case this step will already be done now, because past-you did it. Yay for past-you!)
4) Fold up the edges of the foil, making each one an enclosed parcel, gently sealed at the top by folding it over. Put them on a baking tray and bake for about 20 minutes.
5) Serve! If you’d like some carbs with it, we recommend our tasty versatile rice recipe.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
- Farmed Fish vs Wild-Caught ← don’t underestimate the difference this makes!
- Tasty Polyphenols For Your Heart And Brain
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
Last Tuesday, we wrote about nutritional psychiatry, and the benefits of eating for one’s mental health.
You can check out Dr. Uma Naidoo’s to-dos, here:
The 6 Pillars Of Nutritional Psychiatry
In response, one of our subscribers wrote to mention:
❝Really interesting….just put chia seeds in my diet love them……taking the Drs advice.❞
~ Cindy, 10almonds subscriber
And then! On Friday, our tip at the top of the newsletter was:
Not sure how to incorporate chia seeds into your diet? It’s easier to want the benefits of their many brain-healthy (and otherwise-healthy, too) nutrients, than it is to know what to do with them necessarily, and not everyone enjoys seeds as a snack. So…
When you cook rice, throw in a tablespoon of chia seeds too. The cooking process will soften them and they won’t be texturally any different than the rice, but the nutrients will be all there.
They can also be thrown in with lentils, in the same fashion! Or oatmeal, when cooking it or making overnight oats.
We’ll be honest, it was Cindy’s comment that prompted us to suggest it. But wait! There was more to come in response:
❝You had a teaser ..on Chia seed.would of liked a article on the benefits . I’ve just discovered Chia seeds…❞
~ Cindy, 10almonds subscriber
So, Cindy, this one’s for you:
Nutritional powerhouse
First things first, these tiny seeds have a lot of nutrients. There are not many more nutrient-dense foods than this (there’s a kind of seaweed that might be a contender; we’ll have to do some research and get back to you).
Check them out:
USDA Nutritional Factsheet: Chia Seeds
So much protein and healthy fat, so many vitamins and minerals, and so many miscellaneous other micronutrients that we’d be here all day to list them (which is why we linked the above factsheet instead).
Antioxidants in abundance
These deserve a special mention, because they include quercetin which we’ve written about previously:
Fight Inflammation & Protect Your Brain, With Quercetin
…as well as quite a collection of others (including chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid, which may sound alarming but are great for lowering your blood pressure and against inflammation, respectively):
- The effect of chlorogenic acid on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- Synthesis, preliminary bioevaluation and computational analysis of caffeic acid analogues
There are others too, with cardioprotective effects, liver-healthy effects, and anticancer properties:
Nutritional and therapeutic perspectives of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.): a review
Good for the heart and blood
Check it out:
- Chia flour supplementation reduces blood pressure in hypertensive subjects
- Chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.) supplementation to the diet of adults with type 2 diabetes improved systolic blood pressure: A randomized controlled trial
Oh, and about diabetes? There’s more, this time pertaining to reducing after-dinner blood sugars (or “postpranidial glycemia”, in sciencese):
- Reduction in postprandial glucose excursion and prolongation of satiety: possible explanation of the long-term effects of whole grain Salba (Salvia Hispanica L.)
- Effect of whole and ground Salba seeds (Salvia Hispanica L.) on postprandial glycemia in healthy volunteers: a randomized controlled, dose-response trial
Good for the brain
Regular 10almonds readers will know that “what’s good for the blood, is good for the brain” is a very good rule of thumb already, but their highomega-3 content makes them especially so:
What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
Want some?
We don’t sell them, but you can probably find them in your local supermarket and/or health food store, and if you prefer getting things online, here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Science of Stretch – by Dr. Leada Malek
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is part of a “Science of…” series, of which we’ve reviewed some others before (Yoga | HIIT | Pilates), and needless to say, we like them.
You may be wondering: is this just that thing where a brand releases the same content under multiple names to get more sales, and no, it’s not (long-time 10almonds readers will know: if it were, we’d say so!).
While flexibility and mobility are indeed key benefits in yoga and Pilates, they looked into the science of what was going on in yoga asanas and Pilates exercises, stretchy or otherwise, so the stretching element was not nearly so deep as in this book.
In this one, Dr. Malek takes us on a wonderful tour of (relevant) human anatomy and physiology, far deeper than most pop-science books go into when it comes to stretching, so that the reader can really understand every aspect of what’s going on in there.
This is important, because it means busting a lot of myths (instead of busting tendons and ligaments and things), understanding why certain things work and (critically!) why certain things don’t, how certain stretching practices will sabotage our progress, things like that.
It’s also beautifully clearly illustrated! The cover art is a fair representation of the illustrations inside.
Bottom line: if you want to get serious about stretching, this is a top-tier book and you won’t regret it.
Click here to check out Science of Stretching, and learn what you can do and how!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Why are my muscles sore after exercise? Hint: it’s nothing to do with lactic acid
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As many of us hit the gym or go for a run to recover from the silly season, you might notice a bit of extra muscle soreness.
This is especially true if it has been a while between workouts.
A common misunderstanding is that such soreness is due to lactic acid build-up in the muscles.
Research, however, shows lactic acid has nothing to do with it. The truth is far more interesting, but also a bit more complex.
It’s not lactic acid
We’ve known for decades that lactic acid has nothing to do with muscle soreness after exercise.
In fact, as one of us (Robert Andrew Robergs) has long argued, cells produce lactate, not lactic acid. This process actually opposes not causes the build-up of acid in the muscles and bloodstream.
Unfortunately, historical inertia means people still use the term “lactic acid” in relation to exercise.
Lactate doesn’t cause major problems for the muscles you use when you exercise. You’d probably be worse off without it due to other benefits to your working muscles.
Lactate isn’t the reason you’re sore a few days after upping your weights or exercising after a long break.
So, if it’s not lactic acid and it’s not lactate, what is causing all that muscle soreness?
Muscle pain during and after exercise
When you exercise, a lot of chemical reactions occur in your muscle cells. All these chemical reactions accumulate products and by-products which cause water to enter into the cells.
That causes the pressure inside and between muscle cells to increase.
This pressure, combined with the movement of molecules from the muscle cells can stimulate nerve endings and cause discomfort during exercise.
The pain and discomfort you sometimes feel hours to days after an unfamiliar type or amount of exercise has a different list of causes.
If you exercise beyond your usual level or routine, you can cause microscopic damage to your muscles and their connections to tendons.
Such damage causes the release of ions and other molecules from the muscles, causing localised swelling and stimulation of nerve endings.
This is sometimes known as “delayed onset muscle soreness” or DOMS.
While the damage occurs during the exercise, the resulting response to the injury builds over the next one to two days (longer if the damage is severe). This can sometimes cause pain and difficulty with normal movement.
The upshot
Research is clear; the discomfort from delayed onset muscle soreness has nothing to do with lactate or lactic acid.
The good news, though, is that your muscles adapt rapidly to the activity that would initially cause delayed onset muscle soreness.
So, assuming you don’t wait too long (more than roughly two weeks) before being active again, the next time you do the same activity there will be much less damage and discomfort.
If you have an exercise goal (such as doing a particular hike or completing a half-marathon), ensure it is realistic and that you can work up to it by training over several months.
Such training will gradually build the muscle adaptations necessary to prevent delayed onset muscle soreness. And being less wrecked by exercise makes it more enjoyable and more easy to stick to a routine or habit.
Finally, remove “lactic acid” from your exercise vocabulary. Its supposed role in muscle soreness is a myth that’s hung around far too long already.
Robert Andrew Robergs, Associate Professor – Exercise Physiology, Queensland University of Technology and Samuel L. Torrens, PhD Candidate, Queensland University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The 3 Phases Of Fat Loss (& How To Do It Right!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cori Lefkowith, of “Redefining Strength” and “Strength At Any Age” fame, has advice:
As easy as 1, 2, 3?
Any kind of fat loss plan will not work unless it takes into account that the body can and will adapt to a caloric deficit, meaning that constantly running a deficit will only ever yield short term results, followed by regaining weight (and feeling hungry the whole time). So, instead, if fat loss is your goal, you might want to consider doing it in these stages:
1. Lifestyle adjustments (main phase)
Focus on sustainable, gradual improvements in diet and workouts.
- Key strategies:
- Start with small, manageable changes, for example focusing on making your protein intake around 30–35% of your total calories.
- Track your current habits to identify realistic adjustments.
- Balance strength training and cardio, as maintaining your muscle is (and will remain) important.
- Signs of Progress:
- Slow changes in the numbers on the scale (up to 1 lb/week).
- Inches being lost (but probably not many), improved energy levels, and stable performance in workouts.
Caution: avoid feelings of extreme hunger or restriction. This is not supposed to be arduous.
2. Mini cut (short-term intensive)
Used for quick fat loss or breaking plateaus; lasts 7–14 days.
- Key strategies:
- Larger calorie deficit (e.g: 500 calories).
- High protein intake (40–50% of your total calories).
- Focus on strength training and reduce cardio, to avoid muscle loss.
- Signs of Progress:
- Rapid scale changes (up to 5 lbs/week).
- Reduced bloating, potential energy dips, and cravings.
- Temporary performance stagnation in workouts. Don’t worry about this; it’s expected and fine.
Caution: do not exceed 21 days, to avoid the metabolic adaptation that we talked about.
3. Diet break (rest & reset)
A maintenance period to recharge mentally and physically, typically lasting 7–21 days.
- Key strategies:
- Gradually increase calories (200–500) to maintenance level.
- Focus on performance goals and reintroducing foods you enjoy.
- Combine strength training with steady-state cardio.
- Signs of Progress:
- Increased energy, improved workout performance, and feeling fuller.
- Scale may fluctuate initially but stabilize or decrease by the end.
- Inches will be lost as muscle is built and fat is burned.
The purpose of this third stage is to prevent metabolic adaptation, regain motivation, and (importantly!) test maintenance.
For more on these and how best to implement them, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Key strategies:
-
How To Build a Body That Lasts – by Adam Richardson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is written on a premise, and that premise is: “your age doesn’t define your mobility; your mobility defines your age”.
To this end, we are treated to 328 pages of why and how to improve our mobility (mostly how; just enough on the “why” to keep the motivation flowing).
Importantly, Richardson doesn’t expect that every reader is a regular gym-bunny or about to become one, doesn’t expect you to have several times your bodyweight in iron to life at home, and doesn’t expect that you’ll be doing the vertical splits against a wall any time soon.
Rather, he expects that we’d like to not dislocate a shoulder while putting the groceries away, would like to not slip a disk while being greeted by the neighbor’s dog, and would like to not need a 7-step plan for putting our socks on.
What follows is a guide to “on the good end of normal” mobility that is sustainable for life. The idea is that you might not be winning Olympic gymnastics gold medals in your 90s, but you will be able to get in and out of a car door as comfortably as you did when you were 20, for example.
Bottom line: if you want to be a superathlete, then you might need something more than this book; if you want to be on the healthy end of average when it comes to mobility, and maintain that for the rest of your life, then this is the book for you.
Click here to check out How To Build A Body That Lasts, and build a body that lasts!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: