4 Critical Things Female Runners Should Know
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to keeping up performance in the face of menopause, Shona Hendricks has advice:
Don’t let menopause run you down
- Prioritize recovery! Overtraining without adequate recovery just leads to decreased performance in the long term, and remember, you may not recover as quickly as you used to. If you’re still achey from your previous run, give it another day, or at least make it a lighter run.
- Slow down in easy and long runs! This isn’t “taking the easy way out”; it will improve your overall performance, reducing muscle damage, allowing for quicker recovery and ultimately better fitness gains.
- Focus on nutrition! And that means carbs too. A lot of people fighting menopausal weight gain reduce their intake of food, but without sufficient energy availability, you will not be able to run well. In particular, carbohydrates are vital for energy. Consume them sensibly and with fiber and proteins and fats rather than alone, but do consume them.
- Incorporate strength training! Your run is not “leg day” by itself. Furthermore, do whole-body strength training, to prevent injuries and improve overall performance. A strong core is particularly important.
For more on each of these (and some bonus comments about mobility training for runners), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
End the Insomnia Struggle – by Dr. Colleen Ehrnstrom and Dr. Alisha Brosse
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed sleep books before, and we always try to recommend books that have something a little different than the rest, so what makes this one stand out?
While there is the usual quick overview of the basics that we’re sure you already know (sleep hygiene etc), most of the attention here is given to cold, hard clinical psychology… in a highly personalized way.
How, you may ask, can they personalize a book, that is the same for everyone?
The answer is, by guiding the reader through examining our own situation. With template logbooks, worksheets, and the like—for this reason we recommend getting a paper copy of the book, rather than the Kindle version, in case you’d like to use/photocopy those.
Essentially, reading this book is much like having your own psychologist (or two) to guide you through finding a path to better sleep.
The therapeutic approach, by the way, is a combination of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Acceptance-Commitment Therapy (ACT), which work very well together here.
Bottom line: if you’ve changed your bedsheets and turned off your electronic devices and need something a little more, this book is the psychological “big guns” for removing the barriers between you and good sleep.
Click here to check out End the Insomnia Struggle, and end yours once and for all!
Share This Post
-
How Much Can Hypnotherapy Really Do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sit Back, Relax, And…
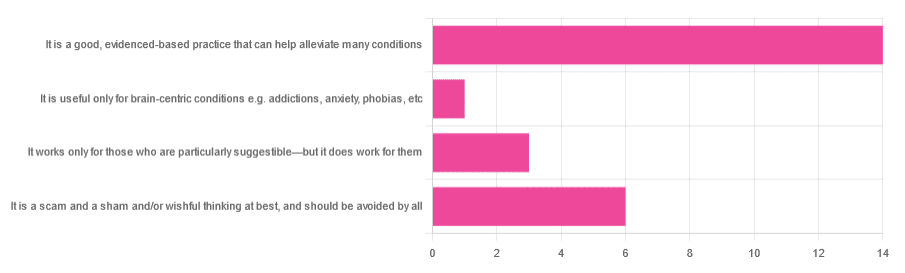
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinions of hypnotherapy, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 58% said “It is a good, evidenced-based practice that can help alleviate many conditions”
- Exactly 25% said “It is a scam and sham and/or wishful thinking at best, and should be avoided by all”
- About 13% said “It works only for those who are particularly suggestible—but it does work for them”
- One (1) person said “It is useful only for brain-centric conditions e.g. addictions, anxiety, phobias, etc”
So what does the science say?
Hypnotherapy is all in the patient’s head: True or False?
True! But guess which part of your body controls much of the rest of it.
So while hypnotherapy may be “all in the head”, its effects are not.
Since placebo effect, nocebo effect, and psychosomatic effect in general are well-documented, it’s quite safe to say at the very least that hypnotherapy thus “may be useful”.
Which prompts the question…
Hypnotherapy is just placebo: True or False?
False, probably. At the very least, if it’s placebo, it’s an unusually effective placebo.
And yes, even though testing against placebo is considered a good method of doing randomized controlled trials, some placebos are definitely better than others. If a placebo starts giving results much better than other placebos, is it still a placebo? Possibly a philosophical question whose answer may be rooted in semantics, but happily we do have a more useful answer…
Here’s an interesting paper which: a) begins its abstract with the strong, unequivocal statement “Hypnosis has proven clinical utility”, and b) goes on to examine the changes in neural activity during hypnosis:
Brain Activity and Functional Connectivity Associated with Hypnosis
It works only for the very suggestible: True or False?
False, broadly. As with any medical and/or therapeutic procedure, a patient’s expectations can affect the treatment outcome.
And, especially worthy of note, a patient’s level of engagement will vastly affect it treatment that has patient involvement. So for example, if a doctor prescribes a patient pills, which the patient does not think will work, so the patient takes them intermittently, because they’re slow to get the prescription refilled, etc, then surprise, the pills won’t get as good results (since they’re often not being taken).
How this plays out in hypnotherapy: because hypnotherapy is a guided process, part of its efficacy relies on the patient following instructions. If the hypnotherapist guides the patient’s mind, and internally the patient is just going “nope nope nope, what a lot of rubbish” then of course it will not work, just like if you ask for directions in the street and then ignore them, you won’t get to where you want to be.
For those who didn’t click on the above link by the way, you might want to go back and have a look at it, because it included groups of individuals with “high/low hypnotizability” per several ways of scoring such.
It works only for brain-centric things, e.g. addictions, anxieties, phobias, etc: True or False?
False—but it is better at those. Here for example is the UK’s Royal College of Psychiatrists’ information page, and if you go to “What conditions can hypnotherapy help to treat”, you’ll see two broad categories; the first is almost entirely brain-stuff; the second is more varied, and includes pain relief of various kinds, burn care, cancer treatment side effects, and even menopause symptoms. Finally, warts and other various skin conditions get their own (positive) mention, per “this is possible through the positive effects hypnosis has on the immune system”:
RCPsych | Hypnosis And Hypnotherapy
Wondering how much psychosomatic effect can do?
You might like this previous article; it’s not about hypnotherapy, but it is about the difference the mind can make on physical markers of aging:
Aging, Counterclockwise: When Age Is A Flexible Number
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Navigating the health-care system is not easy, but you’re not alone.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hello, dear reader!
This is my first column for Healthy Debate as a Patient Navigator. This column will be devoted to providing patients with information to help them through their journey with the health-care system and answering your questions.
Here’s a bit about me: I have been a patient partner at The Ottawa Hospital and Ottawa Hospital Research Institute since 2017, and have joined a variety of governance boards that work on patient and caregiver engagement such as the Patient Advisors Network, the Ontario Health East Region Patient and Family Advisory Council and the Equity in Health Systems Lab.
My journey as a patient partner started much before 2017 though. When I was a teenager, I was diagnosed with a cholesteatoma, a rare and chronic disease that causes the development of fatty tumors in the middle ear. I have had multiple surgeries to try to fix it but will need regular follow-ups to monitor whether the tumor returns. Because of this, I also live with an invisible disability since I have essentially become functionally deaf in one ear and often rely on a hearing aid when I navigate the world.
Having undergone three surgeries in my adolescent years, it was my experience undergoing surgery for an acute hand and wrist injury following a jet ski accident as an adult that was the catalyst for my decision to become a patient partner. There was an intriguing contrast between how I was cared for at two different health-care institutions, my age being the deciding factor at which hospital I went to (a children’s hospital or an adult one).
The most memorable example was how, as a teenager or child, you were never left alone before surgery, and nurses and staff took all the time necessary to comfort me and answer my (and my family’s) questions. I also remember how right before putting me to sleep, the whole staff initiated a surgical pause and introduced themselves and explained to me what their role was during my surgery.
None of that happened as an adult. I was left in a hallway while the operating theater was prepared, anxious and alone with staff walking by not even batting an eye. My questions felt like an annoyance to the care team; as soon as I was wheeled onto the operating room table, the anesthetist quickly put me to sleep. I didn’t even have the time to see who else was there.
Now don’t get me wrong: I am incredibly appreciative with the quality of care I received, but it was the everyday interactions with the care teams that I felt could be improved. And so, while I was recovering from that surgery, I looked for a way to help other patients and the hospital improve its care. I discovered the hospital’s patient engagement program, applied, and the rest is history!
Since then, I have worked on a host of patient-centered policy and research projects and fervently advocate that surgical teams adopt a more compassionate approach with patients before and after surgery.
I’d be happy to talk a bit more about my journey if you ask, but with that out of the way … Welcome to our first patient navigator column about patient engagement.
Conceptualizing the continuum of Patient Engagement
In the context of Canadian health care, patient engagement is a multifaceted concept that involves active collaboration between patients, caregivers, health-care providers and researchers. It involves patients and caregivers as active contributors in decision-making processes, health-care services and medical research. Though the concept is not new, the paradigm shift toward patient engagement in Canada started around 2010.
I like to conceptualize the different levels of patient engagement as a measure of the strength of the relationship between patients and their interlocutors – whether it’s a healthcare provider, administrator or researcher – charted against the duration of the engagement or the scope of input required from the patient.
Defining different levels of Patient Engagement
Following the continuum, let’s begin by defining different levels of patient engagement. Bear in mind that these definitions can vary from one organization to another but are useful in generally labelling the level of patient engagement a project has achieved (or wishes to achieve).
Patient involvement: If the strength of the relationship between patients and their interlocutors is minimal and not time consuming or too onerous, then perhaps it can be categorized as patient involvement. This applies to many instances of transactional engagement.
Patient advisory/consulting: Right in the middle of our continuum, patients can find themselves engaging in patient advisory or consulting work, where projects are limited in scope and duration or complexity, and the relationship is not as profound as a partnership.
Patient partnership: The stronger the relationship is between the patient and their interlocutor, and the longer the engagement activity lasts or how much input the patient is providing, the more this situation can be categorized as patient partnership. It is the inverse of patient involvement.
Examples of the different levels of Patient Engagement
Let’s pretend you are accompanying a loved one to an appointment to manage a kidney disease, requiring them to undergo dialysis treatment. We’ll use this scenario to exemplify what label could be used to describe the level of engagement.
Patient involvement: In our case, if your loved one – or you – fills out a satisfaction or feedback survey about your experience in the waiting room and all that needed to be done was to hand it back to the clerk or care team, then, at a basic level, you could likely label this interaction as a form of patient involvement. It can also involve open consultations around a design of a new look and feel for a hospital, or the understandability of a survey or communications product. Interactions with the care team, administrators or researchers are minimal and often transactional.
Patient advisory/consulting: If your loved one was asked for more detailed information about survey results over the course of a few meetings, this could represent patient advisory/consulting. This could mean that patients meet with program administrators and care providers and share their insights on how things can be improved. It essentially involves patients providing advice to health-care institutions from the perspective of patients, their family members and caregivers.
Patient advisors or consultants are often appointed by hospitals or academic institutions to offer insights at multiple stages of health-care delivery and research. They can help pilot an initiative based on that feedback or evaluate whether the new solutions are working. Often patient advisors are engaged in smaller-term individual projects and meet with the project team as regularly as required.
Patient partnership: Going above and beyond patient advisory, if patients have built a trusting relationship with their care team or administrators, they could feel comfortable enough to partner with them and initiate a project of their own. This could be for a project in which they study a different form of treatment to improve patient-centered outcomes (like the time it takes to feel “normal” following a session); it could be working together to identify and remove barriers for other patients that need to access that type of care. These projects are not fulfilled overnight, but require a collaborative, longstanding and trusting relationship between patients and health-care providers, administrators or researchers. It ensures that patients, regardless of severity or chronicity of their illness, can meaningfully contribute their experiences to aid in improving patient care, or develop or implement policies, pilots or research projects from start to finish.
It is leveraging that lived and living experience to its full extent and having the patient partner involved as an equal voice in the decision-making process for a project – over many months, usually – that the engagement could be labeled a partnership.
Last words
The point of this column will be to answer or explore issues or questions related to patient engagement, health communications or even provide some thoughts on how to handle a particular situation.
I would be happy to collect your questions and feedback at any time, which will help inform future columns. Just email me at [email protected] or connect with me on social media (Linked In, X / Twitter).
It’s not easy to navigate our health-care systems, but you are not alone.
This article is republished from healthydebate under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What Happens To Your Body When You Plank 1 Minute Every Day
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Planks improve strength, flexibility, balance, posture, reduce chronic back pain, lower blood pressure, and enhance physique. But can we really get benefits from just 1 minute per day?
To the core
The benefits that can be expected, according to the science cited in this video, include:
- Within 2–3 weeks, daily planking of just 1 minute per day activates deep core muscles, enhancing balance, which helps in everyday tasks and prevents muscle imbalances.
- Strengthening core muscles through planks also helps alleviate lower back pain, with research supporting its effectiveness within 3 weeks.
- Posture is important for good health, and planks align the spine and hips, improving posture naturally, which also helps alleviate back issues. So, there’s a good kind of synergy to this exercise.
- Of course, many people exercising have the goal of a more toned body; regular planking leads to a toned core, sculpted shoulders, and leaner legs.
- For those who care more about mobility, though, planking enhances flexibility in hamstrings, feet, and toes within 4–6 weeks.
- Anything else? Yes, isometric exercises like planks are highly effective at reducing blood pressure, and, counterintuitively, more so than aerobic exercises.
The video also looks at a study in which participants did 20 minutes per day instead of 1, which predictably also significantly improved strength, endurance, flexibility, and reduced body fat.
However, another study cited gives the stats for just 1 minute daily, and that was not even a whole minute, so much as 30 seconds hold, 1 minute rest, 30 seconds hold—and still showed very good improvements.
For more on all this, plus links to three studies mentioned in the video, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Isometric Exercises That Are Good If You Have Osteoporosis (or if you don’t, but the point is, they are safe and beneficial for people with osteoporosis)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How often should you wash your sheets and towels?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Everyone seems to have a different opinion when it comes to how often towels and bed sheets should be washed. While many people might wonder whether days or weeks is best, in one survey from the United Kingdom, almost half of single men reported not washing their sheets for up to four months at a time.
It’s fairly clear that four months is too long to leave it, but what is the ideal frequency?
Bed linen and towels are quite different and so should be washed at different intervals. While every week or two will generally suffice for sheets, towels are best washed every few days.
Anyway, who doesn’t love the feeling of a fresh set of sheets or the smell of a newly laundered towel?
Why you should wash towels more often
When you dry yourself, you deposit thousands of skin cells and millions of microbes onto the towel. And because you use your towel to dry yourself after a shower or bath, your towel is regularly damp.
You also deposit a hefty amount of dead skin, microbes, sweat and oils onto your sheets every night. But unless you’re a prolific night sweater, your bedding doesn’t get wet after a night’s sleep.
Towels are also made of a thicker material than sheets and therefore tend to stay damp for longer.
So what is it about the dampness that causes a problem? Wet towels are a breeding ground for bacteria and moulds. Moulds especially love damp environments. Although mould won’t necessarily be visible (you would need significant growth to be able to see it) this can lead to an unpleasant smell.
As well as odours, exposure to these microbes in your towels and sheets can cause asthma, allergic skin irritations, or other skin infections.
People don’t always agree on how often to change the sheets.
http://rawpixel.com/ShutterstockSo what’s the ideal frequency?
For bedding, it really depends on factors such as whether you have a bath or shower just before going to bed, or if you fall into bed after a long, sweaty day and have your shower in the morning. You will need to wash your sheets more regularly in the latter case. As a rule of thumb, once a week or every two weeks should be fine.
Towels should ideally be washed more regularly – perhaps every few days – while your facecloth should be cleaned after every use. Because it gets completely wet, it will be wet for a longer time, and retain more skin cells and microbes.
Wash your towels at a high temperature (for example, 65°C) as that will kill many microbes. If you are conscious of saving energy, you can use a lower temperature and add a cup of vinegar to the wash. The vinegar will kill microbes and prevent bad smells from developing.
Clean your washing machine regularly and dry the fold in the rubber after every wash, as this is another place microbes like to grow.
Smelly towels
What if you regularly wash your towels, but they still smell bad? One of the reasons for this pong could be that you’ve left them in the washing machine too long after the wash. Especially if it was a warm wash cycle, the time they’re warm and damp will allow microbes to happily grow. Under lab conditions the number of these bacteria can double every 30 minutes.
It’s important to hang your towel out to dry after use and not to leave towels in the washing machine after the cycle has finished. If possible, hang your towels and bedding out in the sun. That will dry them quickly and thoroughly and will foster that lovely fresh, clean cotton smell. Using a dryer is a good alternative if the weather is bad, but outdoors in the sun is always better if possible.
Also, even if your towel is going to be washed, don’t throw a wet towel into the laundry basket, as the damp, dirty towel will be an ideal place for microbes to breed. By the time you get to doing your washing, the towel and the other laundry around it may have acquired a bad smell. And it can be difficult to get your towels smelling fresh again.
Towels should be washed more often than sheets.
New Africa/ShutterstockWhat about ‘self-cleaning’ sheets and towels?
Some companies sell “quick-dry” towels or “self-cleaning” towels and bedding. Quick-dry towels are made from synthetic materials that are weaved in a way to allow them to dry quickly. This would help prevent the growth of microbes and the bad smells that develop when towels are damp for long periods of time.
But the notion of self-cleaning products is more complicated. Most of these products contain nanosilver or copper, antibacterial metals that kill micro-organisms. The antibacterial compounds will stop the growth of bacteria and can be useful to limit smells and reduce the frequency with which you need to clean your sheets and towels.
However, they’re not going to remove dirt like oils, skin flakes and sweat. So as much as I would love the idea of sheets and towels that clean themselves, that’s not exactly what happens.
Also, excessive use of antimicrobials such as nanosilver can lead to microbes becoming resistant to them.
Rietie Venter, Associate professor, Clinical and Health Sciences, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healing The Modern Brain – by Dr. Drew Ramsey
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We previously reviewed Dr. Ramsey’s Eat To Beat Depression & Anxiety, and this time [it briefly covers that ground again, and then] it’s more about comprehensive brain health and mental fitness.
He tackles this in a methodical fashion, first briefly covering the need for mental fitness, and the obstacles to same, before the main part of the book—which covers the “how”.
The “how” in question is multifaceted, and the “nine tenets” mentioned in the subtitle cover very obvious things like diet, exercise, sleep, etc, as well as less obvious yet very important things like connection, engagement, purpose, and so forth, and some things that don’t get talked about much at all elsewhere, such as the processes of grounding and unburdening, as he describes them.
The style is mostly narrative with many anecdotes to illustrate points, but with practical advice woven throughout also, all very readable. There’s a respectable bibliography at the back.
Bottom line: if you’d like your brain health to get gradually better instead of gradually worse, this book can help set you on the right track.
Click here to check out Healing The Modern Brain, and heal your modern brain!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: