Workout Advice For Busy People
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hampton at Hybrid Calisthenics always has very sound advice in his uplifting videos, and this one’s no exception:
Key tips for optimizing workouts without burning out
“We all have the same 24 hours” is a folly when in fact, some of us have more responsibilities and/or other impediments to getting things done (e.g. disabilities).
A quick word on disabilities first: sometimes people are quick to point out Paralympian athletes, and “if they can do it, so can you!” and forget that these people are in the top percentile of the top percentile of the top percentile of human performance. If you wouldn’t disparagingly say “if Simone Biles/Hussein Bolt/Michael Phelps can do it, so can you”, then don’t for Paralympians either 😉
Now, as for Hampton’s advice, he recommends:
Enjoy short, intense workouts:
- You can get effective results in under 30 minutes (or even just a few minutes per day) with compound exercises (e.g., squats, pull-ups).
- Focus on full-body movements also saves time!
- Push closer to failure when possible to maximize efficiency. It’s the last rep where most of the strength gains are made! Same deal with cardiovascular fitness, too. Nevertheless, do take safety into account in both cases, of course.
Time your rest periods:
- Resting for 2–3 minutes between sets ensures optimal recovery.
- Avoid getting distracted during rest by setting a timer to stay focused.
- 10almonds tip: use this time to practice a mindfulness meditation. That will greatly reduce the chance of you becoming distracted.
Remember holistic fitness:
- Fitness isn’t just about exercise; diet, sleep, and stress management are equally important for your fitness as much as for the rest of your health.
- Better sleep and reduced stress will help you exercise more consistently and avoid junk food.
Address burnout:
- If feeling too exhausted to apply these tips, focus on getting better rest and reducing stress first.
- Taking a short break to reset can help in the long run.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- How To Do High Intensity Interval Training (Without Wrecking Your Body)
- How To Rest More Efficiently (Yes, Really)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Gluten: What’s The Truth?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Gluten: What’s The Truth?
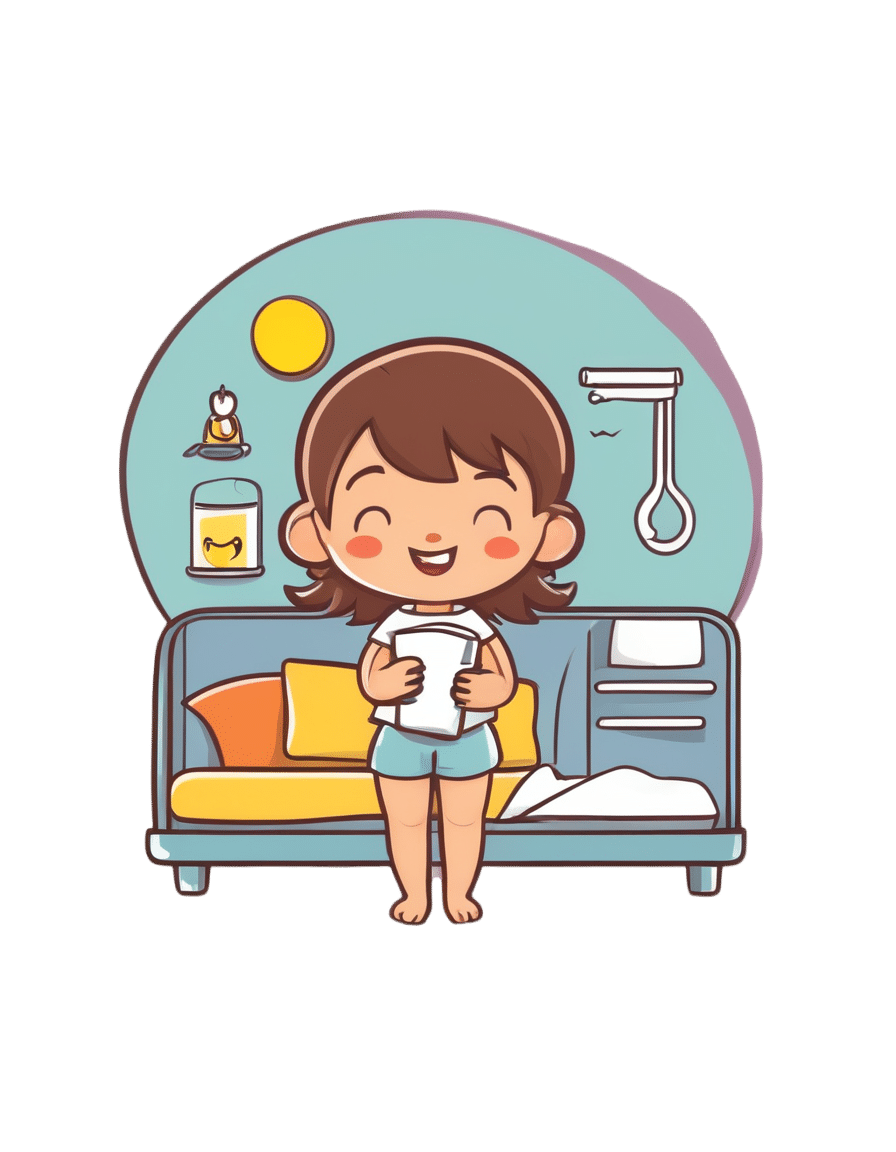
We asked you for your health-related view of gluten, and got the above spread of results. To put it simply:
Around 60% of voters voted for “Gluten is bad if you have an allergy/sensitivity; otherwise fine”
The rest of the votes were split fairly evenly between the other three options:
- Gluten is bad for everyone and we should avoid it
- Gluten is bad if (and only if) you have Celiac disease
- Gluten is fine for all, and going gluten-free is a modern fad
First, let’s define some terms so that we’re all on the same page:
What is gluten?
Gluten is a category of protein found in wheat, barley, rye, and triticale. As such, it’s not one single compound, but a little umbrella of similar compounds. However, for the sake of not making this article many times longer, we’re going to refer to “gluten” without further specification.
What is Celiac disease?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disease. Like many autoimmune diseases, we don’t know for sure how/why it occurs, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors have been strongly implicated, with the latter putatively including overexposure to gluten.
It affects about 1% of the world’s population, and people with Celiac disease will tend to respond adversely to gluten, notably by inflammation of the small intestine and destruction of enterocytes (the cells that line the wall of the small intestine). This in turn causes all sorts of other problems, beyond the scope of today’s main feature, but suffice it to say, it’s not pleasant.
What is an allergy/intolerance/sensitivity?
This may seem basic, but a lot of people conflate allergy/intolerance/sensitivity, so:
- An allergy is when the body mistakes a harmless substance for something harmful, and responds inappropriately. This can be mild (e.g. allergic rhinitis, hayfever) or severe (e.g. peanut allergy), and as such, responses can vary from “sniffly nose” to “anaphylactic shock and death”.
- In the case of a wheat allergy (for example), this is usually somewhere between the two, and can for example cause breathing problems after ingesting wheat or inhaling wheat flour.
- An intolerance is when the body fails to correctly process something it should be able to process, and just ejects it half-processed instead.
- A common and easily demonstrable example is lactose intolerance. There isn’t a well-defined analog for gluten, but gluten intolerance is nonetheless a well-reported thing.
- A sensitivity is when none of the above apply, but the body nevertheless experiences unpleasant symptoms after exposure to a substance that should normally be safe.
- In the case of gluten, this is referred to as non-Celiac gluten sensitivity
A word on scientific objectivity: at 10almonds we try to report science as objectively as possible. Sometimes people have strong feelings on a topic, especially if it is polarizing.
Sometimes people with a certain condition feel constantly disbelieved and mocked; sometimes people without a certain condition think others are imagining problems for themselves where there are none.
We can’t diagnose anyone or validate either side of that, but what we can do is report the facts as objectively as science can lay them out.
Gluten is fine for all, and going gluten-free is a modern fad: True or False?
Definitely False, Celiac disease is a real autoimmune disease that cannot be faked, and allergies are also a real thing that people can have, and again can be validated in studies. Even intolerances have scientifically measurable symptoms and can be tested against nocebo.
See for example:
- Epidemiology and clinical presentations of Celiac disease
- Severe forms of food allergy that can precipitate allergic emergencies
- Properties of gluten intolerance: gluten structure, evolution, and pathogenicity
However! It may not be a modern fad, so much as a modern genuine increase in incidence.
Widespread varieties of wheat today contain a lot more gluten than wheat of ages past, and many other molecular changes mean there are other compounds in modern grains that never even existed before.
However, the health-related impact of these (novel proteins and carbohydrates) is currently still speculative, and we are not in the business of speculating, so we’ll leave that as a “this hasn’t been studied enough to comment yet but we recognize it could potentially be a thing” factor.
Gluten is bad if (and only if) you have Celiac disease: True or False?
Definitely False; allergies for example are well-evidenced as real; same facts as we discussed/linked just above.
Gluten is bad for everyone and we should avoid it: True or False?
False, tentatively and contingently.
First, as established, there are people with clinically-evidenced Celiac disease, wheat allergy, or similar. Obviously, they should avoid triggering those diseases.
What about the rest of us, and what about those who have non-Celiac gluten sensitivity?
Clinical testing has found that of those reporting non-Celiac gluten sensitivity, nocebo-controlled studies validate that diagnosis in only a minority of cases.
In the following study, for example, only 16% of those reporting symptoms showed them in the trials, and 40% of those also showed a nocebo response (i.e., like placebo, but a bad rather than good effect):
This one, on the other hand, found that positive validations of diagnoses were found to be between 7% and 77%, depending on the trial, with an average of 30%:
Re-challenge Studies in Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
In other words: non-Celiac gluten sensitivity is a thing, and/but may be over-reported, and/but may be in some part exacerbated by psychosomatic effect.
Note: psychosomatic effect does not mean “imagining it” or “all in your head”. Indeed, the “soma” part of the word “psychosomatic” has to do with its measurable effect on the rest of the body.
For example, while pain can’t be easily objectively measured, other things, like inflammation, definitely can.
As for everyone else? If you’re enjoying your wheat (or similar) products, it’s well-established that they should be wholegrain for the best health impact (fiber, a positive for your health, rather than white flour’s super-fast metabolites padding the liver and causing metabolic problems).
Wheat itself may have other problems, for example FODMAPs, amylase trypsin inhibitors, and wheat germ agglutinins, but that’s “a wheat thing” rather than “a gluten thing”.
That’s beyond the scope of today’s main feature, but you might want to check out today’s featured book!
For a final scientific opinion on this last one, though, here’s what a respected academic journal of gastroenterology has to say:
From coeliac disease to noncoeliac gluten sensitivity; should everyone be gluten-free?
Share This Post
-
Morning Routines That Just FLOW
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Morning Routines That Just FLOW
“If the hardest thing you have to do in your day is eat a frog, eat that frog first!”, they say.
And, broadly speaking, it is indeed good to get anything stressful out of the way early, so that we can relax afterwards. But…
- Are we truly best at frog-eating when blurry-eyed and sleepy?
- Is there a spoonful of sugar that could make the medicine go down better?
- What do we need to turn eating the frog into an enjoyable activity?
Flow
“Flow” is a concept brought to public consciousness by psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, and it refers to a state in which we feel good about what we’re doing, and just keep doing, at a peak performance level.
Writer’s note: as a writer, for example…
Sometimes I do not want to write, I pace to and fro near my computer, going on side-quests like getting a coffee or gazing out of the window into my garden. But once I get going, suddenly, something magical happens and before I know it, I have to trim my writing down because I’ve written too much. That magical window of effortless productivity was a state of flow.
Good morning!
What is a good morning, to you? Build that into your morning! Set parameters around it so you don’t get carried away timewise and find yourself in the afternoon (unless that would work for you!), but first thing in the morning is the time to light up each part of your brain with appropriate neurotransmitters.
Getting the brain juices flowing
Cortisol
When we wake up, we (unless we have some neurochemical imbalance, such as untreated depression) get a spike of cortisol. Cortisol is much-maligned and feared, and indeed it can be very much deleterious to the health in cases of chronic stress. But a little spike now and again is actually beneficial for us.
Quick Tip: if you want to artificially stimulate (or enhance) a morning cortisol spike, a cold shower is the way to go. Or even just a face-plunge into a bowl of ice-water (put ice in it, give it a couple of minutes to chill the water, then put your face in for a count of 30 seconds, or less if you can’t hold your breath that long).
Serotonin
Serotonin is generally thought of as “the happy chemical”, and it’s stimulated by blue/white light, and also by seeing greenery.
Quick tip: to artificially stimulate (or enhance) a morning serotonin boost, your best friend is sunlight. Even sun through a partly-clouded sky will tend to outperform artificial lighting, including artificial sunlight lighting. Try to get sun between 08:30 and 09:00, if you can. Best of all, do it in your garden or nearby park, as the greenery will be an extra boost!
Dopamine
Generally thought of as “the reward chemical”, but it’s also critical for a lot of kinds of brainwork, including language processing and problem-solving.
Quick Tip: to artificially stimulate* a dopamine surge to get you going, do something that you and/or your body finds rewarding. Examples include:
- Exercise, especially in a vigorous burst
- A good breakfast, a nice coffee, whatever feels right to you
- An app that has motivational bells and whistles, a streak for you to complete, etc
Note: another very enjoyable activity might come to mind that doesn’t even require you getting out of bed. Be aware, however, gentleman-readers specifically, that if you complete that activity, you’ll get a prolactin spike that will wipe out the dopamine you just worked up (because prolactin is antagonistic to dopamine). So that one’s probably better for a lazy morning when you can go back to sleep, than a day when you want to get up and go! Ladies, this is less of a worry for us as the physiology an orgasm driven by estrogen+progesterone rather than testosterone is different; there will not usually be a prolactin spike following the spike of dopamine; our orgasm-related dopamine spike is followed by a wave of oxytocin instead (“the cuddle chemical”), which is much more pleasant than prolactin.
*there’s no “(or enhance)” for this one; you won’t get dopamine from doing nothing, that’s just not how “the reward chemical” works
Flow-building in a stack
When you’ve just woken up and are in a blurry morning haze, that’s not the time to be figuring out “what should I be doing next?”, so instead:
- Work out the things you want to incorporate into your morning routine
- Put them in the order that will be easiest to perform—some things will go a lot better after others!
- Remember to also include things that are simply necessary—morning bathroom ablutions, for example
The goal here is to have a this-and-this-and-this-and-this list of items that you can go through without any deviations, and get in the habit of “after item 1 I automatically do item 2, after which I automatically do item 3, after which…”
Implement this, and your mornings will become practically automated, but in a joyous, life-enhancing way that sets you up in good order for whatever you want/need to do!
Share This Post
-
10 Ways To Delay Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Colin Rose; he is a Senior Associate of the Royal Society of Medicine. He’s also a main contributor to EduScience, a program funded by the E.U. which is designed to enhance the teaching and learning of science in schools in Europe.
His most recent work has been about aging—and how to delay it. We also reviewed his latest book, here:
Delay Ageing – by Dr. Colin Rose
So, what does he want us to know? The key lies in his compilation of ten ways in which we age on a cellular level, and what we can to do slow each one of those:
Damage to DNA accumulates
While DNA can get damaged without any external stimulus to cause that, there are a lot of modifiable factors that we can do to reduce DNA damage. The list is easy: if it causes cancer, it causes aging.
Thus, check out: Stop Cancer 20 Years Ago
Cells become senescent
Our cells are replaced all the time; some sooner than others, but all of them at some point. The problem occurs when cells are outliving their usefulness. If a cell becomes completely immortal, that is cancer, but happily most don’t. Nevertheless, having senescent (aging) cells in the body means that those senescent cells are what get copied forwards by mitosis, and our DNA becomes like a photocopy of a tattered old photocopy of a tattered old photocopy. Which, needless to say, is not good for our health. So, the best thing to do is to kill them earlier:
Yes, really: Fisetin: The Anti-Aging Assassin
Mitochondria become dysfunctional
Without properly functional mitochondria, no living human cell can do its job properly.
Options: 7 Ways To Boost Mitochondrial Health To Fight Disease
Beneficial genes are switched off, harmful genes are on
It’s easy to think of our genes as being immutable, but epigenetics means that our environment (amongst other factors) can mean that our gene expression changes.
Imagine it this way: your genes are a set of instructions for your body. However, your body will act or not on those instructions, depending on other factors. Hormones often play a big part in this; for example sex hormones tell the body which set of genetic instructions to read (and thus what kind of body to build/rebuild), and cortisol or oxytocin can tell the body which set of contingency plans to activate or suppress (respectively). A milder example is gray hair; genes have the program for it, but many other factors inform the body when, if, and how to do it.
Of more concern when it comes to aging is what goes on with more critical systems, such as the brain, in which the aforementioned DNA damage can cause unhelpful instructions to get interpreted, resulting in epigenetic changes that in turn facilitate age-related degeneration.
As to what can be done, see : Klotho: Unzipping The Genes Of Aging?
Stem cells become exhausted
Stem cells can become different kinds of cells, and thus they’re very useful for maintaining a healthy body. However, they get depleted with age. We can slow down the rate of loss, though; for example, intermittent fasting can help:
Per Dr. Li’s 5 Ways To Beat Cancer (And Other Diseases)
And for more detail, see:
Doctor’s Tip: Regeneration (stem cells) — one of your body’s five defense systems
(complete with lists of foods to eat or avoid for stem cell health)
Cells fail to communicate properly
Cells need to talk to each other constantly, to continue doing their jobs. We are one big organism, after all, and not a haphazard colony of the countless cells that constitute such. However, cell signalling gets worse with age, which in turn precipitates others age-related problems. Fortunately, there are nutrients that can improve cellular communication.
For example: PS, We Love You ← this is about phosphatidylserine, also called “PS”
Telomeres become shorter
These protective caps on our DNA suffer the wear-and-tear so that our DNA doesn’t have to. However, as they get shorter, the DNA can start suffering damage. For this reason, telomere length is considered one of the most “Gold Standard” markers of cellular aging.
Here’s what can be done for that: The Stress Prescription (Against Aging!)
The body fails to sense nutritional intake properly
This is mostly about insulin signalling (though problems can occur in other systems too, but we only have so much room here), so it’s important to take care of that.
See: Turn Back The Clock On Insulin Resistance
Proteins accumulate errors
This is due to DNA damage, of course, but there are specific things that can reduce protein error accumulation; see for example:
A quick fix – preventing protein errors extends lifespan
See also: Rapamycin Can Slow Aging By 20% (But Watch Out)
The microbiome becomes unbalanced
We at 10almonds often mention that gut health affects pretty much every other kind of health, and it’s true for aging as well. So, take care of that microbiome!
Here’s a primer: Gut Health 101
Want to know more about delaying aging beyond the cellular level?
Check out: Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Ageless Aging – by Maddy Dychtwald
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Maddy Dychtwald, herself 73, has spent her career working in the field of aging. She’s not a gerontologist or even a doctor, but she’s nevertheless been up-to-the-ears in the industry for decades, mostly as an organizer, strategist, facilitator, and so forth. As such, she’s had her finger on the pulse of the healthy longevity movement for a long time.
This book was written to address a problem, and the problem is: lifespan is increasing (especially for women), but healthspan has not been keeping up the pace.
In other words: people (especially women) are living longer, but often with more health problems along the way than before.
And mostly, it’s for lack of information (or sometimes: too much competing incorrect information).
Fortunately, information is something that a woman in Dychtwald’s position has an abundance of, because she has researchers and academics in many fields on speed-dial and happy to answer her questions (we get a lot of input from such experts throughout the book—which is why this book is so science-based, despite the author not being a scientist).
The book answers a lot of important questions beyond the obvious “what diet/exercise/sleep/supplements/etc are best for healthy aging” (spoiler: it’s quite consistent with the things we recommend here, because guess what, science is science), questions like how best to prepare for this that or the other, how to get a head start on preventative healthcare for some things, how to avoid being a burden to our families (one can argue that families are supposed to look after each other, but still, it’s a legitimate worry for many, and understandably so), and even how to balance the sometimes conflicting worlds of health and finances.
Unlike many authors, she also talks about the different kinds of aging, and tackles each of them separately and together. We love to see it!
Bottom line: this book is a very good one-stop-shop for all things healthy aging. It’s aimed squarely at women, but most advice goes for men the same too, aside from the section on hormones and such.
Click here to check out Ageless Aging, and plan your future!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Reinventing Your Life – by Dr. Jeffrey Young & Dr. Janet Klosko
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is quite unlike any other broadly-CBT-focused books we’ve reviewed before. How so, you may wonder?
Rather than focusing on automatic negative thoughts and cognitive distortions with a small-lens focus on an immediate problem, this one zooms out rather and tackles the cause rather than the symptom.
The authors outline eleven “lifetraps” that we can get stuck in:
- Abandonment
- Mistrust & abuse
- Vulnerability
- Dependence
- Emptional deprivation
- Social exclusion
- Defectiveness
- Failure
- Subjugation
- Unrelenting standards
- Entitlement
They then borrow from other areas of psychology, to examine where these things came from, and how they can be addressed, such that we can escape from them.
The style of the book is very reader-friendly pop-psychology, with illustrative (and perhaps apocryphal, but no less useful for it if so) case studies.
The authors then go on to give step-by-step instructions for dealing with each of the 11 lifetraps, per 6 unmet needs we probably had that got us into them, and per 3 likely ways we tried to cope with this using maladaptive coping mechanisms that got us into the lifetrap(s) we ended up in.
Bottom line: if you feel there’s something in your life that’s difficult to escape from (we cannot outrun ourselves, after all, and bring our problems with us), this book could well contain the key that you need to get out of that cycle.
Click here to check out “Reinventing Your Life” and break free from any lifetrap(s) of your own!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Realistic chronic pain management
We’ve had a number of requests to do a main feature on managing chronic pain, so here it is!
A quick (but important) note before we begin:
Obviously, not all chronic pain is created equal. Furthermore, we know that you, dear reader with chronic pain, have been managing yours for however long you have, learning as you go. You also doubtlessly know your individual condition inside out.
We also know that people with chronic health conditions in general are constantly beset by well-meaning unsolicited advice from friends and family, asking if you’ve heard about [thing you heard about 20 years ago] that will surely change your life and cure you overnight.
It’s frustrating, and we’re going to try to avoid doing that here, while still offering the advice that was asked for. We ask you, therefore, to kindly overlook whatever you already knew, and if you already knew it all, well, we salute you and will not be surprised if that’s the case for at least some readers. Chronic pain’s a… Well, it’s a chronic pain.
All that said, let’s dive in…
How are you treating your body right now?
Are you hydrated; have you eaten; are you standing/sitting/lying in a position that at least should be comfortable for you in principle?
The first two things affect pain perception; the latter can throw a spanner in the works if something’s not quite right.
Move your body (gently!)
You know your abilities, so think about the range of motion that you have, especially in the parts of your body that hurt (if that’s “everywhere”, then, our sympathies, and we hope you find the same advice applies). Think about your specific muscles and joints as applicable, and what the range of motion is “supposed” to be for each. Exercise your range of motion as best you can (gently!) to the point of its limit(s) and/or pain.
- If you take it past that limit, there is a good chance you will make it worse. You don’t want that.
- If you don’t take it to the limit, there is a good chance your range of movement will deteriorate, and your “safe zone” (i.e., body positions that are relatively free from pain) will diminish. You definitely don’t want that, either.
Again, moderation is key. Yes, annoying as the suggestion may be, such things as yoga etc can help, if done carefully and gently. You know your limits; work with those, get rest between, and do what you can.
For most people this will at least help keep the pain from getting worse.
Hot & Cold
Both of these things could ease your pain… Or make it worse. There is an element of “try it and see”, but here’s a good general guide:
Here’s How to Choose Between Using Ice or Heat for Pain
Meditation… Or Distraction
Meditating really does help a lot of people. In the case of pain, it can be counterintuitively helpful to focus for a while on the sensation of the pain… But in a calm, detached fashion. Without judgement.
“Yes, I am experiencing pain. Yes, it feels like I’m being stabbed with hot knives. Yes, this is tortuous; wow, I feel miserable. This truly sucks.”
…it doesn’t sound like a good experience, does it? And it’s not, but paying it attention this way can paradoxically help ease things. Pain is, after all, a messenger. And in the case of chronic pain, it’s in some ways a broken messenger, but what a messenger most needs is to be heard.
The above approach a) is good b) may have a limit in how long you can sustain it at a time, though. So…
The opposite is a can be a good (again, short-term) approach too. Call a friend, watch your favorite movie, play a video game if that’s your thing. It won’t cure anything, but it can give you a little respite.
Massage
Unless you already know this makes your pain worse, this is a good thing to try. It doesn’t have to be a fancy spa; if the nature of your pain and condition permits, you can do self-massage. If you have a partner or close friend who can commit to helping, it can be very worth them learning to give a good massage. There are often local courses available, and failing that, there is also YouTube.
Here’s an example of a good video for myofascial release massage, which can ease a lot of common kinds of chronic pain:
Some quick final things to remember:
- If you find something helps, then it helps, do that.
- That goes for mobility aids and other disability aids too, even if it was designed for a different disability. If it helps, it helps. You’re not stealing anyone’s thunder (or resources) by using something that makes your life easier. We’re not in this life to suffer!
- There is no such thing as “this pain is not too much”. The correct amount of pain is zero. Maybe your body won’t let you reach zero, but more than that is “too much” already.
- You don’t have to be suffering off the scale to deserve relief from pain
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: