Top 10 Causes Of High Blood Pressure
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As Dr. Frita Fisher explains, these are actually the top 10 known causes of high blood pressure. Number zero on the list would be “primary hypertension”, which means high blood pressure with no clear underlying cause.
Superficially, this feels a little like the sometime practice of writing the catch-all “heart failure” as the cause of death on a death certificate, because yes, that heart sure did stop beating. But in reality, primary hypertension is most likely often caused by such things as unmanaged chronic stress—something that doesn’t show up on most health screenings.
Dr. Fisher’s Top 10
- Thyroid disease: both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can cause high blood pressure.
- Obstructive sleep apnea: characterized by snoring, daytime sleepiness, and headaches, this condition can lead to hypertension.
- Chronic kidney disease: diseases ranging from diabetic nephropathy to renal vascular disease can cause high blood pressure.
- Elevated cortisol levels: conditions like Cushing’s syndrome or disease, which involve high cortisol levels, can lead to hypertension—as can a lifestyle with a lot of chronic stress, but that’s less readily diagnosed as such than something one can tell from a blood test.
- Elevated aldosterone levels: excess aldosterone from the adrenal glands causes the body to retain salt and water, increasing blood pressure, because more stuff = more pressure.
- Brain tumor: tumors that increase intracranial pressure can cause a rise in blood pressure to ensure adequate brain perfusion. In these cases, the hypertension is keeping you alive—unless it kills you first. If this seems like a strange bodily response, remember that our bodily response to an infection is often fever, to kill off the infection which can’t survive at such high temperatures (but neither can we, so it becomes a game of chicken with our life on the line), so sometimes our body does kill us with one thing while trying to save us from another.
- Coarctation of the aorta: this congenital heart defect results in narrowing of the aorta, leading to hypertension, especially in the upper body.
- Pregnancy: pregnancy can either induce or worsen existing hypertension.
- Obesity: excess weight increases blood flow and pressure on arteries, raising the risk of hypertension and associated conditions, e.g. diabetes etc.
- Drugs: certain medications and recreational drugs (including, counterintuitively, alcohol!) can elevate blood pressure.
For more information on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
End the Insomnia Struggle – by Dr. Colleen Ehrnstrom and Dr. Alisha Brosse
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed sleep books before, and we always try to recommend books that have something a little different than the rest, so what makes this one stand out?
While there is the usual quick overview of the basics that we’re sure you already know (sleep hygiene etc), most of the attention here is given to cold, hard clinical psychology… in a highly personalized way.
How, you may ask, can they personalize a book, that is the same for everyone?
The answer is, by guiding the reader through examining our own situation. With template logbooks, worksheets, and the like—for this reason we recommend getting a paper copy of the book, rather than the Kindle version, in case you’d like to use/photocopy those.
Essentially, reading this book is much like having your own psychologist (or two) to guide you through finding a path to better sleep.
The therapeutic approach, by the way, is a combination of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Acceptance-Commitment Therapy (ACT), which work very well together here.
Bottom line: if you’ve changed your bedsheets and turned off your electronic devices and need something a little more, this book is the psychological “big guns” for removing the barriers between you and good sleep.
Click here to check out End the Insomnia Struggle, and end yours once and for all!
Share This Post
-
The Intelligence Trap – by David Robson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re including this one under the umbrella of “general wellness”, because it happens that a lot of very intelligent people make stunningly unfortunate choices sometimes, for reasons that may baffle others.
The author outlines for us the various reasons that this happens, and how. From the famous trope of “specialized intelligence in one area”, to the tendency of people who are better at acquiring knowledge and understanding to also be better at acquiring biases along the way, to the hubris of “I am intelligent and therefore right as a matter of principle” thinking, and many other reasons.
Perhaps the greatest value of the book is the focus on how we can avoid these traps, narrow our bias blind spots, and play to our strengths while paying full attention to our weaknesses.
The style is very readable, despite having a lot of complex ideas discussed along the way. This is entirely to be expected of this author, an award-winning science writer.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand the array of traps that disproportionately catch out the most intelligent people (and how to spot such), then this is a great book for you.
Click here to check out The Intelligence Trap, and be more wary!
Share This Post
-
Healthy Longevity As A Lifestyle Choice
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
7 Keys To Healthy Longevity
This is Dr. Luigi Fontana. He’s a research professor of Geriatrics & Nutritional Science, and co-director of the Longevity Research Program at Washington University in St. Louis.
What does he want us to know?
He has a many-fold approach to healthy longevity, most of which may not be news to you, but you might want to prioritize some things:
Consider caloric restriction with optimal nutrition (CRON)
This is about reducing the metabolic load on your body, which frees up bodily resources for keeping yourself young.
Keeping your body young and healthy is your body’s favorite thing to do, but it can’t do that if it never gets a chance because of all the urgent metabolic tasks you’re giving it.
If CRON isn’t your thing (isn’t practicable for you, causes undue suffering, etc) then intermittent fasting is a great CR mimetic, and he recommends that too. See also:
- Is Cutting Calories The Key To Healthy Long Life?
- Fasting Without Crashing? We Sort The Science From The Hype
Keep your waistline small
Whichever approach you prefer to use to look after your metabolic health, keeping your waistline down is much more important for health than BMI.
Specifically, he recommends keeping it:
- under 31.5” for women
- under 37” for men
The disparity here is because of hormonal differences that influence both metabolism and fat distribution.
Exercise as part of your lifestyle
For Dr. Fontana, he loves mountain-biking (this writer could never!) and weight-lifting (also not my thing). But what’s key is not the specifics, but what’s going on:
- Some kind of frequent movement
- Some kind of high-intensity interval training
- Some kind of resistance training
Frequent movement because our bodies are evolved to be moving more often than not:
The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, & Move More
High-Intensity Interval Training because unlike most forms of exercise (which slow metabolism afterwards to compensate), it boosts metabolism for up to 2 hours after training:
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Resistance training because strength (of muscles and bones) matters too:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
Writer’s examples:
So while I don’t care for mountain-biking or weight-lifting, what I do is:
1) movement: walk (briskly!) everywhere and also use a standing desk
2) HIIT: 2-minute bursts of hindu squats and/or exercise bike sprints
3) resistance: pilates and other calisthenicsModeration is not key
Dr. Fontana advises that we do not smoke, and that we do not drink alcohol, for example. He also notes that just as the only healthy amount of alcohol is zero, less ultra-processed food is always better than more.
Maybe you don’t want to abstain completely, but mindful wilful consumption of something unhealthy is preferable to believing “moderate consumption is good for the health” and an unhealthy habit develops!
Greens and beans
Shocking absolutely nobody, Dr. Fontana advocates for (what has been the most evidence-based gold standard of healthy-aging diets for quite some years now) the Mediterranean diet.
See also: Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet ← this is about tweaking the Mediterranean diet per personal area of focus, e.g. anti-inflammatory bonus, best for gut, heart healthiest, and most neuroprotective.
Take it easy
Dr. Fontana advises us (again, with a wealth of evidence) Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction, and to get good sleep.
Not shocked?
To quote the good doctor,
❝There are no shortcuts. No magic pills or expensive procedures can replace the beneficial effects of a healthy diet, exercise, mindfulness, or a regenerating night’s sleep.❞
Always a good reminder!
Want to know more?
You might enjoy his book “The Path to Longevity: How to Reach 100 with the Health and Stamina of a 40-Year-Old”, which we reviewed previously
You might also like this video of his, about changing the conversation from “chronic disease” to “chronic health”:
Want to watch it, but not right now? Bookmark it for later
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Brazil Nuts vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Brazil nuts to cashews, we picked the cashews.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, Brazil nuts have more fat and fiber, while cashews have more carbs and protein. So, it really comes down to what you want to prioritize. We’d generally consider fiber the tie-breaker, making this category a subjective marginal win for Brazil nuts—and especially marginal since they are both low glycemic index foods in any case.
When it comes to vitamins, Brazil nuts have more of vitamins C, E, and choline, while cashews have more of vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and K, so while both are great, this category is a clear by-the-numbers win for cashews.
The category of minerals is an interesting one. Brazil nuts have more calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and selenium, while cashews have more copper, iron, manganese, and zinc. That would be a 4:4 tie, but let’s take a closer look at those selenium levels:
- A cup of cashews contains 109% of the RDA of selenium. Your hair will be luscious and shiny.
- A cup of Brazil nuts contains 10,456% of the RDA of selenium. This is way past the point of selenium toxicity, and your (luscious, shiny) hair will fall out.
For this reason, it’s recommended to eat no more than 3–4 Brazil nuts per day.
We consider that a point against Brazil nuts.
Adding up the section makes for a win for cashews. Of course, enjoy Brazil nuts too if you will, but in careful moderation please!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
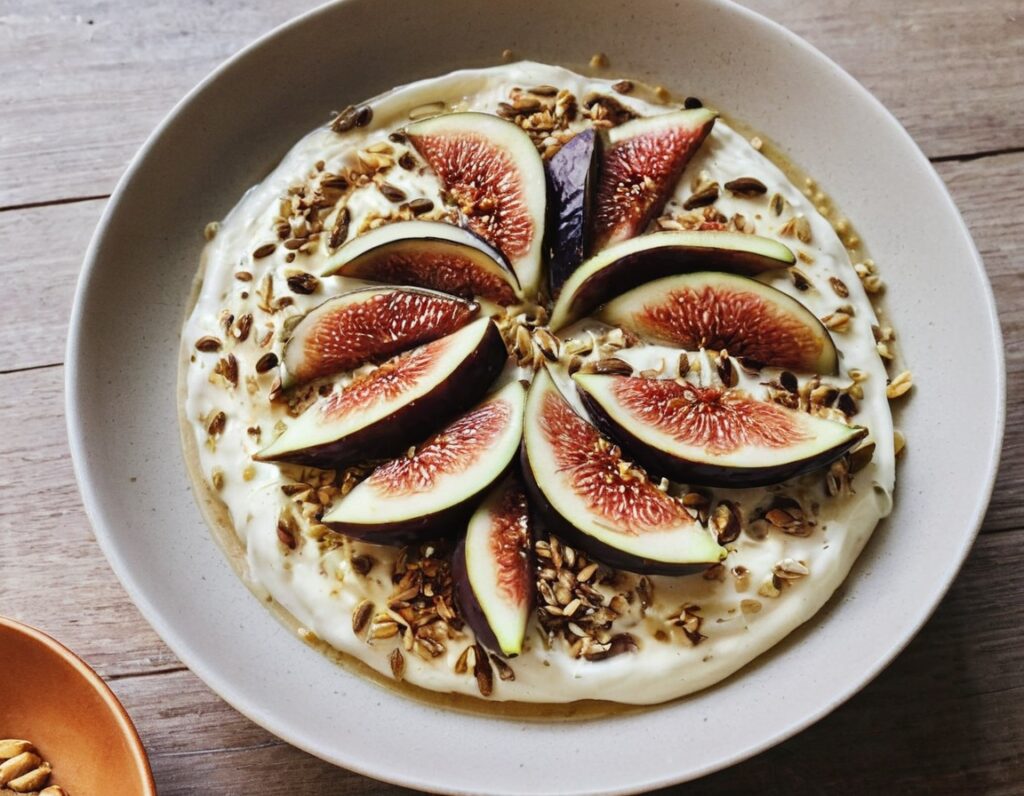
The Gut-Healthiest Yogurt
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Not only is this yogurt, so it’s winning from the start with its probiotic goodness, but also it’s full of several kinds of fiber, and gut-healthy polyphenols too. Plus, it’s delicious. The perfect breakfast, but don’t let us stop you from enjoying it at any time of day!
You will need
- 1 cup yogurt with minimal additives. Live Greek yogurt is a top-tier choice, and plant-based varieties are fine too (just watch out, again, for needless additives)
- 7 dried figs, roughly chopped
- 6 fresh figs, thinly sliced
- 5 oz chopped pitted dates
- 4 tbsp mixed seeds (pumpkin, sunflower, and chia are a great combination)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Soak the dried figs, the dates, and half the seeds in hot water for at least 5 minutes. Drain (be careful not to lose the chia seeds) and put in a blender with ¼ cup cold water.
2) Blend the ingredients from the last step into a purée (you can add a little more cold water if it needs it).
3) Mix this purée into the yogurt in a bowl, and add in the remaining seeds, mixing them in thoroughly.
4) Top with the sliced figs, and serve (or refrigerate, up to a few days, until needed).
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Dates vs Figs – Which is Healthier?
- The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How an Idaho vaccine advocacy org plans its annual goals
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The start of a new year means many nonprofits and community health workers are busy setting goals and reflecting on what’s worked and what hasn’t. For those engaged in vaccine outreach, it also means reflecting on the tools and tactics that help them communicate better with their communities about why vaccines matter.
Across the country, childhood vaccination rates have declined since the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in a resurgence of preventable diseases like pertussis.
Also known as whooping cough, pertussis has surged in states like Idaho, said Karen Jachimowski Sharpnack, executive director of the Idaho Immunization Coalition, in a conversation with PGN about the organization’s 2025 priorities.
Sharpnack shared how spikes in infectious respiratory illnesses can create opportunities to listen better and understand the nuances of the communities they serve.
Here’s more of what Sharpnack said.
[Editor’s note: The contents of this interview have been edited for length and clarity.]
PGN: Whooping cough cases are up in your state. Can you share an example of how your organization is responding?
Karen Jachimowski Sharpnack: If you look at Treasure Valley and Northern Idaho, the majority of those cases have been reported, and it’s like five times as much as we had the previous year.
So, two things that the Coalition is doing in response: First, we put out radio public service announcements throughout those particular areas about what whooping cough is, how contagious it is, and what you should do if you think your child or anyone you know has it.
Second, we are contacting every school superintendent, principal, school nurse, with a letter from us at the Coalition [to warn about] the whooping cough outbreaks in schools right now. Here’s what the symptoms are, here’s what you can do, and then here’s how you can protect yourself and your families.
It doesn’t mean the health district wouldn’t do it, or the Department of Health and Welfare can’t do it. But from our standpoint, at least we are bringing an awareness to the schools that this is happening.
PGN: How does your organization decide when outreach is needed? How do you take a pulse of your communities’ vaccine attitudes?
K.J.S.: We consistently hold listening sessions. We do them in English and Spanish if we need to, and we go around—and I’m talking about the southern part of the state—and bring people together.
We’ve done adults, we’ve done teenagers, we’ve done college students, we’ve done seniors, we’ve done all age groups.
So, we’ll bring eight or 10 people together, and we’ll spend a couple of hours with them. We feed them and we also pay them to be there. We say, ‘We want to hear from you about what you’re hearing about vaccines, what your views are if you’re vaccinated.’ Anytime, by the way, they can get up and leave and still get paid.
We want to hear what they’re hearing on the ground. And these sessions are extremely informational. For one, we learn about the misinformation that goes out there, like immediately. And two, we’re able to then focus [on how to respond]. If we’re hearing this, what kind of media campaign do we need to get together?
PGN: How do these listening sessions inform your work?
K.J.S.: So, a couple times a year we also pay a professional poller to do a poll. And when we get those results we check them against our listening sessions. We want to see: Are we on target? Are we ahead?
We just finished putting a one-pager together for legislators, so we’re ready to go with the new [legislative] session. We do this poll every year in August-September to know how Idahoans are feeling about vaccines. We get the results in October, because we’re getting ready for the next year.
We actually poll 19-to-64-year-olds, really honing in on questions like, ‘Do you believe vaccines are safe and effective?’ ‘Do you believe that school vaccination rules should still be in place?’
And what’s pretty cool is that two-thirds of Idahoans still believe vaccines are safe and effective, want to keep school rules in place, and believe that the infrastructure systems that we have in place for our vaccine registry should remain the same. Those are important to hear, so this is really good information that we can pull out and do something with.
PGN: Like what?
K.J.S.: Here’s the bottom line. It takes money to do this work, so you have to be able to say what you are going to do with the results.
Doing a poll costs anywhere from $15,000 to $35,000. This is an expensive investment, but we know that the polling is so important to us, along with the time that I have my staff go out and do the listening sessions and get feedback.
We take those results to educate, to talk to our legislators, and advocate for vaccines. We actually do these high-level media campaigns around the state. So, we are actually doing something with the polling. We’re not just sharing the results out.
And then we actually ask, what can we do to make a change? What are we hearing that we need to focus on?
That’s why it’s really important, because we are actually pushing this out for 2025. We know where we’re going in 2025 programmatically with marketing, and we know where we’re going with advocacy work.
We’re not guessing. We’re actually listening to people. And then we’re making really concrete decisions on how we’re going to move the organization forward to be able to help our communities.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: