The Toe-Tapping Tip For Better Balance
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Balance is critical for health especially in older age, since it’s amazing how much else can go dramatically and suddenly wrong after a fall. So, here’s an exercise to give great balance and stability:
How to do it
You will need:
- Something to hold onto, such as a countertop
- A target on the floor, such as a mark or a coin
The steps:
- Lift one leg up, bring your foot forward, and tap the object in front of you.
- Then, bring that foot back to where it started.
- Next, switch to the other leg and tap.
- Alternate between your right and left legs, shifting back and forth.
- Your goal is to do this for 10 repetitions on each leg without holding on.
How it works:
Whenever you tap, you have to lift one leg up and reach it out in front of you. Doing this requires you to stand on one leg while moving a weight (namely: your other leg), which is something many people, especially upon getting older, are hesitant to do. If you’re unable to stand on one leg, let alone move your center of gravity (per the counterbalance of the other leg) while doing so, you may end up shuffling and walking with your feet sliding across the ground—something you really want to avoid.
For more on all of this plus a visual demonstration, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Fall Special ← this is about not falling, or, failing that, minimizing injury if you do
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Rebuilding Milo – by Dr. Aaron Horschig
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author, a doctor of physical therapy, also wrote another book that we reviewed a while ago, “The Squat Bible” (which is also excellent, by the way). This time, it’s all about resistance training in the context of fixing a damaged body.
Resistance training is, of course, very important for general health, especially as we get older. However, it’s easy to do it wrongly and injure oneself, and indeed, if one is carrying some injury and/or chronic pain, it becomes necessary to know how to fix that before continuing—without just giving up on training, because that would be a road to ruin in terms of muscle and bone maintenance.
The book explains all the necessary anatomy, with clear illustrations too. He talks equipment, keeping things simple and practical, letting the reader know which things actually matter in terms of quality, and what things are just unnecessary fanciness and/or counterproductive.
Most of the book is divided into chapters per body part, e.g. back pain, shoulder pain, ankle pain, hip pain, knee pain, etc; what’s going on, and how to fix it to rebuild it stronger.
The style is straightforward and simple, neither overly clinical nor embellished with overly casual fluff. Just, clear simple explanations and instructions.
Bottom line: if you’d like to get stronger and/or level up your resistance training, but are worried about an injury or chronic condition, this book can set you in good order.
Click here to check out Rebuilding Milo, and rebuild yourself!
Share This Post
-
The Oxygen Advantage – by Patrick McKeown
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You probably know to breathe through your nose, and use your diaphragm. What else does this book have to offer?
A lot of the book is aimed at fixing specific problems, and optimizing what can be optimized—including with tips and tricks you may not have encountered before. Yet, the offerings are not bizarre either; we don’t need to learn to breathe through our ears while drinking a glass of water upside down or anything.
Rather, such simple things as improving one’s VO₂Max by occasionally holding one’s breath while walking briskly. But, he advises specifically, this should be done by pausing the breath halfway through the exhalation (a discussion of the ensuing physiological response is forthcoming).
Little things like that are woven throughout the book, whose style is mostly anecdotal rather than hard science, yet is consistent with broad scientific consensus in any case.
Bottom line: if you’ve any reason to think your breathing might be anything less than the best it could possibly be, this book is likely to help you to tweak it to be a little better.
Click here to check out The Oxygen Advantage, and get yours!
Share This Post
-
This salt alternative could help reduce blood pressure. So why are so few people using it?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One in three Australian adults has high blood pressure (hypertension). Excess salt (sodium) increases the risk of high blood pressure so everyone with hypertension is advised to reduce salt in their diet.
But despite decades of strong recommendations we have failed to get Australians to cut their intake. It’s hard for people to change the way they cook, season their food differently, pick low-salt foods off the supermarket shelves and accept a less salty taste.
Now there is a simple and effective solution: potassium-enriched salt. It can be used just like regular salt and most people don’t notice any important difference in taste.
Switching to potassium-enriched salt is feasible in a way that cutting salt intake is not. Our new research concludes clinical guidelines for hypertension should give patients clear recommendations to switch.
What is potassium-enriched salt?
Potassium-enriched salts replace some of the sodium chloride that makes up regular salt with potassium chloride. They’re also called low-sodium salt, potassium salt, heart salt, mineral salt, or sodium-reduced salt.
Potassium chloride looks the same as sodium chloride and tastes very similar.
Potassium-enriched salt works to lower blood pressure not only because it reduces sodium intake but also because it increases potassium intake. Insufficient potassium, which mostly comes from fruit and vegetables, is another big cause of high blood pressure.
What is the evidence?
We have strong evidence from a randomised trial of 20,995 people that switching to potassium-enriched salt lowers blood pressure and reduces the risks of stroke, heart attacks and early death. The participants had a history of stroke or were 60 years of age or older and had high blood pressure.
An overview of 21 other studies suggests much of the world’s population could benefit from potassium-enriched salt.
The World Health Organisation’s 2023 global report on hypertension highlighted potassium-enriched salt as an “affordable strategy” to reduce blood pressure and prevent cardiovascular events such as strokes.
What should clinical guidelines say?
We teamed up with researchers from the United States, Australia, Japan, South Africa and India to review 32 clinical guidelines for managing high blood pressure across the world. Our findings are published today in the American Heart Association’s journal, Hypertension.
We found current guidelines don’t give clear and consistent advice on using potassium-enriched salt.
While many guidelines recommend increasing dietary potassium intake, and all refer to reducing sodium intake, only two guidelines – the Chinese and European – recommend using potassium-enriched salt.
To help guidelines reflect the latest evidence, we suggested specific wording which could be adopted in Australia and around the world:
Recommended wording for guidance about the use of potassium-enriched salt in clinical management guidelines. Why do so few people use it?
Most people are unaware of how much salt they eat or the health issues it can cause. Few people know a simple switch to potassium-enriched salt can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of a stroke and heart disease.
Limited availability is another challenge. Several Australian retailers stock potassium-enriched salt but there is usually only one brand available, and it is often on the bottom shelf or in a special food aisle.
Potassium-enriched salts also cost more than regular salt, though it’s still low cost compared to most other foods, and not as expensive as many fancy salts now available.
It looks and tastes like normal salt.
Jimmy Dean/UnsplashA 2021 review found potassium-enriched salts were marketed in only 47 countries and those were mostly high-income countries. Prices ranged from the same as regular salt to almost 15 times greater.
Even though generally more expensive, potassium-enriched salt has the potential to be highly cost effective for disease prevention.
Preventing harm
A frequently raised concern about using potassium-enriched salt is the risk of high blood potassium levels (hyperkalemia) in the approximately 2% of the population with serious kidney disease.
People with serious kidney disease are already advised to avoid regular salt and to avoid foods high in potassium.
No harm from potassium-enriched salt has been recorded in any trial done to date, but all studies were done in a clinical setting with specific guidance for people with kidney disease.
Our current priority is to get people being managed for hypertension to use potassium-enriched salt because health-care providers can advise against its use in people at risk of hyperkalemia.
In some countries, potassium-enriched salt is recommended to the entire community because the potential benefits are so large. A modelling study showed almost half a million strokes and heart attacks would be averted every year in China if the population switched to potassium-enriched salt.
What will happen next?
In 2022, the health minister launched the National Hypertension Taskforce, which aims to improve blood pressure control rates from 32% to 70% by 2030 in Australia.
Potassium-enriched salt can play a key role in achieving this. We are working with the taskforce to update Australian hypertension management guidelines, and to promote the new guidelines to health professionals.
In parallel, we need potassium-enriched salt to be more accessible. We are engaging stakeholders to increase the availability of these products nationwide.
The world has already changed its salt supply once: from regular salt to iodised salt. Iodisation efforts began in the 1920s and took the best part of 100 years to achieve traction. Salt iodisation is a key public health achievement of the last century preventing goitre (a condition where your thyroid gland grows larger) and enhancing educational outcomes for millions of the poorest children in the world, as iodine is essential for normal growth and brain development.
The next switch to iodised and potassium-enriched salt offers at least the same potential for global health gains. But we need to make it happen in a fraction of the time.
Xiaoyue Xu (Luna), Scientia Lecturer, UNSW Sydney; Alta Schutte, SHARP Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine, UNSW Sydney, and Bruce Neal, Executive Director, George Institute Australia, George Institute for Global Health
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
We’ve talked before about how waist circumference is a much more useful indicator of metabolic health than BMI.
So, let’s say you’ve a bit more around the middle than you’d like, but it stubbornly stays there. What’s going on underneath what you can see, why is it going on, and how can you get it to change?
What is visceral fat?
First, let’s talk about subcutaneous fat. That’s the fat directly under your skin. Women usually have more than men, and that’s perfectly healthy (up to a point); it’s supposed to be that way. We (women) will tend to accumulate this mostly in places such as our breasts, hips, and butt, and work outwards from there. Men will tend to put it on more to the belly and face.
Side-note: if you’re undergoing (untreated) menopause, the changes in your hormone levels will tend to result in more subcutaneous fat to the belly and face too. That’s normal, and/but normal is not always good, and treatment options are great (with hormone replacement therapy, HRT, topping the list).
Visceral fat (also called visceral adipose tissue), on the other hand, is the fat of the viscera—the internal organs of the abdomen.
So, this is fat that goes under your abdominal muscles—you can’t squeeze this (directly).
So what can we do?
Famously “you can’t do spot reduction” (lose fat from a particular part of your body by focusing exercises on that area), but that’s about subcutaneous fat. There are things you can do that will reduce your visceral fat in particular.
Some of these advices you may think “that’s just good advice for losing fat in general” and it is, yes. But these are things that have the biggest impact on visceral fat.
Cut alcohol use
This is the biggie. By numerous mechanisms, some of which we’ve talked about before, alcohol causes weight gain in general yes, but especially for visceral fat.
Get better sleep
You might think that hitting the gym is most important, but this one ranks higher. Yes, you can trim visceral fat without leaving your bed (and even without getting athletic in bed, for that matter). Not convinced?
- Here’s a study of 101 people looking at sleep quality and abdominal adiposity
- Oh, and here’s a meta-analysis with 56,000 people (finding the same thing), in case that one study didn’t convince you.
So, the verdict is clear: you snooze, you lose (visceral fat)!
Tweak your diet
You don’t have to do a complete overhaul (unless you want to), but a few changes can make a big difference, especially:
- Getting more fiber (this is the biggie when it comes to diet)
- Eating less sugar (not really a surprise, but relevant to mention)
- Eat whole foods (skip the highly processed stuff)
If you’d like to learn more and enjoy videos, here’s an informative one to get you going!
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically! Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Escape From The Clutches Of Shame
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about managing various emotions, including “negative” ones. We put that in “scare quotes” because they also all have positive aspects, that are just generally overshadowed by the fact that the emotions themselves are not pleasant. But for example…
We evolved our emotions, including the “negative” ones, for our own benefit as a species:
- Stress keeps us safe by making sure we take important situations seriously
- Anger keeps us safe by protecting us from threats
- Disgust keeps us safe by helping us to avoid things that might cause disease
- Anxiety keeps us safe by ensuring we don’t get complacent
- Guilt keeps us safe by ensuring we can function as a community
- Sadness keeps us safe by ensuring we value things that are important to us, and learn to become averse to losing them
- …and so on
You can read more about how to turn these off (or rather, at least pause them) when they’re misfiring and/or just plain not convenient, here:
While it’s generally considered good to process feelings instead of putting them aside, the fact is that sometimes we have to hold it together while we do something, such that we can later have an emotional breakdown at a convenient time and place, instead of the supermarket or bank or office or airport or while entertaining houseguests or… etc.
Today, though, we’re not putting things aside, for the most part (though we will get to that too).
We’ll be dealing with shame, which is closely linked to the guilt we mentioned in that list there.
See also: Reconsidering the Differences Between Shame and Guilt
Shame’s purpose
Shame’s purpose is to help us (as a community) avoid anti-social behavior for which we might be shamed, and thus exiled from the in-group. It helps us all function better together, which is how we thrive as a species.
Shame, therefore, is often assumed to be something we can (and possibly should) use to ensure that we (ourselves and/or others) “do the right thing”.
But there’s a catch…
Shame only works negatively
You may be thinking “well duh, it’s a negative emotion”, but this isn’t about negativity in the subjective sense, but rather, positive vs negative motivation:
- Positive motivation: motivation that encourages us to do a given thing
- Negative motivation: motivation that encourages us to specifically not do a given thing
Shame is only useful as a negative motivation, i.e., encouraging us to specifically not do a given thing.
Examples:
- You cannot (in any way that sticks, at least) shame somebody into doing more housework.
- You can, however, shame somebody out of drinking and driving.
This distinction matters a lot when it comes to how we are with our children, or with our employees (or those placed under us in a management structure), or with people who otherwise look to us as leaders.
It also matters when it comes to how we are with ourselves.
Here’s a paper about this, by the way, with assorted real-world examples:
The negative side of motivation: the role of shame
From those examples, we can see that attempts to shame someone (including oneself) into doing something positive will generally not only fail, they will actively backfire, and people (including oneself) will often perform worse than pre-shaming.
Looking inwards: healthy vs unhealthy shame
Alcoholics Anonymous and similar programs use a degree of pro-social shame to help members abstain from the the act being shamed.
Rather than the unhelpful shame of exiling a person from a group for doing a shameful thing, however, they take an approach of laying out the shame for all to see, feeling the worst of it and moving past it, which many report as being quite freeing emotionally while still [negatively] motivational to not use the substance in question in the future (and similar for activity-based addictions/compulsions, such as gambling, for example).
As such, if you are trying to avoid doing a thing, shame can be a useful motivator. So by all means, if it’s appropriate to your goals, tell your friends/family about how you are now quitting this or that (be it an addiction, or just something generally unhealthy that you’d like to strike off your regular consumption/activity list).
You will still be tempted! But the knowledge of the shame you would feel as a result will help keep you from straying into that temptation.
If you are trying to do a thing, however, (even something thought of in a negative frame, such as “lose weight”), then shame is not helpful and you will do best to set it aside.
You can shame yourself out of drinking sodas (if that’s your plan), but you can’t shame yourself into eating healthy meals. And even if your plan is just shaming yourself out of eating unhealthy food… Without a clear active positive replacement to focus on instead, all you’ll do there is give yourself an eating disorder. You’ll eat nothing when people are looking, and then either a) also eat next to nothing in private or else b) binge in secret, and feel terrible about yourself, neither of which are any good for you whatsoever.
Similarly, you can shame yourself out of bed, but you can’t shame yourself into the gym:
Let it go
There are some cases, especially those where shame has a large crossover with guilt, that it serves no purpose whatsoever, and is best processed and then put aside.
For example, if you did something that you are ashamed of many years ago, and/or feel guilty about something that you did many years ago, but this is not an ongoing thing for you (i.e., it was a one-off bad decision, or a bad habit that have now long since dropped), then feeling shame and/or guilt about that does not benefit you or anyone else.
As to how to process it and put it aside, if your thing harmed someone else, you could see if there’s a way to try to make amends (even if without confessing ill, such as by acting anonymously to benefit the person/group you harmed).
And then, forgive yourself. Regardless of whether you feel like you deserve it. Make the useful choice, that better benefits you, and by extension those around you.
If you are religious, you may find that of help here too. We’re a health science publication not a theological one, but for example: Buddhism preaches compassion including for oneself. Judaism preaches atonement. Christianity, absolution. For Islam, mercy is one of the holiest ideals of the religion, along with forgiveness. So while religion isn’t everyone’s thing, for those for whom it is, it can be an asset in this regard.
For a more worldly approach:
To Err Is Human; To Forgive, Healthy (Here’s How To Do It) ← this goes for when the forgiveness in question is for yourself, too—and we do write about that there (and how)!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Our blood-brain barrier stops bugs and toxins getting to our brain. Here’s how it works
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our brain is an extremely complex and delicate organ. Our body fiercely protects it by holding onto things that help it and keeping harmful things out, such as bugs that can cause infection and toxins.
It does that though a protective layer called the blood-brain barrier. Here’s how it works, and what it means for drug design.
The Conversation, Rattiya Thongdumhyu/Shutterstock, Petr Ganaj/Pexels First, let’s look at the circulatory system
Adults have roughly 30 trillion cells in their body. Every cell needs a variety of nutrients and oxygen, and they produce waste, which needs to be taken away.
Our circulatory system provides this service, delivering nutrients and removing waste.
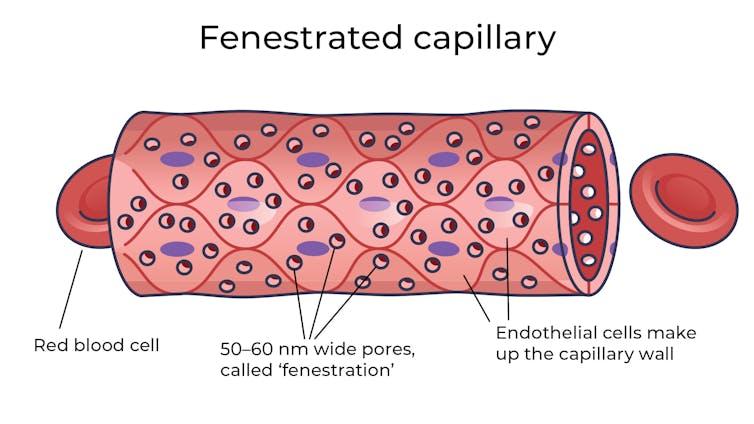
Fenestrated capillaries let nutrients and waste pass through. Vectormine/Shutterstock Where the circulatory system meets your cells, it branches down to tiny tubes called capillaries. These tiny tubes, about one-tenth the width of a human hair, are also made of cells.
But in most capillaries, there are some special features (known as fenestrations) that allow relatively free exchange of nutrients and waste between the blood and the cells of your tissues.
It’s kind of like pizza delivery
One way to think about the way the circulation works is like a pizza delivery person in a big city. On the really big roads (vessels) there are walls and you can’t walk up to the door of the house and pass someone the pizza.
But once you get down to the little suburban streets (capillaries), the design of the streets means you can stop, get off your scooter and walk up to the door to deliver the pizza (nutrients).
We often think of the brain as a spongy mass without much blood in it. In reality, the average brain has about 600 kilometres of blood vessels.
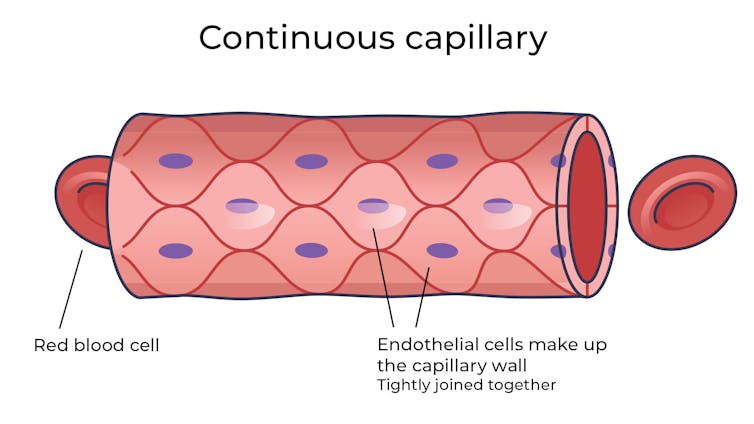
The difference between the capillaries in most of the brain and those elsewhere is that these capillaries are made of specialised cells that are very tightly joined together and limit the free exchange of anything dissolved in your blood. These are sometimes called continuous capillaries.
Continuous capillaries limit the free exchange of anything dissolved in your blood. Vectormine/Shutterstock This is the blood brain barrier. It’s not so much a bag around your brain stopping things from getting in and out but more like walls on all the streets, even the very small ones.
The only way pizza can get in is through special slots and these are just the right shape for the pizza box.
The blood brain barrier is set up so there are specialised transporters (like pizza box slots) for all the required nutrients. So mostly, the only things that can get in are things that there are transporters for or things that look very similar (on a molecular scale).
The analogy does fall down a little bit because the pizza box slot applies to nutrients that dissolve in water. Things that are highly soluble in fat can often bypass the slots in the wall.
Why do we have a blood-brain barrier?
The blood brain barrier is thought to exist for a few reasons.
First, it protects the brain from toxins you might eat (think chemicals that plants make) and viruses that often can infect the rest of your body but usually don’t make it to your brain.
It also provides protection by tightly regulating the movement of nutrients and waste in and out, providing a more stable environment than in the rest of the body.
Lastly, it serves to regulate passage of immune cells, preventing unnecessary inflammation which could damage cells in the brain.
What it means for medicines
One consequence of this tight regulation across the blood brain barrier is that if you want a medicine that gets to the brain, you need to consider how it will get in.
There are a few approaches. Highly fat-soluble molecules can often pass into the brain, so you might design your drug so it is a bit greasy.
The blood-brain barrier stops many medicines getting into the brain. Ron Lach/Pexels Another option is to link your medicine to another molecule that is normally taken up into the brain so it can hitch a ride, or a “pro-drug”, which looks like a molecule that is normally transported.
Using it to our advantage
You can also take advantage of the blood brain barrier.
Opioids used for pain relief often cause constipation. They do this because their target (opioid receptors) are also present in the nervous system of the intestines, where they act to slow movement of the intestinal contents.
Imodium (Loperamide), which is used to treat diarrhoea, is actually an opioid, but it has been specifically designed so it can’t cross the blood brain barrier.
This design means it can act on opioid receptors in the gastrointestinal tract, slowing down the movement of contents, but does not act on brain opioid receptors.
In contrast to Imodium, Ozempic and Victoza (originally designed for type 2 diabetes, but now popular for weight-loss) both have a long fat attached, to improve the length of time they stay in the body.
A consequence of having this long fat attached is that they can cross the blood-brain barrier, where they act to suppress appetite. This is part of the reason they are so effective as weight-loss drugs.
So while the blood brain barrier is important for protecting the brain it presents both a challenge and an opportunity for development of new medicines.
Sebastian Furness, ARC Future Fellow, School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: