The Reason You’re Alone
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you are feeling lonely, then there are likely reasons why, as Kurtzgesagt explains:
Why it happens and how to fix it
Many people feel lonely and disconnected, often not knowing how to make new friends. And yet, social connection strongly predicts happiness, while lack of it is linked to diseases and a shorter life.
One mistake that people make is thinking it has to be about shared interests; that can help, but proximity and shared time are much more important.
Another stumbling block for many is that adult responsibilities and distractions (work, kids, technology) often take priority over friendships—but loneliness is surprisingly highest among young people, worsened by the pandemic’s impact on social interactions.
And even when friendships are made, they fade without attention, often accidentally, impacting both people involved. Other friendships can be lost following big life changes such as moving house or the end of a relationship. And for people above a certain advanced age, friendship groups can shrink due to death, if one’s friends are all in the same age group.
But, all is not lost. We can make friends with people of any age, and old friendships can be revived by a simple invitation. We can also take a “build it and they will come” approach, by organizing events and being the one who invites others.
It’s easy to fear rejection—most people do—but it’s worth overcoming for the potential rewards. That said, building friendships requires time, patience, caring about others, and being open about yourself, which can involve a degree of vulnerability too.
In short: be laid-back while still prioritizing friendships, show genuine interest, and stay open to social opportunities.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Stop Sabotaging Your Weight Loss – by Jennifer Powter, MSc
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is not a dieting book, and it’s not a motivational pep talk.
The book starts with the assumption that you do want to lose weight (it also assumes you’re a woman, and probably over 40… that’s just the book’s target market, but the same advice is good even if that’s not you), and that you’ve probably been trying, on and off, for a while. Her position is simple:
❝I don’t believe that you have a weight loss problem. I believe that you have a self-sabotage problem❞
As to how this sabotage may be occurring, Powter talks about fears that may be holding you back, including but not limited to:
- Fear of failure
- Fear of the unknown
- Fear of loss
- Fear of embarrassment
- Fear of your weight not being the reason your life sucks
Far from putting the reader down, though, Powter approaches everything with compassion. To this end, her prescription starts with encouraging self-love. Not when you’re down to a certain size, not when you’re conforming perfectly to a certain diet, but now. You don’t have to be perfect to be worthy of love.
On the topic of perfection: a recurring theme in the book is the danger of perfectionism. In her view, perfectionism is nothing more nor less than the most justifiable way to hold yourself back in life.
Lastly, she covers mental reframes, with useful questions to ask oneself on a daily basis, to ensure progressing step by step into your best life.
In short: if you’d like to lose weight and have been trying for a while, maybe on and off, this book could get you out of that cycle and into a much better state of being.
Get your copy of “Stop Sabotaging Your Weight Loss” from Amazon today!
Share This Post
-
Debate over tongue tie procedures in babies continues. Here’s why it can be beneficial for some infants
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There is increasing media interest about surgical procedures on new babies for tongue tie. Some hail it as a miracle cure, others view it as barbaric treatment, though adverse outcomes are rare.
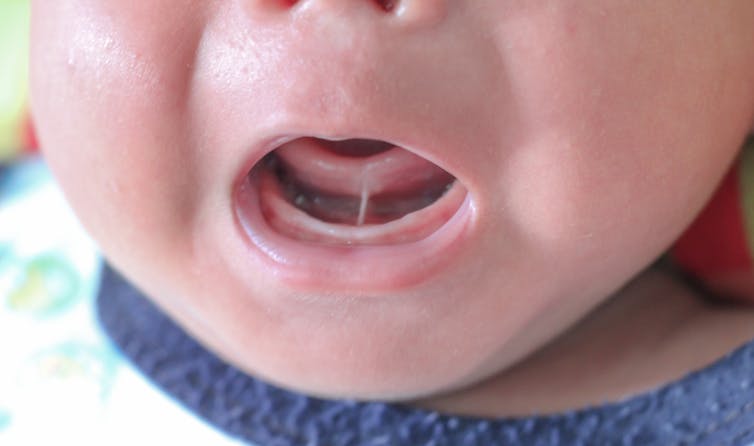
Tongue tie occurs when the tissue under the tongue is attached to the lower gum or floor of the mouth in a way that can restrict the movement or range of the tongue. This can impact early breastfeeding in babies. It affects an estimated 8% of children under one year of age.
While there has been an increase in tongue tie releases (also called division or frenotomy), it’s important to keep this in perspective relative to the increase in breastfeeding rates.
The World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life, with breastfeeding recommended into the second year of life and beyond for the health of mother and baby as well as optimal growth. Global rates of breastfeeding infants for the first six months have increased from 38% to 48% over the past decade. So, it is not surprising there is also an increase in the number of babies being referred globally with breastfeeding challenges and potential tongue tie.
An Australian study published in 2023 showed that despite a 25% increase in referrals for tongue tie division between 2014 and 2018, there was no increase in the number of tongue tie divisions performed. Tongue tie surgery rates increased in Australia in the decade from 2006 to 2016 (from 1.22 per 1,000 population to 6.35) for 0 to 4 year olds. There is no data on surgery rates in Australia over the last eight years.
Tongue tie division isn’t always appropriate but it can make a big difference to the babies who need it. More referrals doesn’t necessarily mean more procedures are performed.
chomplearn/Shutterstock How tongue tie can affect babies
When tongue tie (ankyloglossia) restricts the movement of the tongue, it can make it more difficult for a baby to latch onto the mother’s breast and painlessly breastfeed.
Earlier this month, the International Consortium of oral Ankylofrenula Professionals released a tongue tie position statement and practice guideline. Written by a range of health professionals, the guidelines define tongue tie as a functional diagnosis that can impact breastfeeding, eating, drinking and speech. The guidelines provide health professionals and families with information on the assessment and management of tongue tie.
Tongue tie release has been shown to improve latch during breastfeeding, reduce nipple pain and improve breast and bottle feeding. Early assessment and treatment are important to help mothers breastfeed for longer and address any potential functional problems.
The frenulum is a band of tissue under the tongue that is attached to the gumline base of the mouth. Akkalak Aiempradit/Shutterstock Where to get advice
If feeding isn’t going well, it may cause pain for the mother or there may be signs the baby isn’t attaching properly to the breast or not getting enough milk. Parents can seek skilled help and assessment from a certified lactation consultant or International Board-Certified Lactation Consultant who can be found via online registry.
Alternatively, a health professional with training and skills in tongue tie assessment and division can assist families. This may include a doctor, midwife, speech pathologist or dentist with extended skills, training and experience in treating babies with tongue tie.
When access to advice or treatment is delayed, it can lead to unnecessary supplementation with bottle feeds, early weaning from breastfeeding and increased parental anxiety.
Getting a tongue tie assessment
During assessment, a qualified health professional will collect a thorough case history, including pregnancy and birth details, do a structural and functional assessment, and conduct a comprehensive breastfeeding or feeding assessment.
They will view and thoroughly examine the mouth, including the tongue’s movement and lift. The appearance of where the tissue attaches to the underside of the tongue, the ability of the tongue to move and how the baby can suck also needs to be properly assessed.
Treatment decisions should focus on the concerns of the mother and baby and the impact of current feeding issues. Tongue tie division as a baby is not recommended for the sole purpose of avoiding speech problems in later life if there are no feeding concerns for the baby.
A properly qualified lactation consultant can help with positioning and attachment. HarryKiiM Stock/Shutterstock Treatment options
The Australian Dental Association’s 2020 guidelines provide a management pathway for babies diagnosed with tongue tie.
Once feeding issues are identified and if a tongue tie is diagnosed, non-surgical management to optimise positioning, latch and education for parents should be the first-line approach.
If feeding issues persist during follow-up assessment after non-surgical management, a tongue tie division may be considered. Tongue tie release may be one option to address functional challenges associated with breastfeeding problems in babies.
There are risks associated with any procedure, including tongue tie release, such as bleeding. These risks should be discussed with the treating practitioner before conducting any laser, scissor or scalpel tongue tie procedure.
Post-release support by a certified lactation consultant or feeding specialist is necessary after a tongue tie division. A post-release treatment plan should be developed by a team of health professionals including advice and support for breastfeeding to address both the mother and baby’s individual needs.
We would like to acknowledge the contribution of Raymond J. Tseng, DDS, PhD, (Paediatric Dentist) to the writing of this article.
Sharon Smart, Lecturer and Researcher (Speech Pathology) – School of Allied Health, Curtin University; David Todd, Associate Professor, Neonatology, ANU Medical School, Australian National University, and Monica J. Hogan, PhD student, ANU School of Medicine and Psychology, Australian National University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
What are compound exercises and why are they good for you?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So you’ve got yourself a gym membership or bought a set of home weights. Now what? With the sheer amount of confusing exercise advice out there, it can be hard to decide what to include in a weights routine.
It can help to know there are broadly two types of movements in resistance training (lifting weights): compound exercises and isolation exercises.
So what’s the difference? And what’s all this got to do with strength, speed and healthy ageing?
What’s the difference?
Compound exercises involve multiple joints and muscle groups working together.
In a push up, for example, your shoulder and elbow joints are moving together. This targets the muscles in the chest, shoulder and triceps.
When you do a squat, you’re using your thigh and butt muscles, your back, and even the muscles in your core.
It can help to think about compound movements by grouping them by primary movement patterns.
For example, some lower body compound exercises follow a “squat pattern”. Examples include bodyweight squats, weighted squats, lunges and split squats.
A Bulgarian split squat is a type of compound movement exercise. Evelin Montero/Shutterstock We also have “hinge patterns”, where you hinge from a point on your body (such as the hips). Examples include deadlifts, hip thrusts and kettle bell swings.
Upper body compounded exercises can be grouped into “push patterns” (such as vertical barbell lifts) or “pull patterns” (such as weighted rows, chin ups or lat pull downs, which is where you use a pulley system machine to lift weights by pulling a bar downwards).
In contrast, isolation exercises are movements that occur at a single joint.
For instance, bicep curls only require movement at the elbow joint and work your bicep muscles. Tricep extensions and lateral raises are other examples of isolation exercises.
Many compound exercises mimic movements we do every day. Photo by Ketut Subiyanto/Pexels Compound exercises can make daily life easier
Many compound exercises mimic movements we do every day.
Hinge patterns mimic picking something off the floor. A vertical press mimics putting a heavy box on a high shelf. A squat mimics standing up from the couch or getting on and off the toilet.
That might sound ridiculous to a young, fit person (“why would I need to practise getting on and off a toilet?”).
Unfortunately, we lose strength and muscle mass as we age. Men lose about 5% of their muscle mass per decade, while for women the figure is about 4% per decade.
When this decline begins can vary widely. However, approximately 30% of an adult’s peak muscle mass is lost by the time they are 80.
The good news is resistance training can counteract these age-related changes in muscle size and strength.
So building strength through compound exercise movements may help make daily life feel a bit easier. In fact, our ability to perform compound movements are a good indicator how well we can function as we age.
Want to be able to get stuff down from high shelves when you’re older? Practising compound exercises like a vertical press could help. Galina_Lya/Shutterstock What about strength and athletic ability?
Compound exercises use multiple joints, so you can generally lift heavier weights than you could with isolation exercises. Lifting a heavier weight means you can build muscle strength more efficiently.
One study divided a group of 36 people into two. Three times a week, one group performed isolation exercises, while the other group did compound exercises.
After eight weeks, both groups had lost fat. But the compound exercises group saw much better results on measures of cardiovascular fitness, bench press strength, knee extension strength, and squat strength.
If you play a sport, compound movements can also help boost athletic ability.
Squat patterns require your hip, knee, and ankle to extend at the same time (also known as triple extension).
Our bodies use this triple extension trick when we run, sprint, jump or change direction quickly. In fact, research has found squat strength is strongly linked to being able to sprint faster and jump higher.
Isolation exercises are still good
What if you’re unable to do compound movements, or you just don’t want to?
Don’t worry, you’ll still build strength and muscle with isolation exercises.
Isolation exercises are also typically easier to learn as there is no skill required. They are an easy and low risk way to add extra exercise at the end of the workout, where you might otherwise be too tired to do more compound exercises safely and with correct form.
In fact, both isolation and compound exercises seem to be equally effective in helping us lose body fat and increase fat-free muscle mass when total intensity and volume of exercises are otherwise equal.
Some people also do isolation exercises when they want to build up a particular muscle group for a certain sport or for a bodybuilding competition, for example.
Isolation exercises have their role to play. Photo by Kampus Production/Pexels I just want a time efficient workout
Considering the above factors, you could consider prioritising compound exercises if you’re:
- time poor
- keen to lift heavier weights
- looking for an efficient way to train many muscles in the one workout
- interested in healthy ageing.
That said, most well designed workout programs will include both compound and isolation movements.
Correction: This article has been amended to reflect the fact a weighted row is a pull pattern, not a push pattern.
Mandy Hagstrom, Senior Lecturer, Exercise Physiology. School of Health Sciences, UNSW Sydney and Anurag Pandit, PhD Candidate in Exercise Physiology, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Antibiotics? Think Thrice
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Antibiotics: Useful Even Less Often Than Previously Believed (And Still Just As Dangerous)
You probably already know that antibiotics shouldn’t be taken unless absolutely necessary. Not only does taking antibiotics frivolously increase antibiotic resistance (which is bad, and kills people), but also…
It’s entirely possible for the antibiotics to not only not help, but instead wipe out your gut’s “good bacteria” that were keeping other things in check.
Those “other things” can include fungi like Candida albicans.
Candida, which we all have in us to some degree, feeds on sugar (including the sugar formed from breaking down alcohol, by the way) and refined carbs. Then it grows, and puts its roots through your intestinal walls, linking with your neural system. Then it makes you crave the very things that will feed it and allow it to put bigger holes in your intestinal walls.
Don’t believe us? Read: Candida albicans-Induced Epithelial Damage Mediates Translocation through Intestinal Barriers
(That’s scientist-speak for “Candida puts holes in your intestines, and stuff can then go through those holes”)
And as for how that comes about, it’s like we said:
See also: Candida albicans as a commensal and opportunistic pathogen in the intestine
That’s not all…
And that’s just C. albicans, never mind things like C. diff. that can just outright kill you easily.
We don’t have room to go into everything here, but you might like to check out:
Four Ways Antibiotics Can Kill You
It gets worse (now comes the new news)
So, what are antibiotics good for? Surely, for clearing up chesty coughs, lower respiratory tract infections, right? It’s certainly one of the two things that antibiotics are most well-known for being good at and often necessary for (the other being preventing/treating sepsis, for example in serious and messy wounds).
But wait…
A large, nationwide (US) observational study of people who sought treatment in primary or urgent care settings for lower respiratory tract infections found…
(drumroll please)
…the use of antibiotics provided no measurable impact on the severity or duration of coughs even if a bacterial infection was present.
Read for yourself:
And in the words of the lead author of that study,
❝Lower respiratory tract infections tend to have the potential to be more dangerous, since about 3% to 5% of these patients have pneumonia. But not everyone has easy access at an initial visit to an X-ray, which may be the reason clinicians still give antibiotics without any other evidence of a bacterial infection.❞
So, what’s to be done about this? On a large scale, Dr. Merenstein recommends:
❝Serious cough symptoms and how to treat them properly needs to be studied more, perhaps in a randomized clinical trial as this study was observational and there haven’t been any randomized trials looking at this issue since about 2012.❞
This does remind us that, while not a RCT, there is a good ongoing observational study that everyone with a smartphone can participate in:
Dr. Peter Small’s medical AI: “The Cough Doctor”
In the meantime, he advises that when COVID and SARS have been ruled out, then “basic symptom-relieving medications plus time brings a resolution to most people’s infections”.
You can read a lot more detail here:
Antibiotics aren’t effective for most lower tract respiratory infections
In summary…
Sometimes, antibiotics really are a necessary and life-saving medication. But most of the time they’re not, and given their great potential for harm, they may be best simultaneously viewed as the very dangerous threat they also are, and used only when those “heavy guns” are truly what’s required.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Insomnia Decoded – by Dr. Audrey Porter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written about sleep books before, so what makes this one different? Its major selling point is: most of the focus isn’t on the things that everyone already knows.
Yes, there’s a section on sleep hygiene and yes it’ll tell you to cut the caffeine and alcohol, but most of the advice here is beyond that.
Rather, it looks at finding out (if you don’t already know for sure) what is keeping you from healthy sleep, be it environmental, directly physical, or psychological, and breaking out of the stress-sleep cycle that often emerges from such.
The style is light and conversational, but includes plenty of science too; Dr. Porter knows her stuff.
Bottom line: if you feel like you know what you should be doing, but somehow life keeps conspiring to stop you from doing it, then this is the book that could help you break out that cycle.
Click here to check out Insomnia Decoded, and get regular healthy sleep!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Three Daily Servings of Beans?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Not crazy about the Dr.s food advice. Beans 3X a day?❞
For reference, this is in response to our recent article on the topic of 12 things to aim to get a certain amount of each day:
So, there are a couple of things to look at here:
Firstly, don’t worry, it’s a guideline and an aim. If you don’t hit it on a given day, there is always tomorrow. It’s just good to know what one is aiming for, because without knowing that, achieving it will be a lot less likely!
Secondly, the beans/legumes/pulses category says three servings, but the example serving sizes are quite small, e.g. ½ cup cooked beans, or ¼ cup hummus. And also as you notice, dips/pastes/sauces made from beans count too. So given the portion sizes, you could easily get two servings in by breakfast (and two servings of whole grains, too) if you enjoy frijoles refritos, for example. Many of the recipes we share on this site have “stealth” beans/legumes/pulses in this fashion
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: