The Immunostimulant Superfood –
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this book is not: a “detox cleanse” book of the kind that claims you can flush out the autism if you just eat enough celery.
What it rather is: an overview brain chemistry, gut microbiota, and the very many other bodily systems that interact with these “two brains”.
She also does some mythbusting of popular misconceptions (for example with regard to tryptophan), and explains with good science just what exactly such substances as gluten and casein can and can’t do.
The format is less of a textbook and more a multipart (i.e., chapter-by-chapter) lecture, in pop-science style though, making it very readable. There are a lot of practical advices too, and options to look up foods by effect, and what to eat for/against assorted mental states.
Bottom line: anyone who eats food is, effectively, drugging themselves in one fashion or another—so you might as well make a conscious choice about how to do so.
Click here to check out This Is Your Brain On Food, and choose what kind of day you have!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
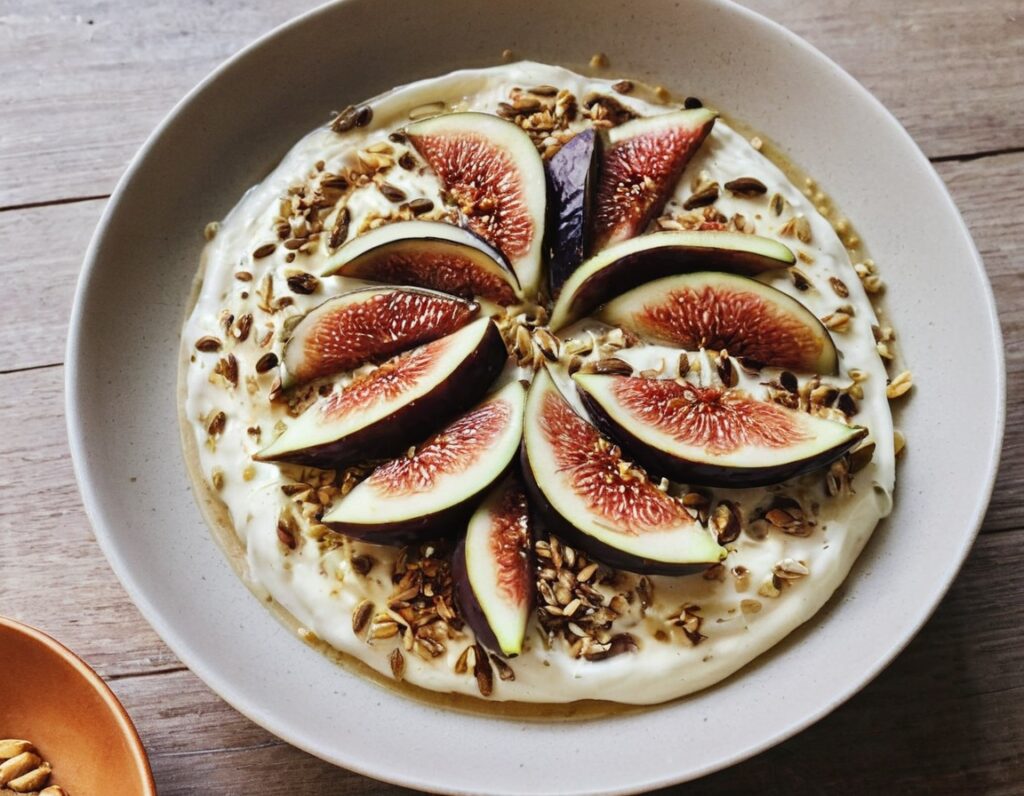
The Gut-Healthiest Yogurt
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Not only is this yogurt, so it’s winning from the start with its probiotic goodness, but also it’s full of several kinds of fiber, and gut-healthy polyphenols too. Plus, it’s delicious. The perfect breakfast, but don’t let us stop you from enjoying it at any time of day!
You will need
- 1 cup yogurt with minimal additives. Live Greek yogurt is a top-tier choice, and plant-based varieties are fine too (just watch out, again, for needless additives)
- 7 dried figs, roughly chopped
- 6 fresh figs, thinly sliced
- 5 oz chopped pitted dates
- 4 tbsp mixed seeds (pumpkin, sunflower, and chia are a great combination)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Soak the dried figs, the dates, and half the seeds in hot water for at least 5 minutes. Drain (be careful not to lose the chia seeds) and put in a blender with ¼ cup cold water.
2) Blend the ingredients from the last step into a purée (you can add a little more cold water if it needs it).
3) Mix this purée into the yogurt in a bowl, and add in the remaining seeds, mixing them in thoroughly.
4) Top with the sliced figs, and serve (or refrigerate, up to a few days, until needed).
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Dates vs Figs – Which is Healthier?
- The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
Take care!
Share This Post
-
What Is Making The Ringing In Your Ears Worse?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Rachael Cook, an audiologist at Applied Hearing Solutions in Phoenix, Arizona, shares her professional insights into managing tinnitus.
If you’re unfamiliar with Tinnitus, it is an auditory condition characterized by a ringing, buzzing, or humming sound, and ffects nearly 10% of the population. We’ve written on Tinnitus, and how it can disrupt your life, in this article.
Key Triggers for Tinnitus
Several everyday habits can make your tinnitus louder. Caffeine and nicotine increase blood pressure, restricting blood flow to the cochlea and worsening tinnitus. Common medications, such as pain relievers, high-dose antibiotics, and antidepressants, can also exacerbate tinnitus, especially with higher or long-term dosages.
Impact of Diet and Sleep
Dietary choices significantly impact tinnitus. Alcohol and salt alter the fluid balance in the cochlea, increasing tinnitus perception. Alcohol changes blood flow patterns and neurotransmitter production, while high salt intake has similar effects. Poor sleep quality elevates stress levels, making it harder to ignore tinnitus signals. Addressing sleep disorders like sleep apnea and insomnia can help manage tinnitus symptoms.
Importance of Treating Hearing Loss
Untreated hearing loss worsens tinnitus. Nearly 90% of individuals with tinnitus have some hearing loss. Hearing aids can reduce tinnitus perception by restoring missing sounds and reducing the brain’s internal compensatory signals. Combining hearing aids with sound therapy is said to provide even greater relief.
Read more about hearing loss in our article on the topic.
Otherwise, for a great guide on managing tinnitus, we recommend watching Dr. Cook’s video:
Here’s hoping your ear’s aren’t ringing too much whilst watching the video!
Share This Post
-
Using the”Task Zero” approach
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Jonathan Frakes Asks You Things” Voice:
- Do you ever find yourself in a room and wonder what you’re doing there?
- Or set about a to-do list, but get quickly distracted by side-quests?
- Finally get through to a person in a call center, they ask how they can help, and your mind goes blank?
- Go to the supermarket and come out with six things, none of which were the one you came for?
This is a “working memory” thing and you’re not alone. There’s a trick that can help keep you on track more often than not:
Don’t try to overburden your working memory. It is very limited (this goes for everyone to a greater or lesser degree). Instead, hold only two tasks at once:
- Task zero (what you are doing right now)
- Task one (your next task)
When you’ve completed task zero, task one becomes the new task zero, and you can populate a new task one from your to-do list.
This way, you will always know what you’re doing right now, and what you’re doing next, and your focus will be so intent on task zero, that you will not get sidetracked by task seventeen!
Happy focusing
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Brown Rice vs Russet Potatoes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing brown rice to russet potatoes, we picked the rice.
Why?
First we’ll note: for brevity and to avoid undue repetitiveness, we’re henceforth going to just say “rice” and “potato”, respectively, but values and conclusions are still for brown rice and russet potatoes. Also, we are including the flesh and skin into the metrics for the potato (without the skin, many nutrients are no longer present).
In terms of macros, the rice has more fiber, carbs, and protein. It’s difficult to compare glycemic indices in this case, because they both need cooking before eating, and how one cooks them (and whether one cools them) along with other preparatory methods will change the GI considerably. Thus, we’ll simply go with the more nutritionally dense option, and that’s the rice.
In the category of vitamins, the rice has much more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, E, and choline, while the potato has more of vitamins C and K. A clear win for rice (and by the way, that’s 60x the vitamin E, but as potatoes don’t have much vitamin E, in practical terms, it’s actually the B-vitamins where rice’s strengths really show, as potatoes aren’t a bad source but rice is amazing).
When it comes to minerals, rice has a lot more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc, while potato has more calcium and potassium. Another easy win for rice.
You may be wondering about phytic acid: brown rice contains this by default, and it is something of an antinutrient (i.e., if left as-is, it reduces the bioavailability of other nutrients), and/but the phytic acid content is reduced to negligible by two things: soaking and heating (especially if those two things are combined) ← doing this the way described results in bioavailability of nutrients that’s even better than if there were just no phytic acid, albeit it requires you having the time to soak, and do so at temperature.
All in all, adding up the sections makes for an overall win for brown rice, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Carb-Strong or Carb-Wrong? Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cherries vs Cranberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cherries to cranberries, we picked the cherries.
Why?
In terms of macros, cherries have a little more protein (but it’s not much) while cranberries have a little more fiber. Despite this, cherries have the lower glycemic index—about half that of cranberries.
In the category of vitamins, cherries have a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B9, and a little more choline, while cranberries have more of vitamins B5, B6, C, E, and K. A modest win for cherries here.
When it comes to minerals, things are more divided: cherries have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while cranberries have more manganese. An easy win for cherries here.
This all adds up to a total win for cherries, but both of these fruits are great and both have their own beneficial properties (see our main features below!)
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Cherries’ Very Healthy Wealth Of Benefits!
- Health Benefits Of Cranberries (But: You’d Better Watch Out)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eat Well With Arthritis – by Emily Johnson, with Dr. Deepak Ravindran
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Author Emily Johnson was diagnosed with arthritis in her early 20s, but it had been affecting her life since the age of 4. Suffice it to say, managing the condition has been integral to her life.
She’s written this book with not only her own accumulated knowledge, but also the input of professional experts; the book contains insights from chronic pain specialist Dr. Deepak Ravindran, and gets an additional medical thumbs-up in a foreword by rheumatologist Dr. Lauren Freid.
The recipes themselves are clear and easy, and the ingredients are not obscure. There’s information on what makes each dish anti-inflammatory, per ingredient, so if you have cause to make any substitutions, that’s useful to know.
Speaking of ingredients, the recipes are mostly plant-based (though there are some chicken/fish ones) and free from common allergens—but not all of them are, so each of those is marked appropriately.
Beyond the recipes, there are also sections on managing arthritis more generally, and information on things to get for your kitchen that can make your life with arthritis a lot easier!
Bottom line: if you have arthritis, cook for somebody with arthritis, or would just like a low-inflammation diet, then this is an excellent book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: