“Slugging” Skin Care Routine (Tips From A Dermatologist)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dermatologist Dr. Jenny Liu weighs in with advice!
Sometimes simplest is best
Slugging is a skincare trend involving applying petrolatum (e.g. Vaseline) as the final step to lock in hydration and repair the skin barrier. It’s particularly useful for dry, sensitive, or eczema-prone skin, and/or damaged skin barriers from overuse of actives or harsh conditions.
How it works: the waterproof layer reduces water loss (up to 99%) and facilitates repair the skin barrier. Thus, it indirectly hydrates the skin, supports natural exfoliation, and reduces fine lines. Best of all, it’s non-irritating, non-comedogenic, and safe for all skin types.
How to do it:
- Cleanse thoroughly to remove makeup and impurities.
- Apply a moisturizer or serum with humectants (e.g. glycerin, hyaluronic acid).
- Seal with petrolatum (e.g. Vaseline or similar).
- Skip areas with stronger active ingredients (e.g. retinoids) and active acne areas.
- Apply 30–60 minutes before bed to reduce product transfer.
- Use a gentle cleanser in the morning to remove residue.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Castor Oil: All-Purpose Life-Changer, Or Snake Oil? ← skincare is one of the things it definitely does work well for, and can be used for slugging also.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
An Unexpected Extra Threat Of Alcohol
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If You Could Use Some Exotic Booze…
…then for health reasons, we’re going to have to say “nay”.
We’ve written about alcohol before, and needless to say, it’s not good:
(the answer is “no, we cannot”)
In fact, the WHO (which unlike government regulatory bodies setting “safe” limits on drinking, makes no profit from taxes on alcohol sales) has declared that “the only safe amount of alcohol is zero”:
WHO: No level of alcohol consumption is safe for our health
Up there, where the air is rarefied…
If you’re flying somewhere this summer (Sinatra-style flying honeymoon or otherwise), you might want to skip the alcohol even if you normally do imbibe, because:
❝…even in young and healthy individuals, the combination of alcohol intake with sleeping under hypobaric conditions poses a considerable strain on the cardiac system and might lead to exacerbation of symptoms in patients with cardiac or pulmonary diseases.
These effects might be even greater in older people; cardiovascular symptoms have a prevalence of 7% of inflight medical emergencies, with cardiac arrest causing 58% of aircraft diversions.❞
Source: Alcohol plus cabin pressure at higher altitude may threaten sleeping plane passengers’ heart health
The experiment divided subjects into a control group and a study group; the study group were placed in simulated cabin pressure as though at altitude, which found, when giving some of them two small(we’re talking the kind given on flights) alcoholic drinks:
❝The combination of alcohol and simulated cabin pressure at cruising altitude prompted a fall in SpO2 to an average of just over 85% and a compensatory increase in heart rate to an average of nearly 88 beats/minute during sleep.❞
In contrast, that was 77 beats/minute for those who had alcohol but weren’t at altitude pressure, or 64 beats/minute for those who neither drank nor were at altitude pressure.
Lots more metrics were recorded and the study is interesting to read; if you’ve ever slept on a plane and thought “that sleep was not restful at all”, then know: it wasn’t just the seat’s fault, nor the engine, nor the recycled nature of the air—it was the reduced pressure causing hypoxia (defined as having oxygen levels lower than the healthy clinical norm of 90%) and almost halving your sleep’s effectiveness for a less than 10% drop in available oxygen in the blood (the sleepers not at altitude pressure averaged 96% SpO2, compared to the 85% at altitude).
We say “almost halving” because the deep sleep phase of sleep was reduced from 84 minutes (control) to 67.5 minutes at altitude without alcohol, or 46.5 minutes at altitude with alcohol.
Again, this was a pressure cabin in a lab—so this wasn’t about the other conditions of an airplane (seats, engine hundreds of other people, etc).
Which means: in an actual airplane it’s probably even worse.
Oh, and the study participants? All healthy individuals aged 18–40, so again probably worse for those older (or younger) than that range, or with existing health conditions!
Want to know more?
You can read the study in full here:
Want to drop the drink at any altitude? Check out:
Want to get that vacation feel without alcohol? You’re going to love:
Mocktails – by Moira Clark (book)
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Plum vs Persimmon – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing plum to persimmon, we picked the plum.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, persimmon has 3x the carbs for only the same amount of fiber, on account of which plum has the lower glycemic index, so we’ll go with plum here, though your opinion could vary.
In terms of vitamins, it’s much less subjective: plums have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, E, K, and choline, while persimmon has more vitamin C. So, unless you have scurvy, plums will be the best choice for most people.
In the category of minerals, plums have more copper, magnesium, manganese, and zinc, while persimmon has more calcium, iron, phosphorus, and potassium—thus, a 4:4 tie on minerals.
Adding up the sections gives an overall win for plums, but of course, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
PS: plums have an extra bonus too; check out the link below…
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← plums kill cancer cells while sparing healthy ones
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Podiatrists Debunk 11 Feet Myths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Podiatrists Dr. Sarah Haller and Dr. Brad Schaeffer put us on a better path:
Don’t get wrong-footed
We’ll not keep the 11 myths a mystery; they are…
- “You have warts because your feet are dirty.”
False! Warts are caused by a virus, not dirt. Viruses can be picked up from surfaces like yoga mats, pools, gyms, and showers. - “Bunions are caused by wearing heels.”
False! Bunions are genetic deformities where the bone behind the big toe shifts. Heels might worsen them but don’t cause them. - “Cutting the sides of my toenail will prevent an ingrown toenail.”
False! Toenails should be cut straight across. Cutting the sides can make ingrown toenails worse. - “Pedicures gave me toenail fungus.”
Partially true! You can get fungus from many places, but safe, sterile pedicures are generally fine. - “Only athletes get athlete’s foot.”
False! Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection caused by warm, moist environments. Anyone can get it, not just athletes. - “My feet are fine because I trained them to walk in stilettos.”
False! You can get used to stilettos, but they aren’t healthy long-term. They shorten the Achilles tendon and put pressure on the foot. - “You can’t do anything for a broken toe.”
False! Broken toes can be treated and should be checked by a doctor. They may need to be set for proper healing. - “It’s normal for your feet to hurt from standing all day.”
False! Foot pain isn’t normal and can be prevented with proper footwear, support, and compression socks. - “All inserts are the same.”
False! Everyone’s feet are different. Some may benefit from over-the-counter insoles, but others need custom orthotics. - “Sprained ankles are no big deal.”
False! Sprains can damage ligaments and lead to instability or arthritis if untreated. Proper stabilization is essential. - “If I can walk after an injury, I don’t need to see a doctor.”
False! You can still have serious injuries like fractures even if you can walk. Always get checked after an injury.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
Take care!
Share This Post
- “You have warts because your feet are dirty.”
Related Posts
-
If Your Adult Kid Calls In Crisis…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Parent(s) To The Rescue?
We’ve written before about the very common (yes, really, it is common) phenomenon of estrangement between parents and adult children:
Family Estrangement & How To Fix It
We’ve also written about the juggling act that can be…
Managing Sibling Relationships In Adult Life
…which includes dealing with such situations as supporting each other through difficult times, while still maintaining healthy boundaries.
But what about when one’s [adult] child is in crisis?
When a parent’s job never ends
Hopefully, we have not been estranged (or worse, bereaved) by our children.
In which case, when crisis hits, we are likely to be amongst the first to whom our children will reach out for support. Naturally, we will want to help. But how can we do that, and where (if applicable) to draw the line?
No “helicopter parenting”
If you’ve not heard the term “helicopter parenting”, it refers to the sort of parents who hover around, waiting to swoop in at a moment’s notice.
This is most often applied to parents of kids of university age and downwards, but it’s worth keeping it in mind at any age.
After all, we do want our kids to be able to solve their own problems if possible!
So, if you’ve ever advised your kid to “take a deep breath and count to 10” (or even if you haven’t), then, consider doing that too, and then…
Listen first!
If your first reaction isn’t to join them in panic, it might be to groan and “oh not again”. But for now, quietly shelve that, and listen to whatever it is.
See also: Active Listening (Without Sounding Like A Furby)
And certainly, do your best to maintain your own calm while listening. Your kid is in all likelihood looking to you to be the rock in the storm, so let’s be that.
Empower them, if you can
Maybe they just needed to vent. If so, the above will probably cover it.
More likely, they need help.
Perhaps they need guidance, from your greater life experience. Sometimes things that can seem like overwhelming challenges to one person, are a thing we dealt with 20 or more years ago (it probably felt overwhelming to us at the time, too, but here we are, the other side of it).
Tip: ask “are you looking for my guidance/advice/etc?” before offering it. Doing so will make it much more likely to be accepted rather than rejected as unsolicited advice.
Chances are, they will take the life-ring offered.
It could be that that’s not what they had in mind, and they’re looking for material support. If so…
When it’s about money or similar
Tip: it’s worth thinking about this sort of thing in advance (now is great, if you have adult kids), and ask yourself nowwhat you’d be prepared to give in that regard, e.g:
- if they need money, how much (if any) are you willing and able to provide?
- if they want/need to come stay with you, how prepared are you for that (including: if they want/need to actually move back in with you for a while, which is increasingly common these days)?
Having these answers in your head ready will make the conversation a lot less difficult in the moment, and will avoid you giving a knee-jerk response you might regret (in either direction).
Have a counteroffer up your sleeve if necessary
Maybe:
- you can’t solve their life problem for them, but you can help them find a therapist (if applicable, for example)
- you can’t solve their money problem for them, but you can help them find a free debt advice service (if applicable, for example)
- you can’t solve their residence problem for them, but you can help them find a service that can help with that (if applicable, for example)
You don’t need to brainstorm now for every option; you’re a parent, not Batman. But it’s a lot easier to think through such hypothetical thought-experiments now, than it will be with your fraught kid on the phone later.
Magic words to remember: “Let’s find a way through this for you”
Don’t forget to look after yourself
Many of us, as parents, will tend to not think twice before sacrificing something for our kid(s). That’s generally laudable, but we must avoid accidentally becoming “the giving tree” who has nothing left for ourself, and that includes our mental energy and our personal peace.
That doesn’t mean that when our kid comes in crisis we say “Shh, stop disturbing my personal peace”, but it does mean that we remember to keep at least some boundaries (also figure out now what they are, too!), and to take care of ourselves too.
The following article was written with a slightly different scenario in mind, but the advice remains just as valid here:
How To Avoid Carer Burnout (Without Dropping Care)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healthy Brain, Happy Life – by Dr. Wendy Suzuki
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We talked about Dr. Wendy Suzuki’s research in the category of exercise and brain-benefits in our main feature the other day. But she has more to say than we can fit into an article!
This book chronicles her discoveries, through her work in memory and neuroplasticity, to her discoveries about exercise, and her dive into broader neurology-based mental health. So what does neurology-based mental health look like?
The answer is: mitigating brain-busters such as stress and anxiety, revitalizing a fatigued brain, boosting creativity, and other such benefits.
Does she argue that exercise is a cure-all? No, not quite. Sometimes there are other things she’s recommending (such as in her chapter on challenging the neurobiology of the stress response, or her chapter on meditation and the brain).
The writing style is mostly casual, interspersed with occasional mini-lectures (complete with diagrams and other illustrations), and is very readable and informative throughout.
Bottom line: if you’d like the more in-depth details of Dr. Suzuki’s work, this book is a very accessible way to get 320 pages of that!
Click here to check out Healthy Brain, Happy Life, and give yours the best!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Brain As A Work-In-Progress
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
And The Brain Goes Marching On!
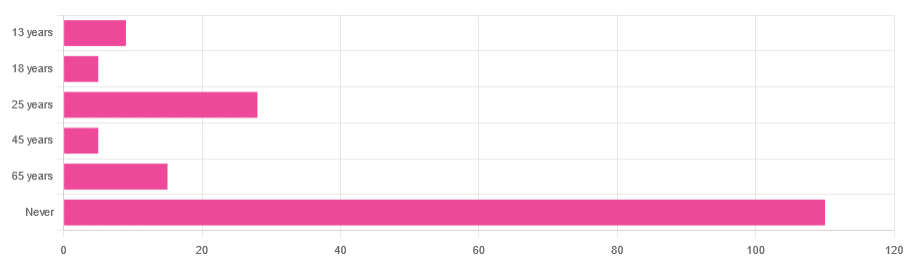
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you “when does the human brain stop developing?” and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 64% of people said “Never”
- About 16% of people said “25 years”
- About 9% of people said “65 years”
- About 5% of people said “13 years”
- About 3% of people said “18 years”
- About 3% of people said “45 years”
Some thoughts, before we get into the science:
An alternative wording for the original question was “when does the human brain finish developing”; the meaning is the same but the feeling is slightly different:
- “When does the human brain stop developing?” focuses attention on the idea of cessation, and will skew responses to later ages
- When does the human brain finish developing?” focuses on attention on a kind of “is it done yet?” and will skew responses to earlier ages
Ultimately, since we had to chose one word or another, we picked the shortest one, but it would have been interesting if we could have done an A/B test, and asked half one way, and half the other way!
Why we picked those ages
We picked those ages as poll options for reasons people might be drawn to them:
- 13 years: in English-speaking cultures, an important milestone of entering adolescence (note that the concept of a “teenager” is not precisely universal as most languages do not have “-teen” numbers in the same way; the concept of “adolescent” may thus be tied to other milestones)
- 18 years: age of legal majority in N. America and many other places
- 25 years: age popularly believed to be when the brain is finished developing, due to a study that we’ll talk about shortly (we guess that’s why there’s a spike in our results for this, too!)
- 45 years: age where many midlife hormonal changes occur, and many professionals are considered to have peaked in competence and start looking towards retirement
- 65 years: age considered “senior” in much of N. America and many other places, as well as the cut-off and/or starting point for a lot of medical research
Notice, therefore, how a lot of things are coming from places they really shouldn’t. For example, because there are many studies saying “n% of people over 65 get Alzheimer’s” or “n% of people over 65 get age-related cognitive decline”, etc, 65 becomes the age where we start expecting this—because of an arbitrary human choice of where to draw the cut-off for the study enrollment!
Similarly, we may look at common ages of legal majority, or retirement pensions, and assume “well it must be for a good reason”, and dear reader, those reasons are more often economically motivated than they are biologically reasoned.
So, what does the science say?
Our brains are never finished developing: True or False?
True! If we define “finished developing” as “we cease doing neurogenesis and neuroplasticity is no longer in effect”.
Glossary:
- Neurogenesis: the process of creating new brain cells
- Neuroplasticity: the process of the brain adapting to changes by essentially rebuilding itself to suit our perceived current needs
We say “perceived” because sometimes neuroplasticity can do very unhelpful things to us (e.g: psychological trauma, or even just bad habits), but on a biological level, it is always doing its best to serve our overall success as an organism.
For a long time it was thought that we don’t do neurogenesis at all as adults, but this was found to be untrue:
How To Grow New Brain Cells (At Any Age)
Summary of conclusions of the above: we’re all growing new brain cells at every age, even if we be in our 80s and with Alzheimer’s disease, but there are things we can do to enhance our neurogenic potential along the way.
Neuroplasticity will always be somewhat enhanced by neurogenesis (after all, new neurons get given jobs to do), and we reviewed a great book about the marvels of neuroplasticity including in older age:
Our brains are still developing up to the age of 25: True or False?
True! And then it keeps on developing after that, too. Now this is abundantly obvious considering what we just talked about, but see what a difference the phrasing makes? Now it makes it sound like it stops at 25, which this statement doesn’t claim at all—it only speaks for the time up to that age.
A lot of the popular press about “the brain isn’t fully mature until the age of 25” stems from a 2006 study that found:
❝For instance, frontal gray matter volume peaks at about age 11.0 years in girls and 12.1 years in boys, whereas temporal gray matter volume peaks at about age at 16.7 years in girls and 16.2 years in boys. The dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex, important for controlling impulses, is among the latest brain regions to mature without reaching adult dimensions until the early 20s.❞
Source: Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Adolescent Brain
There are several things to note here:
- The above statement is talking about the physical size of the brain growing
- Nowhere does he say “and stops developing at 25”
However… The study only looked at brains up to the age of 25. After that, they stopped looking, because the study was about “the adolescent brain” so there has to be a cut-off somewhere, and that was the cut-off they chose.
This is the equivalent of saying “it didn’t stop raining until four o’clock” when the reality is that four o’clock is simply when you gave up on checking.
The study didn’t misrepresent this, by the way, but the popular press did!
Another 2012 study looked at various metrics of brain development, and found:
- Synapse overproduction into the teens
- Cortex pruning into the late 20s
- Prefrontal pruning into middle age at least (they stopped looking)
- Myelination beyond middle age (they stopped looking)
Source: Experience and the developing prefrontal cortex ← check out figure 1, and make sure you’re looking at the human data not the rat data
So how’s the most recent research looking?
Here’s a 2022 study that looked at 123,984 brain scans spanning the age range from mid-gestation to 100 postnatal years, and as you can see from its own figure 1… Most (if not all) brain-things keep growing for life, even though most slow down at some point, they don’t stop:
Brain charts for the human lifespan ← check out figure 1; don’t get too excited about the ventricular volume column as that is basically “brain that isn’t being a brain”. Do get excited about the rest, though!
Want to know how not to get caught out by science being misrepresented by the popular press? Check out:
How Science News Outlets Can Lie To You (Yes, Even If They Cite Studies!)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: