Shoe Wear Patterns: What They Mean, Why It Matters, & How To Fix It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you look under your shoes, do you notice how the tread is worn more in some places than others? Specific patterns of shoe wear correspond to how our body applies force, weight, and rotational movement. This reveals how we move, and uneven wear can indicate problematic movement dynamics.
The clues in your shoes
Common shoe wear patterns include:
- Diagonal wear on the outside of the heel: caused by foot angle, leg position, and instability, leading to joint stress.
- Rotational wear at specific points: due to internal or external rotation, often originating from the hip, pelvis, or torso.
- Wear above the big toe: caused by excessive toe lifting, often associated with a “lighter” or kicking leg.
Fixing movement issues to prevent wear involves correcting posture, improving balance, and adjusting how the legs land during walking/running.
Key fixes include:
- Aligning the center of gravity properly to prevent leg overcompensation.
- Ensuring feet land under the hips and not far in front.
- Stabilizing the torso to avoid unnecessary rotation.
- Engaging the glutes effectively to reduce hip flexor dominance and improve leg mechanics.
- Maintaining even weight distribution on both legs to prevent excessive lifting or twisting.
Posture and walking mechanics are vital to reducing uneven wear, but meaningful, lasting change takes time and focused effort, to build new habits.
For more on all this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Coffee & Your Gut
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Coffee, in moderation, is generally considered a healthful drink—speaking for the drink itself, at least! Because the same cannot be said for added sugar, various sorts of creamers, or iced caramelatte mocha frappucino dessert-style drinks:
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
Caffeine, too, broadly has more pros than cons (again, in moderation):
Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
Some people will be concerned about coffee and the heart. Assuming you don’t have a caffeine sensitivity (or you do but you drink decaf), it is heart-neutral in moderation, though there are some ways of preparing it that are better than others:
Make Your Coffee Heart-Healthier!
So, what about coffee and the gut?
The bacteria who enjoy a good coffee
Amongst our trillions of tiny friends, allies, associates, and enemies-on-the-inside, which ones like coffee, and what kind of coffee do they prefer?
A big (n=35,214) international multicohort analysis examined the associations between coffee consumption and very many different gut microbial species, and found:
115 species were positively associated with coffee consumption, mostly of the kind considered “friendly”, including ones often included in probiotic supplements, such as various Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus species.
The kind that was most strongly associated with coffee consumption, however, was Lawsonibacter asaccharolyticus, a helpful little beast who converts chlorogenic acid (one of the main polyphenols in coffee) into caffeic acid, quinic acid, and various other metabolites that we can use.
More specifically: moderate coffee-drinkers, defined as drinking 1–3 cups per day, enjoyed a 300–400% increase in L. asaccharolyticus, while high coffee-drinkers (no, not that kind of high), defined as drinking 4 or more cups of coffee per day, enjoyed a 400–800% increase, compared to “never/rarely” coffee-drinkers (defined as drinking 2 or fewer cups per month).
Click here to see more data from the study, in a helpful infographic
Things that did not affect the outcome:
- The coffee-making method—it seems the bacteria are not fussy in this regard, as espresso or brewed, and even instant, yielded the same gut microbiome benefits
- The caffeine content—as both caffeinated and decaffeinated yielded the same gut microbiome benefits
You can read the paper itself in full for here:
Want to enjoy coffee, but not keen on the effects of caffeine or the taste of decaffeinated?
Taking l-theanine alongside coffee flattens the curve of caffeine metabolism, and means one can get the benefits without unwanted jitteriness:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Goji Berries vs Cherries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing goji berries to cherries, we picked the goji berries.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, goji berries have more protein, fiber, and carbs, as well as the lower glycemic index, although cherries are great too. Still, a clear and easy win here.
In the category of vitamins, goji berries have more of vitamins A and C, while cherries have more of vitamin K; in the other vitamins these two fruits are close enough to equal that variants in what kind of cherry it is will push it slightly one way or the other. However, it’s worth noting that goji berries have 1,991% more vitamin A and 16,033% more vitamin C, while cherries have only 20% more vitamin K. So, all in all, another clear win for goji berries.
When it comes to minerals, goji berries have more calcium and iron, while cherries have more copper. Again, the margins of difference are very much in goji berries’ favor, with 1,088% more calcium and 2,025% more iron, while cherries have 35% more copper. So, again, a win for goji berries.
The polyphenol contents of cherries differ far too much to comment here, but as a general rule of thumb, goji berries have more antioxidant powers than cherries, but cherries are also excellent for this.
In short, enjoy either or both, but goji berries are the more nutritionally dense!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Coca-Cola vs Diet Coke – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Coca-Cola to Diet Coke, we picked the Diet Coke.
Why?
While the Diet Coke is bad, the Coca-Cola has mostly the same problems plus sugar.
The sugar in a can of Coca-Cola is 39g high-fructose corn syrup (the worst kind of sugar yet known to humanity), and of course it’s being delivered in liquid form (the most bioavailable way to get, which in this case, is bad).
To put those 39g into perspective, the daily recommended amount of sugar is 36g for men or 25g for women, according to the AHA.
The sweetener in Diet Coke is aspartame, which has had a lot of health risk accusations made against it, most of which have not stood up to scrutiny, and the main risk it does have is “it mimics sugar too well” and it can increase cravings for sweetness, and therefore higher consumption of sugars in other products. For this reason, the World Health Organization has recommended to simply reduce sugar intake without looking to artificial sweeteners to help.
Nevertheless, aspartame has been found safe (in moderate doses; the upper tolerance level would equate to more than 20 cans of diet coke per day) by food safety agencies ranging from the FDA to the EFSA, based on a large body of science.
Other problems that Diet Coke has are present in Coca-Cola too, such as its acidic nature (bad for tooth enamel) and gassy nature (messes with leptin/ghrelin balance).
Summary: the Diet Coke is relatively less unhealthy, but is still bad in numerous ways, and remains best avoided.
Read more:
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Ricezempic: is there any evidence this TikTok trend will help you lose weight?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you spend any time looking at diet and lifestyle content on social media, you may well have encountered a variety of weight loss “hacks”.
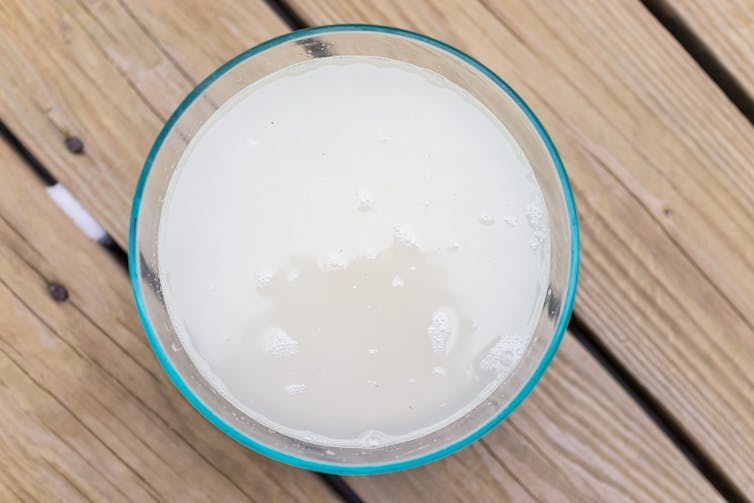
One of the more recent trends is a home-made drink called ricezempic, made by soaking uncooked rice and then straining it to drink the leftover starchy water. Sounds delicious, right?
Its proponents claim it leads to weight loss by making you feel fuller for longer and suppressing your appetite, working in a similar way to the sought-after drug Ozempic – hence the name.
So does this drink actually mimic the weight loss effects of Ozempic? Spoiler alert – probably not. But let’s look at what the evidence tells us.
New Africa/Shutterstock How do you make ricezempic?
While the recipe can vary slightly depending on who you ask, the most common steps to make ricezempic are:
- soak half a cup of white rice (unrinsed) in one cup of warm or hot water up to overnight
- drain the rice mixture into a fresh glass using a strainer
- discard the rice (but keep the starchy water)
- add the juice of half a lime or lemon to the starchy water and drink.
TikTokers advise that best results will happen if you drink this concoction once a day, first thing in the morning, before eating.
The idea is that the longer you consume ricezempic for, the more weight you’ll lose. Some claim introducing the drink into your diet can lead to a weight loss of up to 27 kilograms in two months.
Resistant starch
Those touting ricezempic argue it leads to weight loss because of the resistant starch rice contains. Resistant starch is a type of dietary fibre (also classified as a prebiotic). There’s no strong evidence it makes you feel fuller for longer, but it does have proven health benefits.
Studies have shown consuming resistant starch may help regulate blood sugar, aid weight loss and improve gut health.
Research has also shown eating resistant starch reduces the risk of obesity, diabetes, heart disease and other chronic diseases.
Ricezempic is made by soaking rice in water. Kristi Blokhin/Shutterstock Resistant starch is found in many foods. These include beans, lentils, wholegrains (oats, barley, and rice – particularly brown rice), bananas (especially when they’re under-ripe or green), potatoes, and nuts and seeds (particularly chia seeds, flaxseeds and almonds).
Half a cup of uncooked white rice (as per the ricezempic recipe) contains around 0.6 grams of resistant starch. For optimal health benefits, a daily intake of 15–20 grams of resistant starch is recommended. Although there is no concrete evidence on the amount of resistant starch that leaches from rice into water, it’s likely to be significantly less than 0.6 grams as the whole rice grain is not being consumed.
Ricezempic vs Ozempic
Ozempic was originally developed to help people with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels but is now commonly used for weight loss.
Ozempic, along with similar medications such as Wegovy and Trulicity, is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. These drugs mimic the GLP-1 hormone the body naturally produces. By doing so, they slow down the digestive process, which helps people feel fuller for longer, and curbs their appetite.
While the resistant starch in rice could induce some similar benefits to Ozempic (such as feeling full and therefore reducing energy intake), no scientific studies have trialled ricezempic using the recipes promoted on social media.
Ozempic has a long half-life, remaining active in the body for about seven days. In contrast, consuming one cup of rice provides a feeling of fullness for only a few hours. And simply soaking rice in water and drinking the starchy water will not provide the same level of satiety as eating the rice itself.
Other ways to get resistant starch in your diet
There are several ways to consume more resistant starch while also gaining additional nutrients and vitamins compared to what you get from ricezempic.
1. Cooked and cooled rice
Letting cooked rice cool over time increases its resistant starch content. Reheating the rice does not significantly reduce the amount of resistant starch that forms during cooling. Brown rice is preferable to white rice due to its higher fibre content and additional micronutrients such as phosphorus and magnesium.
2. More legumes
These are high in resistant starch and have been shown to promote weight management when eaten regularly. Why not try a recipe that has pinto beans, chickpeas, black beans or peas for dinner tonight?
3. Cooked and cooled potatoes
Cooking potatoes and allowing them to cool for at least a few hours increases their resistant starch content. Fully cooled potatoes are a rich source of resistant starch and also provide essential nutrients like potassium and vitamin C. Making a potato salad as a side dish is a great way to get these benefits.
In a nutshell
Although many people on social media have reported benefits, there’s no scientific evidence drinking rice water or “ricezempic” is effective for weight loss. You probably won’t see any significant changes in your weight by drinking ricezempic and making no other adjustments to your diet or lifestyle.
While the drink may provide a small amount of resistant starch residue from the rice, and some hydration from the water, consuming foods that contain resistant starch in their full form would offer significantly more nutritional benefits.
More broadly, be wary of the weight loss hacks you see on social media. Achieving lasting weight loss boils down to gradually adopting healthy eating habits and regular exercise, ensuring these changes become lifelong habits.
Emily Burch, Accredited Practising Dietitian and Lecturer, Southern Cross University and Lauren Ball, Professor of Community Health and Wellbeing, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
7 Steps to Get Off Sugar and Carbohydrates – by Susan Neal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We will not keep the steps a mystery; abbreviated, they are:
- decide to really do this thing
- get knowledge and support
- clean out that pantry/fridge/etc and put those things behind you
- buy in healthy foods while starving your candida
- plan for an official start date, so that everything is ready
- change the way you eat (prep methods, timings, etc)
- keep on finding small ways to improve, without turning back
Particularly important amongst those are starving the candida (the fungus in your gut that is responsible for a lot of carb cravings, especially sugar and alcohol—which latter can be broken down easily into sugar), and changing the “how” of eating as well as the “what”; those are both things that are often overlooked in a lot of guides, but this one delivers well.
Walking the reader by the hand through things like that is probably the book’s greatest strength.
In the category of subjective criticism, the author does go off-piste a little at the end, to take a moment while she has our attention to talk about other things.
For example, you may not need “Appendix 7: How to Become A Christian and Disciple of Jesus Christ”.
Of course if that calls to you, then by all means, follow your heart, but it certainly isn’t a necessary step of quitting sugar. Nevertheless, the diversion doesn’t detract from the good dietary change advice that she has just spent a book delivering.
Bottom line: there’s no deep science here, but there’s a lot of very good, very practical advice, that’s consistent with good science.
Click here to check out 7 Steps to Get Off Sugar, and watch your health improve!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What are ‘collarium’ sunbeds? Here’s why you should stay away
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Reports have recently emerged that solariums, or sunbeds – largely banned in Australia because they increase the risk of skin cancer – are being rebranded as “collarium” sunbeds (“coll” being short for collagen).
Commercial tanning and beauty salons in Queensland, New South Wales and Victoria are marketing collariums, with manufacturers and operators claiming they provide a longer lasting tan and stimulate collagen production, among other purported benefits.
A collarium sunbed emits both UV radiation and a mix of visible wavelength colours to produce a pink or red light. Like an old-school sunbed, the user lies in it for ten to 20 minute sessions to quickly develop a tan.
But as several experts have argued, the providers’ claims about safety and effectiveness don’t stack up.
Why were sunbeds banned?
Commercial sunbeds have been illegal across Australia since 2016 (except for in the Northern Territory) under state-based radiation safety laws. It’s still legal to sell and own a sunbed for private use.
Their dangers were highlighted by young Australians including Clare Oliver who developed melanoma after using sunbeds. Oliver featured in the No Tan Is Worth Dying For campaign and died from her melanoma at age 26 in 2007.
Sunbeds lead to tanning by emitting UV radiation – as much as six times the amount of UV we’re exposed to from the summer sun. When the skin detects enough DNA damage, it boosts the production of melanin, the brown pigment that gives you the tanned look, to try to filter some UV out before it hits the DNA. This is only partially successful, providing the equivalent of two to four SPF.
Essentially, if your body is producing a tan, it has detected a significant amount of DNA damage in your skin.
Research shows people who have used sunbeds at least once have a 41% increased risk of developing melanoma, while ten or more sunbed sessions led to a 100% increased risk.
In 2008, Australian researchers estimated that each year, sunbeds caused 281 cases of melanoma, 2,572 cases of squamous cell carcinoma (another common type of skin cancer), and $3 million in heath-care costs, mostly to Medicare.
How are collarium sunbeds supposed to be different?
Australian sellers of collarium sunbeds imply they are safe, but their machine descriptions note the use of UV radiation, particularly UVA.
UVA is one part of the spectrum of UV radiation. It penetrates deeper into the skin than UVB. While UVB promotes cancer-causing mutations by discharging energy straight into the DNA strand, UVA sets off damage by creating reactive oxygen species, which are unstable compounds that react easily with many types of cell structures and molecules. These damage cell membranes, protein structures and DNA.
Evidence shows all types of sunbeds increase the risk of melanoma, including those that use only UVA.
Some manufacturers and clinics suggest the machine’s light spectrum increases UV compatibility, but it’s not clear what this means. Adding red or pink light to the mix won’t negate the harm from the UV. If you’re getting a tan, you have a significant amount of DNA damage.
Collagen claims
One particularly odd claim about collarium sunbeds is that they stimulate collagen.
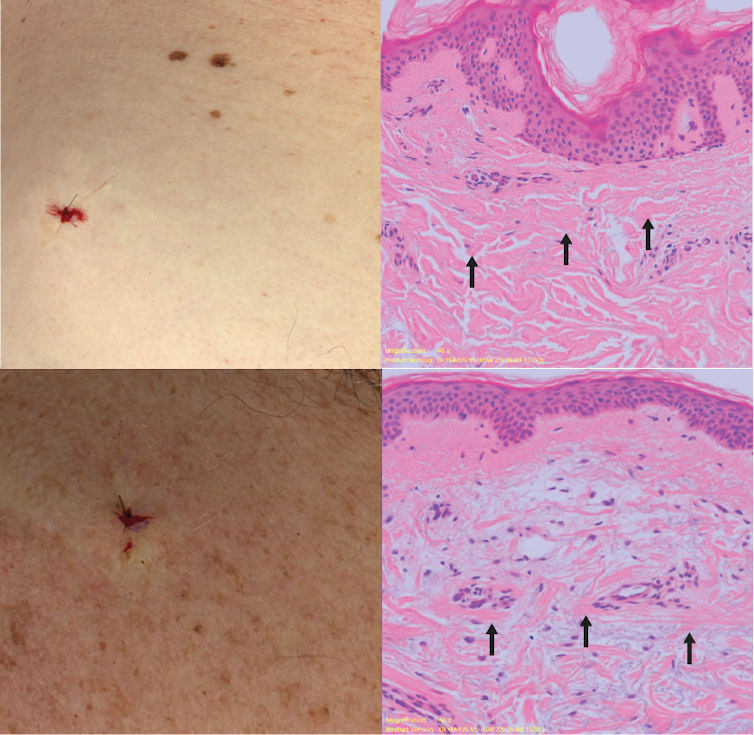
Collagen is the main supportive tissue in our skin. It provides elasticity and strength, and a youthful appearance. Collagen is constantly synthesised and broken down, and when the balance between production and recycling is lost, the skin loses strength and develops wrinkles. The collagen bundles become thin and fragmented. This is a natural part of ageing, but is accelerated by UV exposure.
Sun-protected skin (top) has thick bands of pink collagen (arrows) in the dermis, as seen on microscopic examination. Chronically sun-damaged skin (bottom) has much thinner collagen bands.
Katie Lee/UQThe reactive oxygen species generated by UVA light damage existing collagen structures and kick off a molecular chain of events that downgrades collagen-producing enzymes and increases collagen-destroying enzymes. Over time, a build-up of degraded collagen fragments in the skin promotes even more destruction.
While there is growing evidence red light therapy alone could be useful in wound healing and skin rejuvenation, the UV radiation in collarium sunbeds is likely to undo any benefit from the red light.
What about phototherapy?
There are medical treatments that use controlled UV radiation doses to treat chronic inflammatory skin diseases like psoriasis.
The anti-collagen effects of UVA can also be used to treat thickened scars and keloids. Side-effects of UV phototherapy include tanning, itchiness, dryness, cold sore virus reactivation and, notably, premature skin ageing.
These treatments use the minimum exposure necessary to treat the condition, and are usually restricted to the affected body part to minimise risks of future cancer. They are administered under medical supervision and are not recommended for people already at high risk of skin cancer, such as people with atypical moles.
So what happens now?
It looks like many collariums are just sunbeds rebranded with red light. Queensland Health is currently investigating whether these salons are breaching the state’s Radiation Safety Act, and operators could face large fines.
As the 2024 Australians of the Year – melanoma treatment pioneers Georgina Long and Richard Scolyer – highlighted in their acceptance speech, “there is nothing healthy about a tan”, and we need to stop glamorising tanning.
However, if you’re desperate for the tanned look, there is a safer and easy way to get one – out of a bottle or by visiting a salon for a spray tan.
Katie Lee, PhD Candidate, Dermatology Research Centre, The University of Queensland and Anne Cust, Professor of Cancer Epidemiology, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: