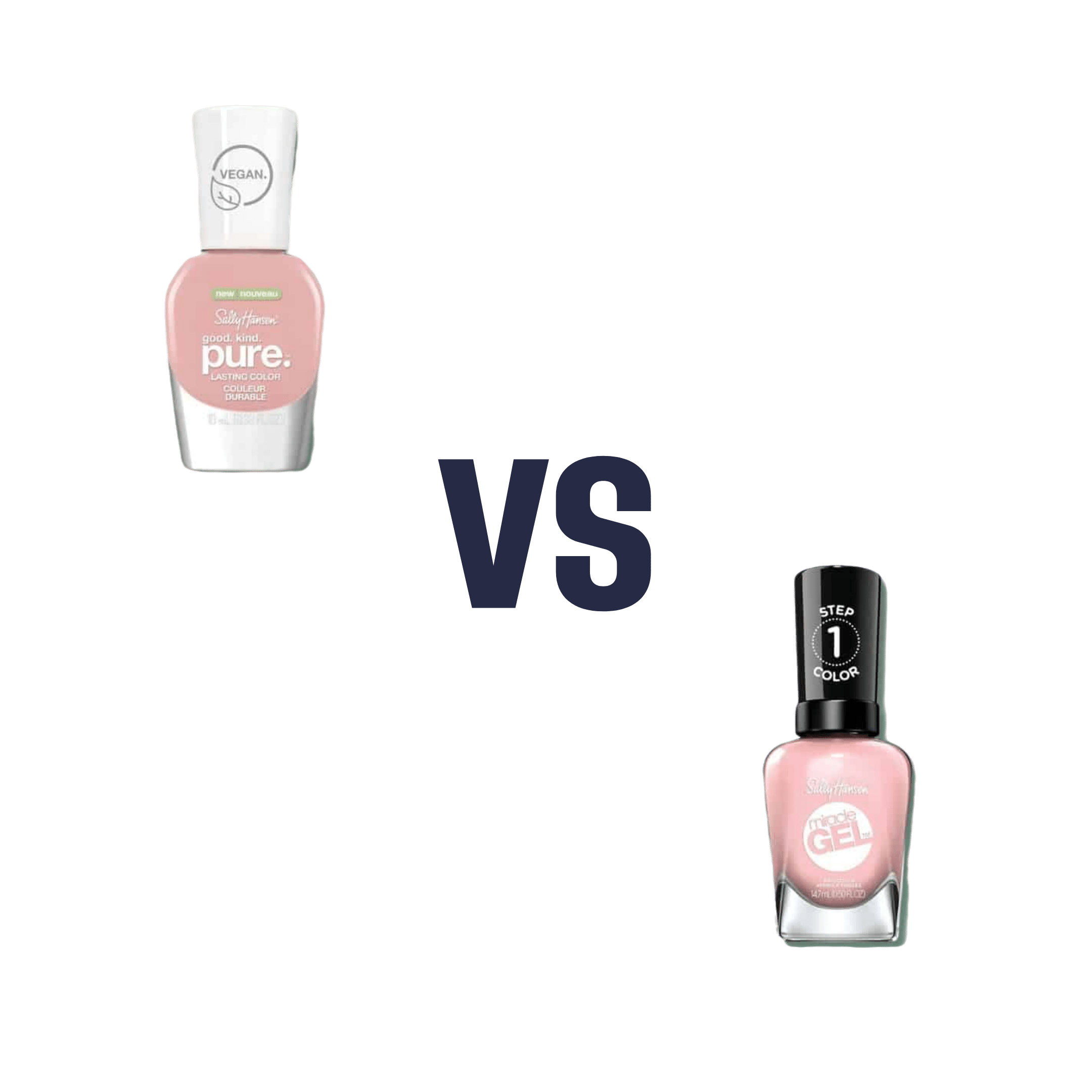
Regular Nail Polish vs Gel Nail Polish – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing regular nail polish to gel nail polish, we picked the regular.
Why?
This one’s less about what’s in the bottle, and more about what gets done to your hands:
- Regular nail polish application involves carefully brushing it on.
- Regular nail polish removal involves wiping with acetone.
…whereas:
- Gel nail polish application involves deliberately damaging (roughing up) the nail to allow the color coat to adhere, then when the top coat is applied, holding the nails (and thus, the attached fingers) under a UV light to set it. That UV lamp exposure is very bad for the skin.
- Gel nail polish removal involves soaking in acetone, which is definitely worse than wiping with acetone. Failure to adequately soak it will result in further damage to the nail while trying to get the base coat off the nail that you already deliberately damaged when first applying it.
All in all, regular nail polish isn’t amazing for nail health (healthiest is for nails to be free and naked), but for those of us who like a little bit of color there, regular is a lot better than gel.
Gel nail polish damages the nail itself by necessity, and presents a cumulative skin cancer risk and accelerated aging of the skin, by way of the UV lamp use.
For your interest, here are the specific products that we compared, but the above goes for any of this kind:
Regular nail polish | Gel nail polish
If you’d like to read more about nail health, you might enjoy reading:
The Counterintuitive Dos and Don’ts of Nail Health
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
It’s Not Hysteria – by Dr. Karen Tan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Firstly, who this book is aimed at: in case it wasn’t clear, this book assumes you have, or at least have had, a uterus. If that’s not you, then well, it’ll still be an interesting read but it won’t be about your reproductive health.
Secondly, about that “reproductive health”: it’s mostly not actually about reproductive health literally, but rather, the health of one’s reproductive organs and the things that they affect—which is a lot more than the ability to reproduce!
Dr. Tang takes us on a (respectably in-depth) tour of the relevant anatomy, before moving on to physiology, before continuing to pathology (i.e. things that can go wrong, and often do), and finally various treatment options, including elective procedures, and the pros and cons thereof.
She also talks the reader through talking about things with gynecologists and other healthcare providers, and making sure concerns are not dismissed out-of-hand (something that happens a lot, of course).
The style throughout is quite detailed prose, but without being difficult at all to read, and (assuming one is interested in the topic) it’s very engaging.
Bottom line: if you would like to know more about uteri and everything that is (or commonly/unfortunately) can be attached to them, the effects they have on the rest of the body and health, and what can be done about things not being quite right, then this is a good book for that.
Click here to check out It’s Not Hysteria, and understand more of what’s going on down there!
Share This Post
-
Pomegranate vs Figs – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pomegranate to figs, we picked the pomegranate.
Why?
In terms of macros, pomegranate has a lot more protein* and fiber, while the fig has more carbs. Thus, a win for pomegranate.
*Why such protein in a fruit? In both cases, it’s mostly from the seeds, which in both cases, we’re eating. However, pomegranates have a much greater seed-to-mass ratio than figs, and thus, a correspondingly higher amount of protein. Also some fats from the seeds, again more than figs, but the margin of difference is smaller, and not really enough to be of relevance.
In the category of vitamins, pomegranates lead with more of vitamins B1, B5, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while figs have more of vitamins A, B3, and B6. The largest margins of difference are in vitamins B9, E, and K, so all in pomegranate’s favor.
The minerals scene is closer to even; pomegranate has more copper, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while figs have more calcium, iron, magnesium, and manganese. Thus, a 5:4 lead for pomegranate, and the larger margins of difference are again for pomegranate.
In short, enjoy both, but pomegranates are the more nutritionally dense. Also, don’t throw away the peel! Dry it, and turn it into a powdered supplement—see our linked article below, for why:
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Pomegranate’s Health Gifts Are Mostly In Its Peel
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Top 10 Causes Of High Blood Pressure
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As Dr. Frita Fisher explains, these are actually the top 10 known causes of high blood pressure. Number zero on the list would be “primary hypertension”, which means high blood pressure with no clear underlying cause.
Superficially, this feels a little like the sometime practice of writing the catch-all “heart failure” as the cause of death on a death certificate, because yes, that heart sure did stop beating. But in reality, primary hypertension is most likely often caused by such things as unmanaged chronic stress—something that doesn’t show up on most health screenings.
Dr. Fisher’s Top 10
- Thyroid disease: both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can cause high blood pressure.
- Obstructive sleep apnea: characterized by snoring, daytime sleepiness, and headaches, this condition can lead to hypertension.
- Chronic kidney disease: diseases ranging from diabetic nephropathy to renal vascular disease can cause high blood pressure.
- Elevated cortisol levels: conditions like Cushing’s syndrome or disease, which involve high cortisol levels, can lead to hypertension—as can a lifestyle with a lot of chronic stress, but that’s less readily diagnosed as such than something one can tell from a blood test.
- Elevated aldosterone levels: excess aldosterone from the adrenal glands causes the body to retain salt and water, increasing blood pressure, because more stuff = more pressure.
- Brain tumor: tumors that increase intracranial pressure can cause a rise in blood pressure to ensure adequate brain perfusion. In these cases, the hypertension is keeping you alive—unless it kills you first. If this seems like a strange bodily response, remember that our bodily response to an infection is often fever, to kill off the infection which can’t survive at such high temperatures (but neither can we, so it becomes a game of chicken with our life on the line), so sometimes our body does kill us with one thing while trying to save us from another.
- Coarctation of the aorta: this congenital heart defect results in narrowing of the aorta, leading to hypertension, especially in the upper body.
- Pregnancy: pregnancy can either induce or worsen existing hypertension.
- Obesity: excess weight increases blood flow and pressure on arteries, raising the risk of hypertension and associated conditions, e.g. diabetes etc.
- Drugs: certain medications and recreational drugs (including, counterintuitively, alcohol!) can elevate blood pressure.
For more information on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
I’ve recovered from a cold but I still have a hoarse voice. What should I do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cold, flu, COVID and RSV have been circulating across Australia this winter. Many of us have caught and recovered from one of these common upper respiratory tract infections.
But for some people their impact is ongoing. Even if your throat isn’t sore anymore, your voice may still be hoarse or croaky.
So what happens to the voice when we get a virus? And what happens after?
Here’s what you should know if your voice is still hoarse for days – or even weeks – after your other symptoms have resolved.
Why does my voice get croaky during a cold?
A healthy voice is normally clear and strong. It’s powered by the lungs, which push air past the vocal cords to make them vibrate. These vibrations are amplified in the throat and mouth, creating the voice we hear.
The vocal cords are two elastic muscles situated in your throat, around the level of your laryngeal prominence, or Adam’s apple. (Although everyone has one, it tends to be more pronounced in males.) The vocal cords are small and delicate – around the size of your fingernail. Any small change in their structure will affect how the voice sounds.
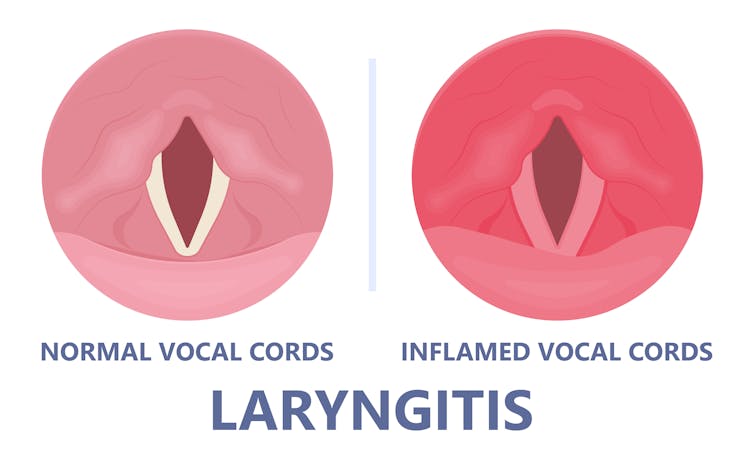
When the vocal cords become inflamed – known as laryngitis – your voice will sound different. Laryngitis is a common part of upper respiratory tract infections, but can also be caused through misuse.
Viruses such as the common cold can inflame the vocal cords. Pepermpron/Shutterstock Catching a virus triggers the body’s defence mechanisms. White blood cells are recruited to kill the virus and heal the tissues in the vocal cords. They become inflamed, but also stiffer. It’s harder for them to vibrate, so the voice comes out hoarse and croaky.
In some instances, you may find it hard to speak in a loud voice or have a reduced pitch range, meaning you can’t go as high or loud as normal. You may even “lose” your voice altogether.
Coughing can also make things worse. It is the body’s way of trying to clear the airways of irritation, including your own mucus dripping onto your throat (post-nasal drip). But coughing slams the vocal cords together with force.
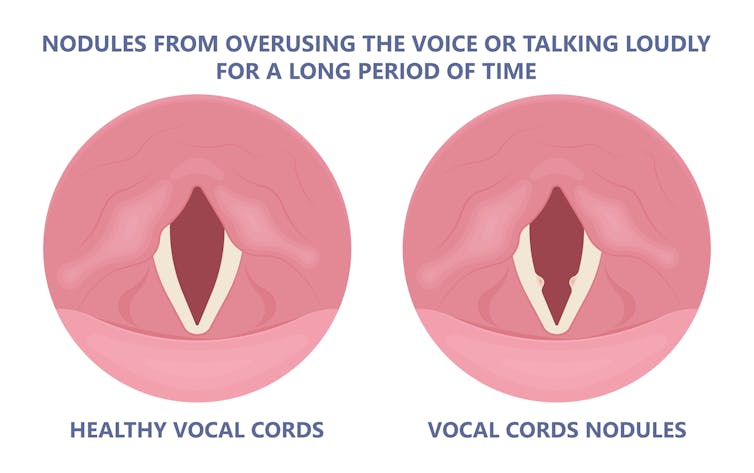
Chronic coughing can lead to persistent inflammation and even thicken the vocal cords. This thickening is the body trying to protect itself, similar to developing a callus when a pair of new shoes rubs.
Thickening on your vocal cords can lead to physical changes in the vocal cords – such as developing a growth or “nodule” – and further deterioration of your voice quality.
Coughing and exertion can cause inflamed vocal cords to thicken and develop nodules. Pepermpron/Shutterstock How can you care for your voice during infection?
People who use their voices a lot professionally – such as teachers, call centre workers and singers – are often desperate to resume their vocal activities. They are more at risk of forcing their voice before it’s ready.
The good news is most viral infections resolve themselves. Your voice is usually restored within five to ten days of recovering from a cold.
Occasionally, your pharmacist or doctor may prescribe cough suppressants to limit additional damage to the vocal cords (among other reasons) or mucolytics, which break down mucus. But the most effective treatments for viral upper respiratory tract infections are hydration and rest.
Drink plenty of water, avoid alcohol and exposure to cigarette smoke. Inhaling steam by making yourself a cup of hot water will also help clear blocked noses and hydrate your vocal cords.
Rest your voice by talking as little as possible. If you do need to talk, don’t whisper – this strains the muscles.
Instead, consider using “confidential voice”. This is a soft voice – not a whisper – that gently vibrates your vocal cords but puts less strain on your voice than normal speech. Think of the voice you use when communicating with someone close by.
During the first five to ten days of your infection, it is important not to push through. Exerting the voice by talking a lot or loudly will only exacerbate the situation. Once you’ve recovered from your cold, you can speak as you would normally.
What should you do if your voice is still hoarse after recovery?
If your voice hasn’t returned to normal after two to three weeks, you should seek medical attention from your doctor, who may refer you to an ear nose and throat specialist.
If you’ve developed a nodule, the specialist would likely refer you to a speech pathologist who will show you how to take care of your voice. Many nodules can be treated with voice therapy and don’t require surgery.
You may have also developed a habit of straining your vocal cords, if you forced yourself to speak or sing while they were inflamed. This can be a reason why some people continue to have a hoarse voice even when they’ve recovered from the cold.
In those cases, a speech pathologist may play a valuable role. They may teach you to exercises that make voicing more efficient. For example, lip trills (blowing raspberries) are a fun and easy way you can learn to relax the voice. This can help break the habit of straining your voice you may have developed during infection.
Yeptain Leung, Postdoctoral Research and Lecturer of Speech Pathology, School of Health Sciences, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Finding Peace at the End of Life – by Henry Fersko-Weiss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is not the most cheery book we’ve reviewed, but it is an important one. From its first chapter, with “a tale of two deaths”, one that went as well as can be reasonably expected, and the other one not so much, it presents a lot of choices.
The book is not prescriptive in its advice regarding how to deal with these choices, but rather, investigative. It’s thought-provoking, and asks questions—tacitly and overtly.
While the subtitle says “for families and caregivers”, it’s as much worth when it comes to managing one’s own mortality, too, by the way.
As for the scope of the book, it covers everything from terminal diagnosis, through the last part of life, to the death itself, to all that goes on shortly afterwards.
Stylewise, it’s… We’d call it “easy-reading” for style, but obviously the content is very heavy, so you might want to read it a bit at a time anyway, depending on how sensitive to such topics you are.
Bottom line: this book is not exactly a fun read, but it’s a very worthwhile one, and a good way to avoid regrets later.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Squat Bible – by Dr. Aaron Horschig
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You probably know the following three things about squats:
- Squatting is great for the health in many ways
- There are many different ways to squat
- Not all of them are correct, and some may even do harm
Dr. Aaron Horschig makes the case for squats being a movement first, and an exercise second. To this end, he takes us on a joint-by-joint tour of the anatomy of squatting, so that we get it right from top to toe.
Or rather: from toe to top, since he starts with the best foundation.
What this means is that if you’ve struggled to squat because you find some discomfort in your ankles, or a weakness in the knees, or you can’t get your back quite right, Dr. Horschig will have a fix for you. He also takes a realistic look about how people’s anatomy varies from person to person, and what differences this makes to how we each should best squat.
The explanations are clear and so are the pictures—we recommend getting the color print edition (linked), as the image quality is better than the black and white and/or Kindle edition.
Bottom-line: squats are one of the single best exercises we can do for our health—but we can miss out on benefits (or even do ourselves harm) if we don’t do them well. This book is a comprehensive reference resource for making sure we get the most out of our squatting ability.
Click here to check out The Squat Bible, and master this all-important movement!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: