Federal Panel Prescribes New Mental Health Strategy To Curb Maternal Deaths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
BRIDGEPORT, Conn. — Milagros Aquino was trying to find a new place to live and had been struggling to get used to new foods after she moved to Bridgeport from Peru with her husband and young son in 2023.
When Aquino, now 31, got pregnant in May 2023, “instantly everything got so much worse than before,” she said. “I was so sad and lying in bed all day. I was really lost and just surviving.”
Aquino has lots of company.
Perinatal depression affects as many as 20% of women in the United States during pregnancy, the postpartum period, or both, according to studies. In some states, anxiety or depression afflicts nearly a quarter of new mothers or pregnant women.
Many women in the U.S. go untreated because there is no widely deployed system to screen for mental illness in mothers, despite widespread recommendations to do so. Experts say the lack of screening has driven higher rates of mental illness, suicide, and drug overdoses that are now the leading causes of death in the first year after a woman gives birth.
“This is a systemic issue, a medical issue, and a human rights issue,” said Lindsay R. Standeven, a perinatal psychiatrist and the clinical and education director of the Johns Hopkins Reproductive Mental Health Center.
Standeven said the root causes of the problem include racial and socioeconomic disparities in maternal care and a lack of support systems for new mothers. She also pointed a finger at a shortage of mental health professionals, insufficient maternal mental health training for providers, and insufficient reimbursement for mental health services. Finally, Standeven said, the problem is exacerbated by the absence of national maternity leave policies, and the access to weapons.
Those factors helped drive a 105% increase in postpartum depression from 2010 to 2021, according to the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
For Aquino, it wasn’t until the last weeks of her pregnancy, when she signed up for acupuncture to relieve her stress, that a social worker helped her get care through the Emme Coalition, which connects girls and women with financial help, mental health counseling services, and other resources.
Mothers diagnosed with perinatal depression or anxiety during or after pregnancy are at about three times the risk of suicidal behavior and six times the risk of suicide compared with mothers without a mood disorder, according to recent U.S. and international studies in JAMA Network Open and The BMJ.
The toll of the maternal mental health crisis is particularly acute in rural communities that have become maternity care deserts, as small hospitals close their labor and delivery units because of plummeting birth rates, or because of financial or staffing issues.
This week, the Maternal Mental Health Task Force — co-led by the Office on Women’s Health and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and formed in September to respond to the problem — recommended creating maternity care centers that could serve as hubs of integrated care and birthing facilities by building upon the services and personnel already in communities.
The task force will soon determine what portions of the plan will require congressional action and funding to implement and what will be “low-hanging fruit,” said Joy Burkhard, a member of the task force and the executive director of the nonprofit Policy Center for Maternal Mental Health.
Burkhard said equitable access to care is essential. The task force recommended that federal officials identify areas where maternity centers should be placed based on data identifying the underserved. “Rural America,” she said, “is first and foremost.”
There are shortages of care in “unlikely areas,” including Los Angeles County, where some maternity wards have recently closed, said Burkhard. Urban areas that are underserved would also be eligible to get the new centers.
“All that mothers are asking for is maternity care that makes sense. Right now, none of that exists,” she said.
Several pilot programs are designed to help struggling mothers by training and equipping midwives and doulas, people who provide guidance and support to the mothers of newborns.
In Montana, rates of maternal depression before, during, and after pregnancy are higher than the national average. From 2017 to 2020, approximately 15% of mothers experienced postpartum depression and 27% experienced perinatal depression, according to the Montana Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System. The state had the sixth-highest maternal mortality rate in the country in 2019, when it received a federal grant to begin training doulas.
To date, the program has trained 108 doulas, many of whom are Native American. Native Americans make up 6.6% of Montana’s population. Indigenous people, particularly those in rural areas, have twice the national rate of severe maternal morbidity and mortality compared with white women, according to a study in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Stephanie Fitch, grant manager at Montana Obstetrics & Maternal Support at Billings Clinic, said training doulas “has the potential to counter systemic barriers that disproportionately impact our tribal communities and improve overall community health.”
Twelve states and Washington, D.C., have Medicaid coverage for doula care, according to the National Health Law Program. They are California, Florida, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Nevada, New Jersey, Oklahoma, Oregon, Rhode Island, and Virginia. Medicaid pays for about 41% of births in the U.S., according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Jacqueline Carrizo, a doula assigned to Aquino through the Emme Coalition, played an important role in Aquino’s recovery. Aquino said she couldn’t have imagined going through such a “dark time alone.” With Carrizo’s support, “I could make it,” she said.
Genetic and environmental factors, or a past mental health disorder, can increase the risk of depression or anxiety during pregnancy. But mood disorders can happen to anyone.
Teresa Martinez, 30, of Price, Utah, had struggled with anxiety and infertility for years before she conceived her first child. The joy and relief of giving birth to her son in 2012 were short-lived.
Without warning, “a dark cloud came over me,” she said.
Martinez was afraid to tell her husband. “As a woman, you feel so much pressure and you don’t want that stigma of not being a good mom,” she said.
In recent years, programs around the country have started to help doctors recognize mothers’ mood disorders and learn how to help them before any harm is done.
One of the most successful is the Massachusetts Child Psychiatry Access Program for Moms, which began a decade ago and has since spread to 29 states. The program, supported by federal and state funding, provides tools and training for physicians and other providers to screen and identify disorders, triage patients, and offer treatment options.
But the expansion of maternal mental health programs is taking place amid sparse resources in much of rural America. Many programs across the country have run out of money.
The federal task force proposed that Congress fund and create consultation programs similar to the one in Massachusetts, but not to replace the ones already in place, said Burkhard.
In April, Missouri became the latest state to adopt the Massachusetts model. Women on Medicaid in Missouri are 10 times as likely to die within one year of pregnancy as those with private insurance. From 2018 through 2020, an average of 70 Missouri women died each year while pregnant or within one year of giving birth, according to state government statistics.
Wendy Ell, executive director of the Maternal Health Access Project in Missouri, called her service a “lifesaving resource” that is free and easy to access for any health care provider in the state who sees patients in the perinatal period.
About 50 health care providers have signed up for Ell’s program since it began. Within 30 minutes of a request, the providers can consult over the phone with one of three perinatal psychiatrists. But while the doctors can get help from the psychiatrists, mental health resources for patients are not as readily available.
The task force called for federal funding to train more mental health providers and place them in high-need areas like Missouri. The task force also recommended training and certifying a more diverse workforce of community mental health workers, patient navigators, doulas, and peer support specialists in areas where they are most needed.
A new voluntary curriculum in reproductive psychiatry is designed to help psychiatry residents, fellows, and mental health practitioners who may have little or no training or education about the management of psychiatric illness in the perinatal period. A small study found that the curriculum significantly improved psychiatrists’ ability to treat perinatal women with mental illness, said Standeven, who contributed to the training program and is one of the study’s authors.
Nancy Byatt, a perinatal psychiatrist at the University of Massachusetts Chan School of Medicine who led the launch of the Massachusetts Child Psychiatry Access Program for Moms in 2014, said there is still a lot of work to do.
“I think that the most important thing is that we have made a lot of progress and, in that sense, I am kind of hopeful,” Byatt said.
Cheryl Platzman Weinstock’s reporting is supported by a grant from the National Institute for Health Care Management Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
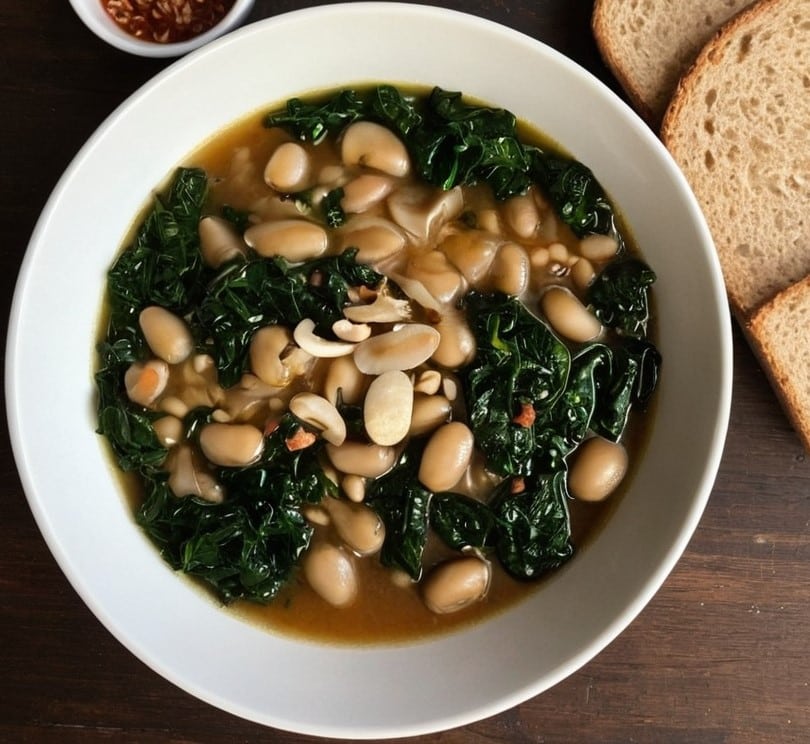
Brothy Beans & Greens
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Eat beans and greens”, we say, “but how”, you ask. Here’s how! Tasty, filling, and fulfilling, this dish is full of protein, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and assorted powerful phytochemicals.
You will need
- 2½ cups low-sodium vegetable stock
- 2 cans cannellini beans, drained and rinsed
- 1 cup kale, stems removed and roughly chopped
- 4 dried shiitake mushrooms
- 2 shallots, sliced
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 1 tbsp white miso paste
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp rosemary leaves
- 1 tsp thyme leaves
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp red chili flakes
- Juice of ½ lemon
- Extra virgin olive oil
- Optional: your favorite crusty bread, perhaps using our Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread recipe
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat some oil in a skillet and fry the shallots for 2–3 minutes.
2) Add the nutritional yeast, garlic, herbs, and spices, and stir for another 1 minute.
3) Add the beans, vegetable stock, and mushrooms. Simmer for 10 minutes.
4) Add the miso paste, stirring well to dissolve and distribute evenly.
5) Add the kale until it begins to wilt, and remove the pot from the heat.
6) Add the lemon juice and stir.
7) Serve; we recommend enjoying it with crusty wholegrain bread.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen ← beans and greens up top!
- The Magic of Mushrooms: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
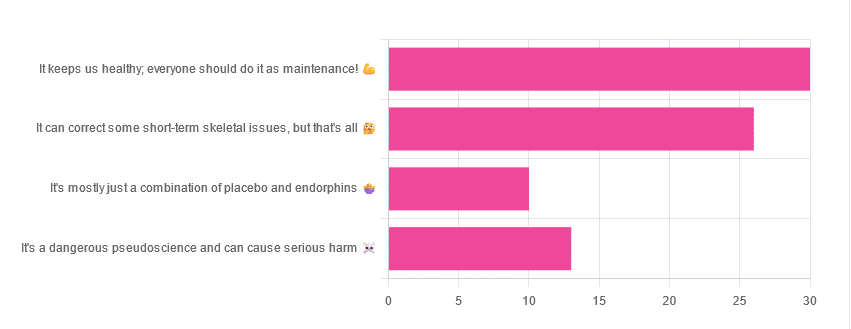
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on chiropractic medicine, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of results:
- 38% of respondents said it keeps us healthy, and everyone should do it as maintenance
- 33% of respondents said it can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all
- 16% of respondents said that it’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause serious harm
- 13% of respondents said that it’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins
Respondents also shared personal horror stories of harm done, personal success stories of things cured, and personal “it didn’t seem to do anything for me” stories.
What does the science say?
It’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause harm: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
That is to say, chiropractic in its simplest form that makes the fewest claims, is not a pseudoscience. If somebody physically moves your bones around, your bones will be physically moved. If your bones were indeed misaligned, and the chiropractor is knowledgeable and competent, this will be for the better.
However, like any form of medicine, it can also cause harm; in chiropractic’s case, because it more often than not involves manipulation of the spine, this can be very serious:
❝Twenty six fatalities were published in the medical literature and many more might have remained unpublished.
The reported pathology usually was a vascular accident involving the dissection of a vertebral artery.
Conclusion: Numerous deaths have occurred after chiropractic manipulations. The risks of this treatment by far outweigh its benefit.❞
Source: Deaths after chiropractic: a review of published cases
From this, we might note two things:
- The abstract doesn’t note the initial sample size; we would rather have seen this information expressed as a percentage. Unfortunately, the full paper is not accessible, and nor are many of the papers it cites.
- Having a vertebral artery fatally dissected is nevertheless not an inviting prospect, and is certainly a very reasonable cause for concern.
It’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins: True or False?
True or False, depending on what you went in for:
- If you went in for a regular maintenance clunk-and-click, then yes, you will get your clunk-and-click and feel better for it because you had a ritualized* experience and endorphins were released.
- If you went in for something that was actually wrong with your skeletal alignment, to get it corrected, and this correction was within your chiropractor’s competence, then yes, you will feel better because a genuine fault was corrected.
*this is not implying any mysticism, by the way. Rather it means simply that placebo effect is strongest when there is a ritual associated with it. In this case it means going to the place, sitting in a pleasant waiting room, being called in, removing your shoes and perhaps some other clothes, getting the full attention of a confident and assured person for a while, this sort of thing.
With regard to its use to combat specifically spinal pain (i.e., perhaps the most obvious thing to treat by chiropractic spinal manipulation), evidence is slightly in favor, but remains unclear:
❝Due to the low quality of evidence, the efficacy of chiropractic spinal manipulation compared with a placebo or no treatment remains uncertain. ❞
Source: Clinical Effectiveness and Efficacy of Chiropractic Spinal Manipulation for Spine Pain
It can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all: True or False?
Probably True.
Why “probably”? The effectiveness of chiropractic treatment for things other than short-term skeletal issues has barely been studied. From this, we may wish to keep an open mind, while also noting that it can hardly claim to be evidence-based—and it’s had hundreds of years to accumulate evidence. In all likelihood, publication bias has meant that studies that were conducted and found inconclusive or negative results were simply not published—but that’s just a hypothesis on our part.
In the case of using chiropractic to treat migraines, a very-related-but-not-skeletal issue, researchers found:
❝Pre-specified feasibility criteria were not met, but deficits were remediable. Preliminary data support a definitive trial of MCC+ for migraine.❞
Translating this: “it didn’t score as well as we hoped, but we can do better. We got some positive results, and would like to do another, bigger, better trial; please fund it”
Source: Multimodal chiropractic care for migraine: A pilot randomized controlled trial
Meanwhile, chiropractors’ claims for very unrelated things have been harshly criticized by the scientific community, for example:
Misinformation, chiropractic, and the COVID-19 pandemic
About that “short-term” aspect, one of our subscribers put it quite succinctly:
❝Often a skeletal correction is required for initial alignment but the surrounding fascia and muscles also need to be treated to mobilize the joint and release deep tissue damage surrounding the area. In combination with other therapies chiropractic support is beneficial.❞
This is, by the way, very consistent with what was said in the very clinically-dense book we reviewed yesterday, which has a chapter on the short-term benefits and limitations of chiropractic.
A truism that holds for many musculoskeletal healthcare matters, holds true here too:
❝In a battle between muscle and bone, muscle will always win❞
In other words…
Chiropractic can definitely help put misaligned bones back where they should be. However, once they’re there, if the cause of their misalignment is not treated, they will just re-misalign themselves shortly after you walking out of your session.
This is great for chiropractors, if it keeps you coming back for endless appointments, but it does little for your body beyond give you a brief respite.
So, by all means go to a chiropractor if you feel so inclined (and you do not fear accidental arterial dissection etc), but please also consider going to a physiotherapist, and potentially other medical professions depending on what seems to be wrong, to see about addressing the underlying cause.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Antiviral Gum Gives Epidemiologists Something To Chew On
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
With viruses on the rise, of course one of our biggest weapons against them is vaccination, but that approach has its limitations:
- In some places such as the US, anti-vaccine sentiments are high, and a vaccine is only as good as its uptake (i.e. if people don’t take it, they will more likely catch the disease and pass it on, including to some people who cannot be vaccinated, so non-vaccinators create a hole in herd immunity)
- Many vaccines can become outdated when viruses mutate more quickly than vaccines can be developed (we’ve seen a lot of this with COVID and Flu viruses, and that’s why we keep needing new ones)
- There are some viruses for which we simply do not yet have vaccines; sometimes this is the case even for very common viruses like Herpes simplex. or, indeed, the common cold (Rhinovirus sp.).
So, antivirals definitely have their place too. To be clear about the difference:
- A vaccine forewarns the immune system “watch out for this thing that you might encounter in the future, and prepare a defense for it according to these specifications” (it only helps if you aren’t already infected with the thing it’s vaccinating against, because otherwise the warning is too late and your body is already trying to mount a defense)
- An antiviral kills, inactivates, or otherwise severely inconveniences the virus directly (it only helps if there is a virus there to fight)
How the antiviral gum works
In few words: you chew it, the antiviral substance is then in your saliva, and it kills/inactivates/inconveniences the virus at the site of infection (e.g. your respiratory tract)
In the case of this specific antiviral gum, it’s more in the category of “severely inconveniences”, because the antiviral substance is a protein trap that binds to the virus, rendering it near-harmless.
In essence, therefore, it works less like a vaccine and more like a facemask (except it’s trapping the virus on the molecular level, rather than trying to stop aerosolized droplets from moving around on the macro level).
This was first developed as a possible tool against COVID:
…and this in turn was based on previous work quite early in 2020:
And yes, those are lablab beans, as in Lablab purpureus, also called hyacinth beans, which may not be available in all supermarkets, but are not very obscure either (common throughout most of Africa and the tropics).
Most recently, researchers have found that 40mg of the broad-spectrum (as in, it affects many viruses) antiviral trap protein, as delivered by a 2g piece of gum, was sufficient to reduce viral loads by more than 95%, including for SARS-CoV-2 as well as H5N1, H3N2, and H7N9 (various kinds of bird flu that affect humans), and HSV-1 and HSV-2 (the two most common variants of herpes, including cold sores):
You can also read a pop-science article about it, with links to more details, here:
Antiviral chewing gum shows promise in reducing influenza and herpes spread
Want to learn more?
Check out:
Winning The Biological Arms Race: Could This Be “The Ultimate Booster”?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
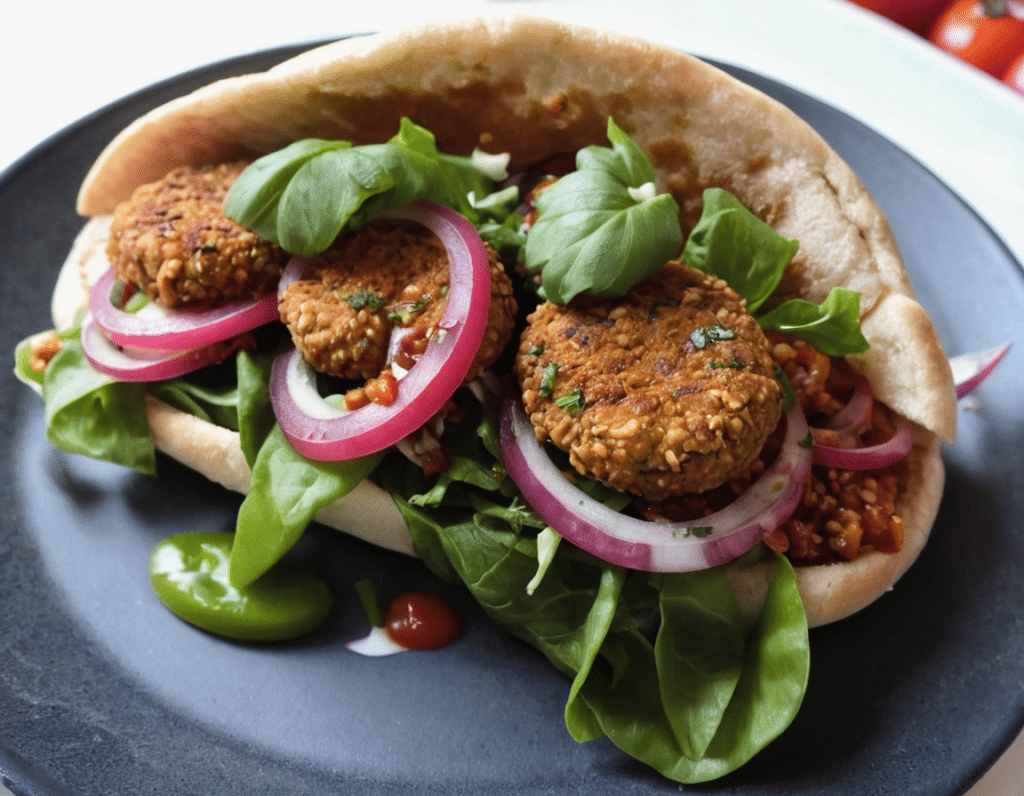
Healthy Harissa Falafel Patties
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You can make these as regular falafel balls if you prefer, but patties are quicker and easier to cook, and are great for popping in a pitta.
You will need
For the falafels:
- 1 can chickpeas, drained, keep the chickpea water (aquafaba)
- 1 red onion, roughly chopped
- 2 tbsp chickpea flour (also called gram flour or garbanzo bean flour)
- 1 bunch parsley
- 1 tbsp harissa paste
- Extra virgin olive oil for frying
For the harissa sauce:
- ½ cup crème fraîche or plant-based equivalent (you can use our Plant-Based Healthy Cream Cheese recipe and add the juice of 1 lemon)*
- 1 tbsp harissa paste (or adjust this quantity per your heat preference)
*if doing this, rather than waste the zest of the lemon, you can add the zest to the falafels if you like, but it’s by no means necessary, just an option
For serving:
- Wholegrain pitta or other flatbread (you can use our Healthy Homemade Flatbreads recipe)
- Salad (your preference; we recommend some salad leaves, sliced tomato, sliced cucumber, maybe some sliced onion, that sort of thing)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the chickpeas, 1 oz of the aquafaba, the onion, the parsley, and the harissa paste, until smooth. Then add in the chickpea flour until you get a thick batter. If you overdo it with the chickpea flour, add a little more of the aquafaba to equalize. Refrigerate the mixture for at least 30 minutes.
2) Heat some oil in a skillet, and spoon the falafel mixture into the pan to make the patties, cooking on both sides (you can use a spatula to gently turn them), and set them aside.
3) Mix the harissa sauce ingredients in a small bowl.
4) Assemble; best served warm, but enjoy it however you like!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in more of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Hero Homemade Hummus ← another great option
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The 7 Known Risk Factors For Dementia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A recent UK-based survey found that…
- while nearly half of adults say dementia is the disease they fear most,
- only a third of those thought you could do anything to avoid it, and
- just 1% could name the 7 known risk factors.
Quick test
Can you name the 7 known risk factors?
Please take a moment to actually try (this kind of mental stimulation is good in any case), and count them out on your fingers (or write them down), and then…
Answer (no peeking if you haven’t listed them yet)
The 7 known risk factors are:
*drumroll please*
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Depression
- Lack of mental stimulation
- Lack of physical activity
How many did you get? If you got them all, well done. If not, then well, now you know, so that’s good.
Did you come here from our “Future-Proof Your Brain” article? If so, you can get back to it here ← and if you didn’t, you should check it out anyway; it’s worth it😉
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Synergistic Brain-Training
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let The Games Begin (But It Matters What Kind)
Exercise is good for brain health; we’ve written about this before, for example:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk ← there are many advices here, but exercise, especially cardiovascular exercise in this case, is an important item on the list!
Today it’s Psychology Sunday though, and we’re going to talk about looking after brain health by means of brain-training, via games.
“Brain-training” gets a lot of hype and flak:
- Hype: do sudoku every day and soon you will have an IQ of 200 and still have a sharp wit at the age of 120
- Flak: brain-training is usually training only one kind of cognitive function, with limited transferability to the rest of life
The reality is somewhere between the two. Brain training really does improve not just outwardly measurable cognitive function, but also internally measurable improvements visible on brain scans, for example:
- Cognitive training modified age-related brain changes in older adults with subjective memory decline
- Functional brain changes associated with cognitive training in healthy older adults: A preliminary ALE meta-analysis
But what about the transferability?
Let us play
This is where game-based brain-training comes in. And, the more complex the game, the better the benefits, because there is more chance of applicability to life, e.g:
- Sudoku: very limited applicability
- Crosswords: language faculties
- Chess: spatial reasoning, critical path analysis, planning, memory, focus (also unlike the previous two, chess tends to be social for most people, and also involve a lot of reading, if one is keen)
- Computer games: wildly varied depending on the game. While an arcade-style “shoot-em-up” may do little for the brain, there is a lot of potential for a lot of much more relevant brain-training in other kinds of games: it could be planning, problem-solving, social dynamics, economics, things that mirror the day-to-day challenges of running a household, even, or a business.
- It’s not that the skills are useful, by the way. Playing “Stardew Valley” will not qualify you to run a real farm, nor will playing “Civilization” qualify you to run a country. But the brain functions used and trained? Those are important.
It becomes easily explicable, then, why these two research reviews with very similar titles got very different results:
- A Game a Day Keeps Cognitive Decline Away? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Commercially-Available Brain Training Programs in Healthy and Cognitively Impaired Older Adults
- Game-based brain training for improving cognitive function in community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-regression
The first review found that game-based brain-training had negligible actual use. The “games” they looked at? BrainGymmer, BrainHQ, CogMed, CogniFit, Dakim, Lumosity, and MyBrainTrainer. In other words, made-for-purpose brain-trainers, not actual computer games per se.
The second reviewfound that game-based training was very beneficial. The games they looked at? They didn’t name them, but based on the descriptions, they were actual multiplayer online turn-based computer games, not made-for-purpose brain-trainers.
To summarize the above in few words: multiplayer online turn-based computer games outperform made-for-purpose brain-trainers for cognitive improvement.
Bringing synergy
However, before you order that expensive gaming-chair for marathon gaming sessions (research suggests a tail-off in usefulness after about an hour of continuous gaming per session, by the way), be aware that cognitive training and (physical) exercise training combined, performed close in time to each other or simultaneously, perform better than the sum of either alone:
See also:
❝Simultaneous training was the most efficacious approach for cognition, followed by sequential combinations and cognitive training alone, and significantly better than physical exercise.
Our findings suggest that simultaneously and sequentially combined interventions are efficacious for promoting cognitive alongside physical health in older adults, and therefore should be preferred over implementation of single-domain training❞
~ Dr. Hanna Malmberg Gavelin et al.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: