What’s Your Personal Life Expectancy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tick Tock… Goes the Death Clock?
This fun little test will ask a few questions about you and your lifestyle, and then make a prediction of your personal life expectancy, based on global statistics from the World Health Organisation.
And then the countdown starts… Literally, it generates a clock for you to see your life-seconds ticking away—this may or may not delight you, but it sure is a curiosity.
Their “Letters” page has a lot of reactions from people who just got their results (spoiler: people’s perspectives on life vary a lot)
Who mostly uses this service? According to their stats page, it’s mostly curious under-45s, with gradually less interest in knowing about it from 45 onwards… until the age of 70, when suddenly everyone wants to know about it again!
So Is It Possible To Pause The Clock On Aging? – Q&A Spotlight Interview
Life extension is sometimes viewed as the domain of the super-rich, and with less than half of Millennials (and almost none of Gen-Z) having retirement plans, often those of us who aren’t super-rich have more mundane (and immediate!) goals than living to 120.
And yet…
Middle class and working class life-extensionists do exist, even if not garnering the same media attention. We think that’s strange—after all, while the whimsies of the super-rich may be entertaining to read about, it’s not nearly as applicable to most people as more relatable stories:
- The twenty-something who gives up smoking and adds (healthier!) years to their life
- The thirty-something who adopts a plant-based diet and is less likely to die of heart disease
- The forty-something who stops drinking, and avoids health conditions and mishaps alike
- The fifty-something who reconsiders their health plan in light of their changing body
- The sixty-something who takes up yoga, or chess, or salsa dancing
- The seventy-something who gets asked what their secret is
- …and so on
But these are ideas, textbook examples. What if we make it more personal?
We interviewed 10 Almonds subscriber and longevity enthusiast Anastasia S., and here’s what she had to say:
Q: What does life extension mean to you, in your life?
A: To me, the key is healthy life extension. People often joke “I don’t want to live longer; the last years are the worst!” but they’re missing the point that after a certain age, those difficulties are coming whether they come at 50 or 70 or 90. Personally, I’d rather keep them at bay if I can.
Q: How do you do that?
A: Firstly, which won’t be a shock: good diet and exercise. Those two things are possibly the biggest active influences on my longevity. I’m vegan, which I don’t think is outright necessary for good health but done right, it can certainly be good. In this house we eat a lot of whole grains, beans, lentils, vegetables in general, nuts too. As for exercise, I do 30–60 minutes of Pilates daily; it’s nothing fancy and it’s just me in my pajamas at home, but it keeps me strong and fit and supple. I also walk everywhere; I don’t even own a car. Beyond that… I don’t drink or smoke (probably the biggest passive influences on my longevity, i.e., things that aren’t there to make it shorter), and I try to take my sleep seriously, making sure to schedule enough time and prepare properly for it.
Q: Take your sleep seriously? How so?
A: Good “sleep hygiene” as some call it—I schedule a little wind-down time before sleep, with no glaring screens or main lights, making a space between my busy day and restful sleep, kicking anything requiring brainpower to the morning, and making a conscious choice not to think more about those things in the meantime. I take care to make my sleeping environment as conducive as possible to good sleep too; I have a good mattress and pillows, I make sure the temperature is cool but cosy. I have a pot of herbal tea on my bedside table—I hydrate a lot.
Q: Do you take any supplements?
A: I do! They’re mostly quite general though, just “covering my bases”, so to speak. I take a daily nootropic stack (a collection of supplements specifically for brain health), too. I buy them in bulk, so they don’t cost so much.
Q: This seems quite a healthy lifestyle! Do you have any vices at all?
A: I definitely drink more coffee than I probably should! But hey, nobody’s perfect. I do love coffee, though, and as vices go, it’s probably not too bad.
Q: How’s it all working out for you? Do you feel younger?
A: I’m 38 and sometimes I feel like a teenager; sometimes I feel like an old lady. But the latter is usually for social reasons, not health-related reasons. I do have streaks of gray in my hair though, and I love that! If people don’t notice my grays, then they often think I’m in my 20s, rather than pushing 40. A little while back, I was stopped in the street by someone wanting to sell me a change of household utilities provider, then she stopped herself mid-sentence and said “Oh but wait, you look a bit too young, never mind”. Most general metrics of health would put me in my 20s.
Q: That’s interesting that you love your gray hairs, for someone who wants to stay young; is it an exception?
A: It’s more that I want to minimize the problems that come with age, and not everything’s a problem. Gray hairs are cool; joint pain, not so much. A long life rich with experiences is cool; memory loss, not so much. So, I try to keep healthy, and wear my years as best I can.
Q: Sounds good to us; good luck with it!
A: Thank you; I do my best!
Here at 10 Almonds, we love featuring what our readers are doing to improve their health; if you’re willing to be featured in our newsletter, let us know by replying to this email (where an actual human will read it, we promise!)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Accidentally Overweight – by Dr. Libby Weaver
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book’s main premise is that for most people who become overweight especially in midlife or later, if there wasn’t an obvious lifestyle change to precipitate this (e.g. started living on fast food for some reason), then in most cases, what’s needed is not drastic action, so much as some metabolic tweaks to correct things that have gone off-piste a little in our physiology.
The book covers nine factors that make an impact, and how each can be managed. They are:
- Insulin
- Stress hormones
- Calories
- Thyroid function
- Nervous system
- Emotions
- Sex hormones
- Liver function
- Gut bacteria
Some will be obvious, but as Dr. Weaver explains, are relative trivial compared to the others; “calories” in one such example of this “yes, it’s a factor, but very overrated” category.
Others are things that most people don’t think too much about, like liver function. And yet, it is indeed very much critical, and a major player in metabolism and adiposity.
The style is on the very light end of pop-science, but she does bring her professional knowledge to bear on topic (her doctorate is a PhD in biochemistry, so a lot of explanations come from that angle).
Bottom line: if you’ve found yourself “accidentally overweight”, and would like to tip the scales back in the other direction without doing anything extreme, then this book provides the tweaks that no amount of cardio or restrictive dieting will.
Click here to check out Accidentally Overweight, and re-adjust it back the other way!
Share This Post
-
New Eye Drops vs Age-Related Macular Degeneration
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written previously on preventative interventions against age-related macular degeneration (AMD):
How To Avoid Age-Related Macular Degeneration
…and then supplemented that, to to speak, with:
Fatty Acids For The Eyes & Brain: The Good And The Bad
However, what if ADM happens anyway?
Not a dry eye in the house
Age-related macular degeneration comes in two forms, wet and dry, of which, dry is by far the most common (being 9 out of 10 of all cases of AMD).
It sounds like the sort of thing that eye drops should be in order for, but in fact, the wetness vs dryness is about what’s going on inside the macula, not what’s happening on the surface of the eye. Up until now, the only treatments available (aside from supplement regimes, which we linked just above) have been injectable drugs, which:
- are not fun (yes, the injection goes into the eyeball)
- don’t actually work very well (modest improvements in vision; significantly better than nothing though)
…and even those won’t help in the late stages.
However, a Korean research team has developed eye drops with peptides that inhibit the interactions between Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and TLR-signalling proteins, in a way that addresses part of the pathogenesis of AMD:
That’s quite a dense read though, so here’s a pop-science article that explains it more simply, but in more detail than we can here:
New eye drop treatment offers hope for dry AMD patients
This is a big improvement from the state of affairs previously, in which eye drops really couldn’t help at all:
What eye drops can treat macular degeneration? ← pop-science article from January 2023
No AMD, and/but want your eye health to be better?
Check out these:
10 Great Exercises to Improve Your Eyesight ← you can quickly see the results for yourself
Take care!
Share This Post
-
What does lion’s mane mushroom actually do, anyway?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may know it as an ingredient in nootropic supplements. You may have heard of lion’s mane mushroom coffee. You may know it as the big shaggy white mushroom that grows in nature and can look very impressive.
What’s special about it?
The lion’s mane mushroom, or Hericium erinaceus (we mention, as studies we’ll cite often use the botanical name) is an adaptogenic agent that has an established ability to promote nerve regeneration through nerve growth factor neurotrophic activity. In other words, it helps (re)grow neurons.
In a 2023 study, researchers wondered if its abilities (well-established in the peripheral nervous system) would work in the central nervous system too, namely the brain, specifically the hippocampus (responsible for memory).
To boil what they found down to a single line, they concluded:
❝[Lion’s mane extract] therefore acts through a novel pan-neurotrophic signaling pathway, leading to improved cognitive performance.❞
You can read the full study for yourself (with pictures!) here:
Limitations of the study
It’s worth noting that the above study was performed on mice brains, not those of humans. As there is a shortage of human volunteers willing to have their brains sliced and examined under microscopes, we do not expect this study to be repeated with humans any time soon.
So, are there human studies that have been done?
There are! Particularly promising was this 2020 study of people with Alzheimer’s disease, wherein supplementation with 1g of lion’s mane mushroom daily for 49 weeks significantly increased cognitive test scores compared with a placebo; you can read about it here:
Additionally, this 2019 study showed that taking 1.2g daily for eight weeks helped relieve depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders in overweight or obese patiences:
Are there other health benefits?
It seems so! Unfortunately, most of its other health claims are only supported by animal studies so far, aside from one small study funded by a supplement company for their supplement that contained mostly Agaricus blazei (a different mushroom) with 14% lion’s mane.
However, in animal studies, lion’s mane has also shown promise:
- For digestion
- Against inflammation
- For cardiovascular health
- For diabetes management
- Against cancer
- Against aging
Where can I get it?
We don’t sell it (or anything else, for that matter) but if you’d like to try it, here’s an example product for your convenience:
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Currants vs Grapes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing currants to grapes, we picked the currants.
Why?
First, a note on nomenclature: when we say “currants”, we are talking about actual currants, of the Ribes genus, and in this case (as per the image) red ones. We are not talking about “currants” that are secretly tiny grapes that also get called currants in the US. So, there are important botanical differences here, beyond how they have been cultivated; they are literally entirely different plants.
So, about those differences…
In terms of macros, currants have nearly 5x the fiber, while grapes are slightly higher in carbs. So there’s an easy choice here in terms of fiber and on the glycemic index front; currants win easily.
In the category of vitamins, currants have more of vitamins B5, B9, C, and choline, while grapes have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, E, and K. So, a win for grapes in this round.
When it comes to minerals, currants have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while grapes have more manganese. A win, therefore, for currants again this time.
In terms of polyphenols, currants have a lot more in terms of total polyphenols, including (as a matter of interest) approximately 5x the resveratrol content compared to grapes—and that’s compared to black grapes, which are the “best” kind of grapes for such. Grapes really aren’t a very good source of resveratrol; people just really like the idea of red wine being a health food, so it has been talked up a lot and got a popular reputation despite its extreme paucity of nutritional value.
In any case, adding up the sections makes for a clear overall win for currants, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
21 Most Beneficial Polyphenols & What Foods Have Them
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s the difference between shyness and social anxiety?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
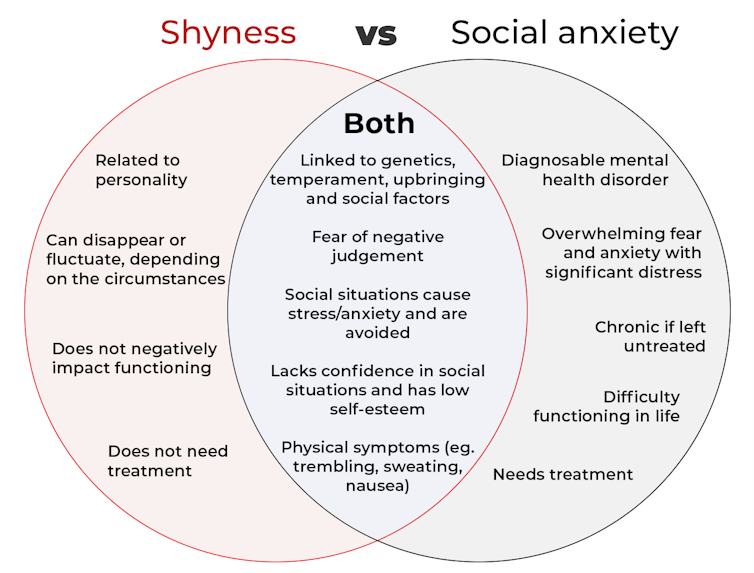
The terms “shyness” and “social anxiety” are often used interchangeably because they both involve feeling uncomfortable in social situations.
However, feeling shy, or having a shy personality, is not the same as experiencing social anxiety (short for “social anxiety disorder”).
Here are some of the similarities and differences, and what the distinction means.
pathdoc/Shutterstock How are they similar?
It can be normal to feel nervous or even stressed in new social situations or when interacting with new people. And everyone differs in how comfortable they feel when interacting with others.
For people who are shy or socially anxious, social situations can be very uncomfortable, stressful or even threatening. There can be a strong desire to avoid these situations.
People who are shy or socially anxious may respond with “flight” (by withdrawing from the situation or avoiding it entirely), “freeze” (by detaching themselves or feeling disconnected from their body), or “fawn” (by trying to appease or placate others).
A complex interaction of biological and environmental factors is also thought to influence the development of shyness and social anxiety.
For example, both shy children and adults with social anxiety have neural circuits that respond strongly to stressful social situations, such as being excluded or left out.
People who are shy or socially anxious commonly report physical symptoms of stress in certain situations, or even when anticipating them. These include sweating, blushing, trembling, an increased heart rate or hyperventilation.
How are they different?
Social anxiety is a diagnosable mental health condition and is an example of an anxiety disorder.
For people who struggle with social anxiety, social situations – including social interactions, being observed and performing in front of others – trigger intense fear or anxiety about being judged, criticised or rejected.
To be diagnosed with social anxiety disorder, social anxiety needs to be persistent (lasting more than six months) and have a significant negative impact on important areas of life such as work, school, relationships, and identity or sense of self.
Many adults with social anxiety report feeling shy, timid and lacking in confidence when they were a child. However, not all shy children go on to develop social anxiety. Also, feeling shy does not necessarily mean a person meets the criteria for social anxiety disorder.
People vary in how shy or outgoing they are, depending on where they are, who they are with and how comfortable they feel in the situation. This is particularly true for children, who sometimes appear reserved and shy with strangers and peers, and outgoing with known and trusted adults.
Individual differences in temperament, personality traits, early childhood experiences, family upbringing and environment, and parenting style, can also influence the extent to which people feel shy across social situations.
Not all shy children go on to develop social anxiety. 249 Anurak/Shutterstock However, people with social anxiety have overwhelming fears about embarrassing themselves or being negatively judged by others; they experience these fears consistently and across multiple social situations.
The intensity of this fear or anxiety often leads people to avoid situations. If avoiding a situation is not possible, they may engage in safety behaviours, such as looking at their phone, wearing sunglasses or rehearsing conversation topics.
The effect social anxiety can have on a person’s life can be far-reaching. It may include low self-esteem, breakdown of friendships or romantic relationships, difficulties pursuing and progressing in a career, and dropping out of study.
The impact this has on a person’s ability to lead a meaningful and fulfilling life, and the distress this causes, differentiates social anxiety from shyness.
Children can show similar signs or symptoms of social anxiety to adults. But they may also feel upset and teary, irritable, have temper tantrums, cling to their parents, or refuse to speak in certain situations.
If left untreated, social anxiety can set children and young people up for a future of missed opportunities, so early intervention is key. With professional and parental support, patience and guidance, children can be taught strategies to overcome social anxiety.
Why does the distinction matter?
Social anxiety disorder is a mental health condition that persists for people who do not receive adequate support or treatment.
Without treatment, it can lead to difficulties in education and at work, and in developing meaningful relationships.
Receiving a diagnosis of social anxiety disorder can be validating for some people as it recognises the level of distress and that its impact is more intense than shyness.
A diagnosis can also be an important first step in accessing appropriate, evidence-based treatment.
Different people have different support needs. However, clinical practice guidelines recommend cognitive-behavioural therapy (a kind of psychological therapy that teaches people practical coping skills). This is often used with exposure therapy (a kind of psychological therapy that helps people face their fears by breaking them down into a series of step-by-step activities). This combination is effective in-person, online and in brief treatments.
Treatment is available online as well as in-person. ImYanis/Shutterstock For more support or further reading
Online resources about social anxiety include:
- This Way Up’s online program for managing excessive shyness and fear of social situations
- Beyond Blue’s resources on social anxiety
- a guide to looking after yourself if you have social anxiety, from the Western Australian health department
- social anxiety online program for children and teens from the University of Queensland
- inroads, a self-guided online program for young adults who drink alcohol to manage their anxiety.
We thank the Black Dog Institute Lived Experience Advisory Network members for providing feedback and input for this article and our research.
Kayla Steele, Postdoctoral research fellow and clinical psychologist, UNSW Sydney and Jill Newby, Professor, NHMRC Emerging Leader & Clinical Psychologist, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Seriously Useful Communication Skills!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Are Communication Skills, Really?
Superficially, communication is “conveying an idea to someone else”. But then again…
Superficially, painting is “covering some kind of surface in paint”, and yet, for some reason, the ceiling you painted at home is not regarded as equally “good painting skills” as Michaelangelo’s, with regard to the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel.
All kinds of “Dark Psychology” enthusiasts on YouTube, authors of “Office Machiavelli” handbooks, etc, tell us that good communication skills are really a matter of persuasive speaking (or writing). And let’s not even get started on “pick-up artist” guides. Bleugh.
Not to get too philosophical, but here at 10almonds, we think that having good communication skills means being able to communicate ideas simply and clearly, and in a way that will benefit as many people as possible.
The implications of this for education are obvious, but what of other situations?
Conflict Resolution
Whether at work or at home or amongst friends or out in public, conflict will happen at some point. Even the most well-intentioned and conscientious partners, family, friends, colleagues, will eventually tread on our toes—or we, on theirs. Often because of misunderstandings, so much precious time will be lost needlessly. It’s good for neither schedule nor soul.
So, how to fix those situations?
I’m OK; You’re OK
In the category of “bestselling books that should have been an article at most”, a top-tier candidate is Thomas Harris’s “I’m OK; You’re OK”.
The (very good) premise of this (rather padded) book is that when seeking to resolve a conflict or potential conflict, we should look for a win-win:
- I’m not OK; you’re not OK ❌
- For example: “Yes, I screwed up and did this bad thing, but you too do bad things all the time”
- I’m OK; you’re not OK ❌
- For example: “It is not I who screwed up; this is actually all your fault”
- I’m not OK; you’re OK ❌
- For example: “I screwed up and am utterly beyond redemption; you should immediately divorce/disown/dismiss/defenestrate me”
- I’m OK; you’re OK ✅
- For example: “I did do this thing which turned out to be incorrect; in my defence it was because you said xyz, but I can understand why you said that, because…” and generally finding a win-win outcome.
So far, so simple.
“I”-Messages
In a conflict, it’s easy to get caught up in “you did this, you did that”, often rushing to assumptions about intent or meaning. And, the closer we are to the person in question, the more emotionally charged, and the more likely we are to do this as a knee-jerk response.
“How could you treat me this way?!” if we are talking to our spouse in a heated moment, perhaps, or “How can you treat a customer this way?!” if it’s a worker at Home Depot.
But the reality is that almost certainly neither our spouse nor the worker wanted to upset us.
Going on the attack will merely put them on the defensive, and they may even launch their own counterattack. It’s not good for anyone.
Instead, what really happened? Express it starting with the word “I”, rather than immediately putting it on the other person. Often our emotions require a little interrogation before they’ll tell us the truth, but it may be something like:
“I expected x, so when you did/said y instead, I was confused and hurt/frustrated/angry/etc”
Bonus: if your partner also understands this kind of communication situation, so much the better! Dark psychology be damned, everything is best when everyone knows the playbook and everyone is seeking the best outcome for all sides.
The Most Powerful “I”-Message Of All
Statements that start with “I” will, unless you are rules-lawyering in bad faith, tend to be less aggressive and thus prompt less defensiveness. An important tool for the toolbox, is:
“I need…”
Softly spoken, firmly if necessary, but gentle. If you do not express your needs, how can you expect anyone to fulfil them? Be that person a partner or a retail worker or anyone else. Probably they want to end the conflict too, so throw them a life-ring and they will (if they can, and are at least halfway sensible) grab it.
- “I need an apology”
- “I need a moment to cool down”
- “I need a refund”
- “I need some reassurance about…” (and detail)
Help the other person to help you!
Everything’s best when it’s you (plural) vs the problem, rather than you (plural) vs each other.
Apology Checklist
Does anyone else remember being forced to write an insincere letter of apology as a child, and the literary disaster that probably followed? As adults, we (hopefully) apologize when and if we mean it, and we want our apology to convey that.
What follows will seem very formal, but honestly, we recommend it in personal life as much as professional. It’s a ten-step apology, and you will forget these steps, so we recommend to copy and paste them into a Notes app or something, because this is of immeasurable value.
It’s good not just for when you want to apologize, but also, for when it’s you who needs an apology and needs to feel it’s sincere. Give your partner (if applicable) a copy of the checklist too!
- Statement of apology—say “I’m sorry”
- Name the offense—say what you did wrong
- Take responsibility for the offense—understand your part in the problem
- Attempt to explain the offense (not to excuse it)—how did it happen and why
- Convey emotions; show remorse
- Address the emotions/damage to the other person—show that you understand or even ask them how it affected them
- Admit fault—understand that you got it wrong and like other human beings you make mistakes
- Promise to be better—let them realize you’re trying to change
- Tell them how you will try to do it different next time and finally
- Request acceptance of the apology
Note: just because you request acceptance of the apology doesn’t mean they must give it. Maybe they won’t, or maybe they need time first. If they’re playing from this same playbook, they might say “I need some time to process this first” or such.
Want to really superpower your relationship? Read this together with your partner:
Hold Me Tight: Seven Conversations for a Lifetime of Love, and, as a bonus:
The Hold Me Tight Workbook: A Couple’s Guide for a Lifetime of Love
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- I’m not OK; you’re not OK ❌