Nonverbal Epiphany – by Dr. Stephen Furlich
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The subtitle of this book, “Steps To Improve Your Nonverbal Communication” suggests that this is principally an instructional book—it’s not. Rather, it’s mostly informational, and it is left to the reader to interpret what to do with that information.
But, what a lot of information!
And well-sourced, too: this book has scientific paper citations at a rate of one or two per page, with many diagrams and infographics too. It is, in effect, a treasure trove of physiological, psychological, and sociological data when it comes to nonverbal communication and the various factors that influence it.
So, what can you hope to gain from this book? A lot of sorting out of science vs suppositions, mostly.
From digit ratios to crossed arms, from eye-contact to attire, do things really mean what we’ve been told they mean?
And if they don’t, will people perceive them that way anyway, or will textbook rules go out the window in a real conversation? How about in real nonverbal interactions?
(What’s a nonverbal interaction? It’s the behavior exhibited between strangers in the street, it’s the impression given and received by your profile picture, things like that).
Bottom line is that this book is data, data, and more data. If ever you wanted to sort the psychology from the pseudoscience, this is the book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Size Breakfast Is Best, By Science?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Breakfast is the most important meal of the day”, the popular wisdom goes. But, what should it consist of, and how much should we be eating for breakfast?
It has been previously established that it is good if breakfast is the largest meal of the day:
…with meals getting progressively smaller thereafter.
Of course, very many people do the inverse: small (or skipped) breakfast, moderate lunch, larger dinner. This, however, is probably more a result of when eating fits around the modern industrialized workday (and thus gets normalized), rather than actual health considerations.
So, what’s the latest science?
A plucky band of researchers led by Dr. Karla-Alejandra Pérez-Vega investigated the importance of breakfast in the context of heart health. This research was done as part of a larger study into the effects of the Mediterranean Diet on cardiovascular health, so if anyone wants a quick recap before we carry on, then:
The Mediterranean Diet: What Is It Good For? ← the answer, by the way, is “pretty much everything”
…and there are also different versions that each use the Mediterranean Diet as the core, while focussing extra on a different area of health, including one to make it extra heart-healthy:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean ← most anti-inflammatory / gut-healthiest / heart-healthiest / brain-healthiest
What they found
In their sample population (n=383) of Spanish adults aged 55–75 with pre-diagnosed metabolic syndrome who, as part of the intervention of this 36-month interventional study, had now for the past 36 months been on a Mediterranean diet but without specific guidance on portion sizes:
- Participants with insufficient breakfast energy intake had the highest adiposity (which is a measure of body fat expressed as a percentage of total mass)
- Participants with low or high (but not moderate) breakfast energy intake had the larger BMI and waist circumference over time
- Participants with low or high (but not moderate) breakfast energy intake had higher triglyceride and lower HDL (good) cholesterol levels
- Participants who consumed 20–30% of their daily calories at breakfast enjoyed the greatest improvements in lipid profiles, with lower triglycerides and higher HDL (good) cholesterol levels
- Participants with lower breakfast quality (lower adherence to Mediterranean Diet) had higher blood pressure levels
- Participants with lower breakfast quality (lower adherence to Mediterranean Diet) had higher blood sugar levels
- Participants with lower breakfast quality (lower adherence to Mediterranean Diet) had lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (which is an indicator of kidney function)
- Participants with higher breakfast quality (higher adherence to Mediterranean Diet) had lower waist circumference, higher HDL cholesterol, and better kidney function
You can see the paper itself here in the Journal of Nutrition, Health, and Aging:
What this means
According to this research, the heart-healthiest breakfast is:
- not skipped
- Mediterranean Diet adherent
- within the range of of 20–30% of the total calories for the day
Want to make it even better?
Consider:
Before You Eat Breakfast: 3 Surprising Facts About Intermittent Fasting
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Toxic Gas That Sterilizes Medical Devices Prompts Safety Rule Update
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Over the past two years, Madeline Beal has heard frustration and even bewilderment during public meetings about ethylene oxide, a cancer-causing gas that is used to sterilize half of the medical devices in the U.S.
Beal, senior risk communication adviser for the Environmental Protection Agency, has fielded questions about why the agency took so long to alert people who live near facilities that emit the chemical about unusually high amounts of the carcinogenic gas in their neighborhoods. Residents asked why the EPA couldn’t close those facilities, and they wanted to know how many people had developed cancer from their exposure.
“If you’re upset by the information you’re hearing tonight, if you’re angry, if it scares you to think about risk to your family, those are totally reasonable responses,” Beal told an audience in Laredo, Texas, in September 2022. “We think the risk levels near this facility are too high.”
There are about 90 sterilizing plants in the U.S. that use ethylene oxide, and for decades companies used the chemical to sterilize medical products without drawing much attention. Many medical device-makers send their products to the plants to be sterilized before they are shipped, typically to medical distribution companies.
But people living around these facilities have been jolted in recent years by a succession of warnings about cancer risk from the federal government and media reports, an awareness that has also spawned protests and lawsuits alleging medical harm.
The EPA is expected to meet a March 1 court-ordered deadline to finalize tighter safety rules around how the toxic gas is used. The proposed changes come in the wake of a 2016 agency report that found that long-term exposure to ethylene oxide is more dangerous than was previously thought.
But the anticipated final rules — the agency’s first regulatory update on ethylene oxide emissions in more than a decade — are expected to face pushback. Medical device-makers worry stricter regulation will increase costs and may put patients at higher risk of infection from devices, ranging from surgical kits to catheters, due to deficient sterilization. The new rules are also not likely to satisfy the concerns of environmentalists or members of the public, who already have expressed frustration about how long it took the federal government to sound the alarm.
“We have been breathing this air for 40 years,” said Connie Waller, 70, who lives with her husband, David, 75, within two miles of such a sterilizing plant in Covington, Georgia, east of Atlanta. “The only way to stop these chemicals is to hit them in their pocketbook, to get their attention.”
The EPA says data shows that long-term exposure to ethylene oxide can increase the risk of breast cancer and cancers of the white blood cells, such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma, myeloma, and lymphocytic leukemia. It can irritate the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs, and has been linked to damage to the brain and nervous and reproductive systems. Children are potentially more vulnerable, as are workers routinely exposed to the chemical, EPA officials say. The agency calculates the risk based on how much of the gas is in the air or near the sterilizing facility, the distance a person is from the plant, and how long the person is exposed.
Waller said she was diagnosed with breast cancer in 2004 and that her husband was found to have non-Hodgkin lymphoma eight years later.
A 2022 study of communities living near a sterilization facility in Laredo found the rates of acute lymphocytic leukemia and breast cancer were greater than expected based on statewide rates, a difference that was statistically significant.
Beal, the EPA risk adviser, who regularly meets with community members, acknowledges the public’s concerns. “We don’t think it’s OK for you to be at increased risk from something that you have no control over, that’s near your house,” she said. “We are working as fast as we can to get that risk reduced with the powers that we have available to us.”
In the meantime, local and state governments and industry groups have scrambled to defuse public outcry.
Hundreds of personal injury cases have been filed in communities near sterilizing plants. In 2020, New Mexico’s then-attorney general filed a lawsuit against a plant in Santa Teresa, and that case is ongoing. In a case that settled last year in suburban Atlanta, a company agreed to pay $35 million to 79 people who alleged ethylene oxide used at the plant caused cancer and other injuries.
In Cook County, Illinois, a jury in 2022 awarded $363 million to a woman who alleged exposure to ethylene oxide gas led to her breast cancer diagnosis. But, in another Illinois case, a jury ruled that the sterilizing company was not liable for a woman’s blood cancer claim.
Greg Crist, chief advocacy officer for the Advanced Medical Technology Association, a medical device trade group that says ethylene oxide is an effective and reliable sterilant, attributes the spate of lawsuits to the litigious nature of trial attorneys.
“If they smell blood in the water, they’ll go after it,” Crist said.
Most states have at least one sterilizing plant. According to the EPA, a handful, like California and North Carolina, have gone further than the agency and the federal Clean Air Act to regulate ethylene oxide emissions. After a media and political firestorm raised awareness about the metro Atlanta facilities, Georgia started requiring sterilizing plants that use the gas to report all leaks.
The proposed rules the EPA is set to finalize would set lower emissions limits for chemical plants and commercial sterilizers and increase some safety requirements for workers within these facilities. The agency is expected to set an 18-month deadline for commercial sterilizers to come into compliance with the emissions rules.
That would help at facilities that “cut corners,” with lax pollution controls that allow emissions of the gas into nearby communities, said Richard Peltier, a professor of environmental health sciences at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst. Stronger regulation also prevents the plants from remaining under the radar. “One of the dirty secrets is that a lot of it is self-regulated or self-policed,” Peltier added.
But the proposed rules did not include protections for workers at off-site warehouses that store sterilized products, which can continue to emit ethylene oxide. They also did not require air testing around the facilities, prompting debate about how effective they would be in protecting the health of nearby residents.
Industry officials also don’t expect an alternative that is as broadly effective as ethylene oxide to be developed anytime soon, though they support researching other methods. Current alternatives include steam, radiation, and hydrogen peroxide vapor.
Increasing the use of alternatives can reduce industry dependence on “the crutch of ethylene oxide,” said Darya Minovi, senior analyst with the Union of Concerned Scientists, an advocacy group.
But meeting the new guidelines will be disruptive to the industry, Crist said. He estimates companies will spend upward of $500 million to comply with the new EPA rules and could struggle to meet the agency’s 18-month timetable. Sterilization companies will also have difficulty adjusting to new rules on how workers handle the gas without a dip in efficiency, Crist said.
The Food and Drug Administration, which regulates drugs and medical devices, is also watching the regulatory moves closely and worries the updated emissions rule could “present some unique challenges” if implemented as proposed, said Audra Harrison, an FDA spokesperson. “The FDA is concerned about the rule’s effects on the availability of medical devices,” she added.
Other groups, like the American Chemistry Council and the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, the state’s environmental agency, assert that ethylene oxide use isn’t as dangerous as the EPA says. The EPA’s toxicity assessment has “severe flaws” and is “overly conservative,” the council said in an emailed statement. Texas, which has several sterilizing plants, has said ethylene oxide isn’t as high a cancer risk as the agency claims, an assessment that the EPA has rejected.
Tracey Woodruff, a researcher at the University of California-San Francisco who previously worked at the EPA, said it can be hard for the agency to keep up with regulating chemicals like ethylene oxide because of constrained resources, the technical complications of rulemaking, and industry lobbying.
But she’s hopeful the EPA can strike a balance between its desire to reduce exposure and the desire of the FDA not to disrupt medical device sterilization. And scrutiny can also help the device sterilization industry think outside the box.
“We continue to discover these chemicals that we’ve already been exposed to were toxic, and we have high exposures,” she said. “Regulation is an innovation forcer.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
8 Signs On Your Breast You Shouldn’t Ignore
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Can you name the 8 signs that may indicate breast cancer? This video discusses them, and also shows what they look like on various different skintones:
Stay abreast:
Dr Simi Adedeji bids us watch out for:
- Inverted nipple: a newly inverted nipple (pointing inward or folded) should be checked by a doctor, especially if it’s a recent change.
- Flaky rash: a flaky, itchy, or red rash around the nipple or areola could indicate an underlying issue and should not be dismissed as just a skin condition.
- Tethering: skin pulling or denting, noticeable when raising your arms, may signal a deeper problem.
- Dimpling: skin resembling an orange peel (po orang sign) with dips and accentuated pores could indicate swelling or thickening and requires medical evaluation.
- Redness or heat: unusual warmth, redness, or tenderness in the breast, particularly if not breastfeeding, should be investigated.
- Nipple discharge: any unusual fluid from the nipple (be it yellow, green, milky, clear, or blood-stained) warrants attention, especially if spontaneous or only from one side.
- Change in size: sudden changes in the size or shape of one breast should not be ignored.
- Breast lump: a firm, irregular, or persistent lump in the breast, armpit, or collarbone area should be checked promptly, even if it’s not always harmful.
The above signs may indicate cancer or something else, but none of them are things that should be ignored (even if you get just one sign).
For more on each of these, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Hormone Therapy That Reduces Breast Cancer Risk & More
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Broad Beans vs Green Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing broad beans to green beans, we picked the broad.
Why?
It’s quite a straightforward one today:
In terms of macros, broad beans have 2.5x the protein, and slightly more fiber and carbs, so we pick the broad beans as the more nutrient-dense option here.
In the category of vitamins, broad beans have more of vitamins B1, B3, B9, and C, while green beans have more of vitamins A and B6 (with comparable margins of difference for both beans’ winning vitamins), so another win for broad beans, based on the 4:2 numerical advantage.
When it comes to minerals, broad beans have more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while green beans have more calcium and manganese. Again, comparable mostly margins of difference (except for broad beans bing 5x richer in selenium, which is a bit of an outlier, but it’s not because broad beans are an amazing source of selenium, but rather, that green beans have only a tiny amount), so it’s a clear 7:2 win for broad beans.
Adding up the three wins for broad beans makes an overall win for them, but by all means, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I Contain Multitudes – by Ed Yong
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A little while back we reviewed a book (Planet of Viruses) about the role of viruses in our lives, beyond the obvious. Today’s book gives the same treatment to microbes in general—mostly bacteria.
We all know about pathogens, and we all know about gut microbiota and that some (hopefully the majority) there are good for our health. This book covers those things too, but also much more.
Pulitzer Prize-winning science writer Ed Yong takes a big picture view (albeit, of some very small things) and looks at the many ways microbes keep us alive, directly or indirectly. From the microbes that convert certain proteins in breast milk into a form that babies can digest (yes, this means we produce nutrients in breast milk that have been evolved solely to feed that bacterium), to those without which agriculture would simply not work, we’re brought to realize how much our continued existence is contingent on our trillions of tiny friends.
The style throughout is easy-reading pop-science, very accessible. There’s also plenty in terms of practical take-away value, when it comes to adjusting our modern lives to better optimize the benefits we get from microbes—inside and out.
Bottom line: if you’d like to learn about the role of microbes in our life beyond “these ones are pathogens” and “these ones help our digestion”, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out I Contain Multitudes, and learn more about yours and those around you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pregnant women can now get a free RSV shot. What other vaccines do you need when you’re expecting?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From today, February 3, pregnant women in Australia will be eligible for a free RSV vaccine under the National Immunisation Program.
This vaccine is designed to protect young infants from severe RSV (respiratory syncytial virus). It does so by generating the production of antibodies against RSV in the mother, which then travel across the placenta to the baby.
While the RSV vaccine is a new addition to the National Immunisation Program, it’s one of three vaccines provided free for pregnant women under the program, alongside ones for influenza and whooping cough. Each offers important protection for newborn babies.
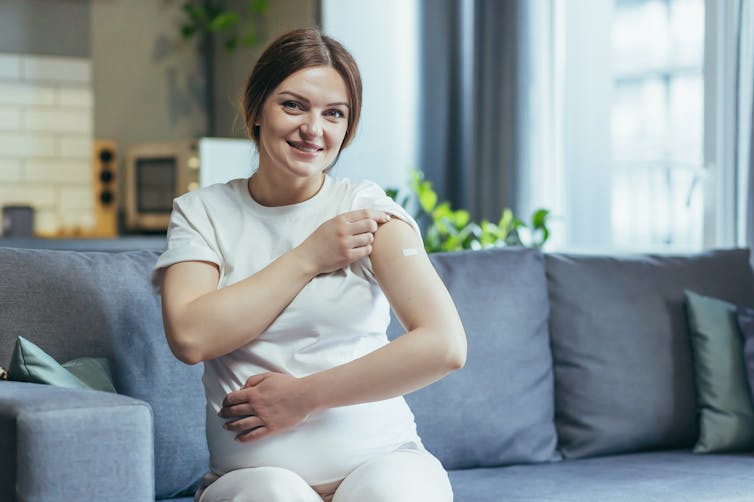
voronaman/Shutterstock The RSV vaccine
RSV is the most common cause of lower respiratory infections (bronchiolitis and pneumonia) in infants. It’s estimated that of every 100 infants born in Australia each year, at least two will be hospitalised with RSV by six months of age.
RSV infection is most common roughly between March and August in the southern hemisphere, but infection can occur year-round, especially in tropical areas.
The vaccine works by conferring passive immunity (from the mother) as opposed to active immunity (the baby’s own immune response). By the time the baby is born, their antibodies are sufficient to protect them during the first months of life when they are most vulnerable to severe RSV disease.
The RSV vaccine registered for use in pregnant women in Australia, Abrysvo, has been used since 2023 in the Americas and Europe. Real-world experience there shows it’s working well.
For example, over the 2024 RSV season in Argentina, it was found to prevent 72.7% of lower respiratory tract infections caused by RSV and requiring hospitalisation in infants aged 0–3 months, and 68% among those aged 0–6 months. This research noted three deaths from RSV, all in infants whose mothers did not receive the RSV vaccine during pregnancy.
This was similar to protection seen in a large multinational clinical trial that compared babies born to mothers who received this RSV vaccine with babies born to mothers who received a placebo. This study found the vaccine prevented 82.4% of severe cases of RSV in infants aged under three months, and 70% under six months, and that the vaccine was safe.
Vaccinating mothers during pregnancy protects the newborn baby. StoryTime Studio/Shutterstock In addition to the maternal vaccine, nirsevimab, a long-acting monoclonal antibody, provides effective protection against severe RSV disease. It’s delivered to the baby by an intramuscular injection, usually in the thigh.
Nirsevimab is recommended for babies born to women who did not receive an RSV vaccine during pregnancy, or who are born within two weeks of their mother having received the shot (most likely if they’re born prematurely). It may also be recommended for babies who are at higher risk of RSV due to a medical condition, even if their mother was vaccinated.
Nirsevimab is not funded under the National Immunisation Program, but is covered under various state and territory-based programs for infants of mothers who fall into the above categories.
But now we have a safe and effective RSV vaccine for pregnancy, all pregnant women should be encouraged to receive it as the first line of prevention. This will maximise the number of babies protected during their first months of life.
Flu and whooping cough
It’s also important pregnant women continue to receive flu and whooping cough vaccines in 2025. Like the RSV vaccine, these protect infants by passing antibodies from mother to baby.
There has been a large whooping cough outbreak in Australia in recent months, including a death of a two-month-old infant in Queensland in November 2024.
The whooping cough vaccine, given in combination with diphtheria and tetanus, prevents more than 90% of whooping cough cases in babies too young to receive their first whooping cough vaccine dose.
Similarly, influenza can be deadly in young babies, and maternal flu vaccination substantially reduces hospital visits associated with influenza for babies under six months. Flu can also be serious for pregnant women, so the vaccine offers important protection for the mother as well.
COVID vaccines are safe in pregnancy, but unless a woman is otherwise eligible, they’re not routinely recommended. You can discuss this with your health-care provider.
When and where can you get vaccinated?
Pregnant women can receive these vaccines during antenatal visits through their GP or in a specialised antenatal clinic.
The flu vaccine is recommended at any time during pregnancy, the whooping cough vaccine from 20 weeks (ideally before 32 weeks), and the RSV vaccine from 28 weeks (before 36 weeks).
It’s safe to receive multiple vaccinations at the same clinic visit.
The RSV vaccine is now available for pregnant women under the National Immunisation Program. Olga Rolenko/Shutterstock We know vaccination rates have declined in a variety of groups since the pandemic, and there’s evidence emerging that suggests this trend has occurred in pregnant women too.
A recent preprint (a study yet to be peer-reviewed) found a decrease of nearly ten percentage points in flu vaccine coverage among pregnant women in New South Wales, from 58.8% in 2020 to 49.1% in 2022. The research showed a smaller drop of 1.4 percentage points for whooping cough, from 79% in 2020 to 77.6% in 2022.
It’s important to work to improve vaccination rates during pregnancy to give babies the best protection in their first months of life.
We know pregnant women would like to receive information about new and routine maternal vaccines early in pregnancy. In particular, many pregnant women want to understand how vaccines are tested for safety, and their effectiveness, which was evident during COVID.
GPs and midwives are trusted sources of information on vaccines in pregnancy. There’s also information available online on Sharing Knowledge About Immunisation, a collaboration led by the National Centre for Immunisation Research and Surveillance.
Archana Koirala, Paediatrician and Infectious Diseases Specialist, University of Sydney; Bianca Middleton, Senior Research Fellow, Menzies School of Health Research; Margie Danchin, Professor of Paediatrics and vaccinologist, Royal Childrens Hospital, University of Melbourne and Murdoch Childrens Research Institute (MCRI); Associate Dean International, University of Melbourne, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute; Peter McIntyre, Professor in Women’s and Children’s Health, University of Otago, and Rebecca Doyle, Adjunct Research Fellow, School of Nursing, Midwifery and Social Work, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: