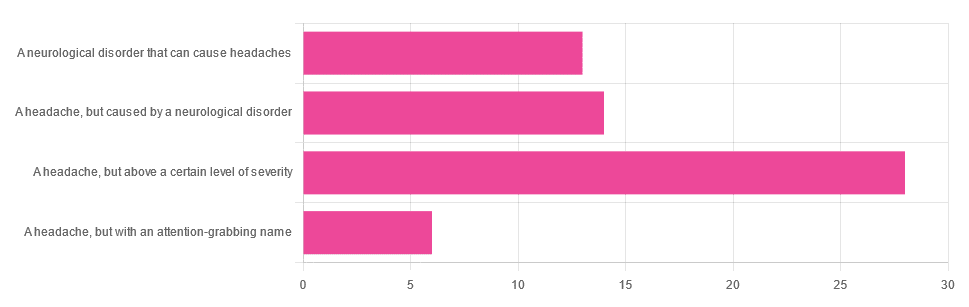Nonverbal Epiphany – by Dr. Stephen Furlich
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The subtitle of this book, “Steps To Improve Your Nonverbal Communication” suggests that this is principally an instructional book—it’s not. Rather, it’s mostly informational, and it is left to the reader to interpret what to do with that information.
But, what a lot of information!
And well-sourced, too: this book has scientific paper citations at a rate of one or two per page, with many diagrams and infographics too. It is, in effect, a treasure trove of physiological, psychological, and sociological data when it comes to nonverbal communication and the various factors that influence it.
So, what can you hope to gain from this book? A lot of sorting out of science vs suppositions, mostly.
From digit ratios to crossed arms, from eye-contact to attire, do things really mean what we’ve been told they mean?
And if they don’t, will people perceive them that way anyway, or will textbook rules go out the window in a real conversation? How about in real nonverbal interactions?
(What’s a nonverbal interaction? It’s the behavior exhibited between strangers in the street, it’s the impression given and received by your profile picture, things like that).
Bottom line is that this book is data, data, and more data. If ever you wanted to sort the psychology from the pseudoscience, this is the book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Debunking the myth that vaccines cause autism
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The myth that autism is linked to childhood vaccines first appeared in a 1998 study by British physician Dr. Andrew Wakefield. The study was later retracted, and Wakefield was discredited. But nearly three decades after the study’s publication, the myth persists, championed by activists, political leaders, and even potential health officials.
There is overwhelming evidence that there is no link between vaccines and autism. “No one has any real or solid evidence that vaccines cause autism,” says Catherine Lord, a psychologist and autism researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Here are just some of the many reasons that we know vaccines don’t cause autism.
The Wakefield study has been thoroughly discredited
In 1998, the Lancet published a study describing a small group of children who reportedly had bowel inflammation and developed autism within a month of getting the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. The study proposed that the vaccination triggered bowel inflammation and developmental delays, including autism. Lead author Andrew Wakefield coined the term “autistic enterocolitis” to describe the condition he and his colleagues claimed to have discovered.
The study received significant media attention and immediate criticism from scientists, who pointed out the study’s small size, lack of controls, and insufficient evidence to support its conclusions.
Subsequent research published over the next few years refuted Wakefield’s findings. A 1999 Lancet study found no link between autism and the MMR vaccine, and a 2001 study found no evidence of a link or the existence of so-called autistic enterocolitis.
In 2010, the Lancet finally retracted Wakefield’s fraudulent study, noting that “several elements” of the study were “incorrect” and that the experiments carried out on children had not been approved by an ethics board. The journal’s editor called the paper’s conclusions “utterly false.”
A few months later, Wakefield was stripped of his medical license by the United Kingdom’s General Medical Council. The council deemed Wakefield “dishonest and irresponsible” and concluded that he conducted unethical experiments on children.
The committee’s investigation also revealed that, less than a year before he published his study claiming that the MMR vaccine was linked to bowel inflammation that triggered autism, Wakefield filed a patent for a standalone measles vaccine and inflammatory bowel disease treatment.
Thimerosal was removed from childhood vaccines in 2001—with no effect on autism rates
A 2003 study published by a conservative group known for promoting anti-science myths—including that HIV doesn’t cause AIDS—first proposed that the preservative thimerosal in childhood vaccines is linked to autism. This supposed link was subsequently disproven.
Thimerosal is added in small amounts to some vaccines to prevent dangerous bacterial and fungal contamination. The substance contains ethylmercury, a form of mercury that the body quickly and safely processes in small doses.
Ethylmercury is different from methylmercury, a far more dangerous form of mercury that is toxic at low doses. By contrast, the small amount of thimerosal in some vaccines is harmless to humans and is equal to the amount of mercury in a can of tuna.
The preservative was removed from childhood vaccines as a precautionary measure in 2001. With the exception of some flu shots, no childhood vaccine contains the preservative and hasn’t for more than two decades. Autism rates have not decreased as a result of thimerosal being removed from childhood immunization vaccines. While some types of the annual flu vaccine contain thimerosal, you can get one without it.
Extensive research also shows that neither thimerosal nor methylmercury at any dose is linked to autism. A 2008 study of statewide California data found that autism rates “increased consistently for children born from 1989 through 2003, inclusive of the period when exposure to [thimerosal-containing vaccines] has declined.”
Autism rates are the same in vaccinated and unvaccinated children
Vaccine opponents often falsely claim that vaccinated children are more likely than unvaccinated children to develop autism. Decades of research disprove this false claim.
A 2002 analysis of every child born in Denmark over eight years found that children who received MMR vaccines were no more likely to be diagnosed with autism than unvaccinated children.
A 2015 study of over 95,000 U.S. siblings found that MMR vaccination is not associated with increased autism diagnosis. This was true even among the siblings of children with autism, who are seven times more likely to develop autism than children without an autistic sibling.
And a 2018 study found some evidence that children with autism—and their siblings—were more likely to be unvaccinated or under-vaccinated than children without autism.
Vaccination also has no impact on autism rates at the population level, regardless of the age at which children get vaccinated.
“In comparing countries that have different timing and levels of vaccination … there’s no difference in autism,” says Lord. “You can look at different countries with different rates of autism, and there’s no relationship between the rates of autism and vaccinations.”
Countries such as Taiwan, Tunisia, Turkey, and Morocco, which have some of the world’s lowest autism rates, have childhood immunization rates that are nearly identical to countries with the highest autism rates, including Sweden, Japan, Brunei, and Singapore.
Improved awareness and diagnosis play a role in rising autism rates
Autism was first described in 1911 when it was considered to be a form of severe schizophrenia. Over a century later, our understanding of autism has changed drastically, as have diagnostic standards.
A 2013 scientific article describing how medical and social perceptions of autism have evolved explains that “the diagnoses of schizophrenia, psychosis and autism in children were largely interchangeable during the 1940s and 1950s.” Beginning in the 1960s, methods of diagnosing autism improved, “increasing the number of children who were considered to display autistic traits.”
The autism diagnosis was changed to autism spectrum disorder in 2013. “This category is now very broad, which was an intentional choice to help provide services to the greatest number of people who might need them,” writes Gideon Meyerowitz-Katz, an epidemiologist and creator of the popular Health Nerd blog.
“Rather than the severe intellectual disability of the 1940s and 50s, [autism spectrum disorder] is a group of behaviours that can be any severity as long as they are persistent and impact people’s daily functioning in a significant way.”
For more information about autism, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Death by Sitting – by Carolyne Thompson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may be wondering: is this a lot of words to say “sit down less”?
And the answer is: there’s a lot more in here than that. Of course, yes, “sit down less” is an important take-away, but there’s a lot about the specific problems caused by sitting in chairs, the health risks are that are increased and how, and the early warning signs to watch out for.
After these chapters of woe, most of the book is given over to solutions; about taking standing and walking breaks, tying movement to productivity, why exercise alone is not enough to offset the damage of sitting, relearning ergonomic posture in the context of mitigating the harm, psychological shifts to break the habit of sitting, redefining social norms around sitting and socializing, rewiring one’s body and retraining better movements as well as postures to always immediately move out of if one finds oneself in, and much much more.
The style is light and easy to read, while still including scientific research as appropriate along with practical, actionable advice.
Bottom line: if you’d like to do better for your body than slowly killing it for however many hours a day, then this book has a wealth of advice far beyond the obvious (but important!) “sit less”.
Share This Post
-
No More Aches/Tripping When Walking: Strengthen This Oft-Neglected Muscle
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Aches and pains while walking (in the feet, shins, and/or knees), as well as fatigue, are actually mostly about the oft-neglected tibialis anterior muscle.
Fortunately, it’s quite easy to strengthen if you know how:
All about the tib
The tibialis anterior is located at the front of the shin. It lifts the toes when walking, preventing trips and stumbles. Weakness in this muscle can cause fatigue as other muscles compensate, tripping as feet catch the floor, and/or general instability while walking.
Happily, there is an easy exercise to do that gives results quite quickly:
Steps:
- Stand with back and shoulders against a wall, feet 12 inches away.
- Slightly bend knees and keep posture relaxed.
- Lift toes off the ground, hold for a few seconds, then lower.
- Repeat for 10–15 reps.
To increase difficulty:
- Step further away from the wall for more ankle movement.
- Perform a “Tib Plank” by lifting hips off the wall and keeping knees straight.
It’s recommended to do 3 sets per day, with 1-minute rests between.
For more on all of this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
The Secret to Better Squats: Foot, Knee, & Ankle Mobility
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Pear vs Prickly Pear – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pear to prickly pear, we picked the prickly.
Why?
Both of these fruits are fine and worthy choices, but the prickly pear wins out in nutritional density.
Looking at the macros to start with, the prickly pear is higher in fiber and lower in carbs, resulting in a much lower glycemic index. However, non-prickly pears are already low GI, so this is not a huge matter. Whether it’s pear’s GI of 38 or prickly pear’s GI of 7, you’re unlikely to experience a glucose spike.
In the category of vitamins, pear has a little more of vitamins B5, B9, E, K, and choline, but the margins are tiny. On the other hand, prickly pear has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, and C, with much larger margins of difference (except vitamin B1; that’s still quite close). Even before taking margins of difference into account, this is a slight win for prickly pear.
When it comes to minerals, things are more pronounced; pear has more manganese, while prickly pear has more calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc.
In short, both pears are great (so do enjoy the pair), but prickly pear is the clear winner where one must be declared.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Apple vs Pear – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Migraine Mythbusting
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Migraine: When Headaches Are The Tip Of The Neurological Iceberg
Yesterday, we asked you “What is a migraine?” and got the above-depicted, below-described spread of responses:
- Just under 46% said “a headache, but above a certain level of severity”
- Just under 23% said “a headache, but caused by a neurological disorder”
- Just over 21% said “a neurological disorder that can cause headaches”
- Just under 10% said “a headache, but with an attention-grabbing name”
So… What does the science say?
A migraine is a headache, but above a certain level of severity: True or False?
While that’s usually a very noticeable part of it… That’s only one part of it, and not a required diagnostic criterion. So, in terms of defining what a migraine is, False.
Indeed, migraine may occur without any headache, let alone a severe one, for example: Abdominal Migraine—though this is much less well-researched than the more common with-headache varieties.
Here are the defining characteristics of a migraine, with the handy mnemonic 5-4-3-2-1:
- 5 or more attacks
- 4 hours to 3 days in duration
- 2 or more of the following:
- Unilateral (affects only one side of the head)
- Pulsating
- Moderate or severe pain intensity
- Worsened by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity
- 1 or more of the following:
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Sensitivity to both light and sound
Source: Cephalalgia | ICHD-II Classification: Parts 1–3: Primary, Secondary and Other
As one of our subscribers wrote:
❝I have chronic migraine, and it is NOT fun. It takes away from my enjoyment of family activities, time with friends, and even enjoying alone time. Anyone who says a migraine is just a bad headache has not had to deal with vertigo, nausea, loss of balance, photophobia, light sensitivity, or a host of other symptoms.❞
Migraine is a neurological disorder: True or False?
True! While the underlying causes aren’t known, what is known is that there are genetic and neurological factors at play.
❝Migraine is a recurrent, disabling neurological disorder. The World Health Organization ranks migraine as the most prevalent, disabling, long-term neurological condition when taking into account years lost due to disability.
Considerable progress has been made in elucidating the pathophysiological mechanisms of migraine, associated genetic factors that may influence susceptibility to the disease❞
Source: JHP | Mechanisms of migraine as a chronic evolutive condition
Migraine is just a headache with a more attention-grabbing name: True or False?
Clearly, False.
As we’ve already covered why above, we’ll just close today with a nod to an old joke amongst people with chronic illnesses in general:
“Are you just saying that because you want attention?”
“Yes… Medical attention!”
Want to learn more?
You can find a lot of resources at…
NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders & Stroke | Migraine
and…
The Migraine Trust ← helpfully, this one has a “Calm mode” to tone down the colorscheme of the website!
Particularly useful from the above site are its pages:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Where Nutrition Meets Habits!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Where Nutrition Meets Habits…
This is Claudia Canu, MSc., INESEM. She’s on a mission to change the way we eat:
Often, diet is a case of…
- Healthy
- Easy
- Cheap
(choose two)
She wants to make it all three, and tasty too. She has her work cut out for her, but she’s already blazed quite a trail personally:
❝Nine months before turning 40 years old, I set a challenge for myself: Arrive to the day I turn 40 as the best possible version of myself, physically, mentally and emotionally.❞
~ Claudia Canu
In Her Own Words: My Journey To My Healthy 40s
And it really was quite a journey:
- September: Changes That Destabilize
- October: Looking for Focus
- November: New Habits
- December: Analyzing The First Results
- January: Traveling & Perfectionism
- February: Habits & Goals
- March: Connection, Cravings, & Organization
- April: Physical & Emotional Changes After 7 Months
- May: Reflections & Considerations
- June: Challenge Is Over
For those of us who’d like the short-cut rather than a nine-month quasi-spiritual journey… based on both her experience, and her academic and professional background in nutrition, her main priorities that she settled on were:
- Making meals actually nutritionally balanced, which meant re-thinking what she thought a meal “should” be
- Making nutritionally balanced meals that didn’t require a lot of skill and/or resources
- That’s it!
But, easier said than done… Where to begin?
She shares an extensive list of recipes, from meals to snacks (I thought I was the only one who made coffee overnight oats!), but the most important thing from her is:
Claudia’s 10 Guiding Principles:
- Buy only fresh ingredients that you are going to cook yourself. If you decide to buy pre-cooked ones, make sure they do not have added ingredients, especially sugar (in all its forms).
- Use easy and simple cooking methods.
- Change ingredients every time you prepare your meals.
- Prepare large quantities for three or four days.
- Store the food separately in tightly closed Tupperware.
- Organize yourself to always have ready-to-eat food in the fridge.
- When hungry, mix the ingredients in the ideal amounts to cover the needs of your body.
- Chew well and take the time to taste your food.
- Eat foods that you like and enjoy.
- Do not overeat but don’t undereat either.
We have only two quibbles with this fine list, which are:
About Ingredients!
Depending on what’s available around you, frozen and/or tinned “one-ingredient” foods can be as nutritional as (if not more nutritional than) fresh ones. By “one-ingredient” foods here we mean that if you buy a frozen pack of chopped onions, the ingredients list will be: “chopped onions”. If you buy a tin of tomatoes, the ingredients will say “Tomatoes” or at most “Tomatoes, Tomato Juice”, for example.
She does list the ingredients she keeps in; the idea that with these in the kitchen, you’ll never be in the position of “oh, we don’t have much in, I guess it’s a pizza delivery night” or “well there are some chicken nuggets at the back of the freezer”.
Check Out And Plan: 10 Types Of Ingredients You Should Always Keep In Your Kitchen
Here Today, Gone Tomorrow?
Preparing large quantities for three or four days can result in food for one or two days if the food is unduly delicious
But! Claudia has a remedy for that:
Read: How To Eliminate Food Cravings And What To Do When They Win
Anyway, there’s a wealth of resources in the above-linked pages, so do check them out!
Perhaps the biggest take-away is to ask yourself:
“What are my guiding principles when it comes to food?”
If you don’t have a ready answer, maybe it’s time to tackle that—whether Claudia’s way or your own!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: