Never Enough – by Dr. Judith Grisel
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed books about addiction before—specifically about alcohol, at least. This one’s more general in that it covers different addictions.
On the other hand, it’s also more specific, in that it covers them from the author’s field: neuroscience.
…and experience too. The author had a plethora of addictions (the serious kind), got sober, and then undertook to study neuroscience. Her hope was to help others avoid, or escape from the same as‚ what she went through.
Dr. Grisel (as she now is) takes a methodical approach in this book. She works her way through the addictive mechanisms of a broad selection of common drugs, explaining each.
The focus here is on neutral explanations, rather than the propagandizing scaremongering that failed at least one generation. Why each drug is alluring, what it really does do—and the neurological price it exacts, down to the molecular level.
She also covers risk factors for addiction; genetic, epigenetic, and environmental. There’s no “if you were stronger”, or “these people made bad choices”, so much as… Many addicts were, in effect, sabotaged from before birth.
That doesn’t mean that to become addicted or not is just fate, but it does mean… There but for the grace of factors completely outside of our control go we.
Why is this useful to us, be we a reader without any meaningful addiction (we’re not counting coffee etc here)? Well, as this book illustrates and explains, many of us could be one (more) mishap away from a crippling addiction and not know it. Forewarned is forearmed.
Bottom line: almost all of us are, have been, or will be touched by addiction in some way. Either directly, or a loved one, or a loved one’s loved one, or perhaps a parent who gave us an epigenetic misfortune. This book gives understanding that can help.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healthy Brain, Happy Life – by Dr. Wendy Suzuki
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We talked about Dr. Wendy Suzuki’s research in the category of exercise and brain-benefits in our main feature the other day. But she has more to say than we can fit into an article!
This book chronicles her discoveries, through her work in memory and neuroplasticity, to her discoveries about exercise, and her dive into broader neurology-based mental health. So what does neurology-based mental health look like?
The answer is: mitigating brain-busters such as stress and anxiety, revitalizing a fatigued brain, boosting creativity, and other such benefits.
Does she argue that exercise is a cure-all? No, not quite. Sometimes there are other things she’s recommending (such as in her chapter on challenging the neurobiology of the stress response, or her chapter on meditation and the brain).
The writing style is mostly casual, interspersed with occasional mini-lectures (complete with diagrams and other illustrations), and is very readable and informative throughout.
Bottom line: if you’d like the more in-depth details of Dr. Suzuki’s work, this book is a very accessible way to get 320 pages of that!
Click here to check out Healthy Brain, Happy Life, and give yours the best!
Share This Post
-
Dr. Dean Ornish’s Program For Reversing Heart Disease – by Dr. Dean Ornish
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Dr. Ornish’s “Undo It!” which is about reversing many kinds of chronic diseases (not all, alas, but quite a few) by undercutting their common etiologies, such as inflammation, insulin resistance, and so forth.
This book is entirely consistent with that one, but the focus here is (as the title says) specifically on reversing heart disease.
Of course, it does not require you to already have heart disease—if you do, well, getting onto this is better sooner than later. If you don’t, and are “merely” in a risk zone, or even just want to be proactive about your heart health, then this book will stand you in good stead.
The book covers all the lifestyle things you’d expect it to (especially diet, but also exercise, and not just “quit smoking” but also how, things like that), and possibly some things you might not expect (chapters on more psychological factors that have a big impact on heart health).
There are recipes (157 pages of them; they are plant-based and good) and there is a 21-day meal plan to get you going.
The style is a little dated (written in the 90s), but the content doesn’t suffer for it, having been updated over the years in any case.
Bottom line: if you want a holistic approach to taking care of your heart that’s not extreme and/but is very effective, then well, you’ve found it.
Share This Post
-
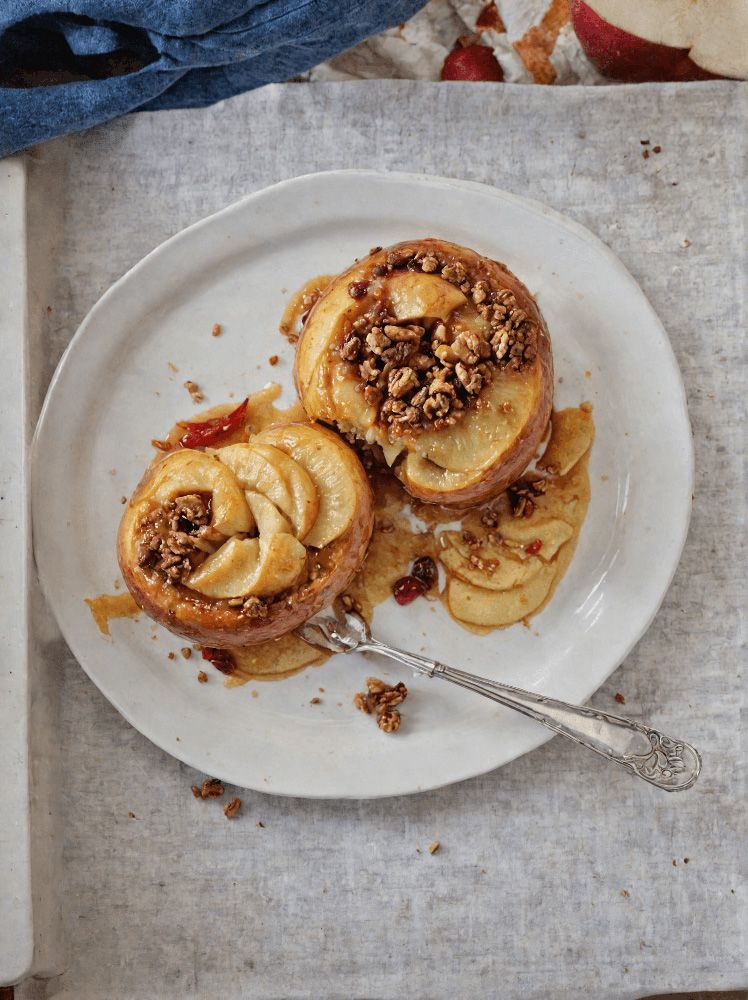
Superfood Baked Apples
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Superfoods, and super-tasty. This is a healthy twist on a classic; your blood sugars will thank you for choosing this tasty sweet delight. It’s also packed with nutrients!
You will need
- 2 large firm baking apples, cored but not peeled
- 1/2 cup chopped walnuts
- 3 tbsp goji berries, rehydrated (soak them in warm water for 10–15minutes and drain)
- 1 tbsp honey, or maple syrup, per your preference (this writer is also a fan of aged balsamic vinegar for its strong flavor and much milder sweetness. If you don’t like things to be too sweet, this is the option for you)
- 2 tsp ground sweet cinnamon
- 1 tsp ground ginger
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 180℃ / 350℉ / gas mark 4
2) Mix the chopped walnuts with the goji berries and the honey (or whatever you used instead of the honey) as well as the sweet cinnamon and the ginger.
3) Place the apples in shallow baking dish, and use the mixture you just made to stuff their holes.
4) Add 1/2 cup water to the dish, around the apples. Cover gently with foil, and bake until soft.
Tip: check them every 20 minutes; they may be done in 40 or it may take 60; in honesty it depends on your oven. If unsure, cook them for longer at a lower temperature.
5) Serve warm.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose C’s
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- The Sugary Food That Lowers Blood Sugars
- Honey vs Maple Syrup – Which is Healthier?
- A Tale Of Two Cinnamons ← this is important, about why we chose the sweet cinnamon
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Your Science-Based Guide To Losing Fat & Toning Up
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This health coach researched the science and crunched the numbers so that you don’t have to:
Body by the numbers
Let’s get mathematical:
Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) consists of:
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): 70% of daily calorie burn (basic body functions, of which the brain is the single biggest calorie-burner)
- Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT): 15% (the normal movements that occur as you go about your daily life)
- Exercise Activity: 5% (actual workouts, often overestimated)
- Thermic Effect of Food (TEF): 10% (energy needed for digestion)
Basic BMR estimate:
- Women: body weight (kg) × 0.9 × 24
- Men: body weight (kg) × 24
But yours may differ, so if you have a fitness tracker or other gadget that estimates it for you, go with that!
Note: muscle burns calories just to maintain it, making muscle mass crucial to increasing one’s BMR.
And now some notes about running a caloric deficit:
- Safe caloric deficit: no more than 500 calories/day.
- Absolute minimum daily intake: 1,200 calories (women), 1,500 calories (men) (not sustainable long-term).
- Tracking calories is useful but not always accurate.
- Extreme calorie restriction slows metabolism and can lead to binge-eating.
- Your body will adjust to calorie deficits over time, making long-term drastic deficits ineffective.
Diet for fat loss & muscle gain:
- Protein Intake: 1.5–2g per pound of body weight.
- Aim for 30g of protein per meal (supports muscle & satiety).
- Protein has a higher thermic effect (20-30%) than carbs (5-10%) & fats (2-4%), meaning more calories are burned digesting protein.
- Fats are essential for hormone health & satiety (0.5–1g per kg of body weight).
- Carbs should be complex (whole grains, vegetables, fruits, etc.).
- Avoid excessive simple carbs (sugar, white bread, white pasta, etc) to maintain stable hunger signals.
- Hydration is key for appetite control & metabolism (often mistaken for hunger).
Exercise for fat loss & muscle gain:
- Resistance training (3-5x per week) is essential for toning & metabolism.
- Cardio is NOT necessary for fat loss but good for overall health.
- NEAT (non-exercise movement) burns significant calories (walking, taking stairs, fidgeting, etc.).
- “Hot girl walks” & daily movement can significantly aid weight loss.
- Women won’t get “bulky” from weight training unless they eat like a bodybuilder (i.e. several times the daily caloric requirement).
Some closing words in addition:
Poor sleep reduces fat loss by 50% and increases hunger. High stress levels lead to fat retention and cravings for unhealthy foods. Thus, managing stress & sleep is as important as diet & exercise for body transformation!
For more on all of this (plus the sources for the science), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Lose Weight (Healthily) ← our own main feature about such; we took a less numbers-based, more principles-based, approach. Both approaches work, so go with whichever suits your personal preference more!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Off-Button For Your Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Off-Button For Your Brain
We evolved our emotions for our own benefit as a species. Even the “negative” ones:
- Stress keeps us safe by making sure we take important situations seriously
- Anger keeps us safe by protecting us from threats
- Disgust keeps us safe by helping us to avoid things that might cause disease
- Anxiety keeps us safe by ensuring we don’t get complacent
- Guilt keeps us safe by ensuring we can function as a community
- Sadness keeps us safe by ensuring we value things that are important to us, and learn to become averse to losing them
- …and so on
But that’s not always useful. What was once a very good response to a common source of fear (for example, a sabre-toothed tiger) is no longer a helpful response to a modern source of fear (for example, an important interview).
Sometimes it’s good to take the time and energy to process our feelings and the event(s) that prompted those feelings. Sometimes, we don’t have that luxury.
For example, if you are stressed about your workload? Then staying awake half the night thinking about it is only going to make your problems worse the next day.
So, how to switch that off, or at least put a pause on it?
The human mind tends to have a “negative bias”, evolved for our own protection. If something is “good enough”, we don’t need to worry about it, so we move on to the next thing, until we find something that is a problem, then we dwell on that. That’s not always helpful, and the good news is, there’s a way to flip the switch on this process:
Identifying the positive, and releasing the rest
This exercise can be done when you’re trying to sleep, or at any time you need a calmer, quieter mind.
Take a moment to notice whatever you’re experiencing.
If it’s something that feels good, or neutral, identify it with a single word. For example:
- Warmth
- Soft
- Security
- Smile
- Peace
If it’s something that feels bad, then instead of identifying it, simply say (or think) to yourself “release”.
You can’t fight bad feelings with force, and you can’t “just not think about them”, but you can dismiss them as soon as they arrive and move onto the next thing. So where your train of thought may previously have been:
It’s good to be in bed ➔ I have eight hours to sleep before my meeting ➔ Have I done everything I was supposed to? ➔ I hope that what I’ve done is good enough ➔ [Mentally rehearsing how the meeting might go] ➔ [various disaster preparations] ➔ What am I even going to wear? ➔ Ugh I forgot to do the laundry ➔ That reminds the electricity bill is due ➔ Etc
Now your train of thought may be more like:
Relief ➔ Rest ➔ But my meeti—release ➔ If I—release ➔ soft ➔ comfort ➔ release ➔ pillow ➔ smile ➔ release ➔ [and before you know it you’re asleep]
And if you do this in a situation where you’re not going to sleep? Same process, just a more wakeful result, for example, let’s move the scene to an office where your meeting will shortly take place:
Five minutes to go ➔ What a day ➔ Ok, I’d better clear my head a bit ➔ release ➔ release ➔ breath ➔ light ➔ chair ➔ what if—release ➔ prepared ➔ ready ➔ calm ➔ [and before you know it you’re impressing your work associate with your calm preparedness]
In summary:
If you need to stop a train of thought, this method may help. Especially if you’re in a situation where you can’t use some external distraction to keep you from thinking about the bad thing!
You’re probably still going to have to deal with the Bad Thing™ at some point—you’ve just recognized that now isn’t the time for that. Mentally postpone that so that you will be well-rested when you choose to deal with the Bad Thing™ later at your convenience.
So remember: identify the positive (with a single word), and anything else, just release.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Fascinating Truth About Aspartame, Cancer, & Neurotoxicity
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is Aspartame’s Reputation Well-Deserved?
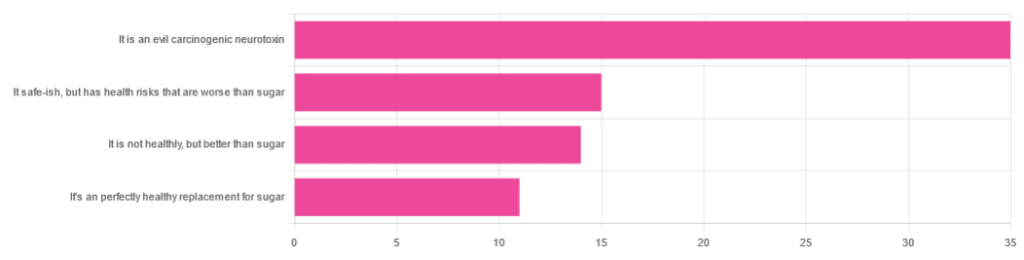
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your health-related opinions on aspartame, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 47% said “It is an evil carcinogenic neurotoxin”
- 20% said “It is safe-ish, but has health risks that are worse than sugar”
- About 19% said “It is not healthy, but better than sugar”
- About 15% said “It’s a perfectly healthy replacement for sugar”
But what does the science say?
Aspartame is carcinogenic: True or False?
False, assuming consuming it in moderation. In excess, almost anything can cause cancer (oxygen is a fine example). But for all meaningful purposes, aspartame does not appear to be carcinogenic. For example,
❝The results of these studies showed no evidence that these sweeteners cause cancer or other harms in people.❞
~ NIH | National Cancer Institute
Source: Artificial Sweeteners and Cancer
Plenty of studies and reviews have also confirmed this; here are some examples:
- Evaluation of aspartame cancer epidemiology studies based on quality appraisal criteria
- Aspartame, low-calorie sweeteners and disease: Regulatory safety and epidemiological issues
- Aspartame: A review of genotoxicity data
Why then do so many people believe it causes cancer, despite all the evidence against it?
Well, there was a small study involving giving megadoses to rats, which did increase their cancer risk. So of course, the popular press took that and ran with it.
But those results have not been achieved outside of rats, and human studies great and small have all been overwhelmingly conclusive that moderate consumption of aspartame has no effect on cancer risk.
Aspartame is a neurotoxin: True or False?
False, again assuming moderate consumption. If you’re a rat being injected with a megadose, your experience may vary. But a human enjoying a diet soda, the aspartame isn’t the part that’s doing you harm, so far as we know.
For example, the European Food Safety Agency’s scientific review panel concluded:
❝there is still no substantive evidence that aspartame can induce such effects❞
~ Dr. Atkin et al (it was a pan-European team of 21 experts in the field)
Source: Report on the Meeting on Aspartame with National Experts
See also,
❝The data from the extensive investigations into the possibility of neurotoxic effects of aspartame, in general, do not support the hypothesis that aspartame in the human diet will affect nervous system function, learning or behavior.
The weight of existing evidence is that aspartame is safe at current levels of consumption as a nonnutritive sweetener.❞
and
❝The safety testing of aspartame has gone well beyond that required to evaluate the safety of a food additive.
When all the research on aspartame, including evaluations in both the premarketing and postmarketing periods, is examined as a whole, it is clear that aspartame is safe, and there are no unresolved questions regarding its safety under conditions of intended use.❞
Source: Regulatory Toxicology & Pharmacology | Aspartame: Review of Safety
Why then do many people believe it is a neurotoxin? This one can be traced back to a chain letter hoax from about 26 years ago; you can read it here, but please be aware it is an entirely debunked hoax:
Urban Legends | Aspartame Hoax
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: