Neuropsychologist Explains What She’s Got Out Of 6 Years Taking L-Theanine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Inka Land, MSc neuropsychology, PgDip(c) Nutrition and Disease, talks about her use of l-theanine and the biochemistry behind it:
So, what’s the tea?
While she’s tested over 60 supplements, she regularly uses only a few. L-theanine made the cut, and has been a staple for over six years due to its noticeable effects on her brain, nervous system in general, and gut. Some notes from the video:
- L-theanine was discovered during university studies as a way to enhance focus and reduce stress. Initially, 50mg doses combined with coffee showed no effect, but increasing to 150mg, paired with 100mg of caffeine, produced significant nootropic benefits.
- L-theanine enhances sustained focus, enabling prolonged attention on repetitive tasks while avoiding distractions. It’s particularly effective for maintaining concentration during monotonous activities.
- L-theanine alleviates gut inflammation by boosting antioxidant activity and supporting glutamine metabolism. Combined with l-glutamine, it is more effective for reducing gut inflammation, and she mentions anecdotally that it seemed to help her personally recover quickly from food poisoning.
- Known for its calming effects, L-theanine reduces anxiety and regulates the nervous system. It is beneficial before stressful or crowded events and has anecdotal support for alleviating social anxiety specifically, though that’s not been formally tested in RCTs (yet). That said, since it has been tested against anxiety in the lab (usually combined with stress tests), it would be strange if it didn’t help alleviate social anxiety too, since what’s required for the nervous system is the same.
- Studies suggest 100–200mg twice daily, but she personally takes 250mg in the morning with coffee or 200–250mg PRN.
Want to try some? Here’s an example product on Amazon 😎
For more on all of this, enjoy (and kindly disregard that she clearly is holding a jar of curcumin in the thumbnail):
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
L-Theanine Against Stress, Anxiety, Inflammation, & More
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Unleashing My Superpowers – by Dr. Patience Mpofu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Patience Mpofu is on a mission to provide women and girls with the inside-information, knowledge, resources, and strategies to break through the glass ceiling. She writes from her experience in STEM, but her lessons are applicable in any field.
Her advices range from the internal (how to deal with imposter syndrome) to the external (how to overcome cultural biases); she also explains and illustrates the importance of both role models and mentors.
While a lot of the book is half instruction manual, half memoir of her incredible life and career (to illustrate her points), and is well-worth reading—and/or perhaps worth gifting to a girl you know with ambitions in STEM?
Share This Post
-
An Unexpected Extra Threat Of Alcohol
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If You Could Use Some Exotic Booze…
…then for health reasons, we’re going to have to say “nay”.
We’ve written about alcohol before, and needless to say, it’s not good:
(the answer is “no, we cannot”)
In fact, the WHO (which unlike government regulatory bodies setting “safe” limits on drinking, makes no profit from taxes on alcohol sales) has declared that “the only safe amount of alcohol is zero”:
WHO: No level of alcohol consumption is safe for our health
Up there, where the air is rarefied…
If you’re flying somewhere this summer (Sinatra-style flying honeymoon or otherwise), you might want to skip the alcohol even if you normally do imbibe, because:
❝…even in young and healthy individuals, the combination of alcohol intake with sleeping under hypobaric conditions poses a considerable strain on the cardiac system and might lead to exacerbation of symptoms in patients with cardiac or pulmonary diseases.
These effects might be even greater in older people; cardiovascular symptoms have a prevalence of 7% of inflight medical emergencies, with cardiac arrest causing 58% of aircraft diversions.❞
Source: Alcohol plus cabin pressure at higher altitude may threaten sleeping plane passengers’ heart health
The experiment divided subjects into a control group and a study group; the study group were placed in simulated cabin pressure as though at altitude, which found, when giving some of them two small(we’re talking the kind given on flights) alcoholic drinks:
❝The combination of alcohol and simulated cabin pressure at cruising altitude prompted a fall in SpO2 to an average of just over 85% and a compensatory increase in heart rate to an average of nearly 88 beats/minute during sleep.❞
In contrast, that was 77 beats/minute for those who had alcohol but weren’t at altitude pressure, or 64 beats/minute for those who neither drank nor were at altitude pressure.
Lots more metrics were recorded and the study is interesting to read; if you’ve ever slept on a plane and thought “that sleep was not restful at all”, then know: it wasn’t just the seat’s fault, nor the engine, nor the recycled nature of the air—it was the reduced pressure causing hypoxia (defined as having oxygen levels lower than the healthy clinical norm of 90%) and almost halving your sleep’s effectiveness for a less than 10% drop in available oxygen in the blood (the sleepers not at altitude pressure averaged 96% SpO2, compared to the 85% at altitude).
We say “almost halving” because the deep sleep phase of sleep was reduced from 84 minutes (control) to 67.5 minutes at altitude without alcohol, or 46.5 minutes at altitude with alcohol.
Again, this was a pressure cabin in a lab—so this wasn’t about the other conditions of an airplane (seats, engine hundreds of other people, etc).
Which means: in an actual airplane it’s probably even worse.
Oh, and the study participants? All healthy individuals aged 18–40, so again probably worse for those older (or younger) than that range, or with existing health conditions!
Want to know more?
You can read the study in full here:
Want to drop the drink at any altitude? Check out:
Want to get that vacation feel without alcohol? You’re going to love:
Mocktails – by Moira Clark (book)
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Cilantro vs Parsley – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cilantro to parsley, we picked the parsley.
Why?
Notwithstanding that some of our recipes include “cilantro, or if you have the this-tastes-like-soap gene, parsley”, that choice is more for the taste profile than the nutrition profile. Both are good, though, and it is quite close!
Like many herbs, they’re both full of vitamins and minerals and assorted phytochemicals.
In the category of vitamins, they’re both very good sources of vitamins A, C, and K, but parsley has more of each (and in vitamin K’s case, 4–5 times more). Parsley also has about twice as much folate. For the other vitamins, they’re mostly quite equal except that cilantro has more vitamin E.
When it comes to minerals, again they’re both good but again parsley is better on average, with several times more iron, and about twice as much calcium, zinc, and magnesium. Cilantro only wins noticeably for selenium.
Both have an array of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals, and each boasts antioxidants with anticancer potential.
Both have mood-improving qualities and have research for their anxiolytic and antidepressant effects—sufficient that these deserve their own main feature sometime.
For now though, we’ll say: healthwise, these two wonderful herbs are equal on most things, except that parsley has the better micronutrient profile.
Enjoy!
Further reading
You might also enjoy:
Herbs For (Evidence-Based) Health & Healing
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Anchovies vs Sardines – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing anchovies to sardines, we picked the sardines.
Why?
In terms of macros, sardines have slightly more protein and more than 2x the fat, but the fat profile is healthier than that of anchovies, meaning that the amount of saturated fat is the same, and sardines have more poly- and monounsaturated fats. Breaking it down further, sardines also have more omega-3. Unless you are for whatever reason especially keen to keep your total fat* intake down, sardines win here.
*or calories, which in this case come almost entirely from the fat, and sardines are consequently nearly 2x higher in calories.
When it comes to vitamins, sardines further distinguish themselves; anchovies have more of vitamins B2 and B3, while sardines have more of vitamins A, B1, B6, B12, B9, E, and K—in some cases, by quite large margins (especially the B12 and K, being 14x more and 26x more, respectively). A clear win for sardines.
Minerals are closer to even; anchovies have more copper, iron, and zinc, while sardines have more calcium, manganese, phosphorus, and selenium. That’s already a slight win for sardines, before we take into account that sardines’ margins of difference are also much greater than anchovies’.
In short, enjoy either in moderation if you are so inclined, but sardines win on overall nutritional density.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught: More Important Than You Might Think
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Millet vs Buckwheat – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing millet to buckwheat, we picked the buckwheat.
Why?
Both of these naturally gluten-free grains* have their merits, but we say buckwheat comes out on top for most people (we’ll discuss the exception later).
*actually buckwheat is a flowering pseudocereal, but in culinary terms, we’ll call it a grain, much like we call tomato a vegetable.
Considering the macros first of all, millet has slightly more carbs while buckwheat has more than 2x the fiber. An easy win for buckwheat (they’re about equal on protein, by the way).
In the category of vitamins, millet has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, and B9, while buckwheat has more of vitamins B5, E, K, and choline. Superficially that’s a 5:4 win for millet, though buckwheat’s margins of difference are notably greater, so the overall vitamin coverage could arguably be considered a tie.
When it comes to minerals, millet has more phosphorus and zinc, while buckwheat has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, and selenium. For most of them, buckwheat’s margins of difference are again greater. An easy win for buckwheat, in any case.
This all adds up to a clear win for buckwheat, but as promised, there is an exception: if you have issues with your kidneys that mean you are avoiding oxalates, then millet becomes the healthier choice, as buckwheat is rather high in oxalates while millet is low in same.
For everyone else: enjoy both! Diversity is good. But if you’re going to pick one, buckwheat’s the winner.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Grains: Bread Of Life, Or Cereal Killer?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
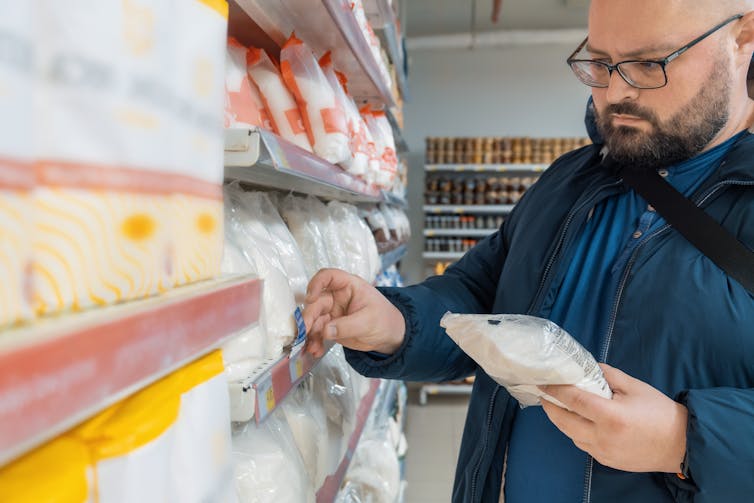
Thinking of trying a new diet? 4 questions to ask yourself before you do
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We live in a society that glorifies dieting, with around 42% of adults globally having tried to lose weight. Messages about dieting and weight loss are amplified on social media, with a never-ending cycle of weight loss fads and diet trends.
Amid often conflicting messages and misinformation, if you’re looking for diet advice online, it’s easy to become confused and overwhelmed.
So before diving into the latest weight loss trend or extreme diet, consider these four questions to help you make a more informed decision.
PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock 1. Is the diet realistic?
Have you considered the financial cost of maintaining the diet or lifestyle, and the time and resources that would be required? For example, do you need to purchase specific products, supplements, or follow a rigid meal plan?
If the diet is coming from someone who is trying to sell you something – such as a particular weight-loss product you need in order to follow the diet – this could be a particular red flag.
Many extreme diet recommendations come from a place of privilege and overlook food access, affordability, cooking skills, where you live, or even your culture and ethics.
If the diet has these sorts of issues it can lead to frustration, stress, stigmatisation and feelings of failure for the person trying to adhere to the diet. But the problem may be with the diet itself – not with you.
Many diets promoted online will be expensive, or require a lot of time and resources. artem evdokimov/Shutterstock 2. Is there evidence to support this diet?
Self-proclaimed “experts” online will often make claims focused on specific groups, known as target populations. This might be 30- to 50-year-old men with diabetes, for example.
In some cases, evidence for claims made may come from animal studies, which might not be applicable to humans at all.
So be aware that if research findings are for a group that doesn’t match your profile, then the results might not be relevant to you.
It takes time and a lot of high-quality studies to tell us a “diet” is safe and effective, not just one study. Ask yourself, is it supported by multiple studies in humans? Be critical and question the claims before you accept them.
For accurate information look for government websites, or ask your GP or dietitian.
3. How will this diet affect my life?
Food is much more than calories and nutrients. It plays many roles in our lives, and likewise diets can influence our lives in ways we often overlook.
Socially and culturally, food can be a point of connection and celebration. It can be a source of enjoyment, a source of comfort, or even a way to explore new parts of the world.
So when you’re considering a new diet, think about how it might affect meaningful moments for you. For example, if you’re going travelling, will your diet influence the food choices you make? Will you feel that you can’t sample the local cuisine? Or would you be deterred from going out for dinner with friends because of their choice of restaurant?
4. Will this diet make me feel guilty or affect my mental health?
What is your favourite meal? Does this diet “allow” you to eat it? Imagine visiting your mum who has prepared your favourite childhood meal. How will the diet affect your feelings about these special foods? Will it cause you to feel stressed or guilty about enjoying a birthday cake or a meal cooked by a loved one?
Studies have shown that dieting can negatively impact our mental health, and skipping meals can increase symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Many diets fail to consider the psychological aspects of eating, even though our mental health is just as important as physical health. Eating should not make you feel stressed, anxious, or guilty.
So before starting another diet, consider how it might affect your mental health.
Moving away from a dieting mindset
We’re frequently told that weight loss is the path to better health. Whereas, we can prioritise our health without focusing on our weight. Constant messages about the need to lose weight can also be harmful to mental health, and not necessarily helpful for physical health.
Our research has found eating in a way that prioritises health over weight loss is linked to a range of positive outcomes for our health and wellbeing. These include a more positive relationship with food, and less guilt and stress.
Our research also indicates mindful and intuitive eating practices – which focus on internal cues, body trust, and being present and mindful when eating – are related to lower levels of depression and stress, and greater body image and self-compassion.
But like anything, it takes practice and time to build a positive relationship with food. Be kind to yourself, seek out weight-inclusive health-care professionals, and the changes will come. Finally, remember you’re allowed to find joy in food.
Melissa Eaton, Accredited Practising Dietitian; PhD Candidate, University of Wollongong; Verena Vaiciurgis, Accredited Practising Dietitian; PhD Candidate, University of Wollongong, and Yasmine Probst, Associate Professor, School of Medical, Indigenous and Health Sciences, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: