Military Secrets (Ssh!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Can you keep a secret?
When actor Christopher Lee was asked about his time as a British special forces operative, he would look furtively around, and ask “can you keep a secret?” Upon getting a yes, he would reply:
“So can I”
We can’t, though! We just can’t help sharing cool, useful information that changes people’s lives. Never is that more critical than now, as the end of January has been called the most depressing time of year, according to Dr. Cliff Arnall at the University of Cardiff. It doesn’t have to be all doom and gloom, though:
Today we’re going to share a trick… It’s called the “secret of eternal happiness” (yes, we know… we didn’t come up with the name!) and is taught to soldiers to fend off the worst kinds of despair.
The soldiers would be ordered to take a moment to reflect on the sheer helplessness of their situation, the ridiculous impossibility of the odds against them, all and any physical pain they might suffer, the weakness of their faltering body… and just when everything feels as bad is it can possibly feel, they’re told to say out loud—as sadly as possible—this single word:
“Boop”
It all but guarantees to result in cracking a smile, no matter the situation.
Now this knowledge is yours too! Keep it secret! Or don’t. Sharing is caring.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
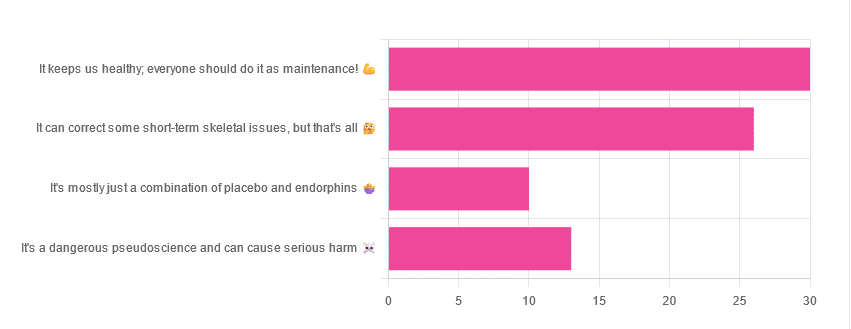
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on chiropractic medicine, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of results:
- 38% of respondents said it keeps us healthy, and everyone should do it as maintenance
- 33% of respondents said it can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all
- 16% of respondents said that it’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause serious harm
- 13% of respondents said that it’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins
Respondents also shared personal horror stories of harm done, personal success stories of things cured, and personal “it didn’t seem to do anything for me” stories.
What does the science say?
It’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause harm: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
That is to say, chiropractic in its simplest form that makes the fewest claims, is not a pseudoscience. If somebody physically moves your bones around, your bones will be physically moved. If your bones were indeed misaligned, and the chiropractor is knowledgeable and competent, this will be for the better.
However, like any form of medicine, it can also cause harm; in chiropractic’s case, because it more often than not involves manipulation of the spine, this can be very serious:
❝Twenty six fatalities were published in the medical literature and many more might have remained unpublished.
The reported pathology usually was a vascular accident involving the dissection of a vertebral artery.
Conclusion: Numerous deaths have occurred after chiropractic manipulations. The risks of this treatment by far outweigh its benefit.❞
Source: Deaths after chiropractic: a review of published cases
From this, we might note two things:
- The abstract doesn’t note the initial sample size; we would rather have seen this information expressed as a percentage. Unfortunately, the full paper is not accessible, and nor are many of the papers it cites.
- Having a vertebral artery fatally dissected is nevertheless not an inviting prospect, and is certainly a very reasonable cause for concern.
It’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins: True or False?
True or False, depending on what you went in for:
- If you went in for a regular maintenance clunk-and-click, then yes, you will get your clunk-and-click and feel better for it because you had a ritualized* experience and endorphins were released.
- If you went in for something that was actually wrong with your skeletal alignment, to get it corrected, and this correction was within your chiropractor’s competence, then yes, you will feel better because a genuine fault was corrected.
*this is not implying any mysticism, by the way. Rather it means simply that placebo effect is strongest when there is a ritual associated with it. In this case it means going to the place, sitting in a pleasant waiting room, being called in, removing your shoes and perhaps some other clothes, getting the full attention of a confident and assured person for a while, this sort of thing.
With regard to its use to combat specifically spinal pain (i.e., perhaps the most obvious thing to treat by chiropractic spinal manipulation), evidence is slightly in favor, but remains unclear:
❝Due to the low quality of evidence, the efficacy of chiropractic spinal manipulation compared with a placebo or no treatment remains uncertain. ❞
Source: Clinical Effectiveness and Efficacy of Chiropractic Spinal Manipulation for Spine Pain
It can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all: True or False?
Probably True.
Why “probably”? The effectiveness of chiropractic treatment for things other than short-term skeletal issues has barely been studied. From this, we may wish to keep an open mind, while also noting that it can hardly claim to be evidence-based—and it’s had hundreds of years to accumulate evidence. In all likelihood, publication bias has meant that studies that were conducted and found inconclusive or negative results were simply not published—but that’s just a hypothesis on our part.
In the case of using chiropractic to treat migraines, a very-related-but-not-skeletal issue, researchers found:
❝Pre-specified feasibility criteria were not met, but deficits were remediable. Preliminary data support a definitive trial of MCC+ for migraine.❞
Translating this: “it didn’t score as well as we hoped, but we can do better. We got some positive results, and would like to do another, bigger, better trial; please fund it”
Source: Multimodal chiropractic care for migraine: A pilot randomized controlled trial
Meanwhile, chiropractors’ claims for very unrelated things have been harshly criticized by the scientific community, for example:
Misinformation, chiropractic, and the COVID-19 pandemic
About that “short-term” aspect, one of our subscribers put it quite succinctly:
❝Often a skeletal correction is required for initial alignment but the surrounding fascia and muscles also need to be treated to mobilize the joint and release deep tissue damage surrounding the area. In combination with other therapies chiropractic support is beneficial.❞
This is, by the way, very consistent with what was said in the very clinically-dense book we reviewed yesterday, which has a chapter on the short-term benefits and limitations of chiropractic.
A truism that holds for many musculoskeletal healthcare matters, holds true here too:
❝In a battle between muscle and bone, muscle will always win❞
In other words…
Chiropractic can definitely help put misaligned bones back where they should be. However, once they’re there, if the cause of their misalignment is not treated, they will just re-misalign themselves shortly after you walking out of your session.
This is great for chiropractors, if it keeps you coming back for endless appointments, but it does little for your body beyond give you a brief respite.
So, by all means go to a chiropractor if you feel so inclined (and you do not fear accidental arterial dissection etc), but please also consider going to a physiotherapist, and potentially other medical professions depending on what seems to be wrong, to see about addressing the underlying cause.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Glycemic Index vs Glycemic Load vs Insulin Index
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Actually Use Those Indices
Carbohydrates are essential for our life, and/but often bring about our early demise. It would be a very conveniently simple world if it were simply a matter of “enjoy in moderation”, but the truth is, it’s not that simple.
To take an extreme example, for the sake of clearest illustration: The person who eats an 80% whole fruit diet (and makes up the necessary protein and fats etc in the other 20%) will probably be healthier than the person who eats a “standard American diet”, despite not practising moderation in their fruit-eating activities. The “standard American diet” has many faults, and one of those faults is how it promotes sporadic insulin spikes leading to metabolic disease.
If your breakfast is a glass of orange juice, this is a supremely “moderate” consumption, but an insulin spike is an insulin spike.
Quick sidenote: if you’re wondering why eating immoderate amounts of fruit is unlikely to cause such spikes, but a single glass of orange juice is, check out:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Glycemic Index
The first tool in our toolbox here is glycemic index, or GI.
GI measures how much a carb-containing food raises blood glucose levels, also called blood sugar levels, but it’s just glucose that’s actually measured, bearing in mind that more complex carbs will generally get broken down to glucose.
Pure glucose has a GI of 100, and other foods are ranked from 0 to 100 based on how they compare.
Sometimes, what we do to foods changes its GI.
- Some is because it changed form, like the above example of whole fruit (low GI) vs fruit juice (high GI).
- Some is because of more “industrial” refinement processes, such as whole grain wheat (medium GI) vs white flour and white flour products (high GI)
- Some is because of other changes, like starches that were allowed to cool before being reheated (or eaten cold).
Broadly speaking, a daily average GI of 45 is considered great.
But that’s not the whole story…
Glycemic Load
Glycemic Load, or GL, takes the GI and says “ok, but how much of it was there?”, because this is often relevant information.
Refined sugar may have a high GI, but half a teaspoon of sugar in your coffee isn’t going to move your blood sugar levels as much as a glass of Coke, say—the latter simply has more sugar in, and just the same zero fiber.
GL is calculated by (grams of carbs / 100) x GI, by the way.
But it still misses some important things, so now let’s look at…
Insulin Index
Insulin Index, which does not get an abbreviation (probably because of the potentially confusing appearance of “II”), measures the rise in insulin levels, regardless of glucose levels.
This is important, because a lot of insulin response is independent of blood glucose:
- Some is because of other sugars, some some is in response to fats, and yes, even proteins.
- Some is a function of metabolic base rate.
- Some is a stress response.
- Some remains a mystery!
Another reason it’s important is that insulin drives weight gain and metabolic disorders far more than glucose.
Note: the indices of foods are calculated based on average non-diabetic response. If for example you have Type 1 Diabetes, then when you take a certain food, your rise in insulin is going to be whatever insulin you then take, because your body’s insulin response is disrupted by being too busy fighting a civil war in your pancreas.
If your diabetes is type 2, or you are prediabetic, then a lot of different things could happen depending on the stage and state of your diabetes, but the insulin index is still a very good thing to be aware of, because you want to resensitize your body to insulin, which means (barring any urgent actions for immediate management of hyper- or hypoglycemia, obviously) you want to eat foods with a low insulin index where possible.
Great! What foods have a low insulin index?
Many factors affect insulin index, but to speak in general terms:
- Whole plant foods are usually top-tier options
- Lean and/or white meats generally have lower insulin index than red and/or fatty ones
- Unprocessed is generally lower than processed
- The more solid a food is, generally the lower its insulin index compared to a less solid version of the same food (e.g. baked potatoes vs mashed potatoes; cheese vs milk, etc)
But do remember the non-food factors too! This means where possible:
- reducing/managing stress
- getting frequent exercise
- getting good sleep
- practising intermittent fasting
See for example (we promise you it’s relevant):
Fix Chronic Fatigue & Regain Your Energy, By Science
…as are (especially recommendable!) the two links we drop at the bottom of that page; do check them out if you can
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Is still water better for you than sparkling water?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Still or sparkling? It’s a question you’ll commonly hear in a café or restaurant and you probably have a preference. But is there any difference for your health?
If you love the fizz, here’s why you don’t have to pass on the sparkling water.
Brent Hofacker/Shutterstock What makes my water sparkle?
This article specifically focuses on comparing still filtered water to carbonated filtered water (called “sparkling water” or “unflavoured seltzer”). Soda water, mineral water, tonic water and flavoured water are similar, but not the same product.
The bubbles in sparkling water are created by adding carbon dioxide to filtered water. It reacts to produce carbonic acid, which makes sparkling water more acidic (a pH of about 3.5) than still (closer to neutral, with a pH around 6.5-8.5).
Which drink is healthiest?
Water is the best way to hydrate our bodies. Research shows when it comes to hydration, still and sparkling water are equally effective.
Some people believe water is healthier when it comes from a sealed bottle. But in Australia, tap water is monitored very carefully. Unlike bottled water, it also has the added benefit of fluoride, which can help protect young children against tooth decay and cavities.
Sparkling or still water is always better than artificially sweetened flavoured drinks or juices.
Isn’t soda water bad for my teeth and bones?
There’s no evidence sparkling water damages your bones. While drinking a lot of soft drinks is linked to increased fractures, this is largely due to their association with higher rates of obesity.
Sparkling water is more acidic than still water, and acidity can soften the teeth’s enamel. Usually this is not something to be too worried about, unless it is mixed with sugar or citrus, which has much higher levels of acidity and can harm teeth.
However, if you grind your teeth often, the softening could enhance the damage it causes. If you’re undertaking a home whitening process, sparkling water might discolour your teeth.
In most other cases, it would take a lot of sparkling water to pass by the teeth, for a long period of time, to cause any noticeable damage.
How does drinking water affect digestion?
There is a misconception drinking water (of any kind) with a meal is bad for digestion.
While theoretically water could dilute stomach acid (which breaks down food), the practice of drinking it doesn’t appear to have any negative effect. Your digestive system simply adapts to the consistency of the meal.
Some people do find that carbonated beverages cause some stomach upset. This is due to the build-up of gases, which can cause bloating, cramping and discomfort. For people with an overactive bladder, the acidity might also aggravate the urinary system.
Interestingly, the fizzy “buzz” you feel in your mouth from sparkling water fades the more you drink it.
Is cold water harder to digest?
You’ve chosen still or sparkling water. What about its temperature?
There are surprisingly few studies about the effect of drinking cold water compared to room temperature. There is some evidence colder water (at two degrees Celsius) might inhibit gastric contractions and slow down digestion. Ice water may constrict blood vessels and cause cramping.
However other research suggests drinking cold water might temporarily boost metabolism, as the body needs to expend energy to warm it up to body temperature. This effect is minimal and unlikely to lead to significant weight loss.
Which water wins?
The bottom line is water is essential, hydrates us and has countless other health benefits. Water, with carbonated bubbles or without, will always be the healthiest drink to choose.
And if you’re concerned about any impact to teeth enamel, one trick is to follow sparkling water with a glass of still. This helps rinse the teeth and return your mouth’s acidity back to normal.
Christian Moro, Associate Professor of Science & Medicine, Bond University and Charlotte Phelps, Senior Teaching Fellow, Medical Program, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How To Survive A Heart Attack When You’re Alone
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Alan Mandel emphasizes the importance of staying calm and following these steps to improve survival chances:
Simple is best
Here’s how you will survive a heart attack alone: briefly.
So, you will need to get help as quickly as possible. 90% of people who make it to a hospital alive, go on to survive their heart attack, so that’s your top priority.
Call emergency services as soon as you suspect you are having a heart attack. Stay on the line, and stay calm.
While having a heart attack is not an experience that’s very conducive to relaxation, heightened emotions will exacerbate things, so focus on breathing calmly. One of the commonly reported symptoms of heart attack that doesn’t often make it to official lists is “a strong sense of impending doom”, and that is actually helpful as it helps separate it from “is this indigestion?” or such, but once you have acknowledged “yes, this is probably a heart attack”, you need to put those feelings aside for later.
If you have aspirin available, Dr. Mandel says that the time to take it is once you have called an ambulance. However, if aspirin is not readily available, do not exert yourself trying to find some; indeed, don’t move more than necessary.
Do not drive yourself to hospital; it will increase the risk of fainting, and you may crash.
While you are waiting, your main job is to remain calm; he recommends deep breathing, and lying with knees elevated or feet on a chair; this latter is to minimize the strain on your heart.
For more on all this, plus the key symptoms and risk factors, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Heart Attack: His & Hers (Be Prepared!)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Revealed: The Soviet Secret Recipe For Success That The CIA Admits Put The US To Shame
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Today’s edition of 10almonds brings you a blast from the past with a modern twist: an ancient Russian peasant food that became a Soviet staple, and today, is almost unknown in the West.
Before we get to that, let’s take a sneaky look at this declassified CIA memorandum from near the end of the Cold War:
(Click here to see a bigger version)
The take-away here is:
- Americans were eating 2–3 times more meat than Soviets
- Soviets were eating nearly double the amount of grain products and potatoes
…and both of these statistics meant that nutritionally speaking, the Soviets were doing better.
Americans also consumed more sugar and fats, which again, wasn’t the best dietary option.
But was the American diet tastier? Depends on whom you ask.
Which brings us to a literal recipe we’re going to be sharing with you today:
It’s not well-known in the West, but in Russia, it’s a famous national comfort food, a bastion of health and nutrition, and it rose to popularity because it was not only cheap and nutritious, but also, you could eat it for days without getting sick of it. And it could be easily frozen for reheating later without losing any of its appeal—it’d still be just as good.
In Russia there are sayings about it:
Щи да каша — пища наша (Shchi da kasha — pishcha nasha)
“Shchi and buckwheat are what we eat”
Top tip: buckwheat makes an excellent (and naturally sweet) alternative to porridge oats if prepared the same way!
Где щи, там и нас ищи (Gdye shchi, tam i nas ishchi)
“Where there’s shchi, us you’ll see”
Голь голью, а луковка во щах есть (Gol’ gol’yu, a lukovka vo shchakh yest’)
“I’m stark naked, but there’s shchi with onions”
There’s a very strong sentiment in Russia that really, all you need is shchi (shchi, shchi… shchi is all you need )
But what, you may ask, is shchi?
Our culinary cultural ambassador Nastja is here to offer her tried-and-tested recipe for…
…Russian cabbage soup (yes, really—bear with us now, and you can thank us later)
There are a lot of recipes for shchi (see for yourself what the Russian version of Lifehacker recommends), and we’ll be offering our favorite…
Nastja’s Nutritious and Delicious Homemade Shchi
Hi, Nastja here! I’m going to share with you my shchi recipe that is:
- Cheap
- So tasty
- Super nutritious*
- Vegan
- Gluten Free
You will also need:
- A cabbage (I use sweetheart, but any white cabbage will do)
- 1 cup (250g) red lentils (other kinds of lentils will work too)
- ½ lb or so (250–300g) tomatoes (I use baby plum tomatoes, but any kind will do)
- ½ lb or so (250–300g) mushrooms (the edible kind)
- An onion (I use a brown onion; any kind will do)
- Salt, pepper, rosemary, thyme, parsley, cumin
- Marmite or similar yeast extract (do you hate it? Me too. Trust me, it’ll be fine, you’ll love it. Omit if you’re a coward.)
- A little oil for sautéing (I use sunflower, but canola is fine, as is soy oil. Do not use olive oil or coconut oil, because the taste is too strong and the flashpoint too low)
First, what the French call mise-en-place, the prep work:
- Chop the cabbage into small strips, ⅛–¼ inch x 1 inch is a good guideline, but you can’t really go wrong unless you go to extremes
- Chop the tomatoes. If you’re using baby plum tomatoes (or cherry tomatoes), cut them in half. If using larger tomatoes, cut them into eighths (halve them, halve the halves, then halve the quarters)
- Chop the mushrooms. If using button mushrooms, half them. If using larger mushrooms, quarter them.
- Chop the onion finely.
- Gather the following kitchenware: A big pan (stock pot or similar), a sauté pan (a big wok or frying pan will do), a small frying pan (here a wok will not do), and a saucepan (a rice cook will also do)
Now, for actual cooking:
- Cook the red lentils until soft (I use a rice cooker, but a saucepan is fine) and set aside
- Sauté the cabbage, put it in the big pot (not yet on the heat!)
- Fry the mushrooms, put them in the big pot (still not yet on the heat!)
When you’ve done this a few times and/or if you’re feeling confident, you can do the above simultaneously to save time
- Blend the lentils into the water you cooked them in, and then add to the big pot.
- Turn the heat on low, and if necessary, add more water to make it into a rich soup
- Add the seasonings to taste, except the parsley. Go easy on the cumin, be generous with the rosemary and thyme, let your heart guide you with the salt and pepper.
- When it comes to the yeast extract: add about one teaspoon and stir it into the pot. Even if you don’t like Marmite, it barely changes the flavour (makes it slightly richer) and adds a healthy dose of vitamin B12.
We did not forget the tomatoes and the onion:
- Caramelize the onion (keep an eye on the big pot) and set it aside
- Fry the tomatoes and add them to the big pot
Last but definitely not least:
- Serve!
- The caramelized onion is a garnish, so put a little on top of each bowl of shchi
- The parsley is also a garnish, just add a little
Any shchi you don’t eat today will keep in the fridge for several days, or in the freezer for much longer.
*That nutritious goodness I talked about? Check it out:
- Lentils are high in protein and iron
- Cabbage is high in vitamin C and calcium
- Mushrooms are high in magnesium
- Tomatoes are good against inflammation
- Black pepper has a host of health benefits
- Yeast extract contains vitamin B12
Let us know how it went! We love to receive emails from our subscribers!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How long does back pain last? And how can learning about pain increase the chance of recovery?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Back pain is common. One in thirteen people have it right now and worldwide a staggering 619 million people will have it this year.
Chronic pain, of which back pain is the most common, is the world’s most disabling health problem. Its economic impact dwarfs other health conditions.
If you get back pain, how long will it take to go away? We scoured the scientific literature to find out. We found data on almost 20,000 people, from 95 different studies and split them into three groups:
- acute – those with back pain that started less than six weeks ago
- subacute – where it started between six and 12 weeks ago
- chronic – where it started between three months and one year ago.
We found 70%–95% of people with acute back pain were likely to recover within six months. This dropped to 40%–70% for subacute back pain and to 12%–16% for chronic back pain.
Clinical guidelines point to graded return to activity and pain education under the guidance of a health professional as the best ways to promote recovery. Yet these effective interventions are underfunded and hard to access.
More pain doesn’t mean a more serious injury
Most acute back pain episodes are not caused by serious injury or disease.
There are rare exceptions, which is why it’s wise to see your doctor or physio, who can check for signs and symptoms that warrant further investigation. But unless you have been in a significant accident or sustained a large blow, you are unlikely to have caused much damage to your spine.
Your doctor or physio can rule out serious damage.
DG fotostock/ShutterstockEven very minor back injuries can be brutally painful. This is, in part, because of how we are made. If you think of your spinal cord as a very precious asset (which it is), worthy of great protection (which it is), a bit like the crown jewels, then what would be the best way to keep it safe? Lots of protection and a highly sensitive alarm system.
The spinal cord is protected by strong bones, thick ligaments, powerful muscles and a highly effective alarm system (your nervous system). This alarm system can trigger pain that is so unpleasant that you cannot possibly think of, let alone do, anything other than seek care or avoid movement.
The messy truth is that when pain persists, the pain system becomes more sensitive, so a widening array of things contribute to pain. This pain system hypersensitivity is a result of neuroplasticity – your nervous system is becoming better at making pain.
Reduce your chance of lasting pain
Whether or not your pain resolves is not determined by the extent of injury to your back. We don’t know all the factors involved, but we do know there are things that you can do to reduce chronic back pain:
- understand how pain really works. This will involve intentionally learning about modern pain science and care. It will be difficult but rewarding. It will help you work out what you can do to change your pain
- reduce your pain system sensitivity. With guidance, patience and persistence, you can learn how to gradually retrain your pain system back towards normal.
How to reduce your pain sensitivity and learn about pain
Learning about “how pain works” provides the most sustainable improvements in chronic back pain. Programs that combine pain education with graded brain and body exercises (gradual increases in movement) can reduce pain system sensitivity and help you return to the life you want.
Some programs combine education with gradual increases in movement.
Halfpoint/ShutterstockThese programs have been in development for years, but high-quality clinical trials are now emerging and it’s good news: they show most people with chronic back pain improve and many completely recover.
But most clinicians aren’t equipped to deliver these effective programs – good pain education is not taught in most medical and health training degrees. Many patients still receive ineffective and often risky and expensive treatments, or keep seeking temporary pain relief, hoping for a cure.
When health professionals don’t have adequate pain education training, they can deliver bad pain education, which leaves patients feeling like they’ve just been told it’s all in their head.
Community-driven not-for-profit organisations such as Pain Revolution are training health professionals to be good pain educators and raising awareness among the general public about the modern science of pain and the best treatments. Pain Revolution has partnered with dozens of health services and community agencies to train more than 80 local pain educators and supported them to bring greater understanding and improved care to their colleagues and community.
But a broader system-wide approach, with government, industry and philanthropic support, is needed to expand these programs and fund good pain education. To solve the massive problem of chronic back pain, effective interventions need to be part of standard care, not as a last resort after years of increasing pain, suffering and disability.
Sarah Wallwork, Post-doctoral Researcher, University of South Australia and Lorimer Moseley, Professor of Clinical Neurosciences and Foundation Chair in Physiotherapy, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: