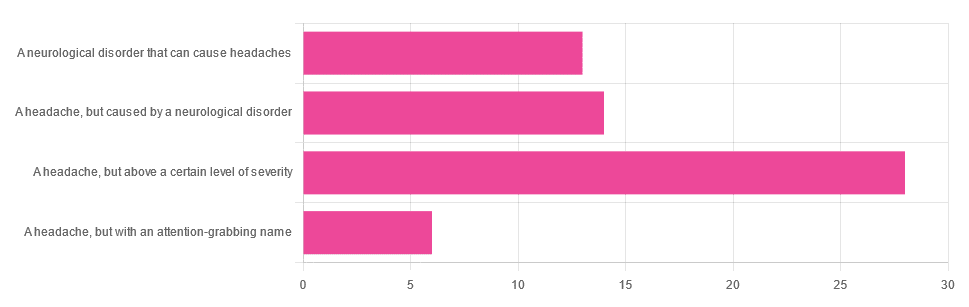
Marrakesh Sorghum Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As the name suggests, it’s a Maghreb dish today! Using sorghum, a naturally gluten-free whole grain with a stack of vitamins and minerals. This salad also comes with fruit and nuts (apricots and almonds; a heavenly combination for both taste and nutrients) as well as greens, herbs, and spices.
Note: to keep things simple today, we’ve listed ras el-hanout as one ingredient. If you’re unfamiliar, it’s a spice blend; you can probably buy a version locally, but you might as well know how to make it yourself—so here’s our recipe for that!
You will need
- 1½ cups sorghum, soaked overnight in water (if you can’t find it locally, you can order it online (here’s an example product on Amazon), or substitute quinoa) and if you have time, soaked overnight and then kept in a jar with just a little moisture for a few days until they begin to sprout—this will be best of all. But if you don’t have time, don’t worry about it; overnight soaking is sufficient already.
- 1 carrot, grated
- ½ cup chopped parsley
- 1 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- ½ tbsp chopped chives
- 2 tbsp ras el-hanout
- 3 cloves garlic, crushed
- 2 tbsp almond butter
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 tsp white miso paste
- ½ cup sliced almonds
- 4 fresh apricots, pitted and cut into wedges
- 1 cup mint leaves, chopped
- To serve: your choice of salad greens; we suggest chopped romaine lettuce and rocket
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the sorghum, which means boiling it for about 45 minutes, or 30 in a pressure cooker. If unsure, err on the side of cooking longer—even up to an hour will be totally fine. You have a lot of wiggle room, and will soon get used to how long it takes with your device/setup. Drain the cooked sorghum, and set it aside to cool. If you’re entertaining, we recommend doing this part the day before and keeping it in the fridge.
2) When it’s cool, add the carrot, the parsley, the chives, the vinegar, and 1 tbsp of the ras el-hanout. Toss gently but thoroughly to combine.
3) Make the dressing, which means putting ¼ cup water into a blender with the other 1 tbsp of the ras el-hanout, the garlic, the almond butter, the lemon juice, and the miso paste. Blend until smooth.
4) Assemble the salad, which means adding the dressing to sorghum-and-ingredients bowl, along with the almonds, apricots, and mint leaves. Toss gently, but sufficiently that everything is coated.
5) Serve on a bed of salad greens.

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet ← including an anti-inflammatory version, which is functionally what we’re doing today. As an aside when people hear “Mediterranean” they often think “Italy and Greece”. Which, sure, but N. Africa (and thus Maghreb cuisine) is also very much Mediterranean, and it shows!
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Managing [E-word] Dysfunction Reactions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
We had several requests pertaining to veganism, meatless mondays, and substitutions in recipes—so we’re going to cover those on a different day!
As for questions we’re answering today…
Q: Information on [e-word] dysfunction for those who have negative reactions to [the most common medications]?
When it comes to that particular issue, one or more of these three factors are often involved:
- Hormones
- Circulation
- Psychology
The most common drugs (that we can’t name here) work on the circulation side of things—specifically, by increasing the localized blood pressure. The exact mechanism of this drug action is interesting, albeit beyond the scope of a quick answer here today. On the other hand, the way that they work can cause adverse blood-pressure-related side effects for some people; perhaps you’re one of them.
To take matters into your own hands, so to speak, you can address each of those three things we just mentioned:
Hormones
Ask your doctor (or a reputable phlebotomy service) for a hormone test. If your free/serum testosterone levels are low (which becomes increasingly common in men over the age of 45), they may prescribe something—such as testosterone shots—specifically for that.
This way, it treats the underlying cause, rather than offering a workaround like those common pills whose names we can’t mention here.
Circulation
Look after your heart health; eat for your heart health, and exercise regularly!
Cold showers/baths also work wonders for vascular tone—which is precisely what you need in this matter. By rapidly changing temperatures (such as by turning off the hot water for the last couple of minutes of your shower, or by plunging into a cold bath), your blood vessels will get practice at constricting and maintaining that constriction as necessary.
Psychology
[E-word] dysfunction can also have a psychological basis. Unfortunately, this can also then be self-reinforcing, if recalling previous difficulties causes you to get distracted/insecure and lose the moment. One of the best things you can do to get out of this catch-22 situation is to not worry about it in the moment. Depending on what you and your partner(s) like to do in bed, there are plenty of other equally respectable options, so just switch track!
Having a conversation about this in advance will probably be helpful, so that everyone’s on the same page of the script in that eventuality, and it becomes “no big deal”. Without that conversation, misunderstandings and insecurities could arise for your partner(s) as well as yourself (“aren’t I desirable enough?” etc).
So, to recap, we recommend:
- Have your hormones checked
- Look after your circulation
- Make the decision to have fun!
Share This Post
-
Apricots vs Plums – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apricots to plums, we picked the apricots.
Why?
Both are great, but it wasn’t close!
In terms of macros, apricots have more fiber, protein, and carbs, with their fiber:carb ratio also giving them the lower glycemic index (although, as usual for any whole fruit, neither are going to give anyone metabolic disease). In any case, by the numbers, and especially for having more fiber, apricots win this category.
In the category of vitamins, apricots have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, E, and choline, while plums have more vitamin K. A clear win for apricots.
When it comes to minerals, apricots have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while plums are not higher in any mineral. Another hands-down win for apricots.
Looking at polyphenols, both have an abundance of many, especially assorted flavanols, including quercetin. However, plums additionally have some anthocyanins (whence the color), so they get a marginal victory in this round.
Still, adding up the sections, it’s a 3:1 win for apricots. Of course, do enjoy either or both, though; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Bird flu has been detected in a pig in the US. Why does that matter?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The United States Department of Agriculture last week reported that a pig on a backyard farm in Oregon was infected with bird flu.
As the bird flu situation has evolved, we’ve heard about the A/H5N1 strain of the virus infecting a range of animals, including a variety of birds, wild animals and dairy cattle.
Fortunately, we haven’t seen any sustained spread between humans at this stage. But the detection of the virus in a pig marks a worrying development in the trajectory of this virus.
David MG/Shutterstock How did we get here?
The most concerning type of bird flu currently circulating is clade 2.3.4.4b of A/H5N1, a strain of influenza A.
Since 2020, A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b has spread to a vast range of birds, wild animals and farm animals that have never been infected with bird flu before.
While Europe is a hotspot for A/H5N1, attention is currently focused on the US. Dairy cattle were infected for the first time in 2024, with more than 400 herds affected across at least 14 US states.
Bird flu has enormous impacts on farming and commercial food production, because infected poultry flocks have to be culled, and infected cows can result in contaminated diary products. That said, pasteurisation should make milk safe to drink.
While farmers have suffered major losses due to H5N1 bird flu, it also has the potential to mutate to cause a human pandemic.
Birds and humans have different types of receptors in their respiratory tract that flu viruses attach to, like a lock (receptors) and key (virus). The attachment of the virus allows it to invade a cell and the body and cause illness. Avian flu viruses are adapted to birds, and spread easily among birds, but not in humans.
So far, human cases have mainly occurred in people who have been in close contact with infected farm animals or birds. In the US, most have been farm workers.
The concern is that the virus will mutate and adapt to humans. One of the key steps for this to happen would be a shift in the virus’ affinity from the bird receptors to those found in the human respiratory tract. In other words, if the virus’ “key” mutated to better fit with the human “lock”.
A recent study of a sample of A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b from an infected human had worrying findings, identifying mutations in the virus with the potential to increase transmission between human hosts.
Why are pigs a problem?
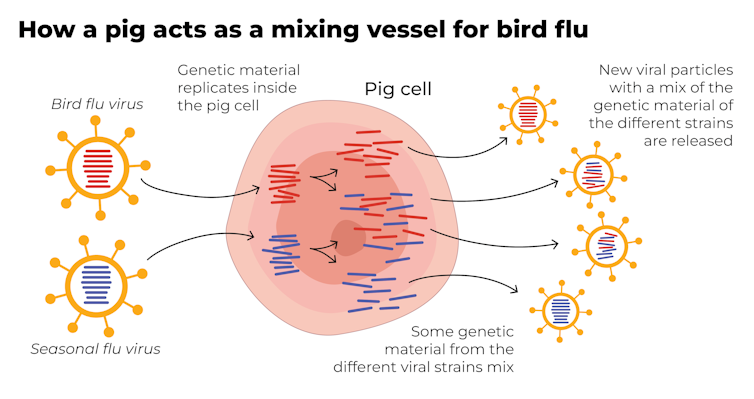
A human pandemic strain of influenza can arise in several ways. One involves close contact between humans and animals infected with their own specific flu viruses, creating opportunities for genetic mixing between avian and human viruses.
Pigs are the ideal genetic mixing vessel to generate a human pandemic influenza strain, because they have receptors in their respiratory tracts which both avian and human flu viruses can bind to.
This means pigs can be infected with a bird flu virus and a human flu virus at the same time. These viruses can exchange genetic material to mutate and become easily transmissible in humans.
The Conversation, CC BY-SA Interestingly, in the past pigs were less susceptible to A/H5N1 viruses. However, the virus has recently mutated to infect pigs more readily.
In the recent case in Oregon, A/H5N1 was detected in a pig on a non-commercial farm after an outbreak occurred among the poultry housed on the same farm. This strain of A/H5N1 was from wild birds, not the one that is widespread in US dairy cows.
The infection of a pig is a warning. If the virus enters commercial piggeries, it would create a far greater level of risk of a pandemic, especially as the US goes into winter, when human seasonal flu starts to rise.
How can we mitigate the risk?
Surveillance is key to early detection of a possible pandemic. This includes comprehensive testing and reporting of infections in birds and animals, alongside financial compensation and support measures for farmers to encourage timely reporting.
Strengthening global influenza surveillance is crucial, as unusual spikes in pneumonia and severe respiratory illnesses could signal a human pandemic. Our EPIWATCH system looks for early warnings of such activity, which can speed up vaccine development.
If a cluster of human cases occurs, and influenza A is detected, further testing (called subtyping) is essential to ascertain whether it’s a seasonal strain, an avian strain from a spillover event, or a novel pandemic strain.
Early identification can prevent a pandemic. Any delay in identifying an emerging pandemic strain enables the virus to spread widely across international borders.
Australia’s first human case of A/H5N1 occurred in a child who acquired the infection while travelling in India, and was hospitalised with illness in March 2024. At the time, testing revealed Influenza A (which could be seasonal flu or avian flu), but subtyping to identify A/H5N1 was delayed.
This kind of delay can be costly if a human-transmissible A/H5N1 arises and is assumed to be seasonal flu because the test is positive for influenza A. Only about 5% of tests positive for influenza A are subtyped further in Australia and most countries.
In light of the current situation, there should be a low threshold for subtyping influenza A strains in humans. Rapid tests which can distinguish between seasonal and H5 influenza A are emerging, and should form part of governments’ pandemic preparedness.
A higher risk than ever before
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the current risk posed by H5N1 to the general public remains low.
But with H5N1 now able to infect pigs, and showing worrying mutations for human adaptation, the level of risk has increased. Given the virus is so widespread in animals and birds, the statistical probability of a pandemic arising is higher than ever before.
The good news is, we are better prepared for an influenza pandemic than other pandemics, because vaccines can be made in the same way as seasonal flu vaccines. As soon as the genome of a pandemic influenza virus is known, the vaccines can be updated to match it.
Partially matched vaccines are already available, and some countries such as Finland are vaccinating high-risk farm workers.
C Raina MacIntyre, Professor of Global Biosecurity, NHMRC L3 Research Fellow, Head, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW Sydney and Haley Stone, Research Associate, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute & CRUISE lab, Computer Science and Engineering, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Migraine Mythbusting
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Migraine: When Headaches Are The Tip Of The Neurological Iceberg
Yesterday, we asked you “What is a migraine?” and got the above-depicted, below-described spread of responses:
- Just under 46% said “a headache, but above a certain level of severity”
- Just under 23% said “a headache, but caused by a neurological disorder”
- Just over 21% said “a neurological disorder that can cause headaches”
- Just under 10% said “a headache, but with an attention-grabbing name”
So… What does the science say?
A migraine is a headache, but above a certain level of severity: True or False?
While that’s usually a very noticeable part of it… That’s only one part of it, and not a required diagnostic criterion. So, in terms of defining what a migraine is, False.
Indeed, migraine may occur without any headache, let alone a severe one, for example: Abdominal Migraine—though this is much less well-researched than the more common with-headache varieties.
Here are the defining characteristics of a migraine, with the handy mnemonic 5-4-3-2-1:
- 5 or more attacks
- 4 hours to 3 days in duration
- 2 or more of the following:
- Unilateral (affects only one side of the head)
- Pulsating
- Moderate or severe pain intensity
- Worsened by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity
- 1 or more of the following:
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Sensitivity to both light and sound
Source: Cephalalgia | ICHD-II Classification: Parts 1–3: Primary, Secondary and Other
As one of our subscribers wrote:
❝I have chronic migraine, and it is NOT fun. It takes away from my enjoyment of family activities, time with friends, and even enjoying alone time. Anyone who says a migraine is just a bad headache has not had to deal with vertigo, nausea, loss of balance, photophobia, light sensitivity, or a host of other symptoms.❞
Migraine is a neurological disorder: True or False?
True! While the underlying causes aren’t known, what is known is that there are genetic and neurological factors at play.
❝Migraine is a recurrent, disabling neurological disorder. The World Health Organization ranks migraine as the most prevalent, disabling, long-term neurological condition when taking into account years lost due to disability.
Considerable progress has been made in elucidating the pathophysiological mechanisms of migraine, associated genetic factors that may influence susceptibility to the disease❞
Source: JHP | Mechanisms of migraine as a chronic evolutive condition
Migraine is just a headache with a more attention-grabbing name: True or False?
Clearly, False.
As we’ve already covered why above, we’ll just close today with a nod to an old joke amongst people with chronic illnesses in general:
“Are you just saying that because you want attention?”
“Yes… Medical attention!”
Want to learn more?
You can find a lot of resources at…
NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders & Stroke | Migraine
and…
The Migraine Trust ← helpfully, this one has a “Calm mode” to tone down the colorscheme of the website!
Particularly useful from the above site are its pages:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can apps and digital resources support your child with autism or ADHD?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Neurodevelopmental conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and autism affect about one in ten children. These conditions impact development, behaviour and wellbeing.
But children with these conditions and their caregivers often can’t get the support they need. Families report difficulties accessing health-care providers and experience long wait lists to receive care.
Digital tools, such as apps and websites, are often viewed as a solution to these gaps. With a single click or a download, families might be able to access information to support their child.
There are lots of digital tools available, but it’s hard to know what is and isn’t useful. Our new study evaluated freely available digital resources for child neurodevelopment and mental health to understand their quality and evidence base.
We found many resources were functional and engaging. However, resources often lacked evidence for the information provided and the claimed positive impact on children and families.
This is a common problem in the digital resource field, where the high expectations and claims of impact from digital tools to change health care have not yet been realised.
Fabio Principe/Shutterstock What type of resources?
Our study identified 3,435 separate resources, of which 112 (43 apps and 69 websites) met our criteria for review. These resources all claimed to provide information or supports for child neurodevelopment, mental health or wellbeing.
Resources had to be freely available, in English and have actionable information for children and families.
The most common focus was on autism, representing 17% of all resources. Resources suggested they provided strategies to promote speech, language and social development, and to support challenging behaviours.
Other common areas included language and communication (14%), and ADHD (10%).
Resources had various purposes, including journalling and providing advice, scheduling support, and delivering activities and strategies for parents. Resources delivered information interactively, with some apps organising content into structured modules.
Resources also provided options for alternative and assistive communication for people with language or communication challenges.
Most apps were functional and accessible
Our first question was about how engaging and accessible the information was. Resources that are hard to use aren’t used frequently, regardless of the information quality.
We evaluated aesthetics, including whether digital tools were easy to use and navigate, stylistically consistent, with clean and appealing graphics for users.
Most resources were rated as highly engaging, with strong accessibility and functionality.
Most apps and websites we evaluated were engaging. jamesteohart/Shutterstock But many lacked quality information
We ranked resources on various features from 1 (inadequate) to 5 (excellent), with a ranking of 3 considered acceptable. These ratings looked at how credible the resource was and whether there was evidence supporting it.
Despite their functionality, 37% of reviewed apps did not meet the minimum acceptable standards for information quality. This means many apps could not be recommended. Most websites fared better than apps.
There also wasn’t a lot of scientific evidence to suggest using either apps or digital resources actually helped families. Studies show long-term engagement with digital tools is rare, and downloads don’t correspond to frequent usage or benefits.
Digital tools are often viewed as a panacea to health-care gaps, but the evidence is yet to show they fill such gaps. Digital health is a fast-moving field and resources are often made available before they have been properly evaluated.
What should you look for in digital resources?
We found the highest quality resources were developed in collaboration with institutions, such as health, university or government groups.
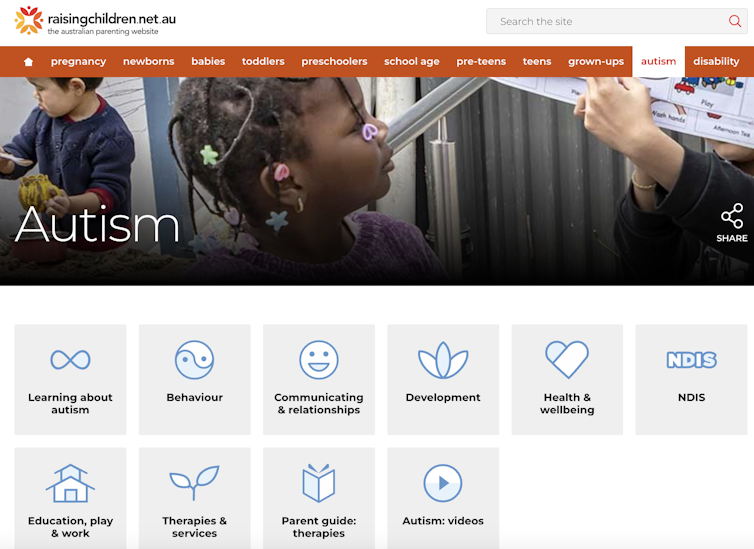
One highly rated resource was the Raising Children’s Network and the associated app, Raising Healthy Minds. These are co-developed with a university and hospital, and by people with appropriate qualifications.
This resource provides information to support children’s overall health, development and wellbeing, with dedicated sections addressing neurodevelopmental needs and concerns.
The Raising Children Network provides resources for child health, including neurodevelopmental needs. Raising Children Network screenshot Our research shows parents can assess whether digital resources are high quality by checking they are:
- factually correct. Look for where the app or resource is getting its information. Does the author have the qualifications and training to provide the information? Are they a registered health expert who is accountable to a regulatory body (such as AHPRA, the Australian Health Practitioners Regulation Agency) for providing information that does not cause harm?
- consistent across multiple credible sources, such as health institutions.
- linked to supporting information. Look for reliable links to reputable institutions. Links to peer-reviewed scientific journals are often helpful as those articles will also usually describe the limitations of the research presented.
- up-to-date. Apps should be frequently updated. For websites, dates of update are usually found on the homepage or at the bottom of individual pages.
Check when information was last updated. fizkes/Shutterstock Beware of red flags
Some things to watch out for are:
- testimonials and anecdotes without evidence and scientific links to back the anecdotes up. If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
- no information provided about conflicts of interest. Organisations gain when you click on their links or take their advice (financial, reputation and brand development). Think about what they gain when you use their information to help keep a balanced perspective.
Remember, the app’s star rating doesn’t mean it will contain factual information from a reliable source or be helpful for you and your child.
The role of digital tools
Digital tools won’t usually replace a health professional, but they can support care in many different ways. They may be used to help to educate and prepare for meetings, and to collaborate with health providers.
They may also be used to collect information about daily needs. Studies show reporting on sleep in children can be notoriously difficult, for example. But tracking sleep behaviour with actigraphy, where movement and activity patterns are measured using a wearable device, can provide information to support clinical care. With the promise of artificial intelligence, there will also be new opportunities to support daily living.
Our findings reflect a broader problem for digital health, however. Much investment is often made in developing products to drive use, with spurious claims of health benefits.
What’s needed is a system that prioritises the funding, implementation and evaluation of tools to demonstrate benefits for families. Only then may we realise the potential of digital tools to benefit those who use them.
Kelsie Boulton, Senior Research Fellow in Child Neurodevelopment, Brain and Mind Centre, University of Sydney and Adam Guastella, Professor and Clinical Psychologist, Michael Crouch Chair in Child and Youth Mental Health, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s the difference between shyness and social anxiety?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
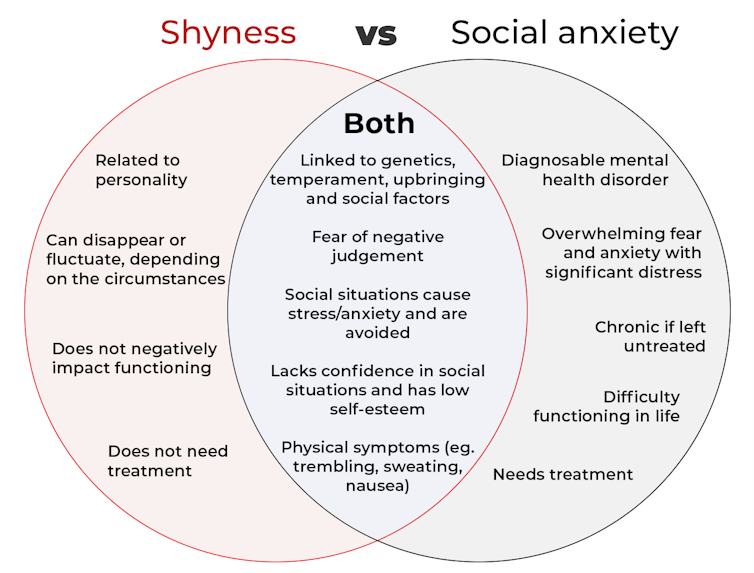
The terms “shyness” and “social anxiety” are often used interchangeably because they both involve feeling uncomfortable in social situations.
However, feeling shy, or having a shy personality, is not the same as experiencing social anxiety (short for “social anxiety disorder”).
Here are some of the similarities and differences, and what the distinction means.
pathdoc/Shutterstock How are they similar?
It can be normal to feel nervous or even stressed in new social situations or when interacting with new people. And everyone differs in how comfortable they feel when interacting with others.
For people who are shy or socially anxious, social situations can be very uncomfortable, stressful or even threatening. There can be a strong desire to avoid these situations.
People who are shy or socially anxious may respond with “flight” (by withdrawing from the situation or avoiding it entirely), “freeze” (by detaching themselves or feeling disconnected from their body), or “fawn” (by trying to appease or placate others).
A complex interaction of biological and environmental factors is also thought to influence the development of shyness and social anxiety.
For example, both shy children and adults with social anxiety have neural circuits that respond strongly to stressful social situations, such as being excluded or left out.
People who are shy or socially anxious commonly report physical symptoms of stress in certain situations, or even when anticipating them. These include sweating, blushing, trembling, an increased heart rate or hyperventilation.
How are they different?
Social anxiety is a diagnosable mental health condition and is an example of an anxiety disorder.
For people who struggle with social anxiety, social situations – including social interactions, being observed and performing in front of others – trigger intense fear or anxiety about being judged, criticised or rejected.
To be diagnosed with social anxiety disorder, social anxiety needs to be persistent (lasting more than six months) and have a significant negative impact on important areas of life such as work, school, relationships, and identity or sense of self.
Many adults with social anxiety report feeling shy, timid and lacking in confidence when they were a child. However, not all shy children go on to develop social anxiety. Also, feeling shy does not necessarily mean a person meets the criteria for social anxiety disorder.
People vary in how shy or outgoing they are, depending on where they are, who they are with and how comfortable they feel in the situation. This is particularly true for children, who sometimes appear reserved and shy with strangers and peers, and outgoing with known and trusted adults.
Individual differences in temperament, personality traits, early childhood experiences, family upbringing and environment, and parenting style, can also influence the extent to which people feel shy across social situations.
Not all shy children go on to develop social anxiety. 249 Anurak/Shutterstock However, people with social anxiety have overwhelming fears about embarrassing themselves or being negatively judged by others; they experience these fears consistently and across multiple social situations.
The intensity of this fear or anxiety often leads people to avoid situations. If avoiding a situation is not possible, they may engage in safety behaviours, such as looking at their phone, wearing sunglasses or rehearsing conversation topics.
The effect social anxiety can have on a person’s life can be far-reaching. It may include low self-esteem, breakdown of friendships or romantic relationships, difficulties pursuing and progressing in a career, and dropping out of study.
The impact this has on a person’s ability to lead a meaningful and fulfilling life, and the distress this causes, differentiates social anxiety from shyness.
Children can show similar signs or symptoms of social anxiety to adults. But they may also feel upset and teary, irritable, have temper tantrums, cling to their parents, or refuse to speak in certain situations.
If left untreated, social anxiety can set children and young people up for a future of missed opportunities, so early intervention is key. With professional and parental support, patience and guidance, children can be taught strategies to overcome social anxiety.
Why does the distinction matter?
Social anxiety disorder is a mental health condition that persists for people who do not receive adequate support or treatment.
Without treatment, it can lead to difficulties in education and at work, and in developing meaningful relationships.
Receiving a diagnosis of social anxiety disorder can be validating for some people as it recognises the level of distress and that its impact is more intense than shyness.
A diagnosis can also be an important first step in accessing appropriate, evidence-based treatment.
Different people have different support needs. However, clinical practice guidelines recommend cognitive-behavioural therapy (a kind of psychological therapy that teaches people practical coping skills). This is often used with exposure therapy (a kind of psychological therapy that helps people face their fears by breaking them down into a series of step-by-step activities). This combination is effective in-person, online and in brief treatments.
Treatment is available online as well as in-person. ImYanis/Shutterstock For more support or further reading
Online resources about social anxiety include:
- This Way Up’s online program for managing excessive shyness and fear of social situations
- Beyond Blue’s resources on social anxiety
- a guide to looking after yourself if you have social anxiety, from the Western Australian health department
- social anxiety online program for children and teens from the University of Queensland
- inroads, a self-guided online program for young adults who drink alcohol to manage their anxiety.
We thank the Black Dog Institute Lived Experience Advisory Network members for providing feedback and input for this article and our research.
Kayla Steele, Postdoctoral research fellow and clinical psychologist, UNSW Sydney and Jill Newby, Professor, NHMRC Emerging Leader & Clinical Psychologist, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: