Leek vs Scallions – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing leek to scallions, we picked the leek.
Why?
In terms of macros, scallions might have a point: scallions have the lower glycemic index, thanks to leek having more carbs for the same amount of fiber. That said, leek already has a low glycemic index, so this is not a big deal.
When it comes to vitamins, leek has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, E, and choline, while scallions have more of vitamins A, C, and K. Noteworthily, a cup of chopped leek already provides the daily dose of vitamins A and K, and the difference in levels of vitamin C is minimal. All in all, an easy 8:3 win for leeks here, even without taking that into account.
In the category of minerals, leek has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while scallions have a little more zinc.
Both of these allium-family plants (i.e., related to garlic) have an abundance of polyphenols, especially kaempferol.
Of course, enjoy whatever goes best with your meal, but if you’re looking for nutritional density, then leek is where it’s at.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Surgery is the default treatment for ACL injuries in Australia. But it’s not the only way
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
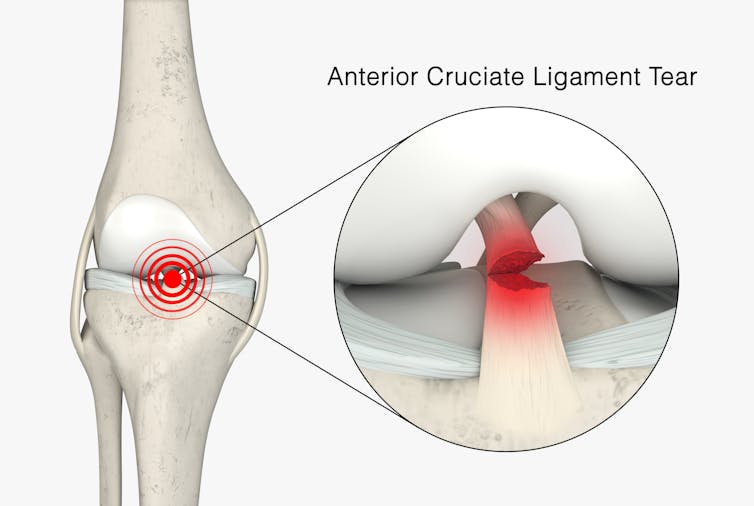
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is an important ligament in the knee. It runs from the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia) and helps stabilise the knee joint.
Injuries to the ACL, often called a “tear” or a “rupture”, are common in sport. While a ruptured ACL has just sidelined another Matildas star, people who play sport recreationally are also at risk of this injury.
For decades, surgical repair of an ACL injury, called a reconstruction, has been the primary treatment in Australia. In fact, Australia has among the highest rates of ACL surgery in the world. Reports indicate 90% of people who rupture their ACL go under the knife.
Although surgery is common – around one million are performed worldwide each year – and seems to be the default treatment for ACL injuries in Australia, it may not be required for everyone.
PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock What does the research say?
We know ACL ruptures can be treated using reconstructive surgery, but research continues to suggest they can also be treated with rehabilitation alone for many people.
Almost 15 years ago a randomised clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine compared early surgery to rehabilitation with the option of delayed surgery in young active adults with an ACL injury. Over half of people in the rehabilitation group did not end up having surgery. After five years, knee function did not differ between treatment groups.
The findings of this initial trial have been supported by more research since. A review of three trials published in 2022 found delaying surgery and trialling rehabilitation leads to similar outcomes to early surgery.
A 2023 study followed up patients who received rehabilitation without surgery. It showed one in three had evidence of ACL healing on an MRI after two years. There was also evidence of improved knee-related quality of life in those with signs of ACL healing compared to those whose ACL did not show signs of healing.
Experts used to think an ACL tear couldn’t heal without surgery – now there’s evidence it can. SKYKIDKID/Shutterstock Regardless of treatment choice the rehabilitation process following ACL rupture is lengthy. It usually involves a minimum of nine months of progressive rehabilitation performed a few days per week. The length of time for rehabilitation may be slightly shorter in those not undergoing surgery, but more research is needed in this area.
Rehabilitation starts with a physiotherapist overseeing simple exercises right through to resistance exercises and dynamic movements such as jumping, hopping and agility drills.
A person can start rehabilitation with the option of having surgery later if the knee remains unstable. A common sign of instability is the knee giving way when changing direction while running or playing sports.
To rehab and wait, or to go straight under the knife?
There are a number of reasons patients and clinicians may opt for early surgical reconstruction.
For elite athletes, a key consideration is returning to sport as soon as possible. As surgery is a well established method, athletes (such as Matilda Sam Kerr) often opt for early surgical reconstruction as this gives them a more predictable timeline for recovery.
At the same time, there are risks to consider when rushing back to sport after ACL reconstruction. Re-injury of the ACL is very common. For every month return to sport is delayed until nine months after ACL reconstruction, the rate of knee re-injury is reduced by 51%.
For people who opt to try rehabilitation, the option of having surgery later is still there. PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock Historically, another reason for having early surgical reconstruction was to reduce the risk of future knee osteoarthritis, which increases following an ACL injury. But a review showed ACL reconstruction doesn’t reduce the risk of knee osteoarthritis in the long term compared with non-surgical treatment.
That said, there’s a need for more high-quality, long-term studies to give us a better understanding of how knee osteoarthritis risk is influenced by different treatments.
Rehab may not be the only non-surgical option
Last year, a study looking at 80 people fitted with a specialised knee brace for 12 weeks found 90% had evidence of ACL healing on their follow-up MRI.
People with more ACL healing on the three-month MRI reported better outcomes at 12 months, including higher rates of returning to their pre-injury level of sport and better knee function. Although promising, we now need comparative research to evaluate whether this method can achieve similar results to surgery.
What to do if you rupture your ACL
First, it’s important to seek a comprehensive medical assessment from either a sports physiotherapist, sports physician or orthopaedic surgeon. ACL injuries can also have associated injuries to surrounding ligaments and cartilage which may influence treatment decisions.
In terms of treatment, discuss with your clinician the pros and cons of management options and whether surgery is necessary. Often, patients don’t know not having surgery is an option.
Surgery appears to be necessary for some people to achieve a stable knee. But it may not be necessary in every case, so many patients may wish to try rehabilitation in the first instance where appropriate.
As always, prevention is key. Research has shown more than half of ACL injuries can be prevented by incorporating prevention strategies. This involves performing specific exercises to strengthen muscles in the legs, and improve movement control and landing technique.
Anthony Nasser, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney; Joshua Pate, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney, and Peter Stubbs, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Counterclockwise – by Dr. Ellen Langer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written previously about Dr. Langer’s famous “Counterclockwise” study that saw reversals in biological markers of aging after a one-week intervention that consisted only of a (albeit rather intensive) mental reframe with regard to their age.
This book, as you might expect from the title, refers to that experiment a lot—but it doesn’t stop there. While the Counterclockwise experiment remains Dr. Langer’s most well-known, it’s not her most recent, and she draws from a wealth of research (her own and that of her colleagues in the field) to show the extent and limit of psychosomatic effect on aging.
Note:
- psychosomatic effect does not mean: “imagining it”
- psychosomatic effect means: “your brain regulates almost everything else in your body, directly or indirectly, including your autonomic functions, which includes immune function, tissue replacement, and more”
And as for when it comes to aging? Aging, like cancer, is in large part a problem of immune dysfunction; in both cases cells (be they senescent or cancerous, respectively) are not being killed when they are supposed to be, and in both cases, better instructions will improve the matter.
Many larger-scale markers of aging, such as mobility, are a case of the body only being able to do what the tissues allow, and the tissues are being constantly rebuilt (for better or for worse) according to autonomically-implemented specifications, and cells’ ability to carry out those orders.
Beyond the cellular physiology, this book discusses (a lot) the brain-down mechanisms by which the most powerful organ in our body can tell the rest of the body how old to be.
Dr. Langer also discusses the matter of “priming”, that is to say, how external factors prime us to believe certain things about our age and, with it, our health. These things can include popular media, conversations with friends and family, and healthcare providers’ framing of certain issues.
For example, a person just under a certain age and a person just over a certain age could both go to the doctor with the same complaint—a pain in a certain joint, let’s say. The doctor may refer the slightly younger patient for an x-ray because “let’s see what’s going on here”, and prescribe the slightly older patient some painkillers because “this is perfectly normal at your age”. One resultant problem is obvious: a difference in the standard of care. But the other resultant problem is less obvious: the older patient has now been primed to believe, by a confident authority figure, “it is natural for my body to be in a state of decline now, and this is what to expect”.
Thus, Dr. Langer prescribes mindfulness, not in the mindfulness meditation sense (though sure, do that too), but rather in the sense of consciously interacting with the world and making our own decisions about our own health and, yes, our own age. Because after all, our body neither knows nor cares how many times it has flown around the sun, and merely responds to physiological stimuli—including those we can influence with psychological reframing.
The book is not, per se, a “how-to” guide, rather it is an explanatory treatise, but it contains more than enough information to put it into practice, and indeed, she does also provide some exercises to do along the way.
The style is… Vivacious, without being especially upbeat. Dr. Langer is enthused about her work, yes, but she’s also angry at how many people are having their health sabotaged on the daily, and calls for a more health-first approach (as opposed to illness-first).
Bottom line: this is the book on our brain’s power over aging, so if that topic interests you, this book absolutely belongs on your bookshelf. Well, in your hands, and then on the bookshelf, and then back in your hands from time to time.
Click here to check out Counterclockwise, and age counterclockwise as her experimental subjects did!
Share This Post
-
Healthy Living in a Contaminated World – by Dr. Donald Hoernschemeyer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a lot going on here, as this book tackles very many kinds of common contaminants, from waste products and industrial chemicals (such as from fracking), pesticides that are banned in most places but not the US, smog and soot from coal and oil power, mercury and other heavy metals, dioxins, Teflon and its close relatives, phthalates, BPA, and other things again regulated out of use in many countries but not entirely in the US (which bans them only in some things, like baby bottles), drinking water issues of various kinds, and much more.
Indeed, there’s a whole chapter on the US and international regulation of toxic substances; the problem is often that on a political level, the same people who are against nebulous “chemicals” are also against environmentalist regulations that would ban them. This is mostly not a political book though, and rather is chiefly a book of chemistry (the author’s field).
It does also cover the medical maladies associated with various contaminants, while the bulk of the data is on the chemistry side of such things as “elimination times for toxic chemicals”, “amounts of pesticides in fruit and vegetables”, “antibiotics and hormones used in animal agriculture”, and so forth.
The style is dense, and/but it is clear the author has made an effort to not be too dry. Still, this is not a fun read; it’s depressing in content and the style is more suited to academia. There are appendices containing glossaries and acronym tables, but reading front-to-back, there’s a lot that’s not explained so unless you also are a PhD chemist, chances are you’ll be needing to leaf forwards and backwards a lot.
Bottom line: this book is not thrilling, but what you don’t know, can kill you.
Click here to check out Healthy Living In A Contaminated World, and improve your odds!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Elderberries vs Gooseberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing elderberries to gooseberries, we picked the elderberries.
Why?
These are both berries more likely found in your garden or local wood than in the supermarket, but if you have convenient access to them, they’re great options for eating!
In terms of macros, elderberry has nearly 2x the carbs and/but also nearly 2x the fiber, which in glycemic index terms, mostly cancels out (although: elderberry has the slightly lower glycemic index of the two)
In the category of vitamins, both are great but elderberries are winning with more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, and C, while gooseberries have more vitamin B5.
When it comes to minerals, elderberries again lead with more calcium, iron, phosphorus, and potassium, while gooseberries have more magnesium.
There is an extra category today, which is “extra medicinal properties”, and elderberries have extra immune-boosting qualities, whereas gooseberries—while being as polyphenol-laden as one usually expects berries to be—do not confer the same kind of benefit in this regard.
You can check out the information about elderberry’s extra properties in the links section below; meanwhile, if you’re choosing between these berries, that’s the clear winner in every category today!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Herbs for Evidence-Based Health & Healing ← including elderberry
- Does It Come In A Pill? ← it does (but it doesn’t have to)
- Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters! ← this article focusses on not-supplements, but does also have a supplement section
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s the difference between period pain and endometriosis pain?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Menstruation, or a period, is the bleeding that occurs about monthly in healthy people born with a uterus, from puberty to menopause. This happens when the endometrium, the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus, is shed.
Endometriosis is a condition that occurs when endometrium-like tissue is found outside the uterus, usually within the pelvic cavity. It is often considered a major cause of pelvic pain.
Pelvic pain significantly impacts quality of life. But how can you tell the difference between period pain and endometriosis?
Polina Zimmerman/Pexels Periods and period pain
Periods involve shedding the 4-6 millimetre-thick endometrial lining from the inside of the uterus.
As the lining detaches from the wall of the uterus, the blood vessels which previously supplied the lining bleed. The uterine muscles contract, expelling the blood and crumbled endometrium.
The crumbled endometrium and blood mostly pass through the cervix and vagina. But almost everyone back-bleeds via their fallopian tubes into their pelvic cavity. This is known as “retrograde menstruation”.
Most of the lining is shed through the vagina. Andrey_Popov/Shutterstock The process of menstrual shedding is caused by inflammatory substances, which also cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, headaches, aches, pains, dizziness, feeling faint, as well as stimulating pain receptors.
These inflammatory substances are responsible for the pain and symptoms in the week before a period and the first few days.
For women with heavy periods, their worst days of pain are usually the heaviest days of their period, coinciding with more cramps to expel clots and more retrograde bleeding.
Many women also have pain when they are releasing an egg from their ovary at the time of ovulation. Ovulation or mid-cycle pain can be worse in those who bleed more, as those women are more likely to bleed into the ovulation follicle.
Around 90% of adolescents experience period pain. Among these adolescents, 20% will experience such severe period pain they need time off from school and miss activities. These symptoms are too often normalised, without validation or acknowledgement.
What about endometriosis?
Many symptoms have been attributed to endometriosis, including painful periods, pain with sex, bladder and bowel-related pain, low back pain and thigh pain.
Other pain-related conditions such migraines and chronic fatigue have also been linked to endometriosis. But these other pain-related symptoms occur equally often in people with pelvic pain who don’t have endometriosis.
One in five adolescents who menstrate experience severe symptoms. CGN089/Shutterstock Repeated, significant period and ovulation pain can eventually lead some people to develop persistent or chronic pelvic pain, which lasts longer than six months. This appears to occur through a process known as central sensitisation, where the brain becomes more sensitive to pain and other sensory stimuli.
Central sensitisation can occur in people with persistent pain, independent of the presence or absence of endometriosis.
Eventually, many people with period and/or persistent pelvic pain will have an operation called a laparoscopy, which allows surgeons to examine organs in the pelvis and abdomen, and diagnose and treat endometriosis.
Yet only 50% of those with identical pain symptoms who undergo a laparoscopy will end up having endometriosis.
Endometriosis is also found in pain-free women. So we cannot predict who does and doesn’t have endometriosis from symptoms alone.
How is this pain managed?
Endometriosis surgery usually involves removing lesions and adhesions. But at least 30% of people return to pre-surgery pain levels within six months or have more pain than before.
After surgery, emergency department presentations for pain are unchanged and 50% have repeat surgery within a few years.
Suppressing periods using hormonal therapies (such as continuous oral contraceptive pills or progesterone-only approaches) can suppress endometriosis and reduce or eliminate pain, independent of the presence or absence of endometriosis.
Not every type or dose of hormonal medications suits everyone, so medications need to be individualised.
The current gold-standard approach to manage persistent pelvic pain involves a multidisciplinary team approach, with the aim of achieving sustained remission and improving quality of life. This may include:
- physiotherapy for pelvic floor and other musculoskeletal problems
- management of bladder and bowel symptoms
- support for self-managing pain
- lifestyle changes including diet and exercise
- psychological or group therapy, as our moods, stress levels and childhood events can affect how we feel and experience pain.
Whether you have period pain, chronic pelvic pain or pain you think is associated with endometriosis, if you feel pain, it’s real. If it’s disrupting your life, you deserve to be taken seriously and treated as the whole person you are.
Sonia R. Grover, Senior Research Fellow, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute; Clinical Professor of Gynaecology, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What is Ryeqo, the recently approved medicine for endometriosis?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For women diagnosed with endometriosis it is often a long sentence of chronic pain and cramping that impacts their daily life. It is a condition that is both difficult to diagnose and treat, with many women needing either surgery or regular medication.
A medicine called Ryeqo has just been approved for marketing specifically for endometriosis, although it was already available in Australia to treat a different condition.
Women who want the drug will need to consult their local doctor and, as it is not yet on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, they will need to pay the full cost of the script.
What does Ryeqo do?
Endometriosis affects 14% of women of reproductive age. While we don’t have a full understanding of the cause, the evidence suggests it’s due to body tissue that is similar to the lining of the uterus (called the endometrium) growing outside the uterus. This causes pain and inflammation, which reduces quality of life and can also affect fertility.
Ryeqo is a tablet containing three different active ingredients: relugolix, estradiol and norethisterone.
Relugolix is a drug that blocks a particular peptide from releasing other hormones. It is also used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Estradiol is a naturally occurring oestrogen hormone in women that helps regulate the menstrual cycle and is used in menopausal hormone therapy. Norethisterone is a synthetic hormone commonly used in birth control medications and to delay menstruation and help with heavy menstrual bleeding.
All three components work together to regulate the levels of oestrogen and progesterone in the body that contribute to endometriosis, alleviating its symptoms.
Relugolix reduces the overall levels of oestrogen and progesterone in the body. The estradiol compensates for the loss of oestrogen because low oestrogen levels can cause hot flushes (also called hot flashes) and bone density loss. And norethisterone blocks the effects of estradiol on the uterus (where too much tissue growth is unwanted).
Is it really new?
The maker of Ryeqo claims it is the first new drug for endometriosis in Australia in 13 years.
But individually, all three active ingredients in Ryeqo have been in use since 2019 or earlier.
Ryeqo has been available in Australia since 2022, but until now was not specifically indicated for endometriosis. It was originally approved for the treatment of uterine fibroids, which share some common symptoms with endometriosis and have related causes.
In addition to Ryeqo, current medical guidance lists other drugs that are suitable for endometriosis and some reformulations of these have also only been recently approved.
The oral medicine Dienogest was approved in 2021, and there have been a number of injectable drugs for endometriosis recently approved, such as Sayana Press which was approved in a smaller dose form for self-injection in 2023.
You can’t take the contraceptive pill with Ryeqo but the endometriosis drug could replace it.
ShutterstockHow to take it and what not to do
Ryeqo is a once-a-day tablet. You can take it with, or without food, but it should be taken about the same time each day.
It is recommended you start taking Ryeqo within the first five days after the start of your next period. If you start at another time during your period, you may experience initial irregular or heavier bleeding.
Because it contains both synthetic and natural hormones, you can’t use the contraceptive pill and Ryeqo together. However, because Ryeqo does contain norethisterone it can be used as your contraception, although it will take at least one month of use to be effective. So, if you are on Ryeqo, you should use a non-hormonal contraceptive – such as condoms – for a month when starting the medicine.
Ryeqo may be incompatible with other medicines. It might not be suitable for you if you take medicines for epilepsy, HIV and AIDS, hepatitis C, fungal or bacterial infections, high blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, angina (chest pain), or organ rejection. You should also not take Ryeqo if you have a liver tumour or liver disease.
The possible side effects of Ryeqo are similar to those of oral contraceptives. Blood clots are a risk with any medicine that contains an oestrogen or a progestogen, which Ryeqo does. Other potential side effects include bone loss, a reduction in menstrual blood loss or loss of your period.
It’s costly for now
Ryeqo can now be prescribed in Australia, so you should discuss whether Ryeqo is right for you with the doctor you usually consult for your endometriosis.
While the maker has made a submission to the Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee, it is not yet subsidised by the Australian government. This means that rather than paying the normal PBS price of up to A$31.60, it has been reported it may cost as much as $135 for a one-month supply. The committee will make a decision on whether to subsidise Ryeqo at its meeting next month.
Correction: this article has been updated to clarify the recent approval of specific formulations of drugs for endometriosis.
Nial Wheate, Associate Professor of the School of Pharmacy, University of Sydney and Jasmine Lee, Pharmacist and PhD Candidate, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: