Improving Women’s Health Across the Lifespan – by Dr. Michelle Tollefson et al.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We say “et al.”, because this hefty book (504 pages) is a compilation of contributions by about 60 authors, of whom, 100% are doctors and about 90% are women.
As one might expect from a book with many small self-contained chapters by such a lot of doctors, the content is very diverse, though the style is consistent throughout, likely due to the authors working from a style sheet, plus the work of the editorial team.
About that content: the focus here is lifestyle medicine, and while much of the advice will go for men too (most people are unlikely to go wrong with “eat more fruits and vegetables and get better sleep” etc), anything more detailed than that (of which there’s a lot) is focussed on women. Hence, we get chapters on optimal nutrition for women, physical activity for women, sleep and women’s health, etc, as well as topics that can affect everyone but disproportionately affect women—ranging from autoimmune diseases to social burdens that affect health in measurable ways. There’s also, as you might expect, plenty about sexual health, pregnancy-related health, menopausal health, and so forth.
The strength of this book is really in its diversity; it’s very much a case of “60 heads are better than one”, and as such, we’re pretty much getting 60 books for the price of one here, as each author brings what they are most specialized in.
Bottom line: if you are a woman and/or love a woman, this book is packed with information that will be of interest and applicable use.
Click here to check out Improving Women’s Health Across The Lifespan, and do just that!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hemp Seeds vs Flax Seeds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing hemp seeds to flax seeds, we picked the flax.
Why?
Both are great, but quite differently so! In other words, they both have their advantages, but on balance, we prefer the flax’s advantages.
Part of this come from the way in which they are sold/consumed—hemp seeds must be hulled first, which means two things as a result:
- Flax seeds have much more fiber (about 8x more)
- Hemp seeds have more protein (about 2x more), proportionally, at least ← this is partly because they lost a bunch of weight by losing their fiber to the hulling, so the “per 100g” values of everything else go up, even though the amount per seed didn’t change
Since people’s diets are more commonly deficient in fiber than protein, and also since 8x is better than 2x, we consider this a win for flax.
Of course, many people enjoy hemp or flax specifically for the healthy fatty acids, so how do they stack up in that regard?
- Flax seeds have more omega-3s
- Hemp seeds have more omega-6s
This, for us, is a win for flax too, as the omega-3s are generally what we need more likely to be deficient in. Hemp enthusiasts, however, may argue that the internal balance of omega-3s to omega-6s is closer to an ideal ratio in hemp—but nutrition doesn’t exist in a vacuum, so we have to consider things “as part of a balanced diet” (because if one were trying to just live on hemp seeds, one would die), and most people’s diets are skewed far too far in favor or omega-6 compared to omega-3. So for most people, the higher levels of omega-3s are the more useful.
Want to learn more?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Feel Great, Lose Weight – by Dr. Rangan Chatterjee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know that losing weight sustainably tends to be harder than simply losing weight. We know that weight loss needs to come with lifestyle change. But how to get there?
One of the biggest problems that we might face while trying to lose weight is that our “metabolic thermostat” has got stuck at the wrong place. Trying to move it just makes our bodies think we are starving, and everything gets even worse. We can’t even “mind over matter” our way through it with willpower, because our bodies will do impressive things on a cellular level in an attempt to save us… Things that are as extraordinary as they are extraordinarily unhelpful.
Dr. Rangan Chatterjee is here to help us cut through that.
In this book, he covers how our metabolic thermostat got stuck in the wrong place, and how to gently tease it back into a better position.
Some advices won’t be big surprises—go for a whole foods diet, avoiding processed food, for example. Probably not a shocker.
Others are counterintuitive, but he explains how they work—exercising less while moving more, for instance. Sounds crazy, but we assure you there’s a metabolic explanation for it that’s beyond the scope of this review. And there’s plenty more where that came from, too.
Bottom line: if your weight has been either slowly rising, or else very stable but at a higher point than you’d like, Dr. Chatterjee can help you move the bar back to where you want it—and keep it there.
Share This Post
-
Compact Tai Chi – by Dr. Jesse Tsao
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A very frustrating thing when practicing tai chi, especially when learning, is the space typically required. We take a step this way and lunge that way and turn and now we’ve kicked a bookcase. Add a sword, and it’s goodnight to the light fixtures at the very least.
While a popular suggestion may be “do it outside”, we do not all have the luxury of living in a suitable climate. We also may prefer to practice in private, with no pressing urge to have an audience.
Tsao’s book, therefore, is very welcome. But how does he do it? The very notion of constriction is antithetical to tai chi, after all.
He takes the traditional forms, keeps the movements mostly the same, and simply changes the order of them. This way, the practitioner revolves around a central point. Occasionally, a movement will become a smaller circle than it was, but never in any way that would constrict movement.
Of course, an obvious question for any such book is “can one learn this from a book?” and the answer is complex, but we would lean towards yes, and insofar as one can learn any physical art from a book, this one does a fine job. It helps that it builds up progressively, too.
All in all, this book is a great choice for anyone who’s interested in taking up tai chi, and/but would like to do so without leaving their home.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Secret to Mental Health – by George Pransky
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book (and its author) have a sizeable popular following, so it definitely can be said that it has been well-received by many people. The premise in this book is that there is fundamentally nothing wrong with anybody’s brain, and rather everything can be broken down into:
- Mind (the energy and intelligence that animates all life)
- Consciousness (the capacity to be aware of one’s life and experiences)
- Thought (the ability to think, allowing individuals to create their personal experience of reality)
The author explains, over the course of 145 pages, that where anyone with any perceived mental health issue is going wrong is by either lacking self-awareness (Consciousness) or erring by creating an undesirable personal experience of reality (Thought).
In terms of the science of this, frequent references are made to “there is evidence that shows”, “new discoveries about mental health suggest…”, etc, but this claimed evidence is never actually presented, just alluded to. Where many books would have a bibliography, this one has simply a collection of what the author has titled “interesting case studies, conversations, papers, and discussions” (there are no actual case studies or papers; it is just a collection of anecdotes).
The style is… Honestly, in this reviewer’s opinion, barely readable. But, apparently lots of people love it, so your mileage may vary.
We don’t usually delve too far into claimed credentials, but because of the interesting writing style and the bold claims without evidence, we were curious as to where this PhD came from, and apparently it came from a now-shut-down diploma mill that was described by the court as “a complete scam”.
Bottom line: we can’t recommend this one, but we read it so that you don’t have to, and we hope that publishing this review will help reassure you that when we do recommend a book, we mean it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
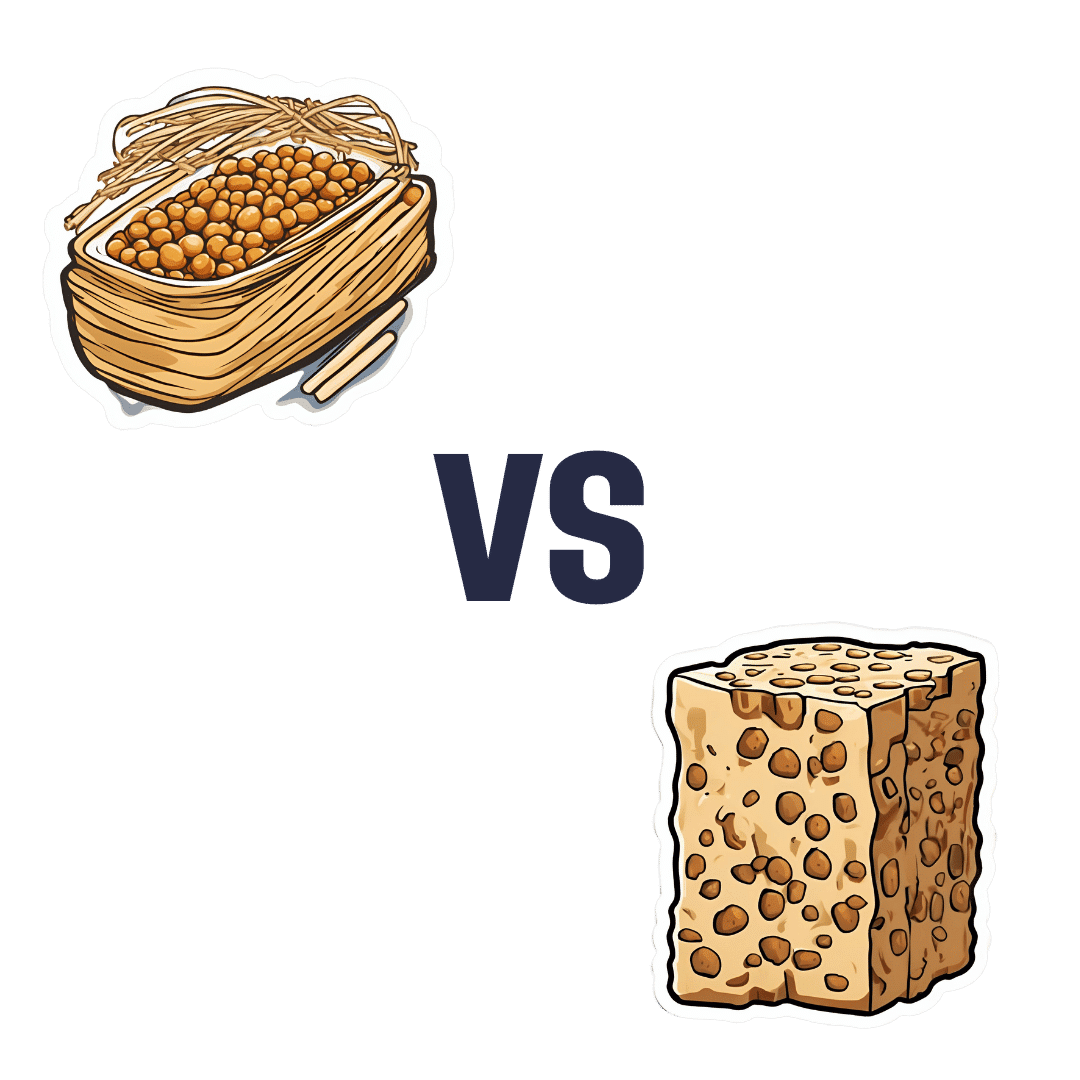
Natto vs Tempeh – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing nattō to tempeh, we picked the nattō.
Why?
Both are great, but in the battle of fermented soybeans vs fermented soybeans with extra steps, it turns out that the simplest option is the best, even if tempeh was a close runner-up:
In terms of macros, nattō has more carbs and fiber for the same protein and fat; we’ll call this category a tie or a marginal win for nattō.
In the category of vitamins, nattō has more of vitamins B1, C, E, K, and choline, while tempeh has more of vitamins B2, B3, B6, and B9. A clearer, yet still modest, win for nattō.
Minerals, however, are what really set them apart: nattō has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while tempeh has more phosphorus. An overwhelming win for nattō this time.
In short: enjoy either or both, but nattō is the more nutritionally dense option!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
21% Stronger Bones in a Year at 62? Yes, It’s Possible (No Calcium Supplements Needed!) ← nattō is featured as part of the diet 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Benefits of Different Tropical Fruits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Would very much like your views of the benefits of different tropical fruits. I do find papaya is excellent for settling the digestion – but keen to know if others have remarkable qualities.❞
Definitely one for a main feature sometime soon! As a bonus while you wait, pineapple has some unique and powerful properties:
❝Its properties include: (1) interference with growth of malignant cells; (2) inhibition of platelet aggregation*; (3) fibrinolytic activity; (4) anti-inflammatory action; (5) skin debridement properties. These biological functions of bromelain, a non-toxic compound, have therapeutic values in modulating: (a) tumor growth; (b) blood coagulation; (c) inflammatory changes; (d) debridement of third degree burns; (e) enhancement of absorption of drugs.❞
*so do be aware of this if you are on blood thinners or otherwise have a bleeding disorder, as you might want to skip the pineapple in those cases!
Source: Bromelain, the enzyme complex of pineapple (Ananas comosus) and its clinical application. An update
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: