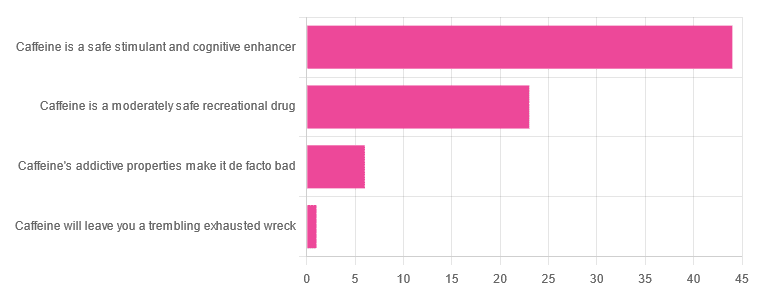
How old’s too old to be a doctor? Why GPs and surgeons over 70 may need a health check to practise
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A growing number of complaints against older doctors has prompted the Medical Board of Australia to announce today that it’s reviewing how doctors aged 70 or older are regulated. Two new options are on the table.
The first would require doctors over 70 to undergo a detailed health assessment to determine their current and future “fitness to practise” in their particular area of medicine.
The second would require only general health checks for doctors over 70.
A third option acknowledges existing rules requiring doctors to maintain their health and competence. As part of their professional code of conduct, doctors must seek independent medical and psychological care to prevent harming themselves and their patients. So, this third option would maintain the status quo.

Haven’t we moved on from set retirement ages?
It might be surprising that stricter oversight of older doctors’ performance is proposed now. Critics of mandatory retirement ages in other fields – for judges, for instance – have long questioned whether these rules are “still valid in a modern society”.
However, unlike judges, doctors are already required to renew their registration annually to practise. This allows the Medical Board of Australia not only to access sound data about the prevalence and activity of older practitioners, but to assess their eligibility regularly and to conduct performance assessments if and when they are needed.
What has prompted these proposals?
This latest proposal identifies several emerging concerns about older doctors. These are grounded in external research about the effect of age on doctors’ competence as well as the regulator’s internal data showing surges of complaints about older doctors in recent years.
Studies of medical competence in ageing doctors show variable results. However, the Medical Board of Australia’s consultation document emphasises studies of neurocognitive loss. It explains how physical and cognitive impairment can lead to poor record-keeping, improper prescribing, as well as disruptive behaviour.
The other issue is the number of patient complaints against older doctors. These “notifications” have surged in recent years, as have the number of disciplinary actions against older doctors.
In 2022–2023, the Medical Board of Australia took disciplinary action against older doctors about 1.7 times more often than for doctors under 70.
In 2023, notifications against doctors over 70 were 81% higher than for the under 70s. In that year, patients sent 485 notifications to the Medical Board of Australia about older doctors – up from 189 in 2015.
While older doctors make up only about 5.3% of the doctor workforce in Australia (less than 1% over 80), this only makes the high numbers of complaints more starkly disproportionate.
It’s for these reasons that the Medical Board of Australia has determined it should take further regulatory action to safeguard the health of patients.
So what distinguishes the two new proposed options?
The “fitness to practise” assessment option would entail a rigorous assessment of doctors over 70 based on their specialisation. It would be required every three years after the age of 70 and every year after 80.
Surgeons, for example, would be assessed by an independent occupational physician for dexterity, sight and the ability to give clinical instructions.
Importantly, the results of these assessments would usually be confidential between the assessor and the doctor. Only doctors who were found to pose a substantial risk to the public, which was not being managed, would be obliged to report their health condition to the Medical Board of Australia.
The second option would be a more general health check not linked to the doctor’s specific role. It would occur at the same intervals as the “fitness to practise” assessment. However, its purpose would be merely to promote good health-care decision-making among health practitioners. There would be no general obligation on a doctor to report the results to the Medical Board of Australia.
In practice, both of these proposals appear to allow doctors to manage their own general health confidentially.
The law tends to prioritise patient safety
All state versions of the legal regime regulating doctors, known as the National Accreditation and Registration Scheme, include a “paramountcy” provision. That provision basically says patient safety is paramount and trumps all other considerations.
As with legal regimes regulating childcare, health practitioner regulation prioritises the health and safety of the person receiving the care over the rights of the licensed professional.
Complicating this further, is the fact that a longstanding principle of health practitioner regulation has been that doctors should not be “punished” for errors in practice.
All of this means that reforms of this nature can be difficult to introduce and that the balance between patient safety and professional entitlements must be handled with care.
Could these proposals amount to age discrimination?
It is premature to analyse the legal implications of these proposals. So it’s difficult to say how these proposals interact with Commonwealth age- and other anti-discrimination laws.
For instance, one complication is that the federal age discrimination statute includes an exemption to allow “qualifying bodies” such as the Medical Board of Australia to discriminate against older professionals who are “unable to carry out the inherent requirements of the profession, trade or occupation because of his or her age”.
In broader terms, a licence to practise medicine is often compared to a licence to drive or pilot an aircraft. Despite claims of discrimination, New South Wales law requires older drivers to undergo a medical assessment every year; and similar requirements affect older pilots and air traffic controllers.
Where to from here?
When changes are proposed to health practitioner regulation, there is typically much media attention followed by a consultation and behind-the-scenes negotiation process. This issue is no different.
How will doctors respond to the proposed changes? It’s too soon to say. If the proposals are implemented, it’s possible some older doctors might retire rather than undergo these mandatory health assessments. Some may argue that encouraging more older doctors to retire is precisely the point of these proposals. However, others have suggested this would only exacerbate shortages in the health-care workforce.
The proposals are open for public comment until October 4.
Christopher Rudge, Law lecturer, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Keep Inflammation At Bay
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
You asked us to do a main feature on inflammation, so here we go!
Before we start, it’s worth noting an important difference between acute and chronic inflammation:
- Acute inflammation is generally when the body detects some invader, and goes to war against it. This (except in cases such as allergic responses) is usually helpful.
- Chronic inflammation is generally when the body does a civil war. This is almost never helpful.
We’ll be tackling the latter, which frees up your body’s resources to do better at the former.
First, the obvious…
These five things are as important for this as they are for most things:
- Get a good diet—the Mediterranean diet is once again a top-scorer
- Exercise—move and stretch your body; don’t overdo it, but do what you reasonably can, or the inflammation will get worse.
- Reduce (or ideally eliminate) alcohol consumption. When in pain, it’s easy to turn to the bottle, and say “isn’t this one of red wine’s benefits?” (it isn’t, functionally*). Alcohol will cause your inflammation to flare up like little else.
- Don’t smoke—it’s bad for everything, and that goes for inflammation too.
- Get good sleep. Obviously this can be difficult with chronic pain, but do take your sleep seriously. For example, invest in a good mattress, nice bedding, a good bedtime routine, etc.
*Resveratrol (which is a polyphenol, by the way), famously found in red wine, does have anti-inflammatory properties. However, to get enough resveratrol to be of benefit would require drinking far more wine than will be good for your inflammation or, indeed, the rest of you. So if you’d like resveratrol benefits, consider taking it as a supplement. Superficially it doesn’t seem as much fun as drinking red wine, but we assure you that the results will be much more fun than the inflammation flare-up after drinking.
About the Mediterranean Diet for this…
There are many causes of chronic inflammation, but here are some studies done with some of the most common ones:
- Beneficial effect of Mediterranean diet in systemic lupus erythematosus patients
- How the Mediterranean diet and some of its components modulate inflammatory pathways in arthritis
- The effects of the Mediterranean diet on biomarkers of vascular wall inflammation and plaque vulnerability in subjects with high risk for cardiovascular disease
- Adherence to Mediterranean diet and 10-year incidence of diabetes: correlations with inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers*
*Type 1 diabetes is a congenital autoimmune disorder, as the pancreas goes to war with itself. Type 2 diabetes is different, being a) acquired and b) primarily about insulin resistance, and/but this is related to chronic inflammation regardless. It is also possible to have T1D and go on to develop insulin resistance, and that’s very bad, and/but beyond the scope of today’s newsletter, in which we are focusing on the inflammation aspects.
Some specific foods to eat or avoid…
Eat these:
- Leafy greens
- Cruciferous vegetables
- Tomatoes
- Fruits in general (berries in particular)
- Healthy fats, e.g. olives and olive oil
- Almonds and other nuts
- Dark chocolate (choose high cocoa, low sugar)
Avoid these:
- Processed meats (absolute worst offenders are hot dogs, followed by sausages in general)
- Red meats
- Sugar (includes most fruit juices, but not most actual fruits—the difference with actual fruits is they still contain plenty of fiber, and in many cases, antioxidants/polyphenols that reduce inflammation)
- Dairy products (unless fermented, in which case it seems to be at worst neutral, sometimes even a benefit, in moderation)
- White flour (and white flour products, e.g. white bread, white pasta, etc)
- Processed vegetable oils
See also: 9 Best Drinks To Reduce Inflammation, Says Science
Supplements?
Some supplements that have been found to reduce inflammation include:
(links are to studies showing their efficacy)
Consider Intermittent Fasting
Remember when we talked about the difference between acute and chronic inflammation? It’s fair to wonder “if I reduce my inflammatory response, will I be weakening my immune system?”, and the answer is: generally, no.
Often, as with the above supplements and dietary considerations, reducing inflammation actually results in a better immune response when it’s actually needed! This is because your immune system works better when it hasn’t been working in overdrive constantly.
Here’s another good example: intermittent fasting reduces the number of circulating monocytes (a way of measuring inflammation) in healthy humans—but doesn‘t compromise antimicrobial (e.g. against bacteria and viruses) immune response.
See for yourself: Dietary Intake Regulates the Circulating Inflammatory Monocyte Pool ← the study is about the anti-inflammatory effects of fasting
Share This Post
-
Vegetarian & Vegan Diets: Good Or Bad For Brain Health?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s well-established that most people should eat more plants, and generally speaking, less meat. But what about abstaining from meat completely? And what about abstaining from all animal products?
For a more general overview (rather than specifically brain health), check out: Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy?
Now, about brains…
Before Homo sapiens was a thing, our precursors such as Homo habilis developed language (thus: greatly enhanced collaborative teamwork) and cooking, resulting in Homo ergaster (who came approximately next in line, give or take taxonomical quibbles) having twice the cranial capacity, generally attributed to being able to acquire and—where appropriate—cook calorie-dense food, which included meat, and also tubers that can’t be safely eaten raw. It’s estimated (based on forensic examination of tooth wear, mineralization, microdeposits of various kinds, etc) that our consumption of animal products in that era was around 10% of our diet (fluctuating by region, of course), but it likely was an important one.
By the time we got to Homo erectus, our skulls (including our cranial cavities, and thus it is presumed, our brains) were actually larger than in Homo sapiens. You may be wondering about Homo neanderthalensis; our cousins (or in some cases, ancestors—but that is beyond the scope of today’s article) also had larger cranial cavities than us, and certainly enjoyed comparatively advanced culture, arts, religion, etc.
Fast-forward to the present day. Nothing is going to meaningfully change our skull size, as individuals. Brain size? Well, keep hydrated or it’ll shrink. Don’t overhydrate or it’ll swell. Neuroplasticity means we can increase (or lose) volume in specific areas of the brain, according to what we do most of. For example, if you were to scan this writer’s brain, you’d probably find overdevelopment in the various areas pertaining to language and memory, as that’s been “my thing” for as long as I can remember (which is a long way). See also: An Underrated Tool Against Alzheimer’s
The impact of diet in the modern day
Unlike our distant ancestors, if we want a high-calorie snack we can buy some nuts from the supermarket, and if anything, this can be a problem (as many people’s go-to high-calorie snack may be a lot less healthy than that), and in turn cause problems for the brain, because too many pizzas, cheeseburgers, tater tots, and so forth cause chronic inflammation, and thus, neuroinflammation.
See also: 6 Worst Foods That Cause Dementia
So much for “calories for the brain”. Yes, the brain definitely needs calories (it expends a very large portion of our daily calorie intake), but you can have too much of a good thing.
In any case, the brain needs more than just calories!
For example, you may remember the “6 Pillars Of Nutritional Psychiatry”, which are:
- Be whole; eat whole
- Eat the rainbow
- The greener, the better
- Tap into your body intelligence
- Consistency & balance are key
- Avoid anxiety-triggering foods
For more on all of those, see Dr. Uma Naidoo’s 6 Pillars Of Nutritional Psychiatry ← She’s a Harvard-trained psychiatrist, professional chef graduating with her culinary school’s most coveted award, and a trained nutritionist. Between those three qualifications, she knows her stuff when it comes to the niche that is nutritional psychiatry.
When it comes to any potential nutritional deficiencies of a vegetarian or vegan diet, it’s a matter of planning.
Properly planned vegetarian diets are rich in essential nutrients like carbohydrates, fiber, magnesium, potassium, folate, vitamins C and E, and an abundance of phytochemicals, which support brain health (and overall health too, but today is about brain health).
However, if not well-planned, they can indeed lack certain nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are critical for brain function.
In essence, there’s a difference between a “whole foods plant-based diet” and junk food that just happens to be vegetarian or vegan.
Vitamin B12 is usually supplemented by vegans, but it can also be enjoyed from nutritional yeast used in cooking (it adds a cheesy flavor to dishes for which that’d be appropriate).
Iron is a fascinating beast, because while everyone thinks of red meat (which is indeed rich in iron), not only are there good plant-based sources of iron, but there are important considerations when it comes to bioavailability differences between heme and non-heme iron. In few words, heme iron (from blood etc) is more bioavailable by 1.8x, but all iron, including non-heme iron (from beans, greens, etc) can have its bioavailability multiplied by 5x just by having it with vitamin C:
Avoiding Anemia (More Than Just “Get More Iron”)
Omega-3 fatty acids, for vegetarians that mostly means eggs. See: Eggs: All Things In Moderation?
For vegans, we must look to nuts and seeds, for the most part. Or supplement—many omega 3 supplements are vegan, made from algae, or seaweed (that in turn is composed partially or entirely of algae):
So really, it comes down to “make sure you still get these things”, and once you’re used to it, it’s easy.
For those who prefer to keep some meat in their diet
Our summary in our top-linked article (Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy?) concluded:
- Most of us can live healthily and happily on just plants if we so choose.
- Some people cannot, and will require varying kinds (and quantities) of animal products.
- As for red and/or processed meats, we’re not the boss of you, but from a health perspective, the science is clear: unless you have a circumstance that really necessitates it, just don’t.
- Same goes for pork, which isn’t red and may not be processed, but metabolically it’s associated with the same problems.
- The jury is out on poultry, but it strongly appears to be optional, healthwise, without making much of a difference either way
- Fish is roundly considered healthful in moderation. Enjoy it if you want, don’t if you don’t.
And the paper from which we’ve largely been working from today included such comments as:
❝ Evidence suggests that vegan and vegetarian diets, when well planned, can be rich in phytonutrients and antioxidants, which have been associated with lower levels of inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). These findings indicate a potential role in reducing systemic inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are linked to neurodegenerative diseases.
However, deficiencies in critical nutrients such as vitamin B12, DHA, EPA, and iron have been consistently associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline, mood disturbances, and neurodegenerative disorders.
While plant-based diets provide anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits, their neurological implications depend on nutrient adequacy. Proper planning, supplementation, and food preparation techniques are essential to mitigate risks and enhance cognitive health.❞
Source: Impact of Vegan and Vegetarian Diets on Neurological Health: A Critical Review ← you can see that they also cover the same nutrients that we do
One final note, not discussed above
We often say “what’s good for your heart is good for your brain”, because the former feeds the latter (with oxygen and nutrients) and assists in cleanup (of detritus that otherwise brings about cognitive decline).
So with that in mind…
What Matters Most For Your Heart? ← hint: it’s fiber. So whether you eat animal products or not, please do eat plenty of plants!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Two Sides Of Caffeine
We asked you for your health-related opinions on caffeine itself, not necessarily the coffee, tea, energy drinks, etc that might contain it.
We have, by the way previously written about the health effects of coffee and tea specifically:
As for our question about caffeine itself, though, we got the above-depicted, below-described, set of results:
- About 59% said “caffeine is a safe stimulant and cognitive enhancer”
- About 31% said “caffeine is a moderately safe recreational drug”
- About 8% said “caffeine’s addictive properties make it de facto bad”
- One (1) person said “caffeine will leave you a trembling exhausted wreck”
But what does the science say?
Caffeine is addictive: True or False?
True, though one will find occasional academics quibbling the definition. Most of the studies into the mechanisms of caffeine addiction have been conducted on rats, but human studies exist too and caffeine is generally considered addictive for humans, for example:
See also:
Notwithstanding its addictive status, caffeine is otherwise safe: True or False?
True-ish, for most people. Some people with heart conditions or a hypersensitivity to caffeine may find it is not safe for them at all, and for the rest of us, the dose makes the poison. For example:
❝Can too much caffeine kill you? Although quite rare, caffeine can be fatal in cases of overdose; such circumstances are generally not applicable to healthy individuals who typically consume caffeine via beverages such as tea or coffee.❞
this paper, by the way, also includes a good example of academics quibbling the definition of addiction!
Caffeine is a cognitive enhancer: True or False?
True, but only in the case of occasional use. If you are using it all the time, your physiology will normalize it and you will require caffeine in order to function at your normal level. To attain higher than that, once addicted to caffeine, would now require something else.
Read more: Caffeine: benefits and drawbacks for technical performance
Caffeine will leave you a trembling exhausted wreck: True or False?
True or False depending on usage:
- The famously moderate 3–5 cups per day will not, for most people, cause any such problems.
- Using/abusing it to make up for lost sleep (or some other source of fatigue, such as physical exhaustion from exertion), however, is much more likely to run into problems.
In the latter case, caffeine really is the “payday loan” of energy! It’ll give you an adrenal boost now (in return, you must suffer the adrenal dumping later, along with lost energy expended in the adrenaline surge), and also, the tiredness that you thought was gone, was just caffeine’s adenosine-blocking activities temporarily preventing you from being able to perceive the tiredness. So you’ll have to pay that back later, with interest, because of the extra time/exertion too.
Want to make caffeine a little more gentle on your system?
Taking l-theanine alongside caffeine can ameliorate some of caffeine’s less wonderful effects—and as a bonus, l-theanine has some nifty benefits of its own, too:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Younger Next Year – by Chris Crowley & Dr. Henry Lodge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is it diet and exercise? Well, of course that’s a component. Specific kinds of exercise, too. But, as usual when we feature a book, there’s more:
In this case, strong throughout is the notion of life being a marathon not a sprint—and training for it accordingly.
Doing the things now that you’ll really wish you’d started doing sooner, and finding ways to build them into daily life.
Not just that, though! The authors take a holistic approach to life and health, and thus also cover work life, social life, and so forth. Now, you may be thinking “I’m already in the 80 and beyond category; I don’t work” and well, the authors advise that you do indeed work. You don’t have to revamp your career, but science strongly suggests that people who work longer, live longer.
Of course that doesn’t have to mean going full-throttle like a 20-year-old determined to make their mark on the world (you can if you want, though). It could be volunteering for a charity, or otherwise just finding a socially-engaging “work-like” activity that gives you purpose.
About the blend of motivational pep talk and science—this book is heavily weighted towards the former. It has, however, enough science to keep it on the right track throughout. Hence the two authors! Crowley for motivational pep, and Dr. Lodge for the science (with extra input from brain surgeon Dr. Hamilton, too).
Bottom line: if you want to feel the most prepared possible for the coming years and decades, this is a great book that covers a lot of bases.
Click here to check out “Younger Next Year” and get de-aging!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Understanding and Responding to Self-Harm – by Dr. Allan House
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Whether it’s yourself, or (statistically much more likely) a loved one, it’s common to be faced with the deeply unpleasant reality of self-harm. This is a case where most definitely, “forewarned is forearmed”.
Dr. House covers not just the “what” and “why” of self-harm, but also the differences between suicidal and non-suicidal self-harm, as well as the impulsive and the planned.
Stylistically, the book is well-written, well-edited, and well-formatted. All this makes for easy reading and efficient learning.
Much of the book is, of course, given over to how to help in cases of self-harm. More specifically: how to approach things with both seriousness and compassion, and how to help in a way that doesn’t create undue pressure.
Because, as Dr. House explains and illustrates, a lot of well-meaning people end up causing more harm, by their botched attempts to help.
This book looks to avoid such tragedies.
Bottom line: if you’d rather know these things now, instead of wishing you’d known later, then this book is the one-stop guide it claims to be.
Click here to check out Understanding and Responding to Self-Harm, and be prepared!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Physical Sunscreen or Chemical Sunscreen – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing physical sunscreens to chemical sunscreens, we picked the physical sunscreens.
Why?
It’s easy to vote against chemical sunscreens, because it has “chemical” in the name, which tends to be offputting PR-wise no matter how healthy something is.
But in this case, there’s actual science here too!
Physical sunscreens physically block the UV rays.
- On the simplest of levels, mud is a physical sunscreen, as you can see widely used by elephants, hippos, pigs, and other animals.
- On a more sophisticated level, modern physical sunscreens often use tiny zinc particles (or similar) to block the UV rays in a way that isn’t so obvious to the naked eye—so we can still see our skin, and it looks just like we applied an oil or other moisturizer.
Chemical sunscreens interact with the UV rays in a way that absorbs them.
- Specifically, they usually convert it into relatively harmless thermal energy (heat)
- However, this can cause problems if there’s too much heat!
- Additionally, chemical sunscreens can get “used up” in a way that physical sunscreens can’t* becoming effectively deactivated once the chemical reaction has run its course and there is no more reagent left unreacted.
- Worse, some of the reagents, when broken down by the UV rays, can potentially cause harm when absorbed by the skin.
*That said, physical sunscreens will still need “topping up” because we are a living organism and our body can’t resist redistributing and using stuff—plus, depending on the climate and our activities, we can lose some externally too.
Further reading
We wrote about sunscreens (of various kinds) here:
And you can also read specifically about today’s topic in more detail, here:
What’s The Difference Between Physical And Chemical Sunscreens?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: