Feeding You Lies – by Vani Hari
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to advertising, we know that companies will often be as misleading as they can get away with. But just how misleading is it?
Vani Hari, of “Food Babe” fame, is here to unravel it all.
The book covers many areas of food and drink advertising and marketing, and gives particular attention to:
- Sodas (with and without sugar), and how deleterious they are to the health—as well as not even helping people lose weight, but actively hindering
- Nutritionally fortified foods, and what we may or may not actually get from them by the time the processing is done
- Organic food, and what that may or may not mean
She also covers a lot of what happens outside of supermarkets, way back in universities and corporate boardrooms. In short, who is crossing whose palms with silver for a seal of approval… And what that means for us as consumers.
A strength of this book that sets it apart from many of its genre, by the way, is that while being deeply critical of certain institutions’ practices, it doesn‘t digress into tinfoil-hat pseudoscientific scaremongering, either. Here at 10almonds we love actual science, so that was good to see too.
Bottom line: is you’d like to know “can they say that and get away with it if it’s not true?” and make decisions based on the actual nutritional value of things, this is a great book for you.
Click here to check out “Feeding You Lies” on Amazon and make your shopping healthier!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Bates Method for Better Eyesight Without Glasses − by Dr. William Bates
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a very popular book and method, albeit not a very new one. It was first published in 1920; self-published by Dr. Bates, as the American Medical Association (AMA) considered it quackery.
Of course, our understanding of eyesight has improved a lot in the past 100 years, so, with the benefit of an extra century of ophthalmological research, who was on the right side of history?
As it turns out, all of Dr. Bates’ ideas have been firmly disproven, and eyes simply do not work the way he thought they do (for example, he believed that rather than adjusting the lens for focus, the muscles around the eye elongate the eyeball; this absolutely is not how focusing works, and while how much those muscles squeeze the eye does vary depending on some physiological factors, there are no known exercises that can change them).
Nevertheless, for the interested, his techniques include such things as:
- putting pressure on one’s eyes with one’s hands (which can increase glaucoma risk)
- visualization, rather than actual viewing, of an eye chart (this is ironic, because the book cover promises that an eye chart is included; it is not; perhaps it was hoped that we would visualize it more vividly and thus see it?)
- sunning, which is not only directly looking at the sun, but also using a burning glass to increase the focus of the sunlight onto one’s eye (please do not do this under any circumstances)
His primary thesis in this work, though, is that eyesight problems of all kinds (from short- and long-sightedness, to more serious things like cataracts and glaucoma) are caused by the tension produced by reading books, so relaxation exercises are his prescription for this.
The style is characteristic of its era and then some; bold claims are made with no evidence, there are no references, and the text is (ironically, given his opinions on tension being produced by reading books) quite dense. It certainly doesn’t lend itself well to skimming, for example, because something critical can easily be buried in a wall of text of what is, honestly, mostly waffle.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your eyesight and reduce your dependency on glasses, then we absolutely cannot recommend this book, and would direct you instead to Vision for Life, Revised Edition – by Dr. Meir Schneider, which is much more consistent with actual science.
Click here if you are, nonetheless, curious about Dr. Bates’ book and wish to check it out!
PS: Dr. Bates certainly was an interesting fellow; he disappeared mysteriously, but was found working as a medical assistant a few weeks later by his wife, whom he now claimed to not recognize. Then he disappeared again two days later (his wife never found him, this time, despite trying for many years), only to show up again, 13 years later, shortly after his wife’s death, whereupon he remarried (to his long-time personal assistant). None of this has anything to do with his fascinating opinions on eyesight, but it’s a story worth mentioning.
Share This Post
-
Try This At Home: ABI Test For Clogged Arteries
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Arterial plaque is a big deal, and statistically it’s more of a risk as we get older, often coming to a head around age 72 for women and 65 for men—these are the median ages at which people who are going to get heart attacks, get them. Or get it, because sometimes one is all it takes.
The Ankle-Brachial Index Test
Dr. Brewer recommends a home test for detecting arterial plaque called the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI), which uses a blood pressure monitor. The test involves measuring blood pressure in both the arms and ankles, then calculating the ratio of these measurements:
- A healthy ABI score is between 1.0 and 1.4; anything outside this range may indicate arterial problems.
- Low ABI scores (below 0.8) suggest plaque is likely obstructing blood flow
- High ABI scores (above 1.4) may indicate artery hardening
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), associated with poor ABI results (be they high or low), can cause a whole lot of problems that are definitely better tackled sooner rather than later—remember that atherosclerosis is a self-worsening thing once it gets going, because narrower walls means it’s even easier for more stuff to get stuck in there (and thus, the new stuff that got stuck also becomes part of the walls, and the problem gets worse).
If you need a blood pressure monitor, by the way, here’s an example product on Amazon.
Do note also that yes, if you have plaque obstructing blood flow and hardened arteries, your scores may cancel out and give you a “healthy” score, despite your arteries being very much not healthy. For this reason, this test can be used to raise the alarm, but not to give the “all clear”.
For more on all of the above, plus a demonstration and more in-depth explanation of the test, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Pine Nuts vs Macadamia Nuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pine nuts to macadamias, we picked the pine nuts.
Why?
In terms of macros, it’s subjective depending on what you want to prioritize; the two nuts are equal in carbs, but pine nuts have more protein and macadamias have more fiber. We’d generally prioritize the fiber, which so far would give macadamias a win in this category, but if you prefer the protein, then consider it pine nuts. Next, we must consider fats; macadamias have slightly more fat, and of which, proportionally more saturated fat, resulting in 3x the total saturated fat compared to pine nuts, gram for gram. With this in mind, we consider this category a tie or a marginal nominal win for pine nuts.
In the category of vitamins, pine nuts have more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B9, E, K, and choline, while macadamias have more of vitamins B1, B5, B6, and C. A clear win for pine nuts this time, especially with pine nuts having more than 17x the vitamin E of macadamias.
When it comes to minerals, pine nuts have more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while macadamias have more calcium and selenium. Another easy win for pine nuts.
In short, enjoy either or both (diversity is good), but pine nuts are the healthier by most metrics.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
Piperine, a compound found in Piper nigrum (black pepper, to its friends), has many health benefits. It’s included as a minor ingredient in some other supplements, because it boosts bioavailability. In its form as a kitchen spice, it’s definitely a superfood.
What does it do?
First, three things that generally go together:
These things often go together for the simple reason that oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer often go together. In each case, it’s a matter of cellular wear-and-tear, and what can mitigate that.
For what it’s worth, there’s generally a fourth pillar: anti-aging. This is again for the same reason. That said, black pepper hasn’t (so far as we could find) been studied specifically for its anti-aging properties, so we can’t cite that here as an evidence-based claim.
Nevertheless, it’s a reasonable inference that something that fights oxidation, inflammation, and cancer, will often also slow aging.
Special note on the anti-cancer properties
We noticed two very interesting things while researching piperine’s anti-cancer properties. It’s not just that it reduces cancer risk and slows tumor growth in extant cancers (as we might expect from the above-discussed properties). Let’s spotlight some studies:
It is selectively cytotoxic (that’s a good thing)
Piperine was found to be selectively cytotoxic to cancerous cells, while not being cytotoxic to non-cancerous cells. To this end, it’s a very promising cancer-sniper:
Piperine as a Potential Anti-cancer Agent: A Review on Preclinical Studies
It can reverse multi-drug resistance in cancer cells
P-glycoprotein, found in our body, is a drug-transporter that is known for “washing out” chemotherapeutic drugs from cancer cells. To date, no drug has been approved to inhibit P-glycoprotein, but piperine has been found to do the job:
Targeting P-glycoprotein: Investigation of piperine analogs for overcoming drug resistance in cancer
What’s this about piperine analogs, though? Basically the researchers found a way to “tweak” piperine to make it even more effective. They called this tweaked version “Pip1”, because calling it by its chemical name,
((2E,4E)-5-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-1-(6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1 H)-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one)
…got a bit unwieldy.
The upshot is: Pip1 is better, but piperine itself is also good.
Other benefits
Piperine does have other benefits too, but the above is what we were most excited to talk about today. Its other benefits include:
- Neuroprotective effects (against Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and more)
- Blood-sugar balancing / antidiabetic effect
- Good for gut microbiome diversity
- Heart health benefits, including cholesterol-balancing
- Boosts bioavailability of other nutrients/drugs
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Inflamed Mind – by Dr. Edward Bullmore
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Firstly, let’s note that this book was published in 2018, so the “radical new” approach is more like “tried and tested and validated” now.
Of course, inflammation in the brain is also linked to Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other neurodegenerative disorders, but that’s not the main topic here.
Dr. Bullmore, a medical doctor, psychiatrist, and neuroscientist with half the alphabet after his name, knows his stuff. We don’t usually include author bio information here, but it’s also relevant that he has published more than 500 scientific papers and is one of the most highly cited scientists worldwide in neuroscience and psychiatry.
What he explores in this book, with a lot of hard science made clear for the lay reader, is the mechanisms of action of depression treatments that aren’t just SSRIs, and why anti-inflammatory approaches can work for people with “treatment-resistant depression”.
The book was also quite prescient in its various declarations of things he expects to happen in the field in the next five years, because they’ve happened now, five years later.
Bottom line: if you’d like to understand how the mind and body affect each other in the cases of inflammation and depression, with a view to lessening either or both of those things, this is a book for you.
Click here to check out The Inflamed Mind, and take good care of yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cupping: How It Works (And How It Doesn’t)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Good Health By The Cup?
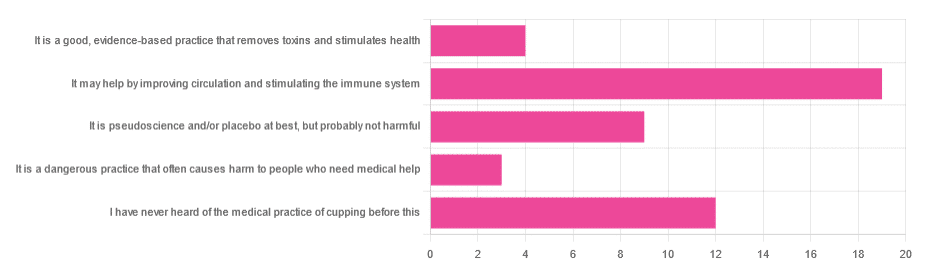
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of cupping (the medical practice), and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 40% said “It may help by improving circulation and stimulating the immune system”
- About 26% said “I have never heard of the medical practice of cupping before this”
- About 19% said “It is pseudoscience and/or placebo at best, but probably not harmful
- About 9% said “It is a good, evidence-based practice that removes toxins and stimulates health”
- About 6% said “It is a dangerous practice that often causes harm to people who need medical help”
So what does the science say?
First, a quick note for those unfamiliar with cupping: it is the practice of placing a warmed cup on the skin (open side of the cup against the skin). As the warm air inside cools, it reduces the interior air pressure, which means the cup is now (quite literally) a suction cup. This pulls the skin up into the cup a little. The end result is visually, and physiologically, the same process as what happens if someone places the nozzle of a vacuum cleaner against their skin. For that matter, there are alternative versions that simply use a pump-based suction system, instead of heated cups—but the heated cups are most traditional and seem to be most popular. See also:
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health | Cupping
It is a dangerous practice that often causes harm to people who need medical help: True or False?
False, for any practical purposes.
- Directly, it can (and usually does) cause minor superficial harm, much like many medical treatments, wherein the benefits are considered to outweigh the harm, justifying the treatment. In the case of cupping, the minor harm is usually a little bruising, but there are other risks; see the link we gave just above.
- Indirectly, it could cause harm by emboldening a person to neglect a more impactful treatment for their ailment.
But, there’s nothing for cupping akin to the “the most common cause of death is when someone gets a vertebral artery fatally severed” of chiropractic, for example.
It is a good, evidence-based practice that removes toxins and stimulates health: True or False?
True and False in different parts. This one’s on us; we included four claims in one short line. But let’s look at them individually:
- Is it good? Well, those who like it, like it. It legitimately has some mild health benefits, and its potential for harm is quite small. We’d call this a modest good, but good nonetheless.
- Is it evidence-based? Somewhat, albeit weakly; there are some papers supporting its modest health claims, although the research is mostly only published in journals of alternative medicine, and any we found were in journals that have been described by scientists as pseudoscientific.
- Does it remove toxins? Not directly, at least. There is also a version that involves making a small hole in the skin before applying the cup, the better to draw out the toxins (called “wet cupping”). This might seem a little medieval, but this is because it is from early medieval times (wet cupping’s first recorded use being in the early 7th century). However, the body’s response to being poked, pierced, sucked, etc is to produce antibodies, and they will do their best to remove toxins. So, indirectly, there’s an argument.
- Does it stimulate health? Yes! We’ll come to that shortly. But first…
It is pseudoscience and/or placebo at best, but probably not harmful: True or False?
True in that its traditionally-proposed mechanism of action is a pseudoscience and placebo almost certainly plays a strong part, and also in that it’s generally not harmful.
On it being a pseudoscience: we’ve talked about this before, but it bears repeating; just because something’s proposed mechanism of action is pseudoscience, doesn’t necessarily mean it doesn’t work by some other mechanism of action. If you tell a small child that “eating the rainbow” will improve their health, and they believe this is some sort of magical rainbow power imbuing them with health, then the mechanism of action that they believe in is a pseudoscience, but eating a variety of colorful fruit and vegetables will still be healthy.
In the case of cupping, its proposed mechanism of action has to do withbalancing qi, yin and yang, etc (for which scientific evidence does not exist), in combination with acupuncture lore (for which some limited weak scientific evidence exists). On balancing qi, yin and yang etc, this is a lot like Europe’s historically popular humorism, which was based on the idea of balancing the four humors (blood, yellow bile, black bile, phlegm). Needless to say, humorism was not only a pseudoscience, but also eventually actively disproved with the advent of germ theory and modern medicine. Cupping therapy is not more scientifically based than humorism.
On the placebo side of things, there probably is a little more to it than that; much like with acupuncture, a lot of it may be a combination of placebo and using counter-irritation, a nerve-tricking method to use pain to reduce pain (much like pressing with one’s nail next to an insect bite).
Here’s one of the few studies we found that’s in what looks, at a glance, to be a reputable journal:
Cupping therapy and chronic back pain: systematic review and meta-analysis
It may help by improving circulation and stimulating the immune system: True or False?
True! It will improve local circulation by forcing blood into the area, and stimulate the immune system by giving it a perceived threat to fight.
Again, this can be achieved by many other means; acupuncture (or just “dry needling”, which is similar but without the traditional lore), a cold shower, and/or exercise (and for that matter, sex—which combines exercise, physiological arousal, and usually also foreign bodies to respond to) are all options that can improve circulation and stimulate the immune system.
You can read more about using some of these sorts of tricks for improving health in very well-evidenced, robustly scientific ways here:
The Stress Prescription (Against Aging!)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: