Exercise with Type 1 Diabetes – by Ginger Vieira
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you or a loved one has Type 1 Diabetes, you’ll know that exercise can be especially frustrating…
- If you don’t do it, you risk weight gain and eventual insulin resistance.
- If you do it, you risk dangerous hypos, or perhaps hypers if you took off your pump or skipped a bolus.
Unfortunately, the popular medical advice is “well, just do your best”.
Ginger Vieira is Type 1 Diabetic, and writes with 20+ experience of managing her diabetes while being a keen exerciser. As T1D folks out there will also know, comorbidities are very common; in her case, fibromyalgia was the biggest additional blow to her ability to exercise, along with an underactive thyroid. So when it comes to dealing with the practical nuts and bolts of things, she (while herself observing she’s not a doctor, let alone your doctor) has a lot more practical knowledge than an endocrinologist (without diabetes) behind a desk.
Speaking of nuts and bolts, this book isn’t a pep talk.
It has a bit of that in, but most of it is really practical information, e.g: using fasted exercise (4 hours from last meal+bolus) to prevent hypos, counterintuitive as that may seem—the key is that timing a workout for when you have the least amount of fast-acting insulin in your body means your body can’t easily use your blood sugars for energy, and draws from your fat reserves instead… Win/Win!
That’s just one quick tip because this is a 1-minute review, but Vieira gives:
- whole chapters, with example datasets (real numbers)
- tech-specific advice, e.g. pump, injection, etc
- insulin-specific advice, e.g. fast vs slow, and adjustments to each in the context of exercise
- timing advice re meal/bolus/exercise for different insulins and techs
- blood-sugar management advice for different exercise types (aerobic/anaerobic, sprint/endurance, etc)
…and lots more that we don’t have room to mention here
Basically… If you or a loved one has T1D, we really recommend this book!
Order a copy of “Exercise with Type 1 Diabetes” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Does Eating Shellfish Contribute To Gout?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝I have a question about seafood as healthy, doesn’t eating shellfish contribute to gout?❞
It can do! Gout (a kind of inflammatory arthritis characterized by the depositing of uric acid crystals in joints) has many risk factors, and diet is one component, albeit certainly the most talked-about one.
First, you may be wondering: isn’t all arthritis inflammatory? Since arthritis is by definition the inflammation of joints, this is a reasonable question, but when it comes to classifying the kinds, “inflammatory” arthritis is caused by inflammation, while “non-inflammatory” arthritis (a slightly confusing name) merely has inflammation as one of its symptoms (and is caused by physical wear-and-tear). For more information, see:
- Tips For Avoiding/Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis ←inflammatory
- Tips For Avoiding/Managing Osteoarthritis ← “non-inflammatory”
As for gout specifically, top risk factors include:
- Increasing age: risk increases with age
- Being male: women do get gout, but much less often
- Hypertension: all-cause hypertension is the biggest reasonably controllable factor
There’s not a lot we can do about age (but of course, looking after our general health will tend to slow biological aging, and after all, diseases only care about the state of our body, not what the date on the calendar is).
As for sex, this risk factor is hormones, and specifically has to do with estrogen and testosterone’s very different effects on the immune system (bearing in mind that chronic inflammation is a disorder of the immune system). However, few if any men would take up feminizing hormone therapy just to lower their gout risk!
That leaves hypertension, which happily is something that we can all (barring extreme personal circumstances) do quite a bit about. Here’s a good starting point:
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
…and for further pointers:
How To Lower Your Blood Pressure (Cardiologists Explain)
As for diet specifically (and yes, shellfish):
The largest study into this (and thus, one of the top ones cited in a lot of other literature) looked at 47,150 men with no history of gout at the baseline.
So, with the caveat that their findings could have been different for women, they found:
- Eating meat in general increased gout risk
- Narrowing down specific meats: beef, pork, and lamb were the worst offenders
- Eating seafood in general increased gout risk
- Narrowing down specific seafoods: all seafoods increased gout risk within a similar range
- As a specific quirk of seafoods: the risk was increased if the man had a BMI under 25
- Eating dairy in general was not associated with an increased risk of gout
- Narrowing down specific dairy foods: low-fat dairy products such as yogurt were associated with a decreased risk of gout
- Eating purine-rich vegetables in general was not associated with an increased risk of gout
- Narrowing down to specific purine-rich vegetables: no purine-rich vegetable was associated with an increase in the risk of gout
Dairy products were included in the study, as dairy products in general and non-fermented dairy products in particular are often associated with increased inflammation. However, the association was simply not found to exist when it came to gout risk.
Purine-rich vegetables were included in the study, as animal products highest in purines have typically been found to have the worst effect on gout. However, the association was simply not found to exist when it came to plants with purines.
You can read the full study here:
Purine-Rich Foods, Dairy and Protein Intake, and the Risk of Gout in Men
So, the short answer to your question of “doesn’t eating shellfish contribute to the risk of gout” is:
Yes, it can, but occasional consumption probably won’t result in gout unless you have other risk factors going against you.
If you’re a slim male 80-year-old alcoholic smoker with hypertension, then definitely do consider skipping the lobster, but honestly, there may be bigger issues to tackle there.
And similarly, obviously skip it if you have a shellfish allergy, and if you’re vegan or vegetarian or abstain from shellfish for religious reasons, then you can certainly live very healthily without ever having any.
See also: Do We Need Animal Products, To Be Healthy?
For most people most of the time, a moderate consumption of seafood, including shellfish if you so desire, is considered healthy.
As ever, do speak with your own doctor to know for sure, as your individual case may vary.
For reference, this question was surely prompted by the article:
Lobster vs Crab – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Wakefulness, Cognitive Enhancement, AND Improved Mood?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Old Drug, New Tricks?
Modafinil (also known by brand names including Modalert and Provigil) is a dopamine uptake inhibitor.
What does that mean? It means it won’t put any extra dopamine in your brain, but it will slow down the rate at which your brain removes naturally-occuring dopamine.
The result is that your brain will get to make more use of the dopamine it does have.
(dopamine is a neutrotransmitter that allows you to feel wakeful and happy, and perform complex cognitive tasks)
Modafinil is prescribed for treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness. Often that’s caused by shift work sleep disorder, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or narcolepsy.
Read: Overview of the Clinical Uses, Pharmacology, and Safety of Modafinil
Many studies done on humans (rather than rats) have been military experiments to reduce the effects of sleep deprivation:
Click Here To See A Military Study On Modafinil!
They’ve found modafinil to be helpful, and more effective and more long-lasting than caffeine, without the same “crash” later. This is for two reasons:
1) while caffeine works by blocking adenosine (so you don’t feel how tired you are) and by constricting blood vessels (so you feel more ready-for-action), modafinil works by allowing your brain to accumulate more dopamine (so you’re genuinely more wakeful, and you get to keep the dopamine)
2) the biological half-life of modafinil is 12–15 hours, as opposed to 4–8 hours* for caffeine.
*Note: a lot of sources quote 5–6 hours for caffeine, but this average is misleading. In reality, we are each genetically predetermined to be either a fast caffeine metabolizer (nearer 4 hours) or a slow caffeine metabolizer (nearer 8 hours).
What’s a biological half-life (also called: elimination half-life)?
A substance’s biological half-life is the time it takes for the amount in the body to be reduced by exactly half.
For example: Let’s say you’re a fast caffeine metabolizer and you have a double-espresso (containing 100mg caffeine) at 8am.
By midday, you’ll have 50mg of caffeine left in your body. So far, so simple.
By 4pm you might expect it to be gone, but instead you have 25mg remaining (because the amount halves every four hours).
By 8pm, you have 12.5mg remaining.
When midnight comes and you’re tucking yourself into bed, you still have 6.25mg of caffeine remaining from your morning coffee!
Use as a nootropic
Many healthy people who are not sleep-deprived use modafinil “off-label” as a nootropic (i.e., a cognitive enhancer).
Read: Modafinil for cognitive neuroenhancement in healthy non-sleep-deprived subjects: A systematic review
Important Note: modafinil is prescription-controlled, and only FDA-approved for sleep disorders.
To get around this, a lot of perfectly healthy biohackers describe the symptoms of sleep pattern disorder to their doctor, to get a prescription.
We do not recommend lying to your healthcare provider, and nor do we recommend turning to the online “grey market”.
Such websites often use anonymized private doctors to prescribe on an “informed consent” basis, rather than making a full examination. Those websites then dispense the prescribed medicines directly to the patient with no further questions asked (i.e. very questionable practices).
Caveat emptor!
A new mood-brightener?
Modafinil was recently tested head-to-head against Citalapram for the treatment of depression, and scored well:
See its head-to-head scores here!
How does it work? Modafinil does for dopamine what a lot of anti-depressants do for serotonin. Both dopamine and serotonin promote happiness and wakefulness.
This is very promising, especially as modafinil (in most people, at least) has fewer unwanted side-effects than a lot of common anti-depressant medications.
Share This Post
-
Smart Sex – by Dr. Emily Morse
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this isn’t: this isn’t a mere book of sex positions and party tricks, nor is it a book of Cosmo-style “drive your man wild by using hot sauce as lube” advice.
What it offers instead, is a refreshingly mature take on sex, free from the “teehee” titillations and blushes that many books of the genre go for.
Dr. Emily Morse outlines five pillars of sex:
- Embodiment
- Health
- Collaboration
- Self-knowledge
- Self-acceptance
…and talks about each of them in detail, and how we can bring them together. And, of course, how we or our partner(s) could accidentally sabotage ourselves or each other, and the conversations we can (and should!) have, to work past that.
She also, critically, and this is a big source of value in the book, looks at “pleasure thieves”: stress, trauma, and shame. The advice for overcoming these is not “don’t worry; be happy” but rather is actual practical steps one can take.
The style throughout is direct and unpatronizing. Since the advice within pertains to everyone who has and/or wants an active sex life, very little is divided by gender etc.
There is some attention given to anatomy and physiology, complete with clear diagrams. Honestly, most people could benefit from these, because most people’s knowledge of the relevant anatomy stopped with a very basic high school text book diagram that missed a lot out.
Bottom line: this book spends more time on what’s between your ears than what’s between your legs, and yet is very comprehensive in all areas. Everyone has something to gain from this one.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
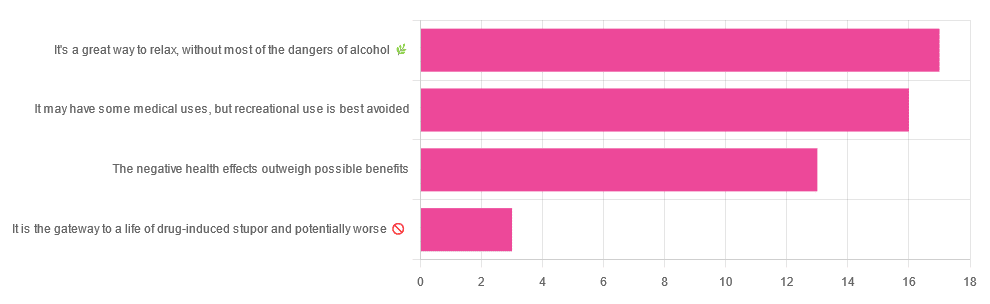
We asked you for your (health-related) opinion on cannabis use—specifically, the kind with psychoactive THC, not just CBD. We got the above-pictured, below-described, spread of responses:
- A little over a third of you voted for “It’s a great way to relax, without most of the dangers of alcohol”.
- A little under a third of you voted for “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”.
- About a quarter of you voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits”
- Three of you voted for “It is the gateway to a life of drug-induced stupor and potentially worse”
So, what does the science say?
A quick legal note first: we’re a health science publication, and are writing from that perspective. We do not know your location, much less your local laws and regulations, and so cannot comment on such. Please check your own local laws and regulations in that regard.
Cannabis use can cause serious health problems: True or False?
True. Whether the risks outweigh the benefits is a personal and subjective matter (for example, a person using it to mitigate the pain of late stage cancer is probably unconcerned with many other potential risks), but what’s objectively true is that it can cause serious health problems.
One subscriber who voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits” wrote:
❝At a bare minimum, you are ingesting SMOKE into your lungs!! Everyone SEEMS TO BE against smoking cigarettes, but cannabis smoking is OK?? Lung cancer comes in many forms.❞
Of course, that is assuming smoking cannabis, and not consuming it as an edible. But, what does the science say on smoking it, and lung cancer?
There’s a lot less research about this when it comes to cannabis, compared to tobacco. But, there is some:
❝Results from our pooled analyses provide little evidence for an increased risk of lung cancer among habitual or long-term cannabis smokers, although the possibility of potential adverse effect for heavy consumption cannot be excluded.❞
Read: Cannabis smoking and lung cancer risk: Pooled analysis in the International Lung Cancer Consortium
Another study agreed there appears to be no association with lung cancer, but that there are other lung diseases to consider, such as bronchitis and COPD:
❝Smoking cannabis is associated with symptoms of chronic bronchitis, and there may be a modest association with the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Current evidence does not suggest an association with lung cancer.❞
Read: Cannabis Use, Lung Cancer, and Related Issues
Cannabis edibles are much safer than smoking cannabis: True or False?
Broadly True, with an important caveat.
One subscriber who selected “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”, wrote:
❝I’ve been taking cannabis gummies for fibromyalgia. I don’t know if they’re helping but they’re not doing any harm. You cannot overdose you don’t become addicted.❞
Firstly, of course consuming edibles (rather than inhaling cannabis) eliminates the smoke-related risk factors we discussed above. However, other risks remain, including the much greater ease of accidentally overdosing.
❝Visits attributable to inhaled cannabis are more frequent than those attributable to edible cannabis, although the latter is associated with more acute psychiatric visits and more ED visits than expected.❞
Note: that “more frequent” for inhaled cannabis, is because more people inhale it than eat it. If we adjust the numbers to control for how much less often people eat it, suddenly we see that the numbers of hospital admissions are disproportionately high for edibles, compared to inhaled cannabis.
Or, as the study author put it:
❝There are more adverse drug events associated on a milligram per milligram basis of THC when it comes in form of edibles versus an inhaled cannabis. If 1,000 people smoked pot and 1,000 people at the same dose in an edible, then more people would have more adverse drug events from edible cannabis.❞
See the numbers: Acute Illness Associated With Cannabis Use, by Route of Exposure
Why does this happen?
- It’s often because edibles take longer to take effect, so someone thinks “this isn’t very strong” and has more.
- It’s also sometimes because someone errantly eats someone else’s edibles, not realising what they are.
- It’s sometimes a combination of the above problems: a person who is now high, may simply forget and/or make a bad decision when it comes to eating more.
On the other hand, that doesn’t mean inhaling it is necessarily safer. As well as the pulmonary issues we discussed previously, inhaling cannabis has a higher risk of cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (and the resultant cyclic vomiting that’s difficult to treat).
You can read about this fascinating condition that’s sometimes informally called “scromiting”, a portmanteau of screaming and vomiting:
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome
You can’t get addicted to cannabis: True or False?
False. However, it is fair to say that the likelihood of developing a substance abuse disorder is lower than for alcohol, and much lower than for nicotine.
See: Prevalence of Marijuana Use Disorders in the United States Between 2001–2002 and 2012–2013
If you prefer just the stats without the science, here’s the CDC’s rendering of that:
Addiction (Marijuana or Cannabis Use Disorder)
However, there is an interesting complicating factor, which is age. One is 4–7 times more likely to develop a substance abuse disorder, if one starts use as an adolescent, rather than later in life:
Cannabis is the gateway to use of more dangerous drugs: True or False?
False, generally speaking. Of course, for any population there will be some outliers, but there appears to be no meaningful causal relation between cannabis use and other substance use:
Interestingly, the strongest association (where any existed at all) was between cannabis use and opioid use. However, rather than this being a matter of cannabis use being a gateway to opioid use, it seems more likely that this is a matter of people looking to both for the same purpose: pain relief.
As a result, growing accessibility of cannabis may actually reduce opioid problems:
- Cannabis as a Gateway Drug for Opioid Use Disorder
- Association between medical cannabis laws and opioid overdose mortality has reversed over time
Some final words…
Cannabis is a complex drug with complex mechanisms and complex health considerations, and research is mostly quite young, due to its historic illegality seriously cramping science by reducing sample sizes to negligible. Simply put, there’s a lot we still don’t know.
Also, we covered some important topics today, but there were others we didn’t have time to cover, such as the other potential psychological benefits—and risks. Likely we’ll revisit those another day.
Lastly, while we’ve covered a bunch of risks today, those of you who said it has fewer and lesser risks than alcohol are quite right—the only reason we couldn’t focus on that more, is because to talk about all the risks of alcohol would make this feature many times longer!
Meanwhile, whether you partake or not, stay safe and stay well.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Build a Body That Lasts – by Adam Richardson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is written on a premise, and that premise is: “your age doesn’t define your mobility; your mobility defines your age”.
To this end, we are treated to 328 pages of why and how to improve our mobility (mostly how; just enough on the “why” to keep the motivation flowing).
Importantly, Richardson doesn’t expect that every reader is a regular gym-bunny or about to become one, doesn’t expect you to have several times your bodyweight in iron to life at home, and doesn’t expect that you’ll be doing the vertical splits against a wall any time soon.
Rather, he expects that we’d like to not dislocate a shoulder while putting the groceries away, would like to not slip a disk while being greeted by the neighbor’s dog, and would like to not need a 7-step plan for putting our socks on.
What follows is a guide to “on the good end of normal” mobility that is sustainable for life. The idea is that you might not be winning Olympic gymnastics gold medals in your 90s, but you will be able to get in and out of a car door as comfortably as you did when you were 20, for example.
Bottom line: if you want to be a superathlete, then you might need something more than this book; if you want to be on the healthy end of average when it comes to mobility, and maintain that for the rest of your life, then this is the book for you.
Click here to check out How To Build A Body That Lasts, and build a body that lasts!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What are house dust mites and how do I know if I’m allergic to them?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
People often believe they are allergic to house dust. But of the 20% of Australians suffereing with allergies, a number are are actually allergic to microscopic house dust mites.
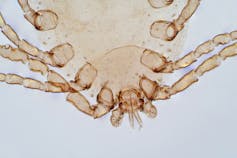
House dust mites belong to the same family as spiders and ticks. They measure just 0.2-0.3 mm, with 50 fitting on a single pinhead. They live for 65–100 days, and females lay 60–100 eggs in their life.
Some 50 house dust mites can fit on one pinhead. Choksawatdikorn/Shutterstock House dust mites love temperate climates and humidity. They feed off the skin cells we and animals shed, as well as mould, which they digest using special enzymes. These enzymes are excreted in their poo about 20 times a day. They also shed fragments of their exoskeletons.
All these fragments trigger allergies in people with this type of allergic rhinitis (which is also known as hay fever)
shuttertock. PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock What are the symptoms?
When people with house dust mite allergy inhale the allergens, they penetrate the mucous membranes of the airways and eyes. Their body recognises the allergens as a threat, releasing chemicals including one called histamine.
This causes symptoms including a runny nose, an itchy nose, eyes and throat, sneezing, coughing and a feeling of mucus at the back of your throat (known as a post-nasal drip).
People with this type of allergy usually mouth breath, snore, rub their nose constantly (creating a nasal crease called the “dust mite salute”) and have dark shadows under their eyes.
House dust mite allergy can also cause poor sleep, constant tiredness, reduced concentration at work or school and lower quality of life.
For people with eczema, their damaged skin barrier can allow house dust mite proteins in. This prompts immune cells in the skin to release chemicals which make already flared skin become redder, sorer and itchier, especially in children.
Symptoms of house dust mite allergy occur year round, and are often worse after going to bed and when waking in the morning. But people with house dust mite allergy and pollen allergies find their year-round symptoms worsen in spring.
How is it diagnosed?
House dust mite allergy symptoms often build up over months, or even years before people seek help. But an accurate diagnosis means you can not only access the right treatment – it’s also vital for minimising exposure.
Your clinician can talk you through treatment options and how to minimise exposure. Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock Doctor and nurse practitioners can order a blood test to check for house dust mite allergy.
Alternatively, health care providers with specialised allergy training can perform skin prick tests. This involves placing drops of the allergens on the arm, along with a positive and negative “control”. After 15 minutes, those who test positive will have developed a mosquito bite-like mark.
How is it treated?
Medication options include one or a combination of:
- daily non-sedating antihistamines
- a steroid nasal spray
- allergy eye drops.
Your health care professional will work with you to develop a rhinitis (hay fever) medical management plan to reduce your symptoms. If you’re using a nasal spray, your health provider will show you how to use it, as people often use it incorrectly.
If you also have asthma or eczema which is worsened by dust mites, your health provider will adapt your asthma action plan or eczema care plan accordingly.
If you experience severe symptoms, a longer-term option is immunotherapy. This aims to gradually turn off your immune system’s ability to recognise house dust mites as a harmful allergen.
Immunotherapy involves taking either a daily sublingual tablet, under the tongue, or a series of injections. Injections require monthly attendances over three years, after the initial weekly build-up phase.
These are effective, but are costly (as well as time-consuming). So it’s important to weigh up the potential benefits and downsides with your health-care provider.
How can you minimise house dust mites?
There are also important allergy minimisation measures you can take to reduce allergens in your home.
Each week, wash your bedding and pyjamas in hot water (over 60°C). This removes house dust mite eggs and debris.
Opt for doonas, covers or quilts that can be washed in hot water above 60°C. Alternatively, low-cost waterproof or leak proof covers can keep house dust mites out.
If you can, favour blinds and wood floors over curtains and carpet. Dust blinds and surfaces with a damp cloth each week and vacuum while wearing a mask, or have someone else do it, as house dust mites can become airborne during cleaning.
But beware of costly products with big marketing budgets and little evidence to support their use. A new mattress, for example, will always be house dust mite-free. But once slept on, the house dust mite life cycle can start.
Mattress protectors and toppers commonly claim to be “hypoallergenic”, “anti-allergy” or “allergy free”. But their pore sizes are not small enough to keep house dust mites and their poo out, or shed skin going through.
Sprays claiming to kill mites require so much spray to penetrate the product that it’s likely to become wet, may smell like the spray and, unless dried properly, may grow mould.
Finally, claims that expensive vacuum cleaners can extract all the house dust mites are unsubstantiated.
For more information, visit healthdirect.gov.au or the Australian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy.
Deryn Lee Thompson, Eczema and Allergy Nurse; Lecturer, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: