Eat to Beat Depression and Anxiety – by Dr. Drew Ramsey
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most of us could use a little mood boost sometimes, and some of us could definitely stand to have our baseline neurochemistry elevated a bit. We’ve probably Googled “foods to increase dopamine”, and similar phrases. So, why is this a book, and not just an article saying to eat cashews and dark chocolate?
Dr. Drew Ramsey takes a holistic approach to health. By this we mean that to have good health, the whole body and mind must be kept healthy. Let a part slip, and the others will soon follow. Improve a part, and the others will soon follow, too.
Of course, there is only so much that diet can do. Jut as no diet will replace a Type 1 Diabetic’s pancreas with a working one, no diet will treat the causes of some kinds of depression and anxiety.
For this reason, Dr. Ramsey, himself a psychiatrist (and a farmer!) recommends a combination of talking therapy and diet, with medications as a “third leg” to be included when necessary. The goal, for him, is to reduce dependence on medications, while still recognizing when they can be useful or even necessary.
As for the practical, actionable advices in the book, he does (unsurprisingly) recommend a Mediterranean diet. Heavy on the greens and beans, plenty of colorful fruit and veg, small amounts of fish and seafood, even smaller amounts of grass-fed beef and fermented dairy. He also discusses a bunch of “superfoods” he particularly recommends.
Nor does he just hand-wave the process; he talks about the science of how and why each of these things helps.
And in practical terms, he even devotes some time to helping the reader get our kitchen set up, if we’re not already ready-to-go in that department. He also caters to any “can’t cook / won’t cook” readers and how to work around that too.
Bottom line: if you’d like to get rewiring your brain (leveraging neuroplasticity is a key component of the book), this will get you on track. A particular strength is how the author “thinks of everything” in terms of common problems that people (especially: depressed and anxious people!) might have in implementing his advices.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
“I Stretched Every Day For 30 Days: Game Changer!”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How much can an unflexible person really improve in just 20 minutes per day for a month? Makari Espe finds out:
Consistency really is key
We’re supposed to stretch at least 3 times per week; for many people, the reality is often more like 2 times per year (often the 1st and 2nd of January).
So, how quickly can such neglect be turned around?
Upon initial testing, she found she was even less flexible than thought, and set about her work:
The stretches she used were from random 20-minute full body stretch videos on YouTube, of which there are many, but she used a different one each day. As she went along, she found some favorite kinds of stretching and some favorite instructors, and settled on mostly Peloton stretching videos—she also switched to evening stretching sessions instead of morning.
Along the way, she already noticed gradual improvement in mobility and reduced body tension, and after 3 weeks, it had become a habit that she started craving.
The final test? There’s a marked improvement; see the video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Yoga Teacher: “If I wanted to get flexible in 2025, here’s what I’d do”
Take care!
Share This Post
-
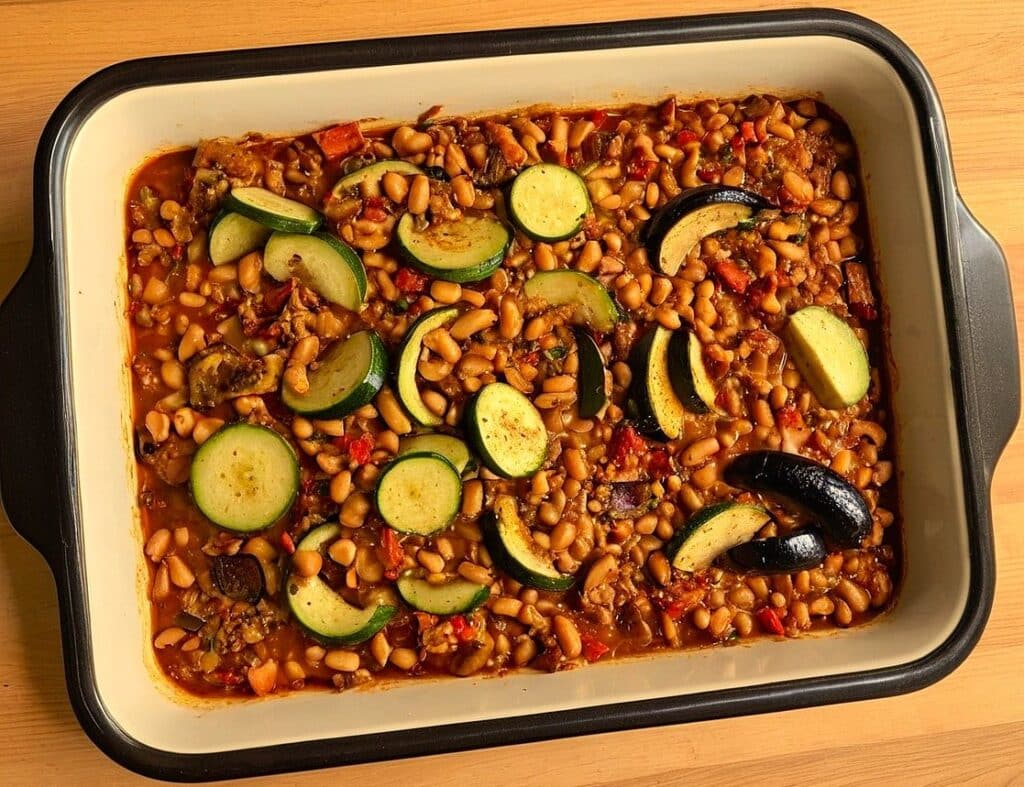
Oven-Roasted Ratatouille
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a supremely low-effort, high-yield dish. It’s a nutritional tour-de-force, and very pleasing to the tastebuds too. We use flageolet beans in this recipe; they are small immature kidney beans. If they’re not available, using kidney beans or really any other legume is fine.
You will need
- 2 large zucchini, sliced
- 2 red peppers, sliced
- 1 large eggplant, sliced and cut into semicircles
- 1 red onion, thinly sliced
- 2 cans chopped tomatoes
- 2 cans flageolet beans, drained and rinsed (or 2 cups same, cooked, drained, and rinsed)
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp balsamic vinegar
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tbsp red chili pepper flakes (omit or adjust per your heat preferences)
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Mixed herbs, per your preference. It’s hard to go wrong with this one, but we suggest leaning towards either basil and oregano or rosemary and thyme. We also suggest having some finely chopped to go into the dish, and some held back to go on the dish as a garnish.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 350℉ / 180℃.
2) Mix all the ingredients (except the tomatoes and herbs) in a big mixing bowl, ensuring even distribution.
2) Add the tomatoes. The reason we didn’t add these before is because it would interfere with the oil being distributed evenly across the vegetables.
3) Transfer to a deep-walled oven tray or an ovenproof dish, and roast for 30 minutes.
4) Stir, add the chopped herbs, stir again, and return to the oven for another 30 minutes.
5) Serve (hot or cold), adding any herb garnish you wish to use.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Toxic Gas That Sterilizes Medical Devices Prompts Safety Rule Update
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Over the past two years, Madeline Beal has heard frustration and even bewilderment during public meetings about ethylene oxide, a cancer-causing gas that is used to sterilize half of the medical devices in the U.S.
Beal, senior risk communication adviser for the Environmental Protection Agency, has fielded questions about why the agency took so long to alert people who live near facilities that emit the chemical about unusually high amounts of the carcinogenic gas in their neighborhoods. Residents asked why the EPA couldn’t close those facilities, and they wanted to know how many people had developed cancer from their exposure.
“If you’re upset by the information you’re hearing tonight, if you’re angry, if it scares you to think about risk to your family, those are totally reasonable responses,” Beal told an audience in Laredo, Texas, in September 2022. “We think the risk levels near this facility are too high.”
There are about 90 sterilizing plants in the U.S. that use ethylene oxide, and for decades companies used the chemical to sterilize medical products without drawing much attention. Many medical device-makers send their products to the plants to be sterilized before they are shipped, typically to medical distribution companies.
But people living around these facilities have been jolted in recent years by a succession of warnings about cancer risk from the federal government and media reports, an awareness that has also spawned protests and lawsuits alleging medical harm.
The EPA is expected to meet a March 1 court-ordered deadline to finalize tighter safety rules around how the toxic gas is used. The proposed changes come in the wake of a 2016 agency report that found that long-term exposure to ethylene oxide is more dangerous than was previously thought.
But the anticipated final rules — the agency’s first regulatory update on ethylene oxide emissions in more than a decade — are expected to face pushback. Medical device-makers worry stricter regulation will increase costs and may put patients at higher risk of infection from devices, ranging from surgical kits to catheters, due to deficient sterilization. The new rules are also not likely to satisfy the concerns of environmentalists or members of the public, who already have expressed frustration about how long it took the federal government to sound the alarm.
“We have been breathing this air for 40 years,” said Connie Waller, 70, who lives with her husband, David, 75, within two miles of such a sterilizing plant in Covington, Georgia, east of Atlanta. “The only way to stop these chemicals is to hit them in their pocketbook, to get their attention.”
The EPA says data shows that long-term exposure to ethylene oxide can increase the risk of breast cancer and cancers of the white blood cells, such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma, myeloma, and lymphocytic leukemia. It can irritate the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs, and has been linked to damage to the brain and nervous and reproductive systems. Children are potentially more vulnerable, as are workers routinely exposed to the chemical, EPA officials say. The agency calculates the risk based on how much of the gas is in the air or near the sterilizing facility, the distance a person is from the plant, and how long the person is exposed.
Waller said she was diagnosed with breast cancer in 2004 and that her husband was found to have non-Hodgkin lymphoma eight years later.
A 2022 study of communities living near a sterilization facility in Laredo found the rates of acute lymphocytic leukemia and breast cancer were greater than expected based on statewide rates, a difference that was statistically significant.
Beal, the EPA risk adviser, who regularly meets with community members, acknowledges the public’s concerns. “We don’t think it’s OK for you to be at increased risk from something that you have no control over, that’s near your house,” she said. “We are working as fast as we can to get that risk reduced with the powers that we have available to us.”
In the meantime, local and state governments and industry groups have scrambled to defuse public outcry.
Hundreds of personal injury cases have been filed in communities near sterilizing plants. In 2020, New Mexico’s then-attorney general filed a lawsuit against a plant in Santa Teresa, and that case is ongoing. In a case that settled last year in suburban Atlanta, a company agreed to pay $35 million to 79 people who alleged ethylene oxide used at the plant caused cancer and other injuries.
In Cook County, Illinois, a jury in 2022 awarded $363 million to a woman who alleged exposure to ethylene oxide gas led to her breast cancer diagnosis. But, in another Illinois case, a jury ruled that the sterilizing company was not liable for a woman’s blood cancer claim.
Greg Crist, chief advocacy officer for the Advanced Medical Technology Association, a medical device trade group that says ethylene oxide is an effective and reliable sterilant, attributes the spate of lawsuits to the litigious nature of trial attorneys.
“If they smell blood in the water, they’ll go after it,” Crist said.
Most states have at least one sterilizing plant. According to the EPA, a handful, like California and North Carolina, have gone further than the agency and the federal Clean Air Act to regulate ethylene oxide emissions. After a media and political firestorm raised awareness about the metro Atlanta facilities, Georgia started requiring sterilizing plants that use the gas to report all leaks.
The proposed rules the EPA is set to finalize would set lower emissions limits for chemical plants and commercial sterilizers and increase some safety requirements for workers within these facilities. The agency is expected to set an 18-month deadline for commercial sterilizers to come into compliance with the emissions rules.
That would help at facilities that “cut corners,” with lax pollution controls that allow emissions of the gas into nearby communities, said Richard Peltier, a professor of environmental health sciences at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst. Stronger regulation also prevents the plants from remaining under the radar. “One of the dirty secrets is that a lot of it is self-regulated or self-policed,” Peltier added.
But the proposed rules did not include protections for workers at off-site warehouses that store sterilized products, which can continue to emit ethylene oxide. They also did not require air testing around the facilities, prompting debate about how effective they would be in protecting the health of nearby residents.
Industry officials also don’t expect an alternative that is as broadly effective as ethylene oxide to be developed anytime soon, though they support researching other methods. Current alternatives include steam, radiation, and hydrogen peroxide vapor.
Increasing the use of alternatives can reduce industry dependence on “the crutch of ethylene oxide,” said Darya Minovi, senior analyst with the Union of Concerned Scientists, an advocacy group.
But meeting the new guidelines will be disruptive to the industry, Crist said. He estimates companies will spend upward of $500 million to comply with the new EPA rules and could struggle to meet the agency’s 18-month timetable. Sterilization companies will also have difficulty adjusting to new rules on how workers handle the gas without a dip in efficiency, Crist said.
The Food and Drug Administration, which regulates drugs and medical devices, is also watching the regulatory moves closely and worries the updated emissions rule could “present some unique challenges” if implemented as proposed, said Audra Harrison, an FDA spokesperson. “The FDA is concerned about the rule’s effects on the availability of medical devices,” she added.
Other groups, like the American Chemistry Council and the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, the state’s environmental agency, assert that ethylene oxide use isn’t as dangerous as the EPA says. The EPA’s toxicity assessment has “severe flaws” and is “overly conservative,” the council said in an emailed statement. Texas, which has several sterilizing plants, has said ethylene oxide isn’t as high a cancer risk as the agency claims, an assessment that the EPA has rejected.
Tracey Woodruff, a researcher at the University of California-San Francisco who previously worked at the EPA, said it can be hard for the agency to keep up with regulating chemicals like ethylene oxide because of constrained resources, the technical complications of rulemaking, and industry lobbying.
But she’s hopeful the EPA can strike a balance between its desire to reduce exposure and the desire of the FDA not to disrupt medical device sterilization. And scrutiny can also help the device sterilization industry think outside the box.
“We continue to discover these chemicals that we’ve already been exposed to were toxic, and we have high exposures,” she said. “Regulation is an innovation forcer.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Getting COMFY – by Jordan Gross
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s easy to see how good “morning people” seem to have it; it’s harder, it seems, to become one.
And, if we’re forced by circumstance to be the morning person we’re not? We all-too-easily find ourselves greeting each coming day without the joy that, in an ideal world, we might.
So, is it possible to learn this power? Jordan Gross has it mapped out for it us…
The “COMFY” of the title is indeed an acronym, and it stands for:
- Calm
- Openness
- Movement
- Funny
- You
There’s a chapter explaining each in detail, and they’re bookended with other chapters explaining more about the whys and the hows.
As you might expect, the key to a good morning starts the night before, but there’s also a formula to follow. Of course, you can change it up, mix and match if you like… but this book provides a base framework to build from, which is something that can make a huge difference!
Bottom line: it’s a highly enjoyable book to read, and also provides genuine powerful help to bring us the brighter happier mornings we deserve—the set-up to the perfect day!
Click here to check out “Getting COMFY” and perk up your mornings—you deserve it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are You Taking PIMs?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Getting Off The Overmedication Train
The older we get, the more likely we are to be on more medications. It’s easy to assume that this is because, much like the ailments they treat, we accumulate them over time. And superficially at least, that’s what happens.
And yet, almost half of people over 65 in Canada are taking “potentially inappropriate medications”, or PIMs—in other words, medications that are not needed and perhaps harmful. This categorization includes medications where the iatrogenic harms (side effects, risks) outweigh the benefits, and/or there’s a safer more effective medication available to do the job.
You may be wondering: what does this mean for the US?
Well, we don’t have the figures for the US because we’re working from Canadian research today, but given the differences between the two country’s healthcare systems (mostly socialized in Canada and mostly private in the US), it seems a fair hypothesis that if it’s almost half in Canada, it’s probably more than half in the US. Socialized healthcare systems are generally quite thrifty and seek to spend less on healthcare, while private healthcare systems are generally keen to upsell to new products/services.
The three top categories of PIMs according to the above study:
- Gabapentinoids (anticonvulsants also used to treat neuropathic pain)
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
- Antipsychotics (especially, to people without psychosis)
…but those are just the top of the list; there are many many more.
The list continues: opioids, anticholinergics, sulfonlyurea, NSAIDs, benzodiazepines and related rugs, and cholinesterase inhibitors. That’s where the Canadian study cuts off (although it also includes “others” just before NSAIDs), but still, you guessed it, there are more (we’re willing to bet statins weigh heavily in the “others” section, for a start).
There are two likely main causes of overmedication:
The side effect train
This is where a patient has a condition and is prescribed drug A, which has some undesired side effects, so the patient is prescribed drug B to treat those. However, that drug also has some unwanted side effects of its own, so the patient is prescribed drug C to treat those. And so on.
For a real-life rundown of how this can play out, check out the case study in:
The Hidden Complexities of Statins and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
The convenience factor
No, not convenient for you. Convenient for others. Convenient for the doctor if it gets you out of their office (socialized healthcare) or because it was easy to sell (private healthcare). Convenient for the staff in a hospital or other care facility.
This latter is what happens when, for example, a patient is being too much trouble, so the staff give them promazine “to help them settle down”, notwithstanding that promazine is, besides being a sedative, also an antipsychotic whose common side effects include amenorrhea, arrhythmias, constipation, drowsiness and dizziness, dry mouth, impotence, tiredness, galactorrhoea, gynecomastia, hyperglycemia, insomnia, hypotension, seizures, tremor, vomiting and weight gain.
This kind of thing (and worse) happens more often towards the end of a patient’s life; indeed, sometimes precipitating that end, whether you want it or not:
Mortality, Palliative Care, & Euthanasia
How to avoid it
Good practice is to be “open-mindedly skeptical” about any medication. By this we mean, don’t reject it out of hand, but do ask questions about it.
Ask your prescriber not only what it’s for and what it’ll do, but also what the side effects and risks are, and an important question that many people don’t think to ask, and for which doctors thus don’t often have a well-prepared smooth-selling reply, “what will happen if I don’t take this?”
And look up unbiased neutral information about it, from reliable sources (Drugs.com and The BNF are good reference guides for this—and if it’s important to you, check both, in case of any disagreement, as they function under completely different regulatory bodies, the former being American and the latter being British. So if they both agree, it’s surely accurate, according to best current science).
Also: when you are on a medication, keep a journal of your symptoms, as well as a log of your vitals (heart rate, blood pressure, weight, sleep etc) so you know what the medication seems to be helping or harming, and be sure to have a regular meds review with your doctor to check everything’s still right for you. And don’t be afraid to seek a second opinion if you still have doubts.
Want to know more?
For a more in-depth exploration than we have room for here, check out this book that we reviewed not long back:
To Medicate or Not? That is the Question! – by Dr. Asha Bohannon
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Seven Sins Of Memory – by Dr. Daniel Schacter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As we get older, we often become more forgetful—despite remembering many things clearly from decades past. Why?
Dr. Daniel Shacter takes us on a tour of the brain, and also through evolution, to show how memory is not just one thing, but many. And furthermore, it’s not just our vast memory that’s an evolutionary adaptation, but also, our capacity to forget.
He does also discusses disease that affect memory, including Alzheimer’s, and explores the biological aspects of memory too.
The “seven sins” of the title are seven ways our (undiseased, regular) memory “lets us down”, and why, and how that actually benefits us as individuals and as a species, and/but also how we can modify that if we so choose.
The book’s main strength is in how it separates—or bids us separate for ourselves—what is important to us and our lives and what is not. How and why memory and information processing are often at odds with each other (and what that means for us). And, on a practical note, how we can tip the scales for or against certain kinds of memory.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand human memory in all its glorious paradoxes, and put into place practical measures to make it work for you the way you want, this is a fine book for you.
Click here to check out The Seven Sins of Memory, and get managing yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: